Java框架--SSM&Oracle&Maven高级
〇、内容介绍
一、MyBatis01:框架概述、环境搭建及入门案例、自定义框架
1、介绍
- 框架:封装细节,是开发中的解决方案
- 三层架构与SSM的关系
- 表示层web:SpringMVC框架
- 业务层service:Spring的IOC和AOP
- 持久层dao:Mybatis
- 持久层技术
- JDBC是规范:资源浪费、难以维护
- JdbcTemplate和DBUtils是工具类
- Mybatis概述--持久层框架,内部封装JDBC
- 使用XML或注解配置statement
- 采用ORM思想实现实体类和数据库的映射---对象关系映射(Object Relational Mapping,简称 ORM)
2、入门案例(不需要写实现类)
- 环境搭建--基于xml的配置方式
- 坐标、实体类、Dao接口(UserDao或UserMapper)
- 持久层接口映射文件resources/com/itheima/dao/IUserDao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.IUserDao">
<!-- 配置查询所有操作 -->
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.itheima.domain.User">
select * from user
</select>
</mapper>
- 主配置文件resources/SqlMapConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration>
<!-- 配置 mybatis 的环境 -->
<environments default="mysql">
<!-- 配置 mysql 的环境 -->
<environment id="mysql">
<!-- 配置事务的类型 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- 配置连接数据库的信息:用的是数据源(连接池) -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost: 3306/ee50"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="1234"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 告知 mybatis 映射配置的位置 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/itheima/dao/IUserDao.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 环境搭建--基于注解的配置方式
- 移除IUserDao.xml,在Dao方法上使用@Select注解,并指定SQL语句
- SqlMapConfig.xml中的mapper配置时,使用class属性指定被注解的dao全限定类名
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.itheima.dao.IUserDao"/>
</mappers>
- 测试
package com.itcast.test;
import com.itcast.dao.IUserDao;
import com.itcast.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 入门案例
*/
public class MybatisTest {
/**
* 入门案例
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in);
//3.使用工厂生产SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//4.使用SqlSession创建Dao接口的代理对象
IUserDao userDao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<User> users = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
//6.释放资源
session.close();
in.close();
}
}
- 设计模式分析
- 构建者Builder模式
- 通过给施工队钱盖工厂:SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in);
- 工厂Factory模式
- 不再通过频繁修改实现类,使用工厂创建即可。
- SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
- 代理模式:在不修改源码的基础上对已有方法进行增强
- 相当于通过注解/配置文件创建了IUserDao的实现类
- 构建者Builder模式
二、MyBatis02:流程分析、注解、代理dao实现CRUD、参数深入、传统DAO、配置
1、自定义Mybatis的流程分析
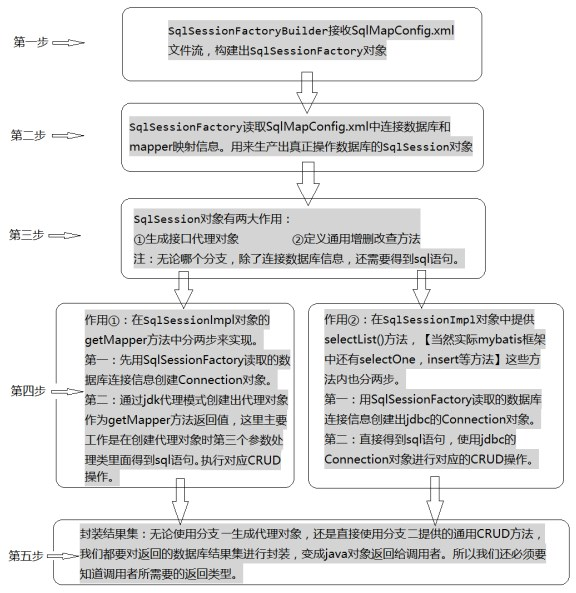
2、CRUD操作的实现
public class MyBatisTest {
private InputStream in;
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private IUserDao userDao;
/**
* 在测试方法执行之前执行
* @throws IOException
*/
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
//1.读取配置文件,生成字节输入流
in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.获取SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//3.获取SQLSession对象
sqlSession = factory.openSession();
//4.获取dao的代理对象
userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
}
/**
* 释放资源
* 在测试方法之后执行
*/
@After
public void destroy() throws IOException {
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
in.close();
}
}
- 保存--使用Apache提供的ognl表达式
- Object Graphic Navigation Language 对象图导航语言
按照一定的语法格式来获取数据,语法格式就是使用 #{对象.对象}的方式,如#{user.username}
- 省略Bean中的get后的剩余部分
<!-- 保存用户-->
<insert id="saveUser" parameterType="com.itheima.domain.User">
insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
- 需求:保存后返回保存用户的id值
<insert id="saveUser" parameterType="USER">
<!-- 配置保存时获取插入的 id -->
<selectKey keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" resultType="int">
select last_insert_id();
</selectKey>
insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
- 查询一个
- 修改
- 删除
- 模糊查询
<select id="findByName" parameterType="String" resultType="com.itcast.domain.User">
两种方式,函数内只需要传递字符串即可
select * from user where username like '#{username}';
select * from user where username like '%${value}%';
</select>
- 聚合函数
3、Mybatis的深入
- 实体类属性和数据库列名不一致
- 起别名
- 配置对应关系
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.itcast.domain.User">
<!--主键字段的对应-->
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<!--非主键字段的对应-->
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<!--等-->
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
select * from user;
</select>
- 编写DAO实现类
- 查询
public class UserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
public UserDaoImpl(SqlSessionFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
@Override
public List<User> findAll() {
//1.根据factory获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//2.调用SQLSession中的方法实现查询列表
List<User> users = session.selectList("com.itcast.dao.IUserDao.findAll");//参数就是能获取配置信息的key
//3.释放资源
session.close();
return users;
}
- 保存
@Override
public void saveUser(User user) {
//1.根据factory获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//2.调用SQLSession中的方法实现查询列表
session.insert("com.itcast.dao.IUserDao.saveUser",user);
//3.提交事务
session.commit();
//4.关闭
session.close();
}
4、标签的使用
- properties标签
<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties">
<!--<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>-->
</properties>
<!--配置环境-->
<environments default="mysql">
<!--配置mysql的环境-->
<environment id="mysql">
<!--配置事务-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!--配置连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</dataSource>
</environment>
- typeAliases标签和package标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties">
<!--<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>-->
</properties>
<!--使用typeAliases配置别名,只能配置domain中类的别名-->
<typeAliases>
<!--typeAliases配置别名,type指定全限定类名,alias指定别名,指定别名后不再区分大小写,全局配置,在IUserDao.xml中使用-->
<typeAlias type="com.itcast.domain.User" alias="user"></typeAlias>
<!--package用于指定要配置别名的包,当指定后,该报下的实体类都会注册别名,并且类名就是别名,不再区分大小写-->
<package name="com.itcast.domain.User"></package>
</typeAliases>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/itcast/dao/IUserDao.xml"></mapper>
<!--用于指定dao接口所在的包,当指定完成之后就不需要再写mapper、resource或class了-->
<package name="com.itcast.dao"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
三、MyBatis03:连接池及事务控制、xml动态SQL语句、多表操作
1、Mybatis连接池和事务控制
- 连接池:存储连接的容器,该容器是线程安全(两个线程不能拿到同一个连接)的,实现了队列的先进先出
- 模拟
while (conn == null) { //连接为空时创建
synchronized (state) {
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {
// Pool has available connection
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
}
}
- 连接池的分类:SqlMapConfig.xml的dataSource标签中的type属性表示采用何种连接池方式
- POOLED:采用DataSource规范的连接池--从连接池中获取一个连接
- UNPOOLED:实现了DataSource规范,但没有使用连接池。每次都会获取一个新的连接。--注册驱动,获取连接
- JNDI:由服务器提供的DataSource实现对象
- 只有web工程或基于maven的war工程可以使用
- tomcat服务器采用的JNDI连接池为DHCP连接池
- 概念、ACID特性、会产生的问题、四种隔离级别
- 设置事务的自动提交
事务控制:通过sqlSession对象的commit方法和rollback方法实现
@Override
public void saveUser(User user) {
//1.根据factory获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession(true);
//2.调用SQLSession中的方法实现查询列表
session.insert("com.itcast.dao.IUserDao.saveUser",user);
//3.提交事务
//session.commit();
//4.关闭
session.close();
}
2、动态SQL语句/映射文件的SQL深入
- if标签
<!--根据条件查询-->
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultType="com.itcast.domain.User" parameterType="user">
select * from user where 1=1
<if test="username != null">
and username = #{username}
</if>
</select>
- where标签
<!--根据条件查询-->
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultType="com.itcast.domain.User" parameterType="user">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="username != null">
and username = #{username}
</if>
<if test="sex != null">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
- foreach
<!--根据queryvo中的id集合实现查询用户列表-->
<select id="findByUserInIds" resultType="com.itcast.domain.User">
select * from user where id
<where>
<if test="ids != null and ids.size()>0">
<foreach collection="ids" open="id in(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
- SQL标签抽取代码片段
<sql id="defaultUser">
select * from user
</sql>
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.itcast.domain.User" >
<include refid="defaultUser"></include>
</select>
3、Mybatis的多表操作
- 一对一操作(建立实体类关系)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itcast.dao.IAccountDao">
<!--定义封装account和user的resultMap-->
<resultMap id="accountUserMap" type="account">
<id property="id" column="aid"></id>
<result property="uid" column="uid"></result>
<result property="money" column="money"></result>
<!--应当建立一对一的关系映射:配置封装user的内容-->
<association property="user" column="uid" javaType="user">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="address" column="address"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="accountUserMap" >
SELECT u.*,a.id AS aid,a.money,a.uid FROM account a, USER u WHERE a.uid = u.id
</select>
<!--查询所有账户同时包含用户名和地址信息-->
<select id="findAllAccount" resultType="accountuser" >
SELECT a.*,u.username,u.address FROM account a, USER u WHERE a.uid = u.id
</select>
</mapper>
- 一对多操作
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.itcast.dao.IUserDao">
<!--定义user的resultMap-->
<resultMap id="userAccountMap" type="user">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="address" column="address"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result>
<!--配置user对象中account集合的映射-->
<collection property="accounts" ofType="account">
<id column="aid" property="id"></id>
<result column="uid" property="uid"></result>
<result column="money" property="money"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userAccountMap" >
SELECT * FROM USER u LEFT OUTER JOIN account a ON u.id = a.UID
</select>
</mapper>
- 多对多操作
- 查询角色下的用户
<mapper namespace="com.itcast.dao.IRoleDao">
<!--定义role表的resultMap-->
<resultMap id="roleMap" type="role">
<id property="roleId" column="id"></id>
<!--windows不区分大小写,linux区分大小写-->
<result property="roleName" column="role_name"></result>
<result property="roleDesc" column="role_desc"></result>
<collection property="users" ofType="user">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="address" property="address"></result>
<result column="sex" property="sex"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="roleMap">
SELECT u.*,r.`ID` rid,r.`ROLE_NAME`,r.`ROLE_DESC` FROM role r
LEFT OUTER JOIN user_role ur ON r.id = ur.`RID`
LEFT OUTER JOIN USER u ON u.id = ur.`UID`
</select>
</mapper>
- 查询用户下的角色
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.itcast.dao.IUserDao">
<!--定义user的resultMap-->
<resultMap id="userAccountMap" type="user">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="address" column="address"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result>
<!--配置角色集合的映射-->
<collection property="roles" ofType="role">
<id property="roleId" column="rid"></id>
<result property="roleName" column="role_name"></result>
<result property="roleDesc" column="role_desc"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap" >
SELECT u.*,r.ID rid,r.ROLE_NAME,r.ROLE_DESC FROM USER u
LEFT OUTER JOIN user_role ur ON u.id = ur.UID
LEFT OUTER JOIN role r ON r.id = ur.RID
</select>
</mapper>
4、JNDI介绍(连接池类型,目的是模仿注册表)
- 概念:JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface,Java命名和目录接口),标准的Java命名系统接口。
- 创建context.xml配置文件
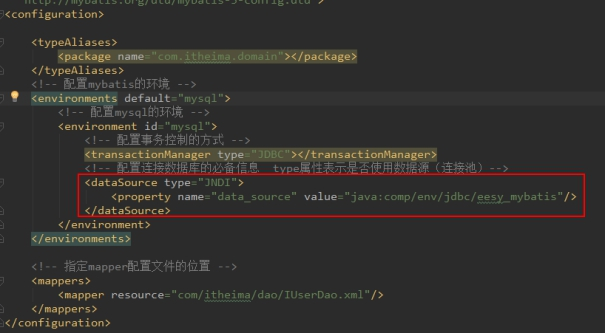
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Context>
<!--
<Resource
name="jdbc/eesy_mybatis" 数据源的名称
type="javax.sql.DataSource" 数据源类型
auth="Container" 数据源提供者
maxActive="20" 最大活动数
maxWait="10000" 最大等待时间
maxIdle="5" 最大空闲数
username="root" 用户名
password="1234" 密码
driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" 驱动类
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy_mybatis" 连接url字符串
/>
-->
</Context>
- 修改主配置文件
四、Mybatis04:延迟加载、一二级缓存、注解开发
1、延迟加载
- 背景
- 查询用户的账户:什么时候用到什么时候查(一对多,多对多:延迟加载/懒加载)
- 查询账户关联的用户:随账户一起查询出来(多对一,一对一:立即加载)
- 一对一--association
- 一对多--collection
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties">
</properties>
<settings>
<!--开启Mybatis支持延迟加载-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--Mybatis每个属性都会按需加载-->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>
</configuration>
2、Mybatis的一二级缓存
- 概念:
- 存放在内存中的临时数据,减少与DB交互,提高效率
- 适用于:不常改变且经常查询,数据正确与否对结果影响不大
- 一级缓存:存放在SqlSession对象中的缓存
- 触发清空一级缓存的情况:一级缓存是 SqlSession 范围的缓存,当调用 SqlSession 的修改,添加,删除,commit(),close()等方法时,就会清空一级缓存。
/**
* session关闭,缓存消失
*/
@Test
public void testFirstLevelCache(){
sqlSession = factory.openSession();
userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user1 = userDao.findById(41);
System.out.println(user1);
//关闭session sqlSession.close();
//SQLSession清空缓存的方法,也可以清空缓存,执行两次查询
sqlSession.clearCache();
//userDao.updateUser(user1);
User user2 = userDao.findById(41);
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println(user1==user2);
}
- 二级缓存:SqlSessionFactory对象的缓存(存放数据,而非对象)
- 步骤:
- 框架支持:SqlMapConfig.xml
- 步骤:
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties">
</properties>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--默认为true-->
</settings>
- 映射文件支持:IUserDao.xml中配置
- 当前操作支持:select标签中配置
<mapper namespace="com.itcast.dao.IUserDao">
<!--开启user支持二级缓存-->
<select id="findAll" resultType="user" useCache="true">
SELECT * FROM USER
</select>
存放的是数据,而不是对象,每次都会创建新的用户对象
/**
* session关闭,缓存消失
*/
@Test
public void testFirstLevelCache(){
SqlSession sqlSession1 = factory.openSession();
IUserDao dao1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user1 = dao1.findById(41);
System.out.println(user1);
sqlSession1.close();//一级缓存消失
SqlSession sqlSession2 = factory.openSession();
IUserDao dao2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user2 = dao2.findById(41);
System.out.println(user2);
sqlSession2.close();
System.out.println(user1==user2);
}
//结果不可以
3、注解开发
- 注解开发--主配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 引入外部配置文件 -->
<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties"></properties>
<!-- 配置别名 -->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.itheima.domain"></package>
</typeAliases>
<!-- 配置环境 -->
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="jdbc"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 指定带有注解的dao接口所在位置 -->
<mappers>
<package name="com.itheima.dao"></package>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 注解开发--注解类
package com.itheima.dao;
import com.itheima.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 在Mybatis中,针对CRUD共有4个注解
* @Select @Insert @Update @Delete
*/
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> findAll();
/**
* 删除用户
* @param userId
*/
@Delete("delete from user where id = #{id}")
void deleteUser(Integer userId); /**
* 根据id查询用户
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}")
User findById(Integer userId);
/**
* 根据用户名称模糊查询
* @param username
* @return
*/
//@Select("select * from user where username like #{username}")---字符串拼接
//模糊查询的另外一种写法,固定属性名称value---参数占位符
@Select("select * from user where username like '%${value}%'")
List<User> findByName(String username);
/**
* 查询总用户数量
* @return
*/
@Select("select count(*) from user")
int findTotal();
}
- 注解开发--测试
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.dao.IUserDao;
import com.itheima.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class AnnotationCRUDTest {
private InputStream in;
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private IUserDao userDao;
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
/**
* 在测试方法执行之前执行
* @throws IOException
*/
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
//1.读取配置文件,生成字节输入流
in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.获取SqlSessionFactory
factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//3.使用工厂对象,创建dao对象
//userDao = new UserDaoImpl(factory);
sqlSession = factory.openSession();
//4.获取dao的代理对象
userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
}
/**
* 释放资源
* 在测试方法之后执行
*/
@After
public void destroy() throws IOException {
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
in.close();
}
@Test
public void testDelete(){
/*User user = new User();
user.setId(52);*/
userDao.deleteUser(52);
}
@Test
public void testFindOne(){
User user = userDao.findById(53);
System.out.println(user);
}
@Test
public void testFindByName(){
//List<User> users = userDao.findByName("%王%");
List<User> users = userDao.findByName("王");
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
@Test
public void testFindTotal(){
int total = userDao.findTotal();
System.out.println(total);
}
}
- 注解开发--建立实体类属性和数据库表中列的对应关系
package com.itheima.dao;
import com.itheima.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 在Mybatis中,针对CRUD共有4个注解
* @Select @Insert @Update @Delete
*/
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id="userMap",value={
@Result(id=true,column = "id",property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "username",property = "userName"),
@Result(column = "address",property = "userAddress"),
@Result(column = "sex",property = "userSex"),
@Result(column = "birthday",property = "userBirthday"),
})
List<User> findAll();
}
- 注解开发--一对一的查询配置(多表查询)
package com.itheima.dao; import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.One;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Result;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Results;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.FetchType; import java.util.List; public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 查询所有账户,并且获取每个账户的用户信息
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from account")
@Results(id = "accountMap",value = {
@Result(id = true,column = "id",property = "id"),
@Result(column = "uid",property = "uid"),
@Result(column = "money",property = "money"),
@Result(property = "user",column = "uid",one=@One(select="com.itheima.dao.IUserDao.findById",fetchType= FetchType.EAGER))
})
List<Account> findAll();
}
- 注解开发--一对多的查询配置
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id="userMap",value={
@Result(id=true,column = "id",property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "username",property = "userName"),
@Result(column = "address",property = "userAddress"),
@Result(column = "sex",property = "userSex"),
@Result(column = "birthday",property = "userBirthday"),
@Result(property = "accounts",column = "id",
many=@Many(select = "com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao.findAccountByUid",
fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
List<User> findAll();
- 注解开发--使用二级缓存
<configuration>
<!-- 引入外部配置文件 -->
<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties"></properties>
<!--全局配置:开启二级缓存(默认开启)-->
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settingspackage com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.dao.IUserDao;
import com.itheima.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List; public class AnnotationCRUDTest {
private InputStream in;
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private IUserDao userDao;
private SqlSessionFactory factory; /**
* 在测试方法执行之前执行
* @throws IOException
*/
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
//1.读取配置文件,生成字节输入流
in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.获取SqlSessionFactory
factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//3.使用工厂对象,创建dao对象
//userDao = new UserDaoImpl(factory);
sqlSession = factory.openSession();
//4.获取dao的代理对象
userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
} /**
* 释放资源
* 在测试方法之后执行
*/
@After
public void destroy() throws IOException {
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
in.close();
}
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
List<User> users = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println("---每个用户的信息:---");
System.out.println(user);
//实现了延迟加载,没有立即查询account
//System.out.println(user.getAccounts()); }
}
}
@CacheNamespace(blocking = true)
public interface IUserDao {
五、Spring01:概述、工厂模式解耦、Spring中的IOC
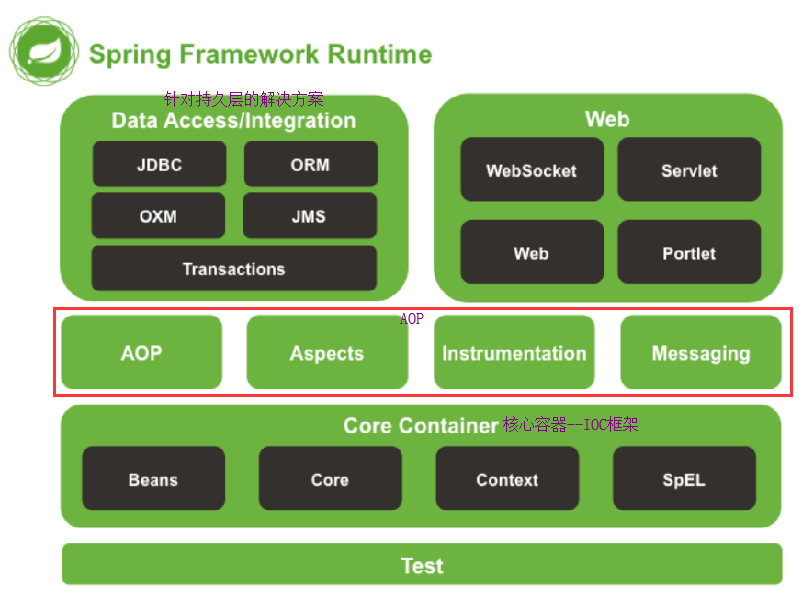
1、概述(表示层SpringMVC、业务层√、持久层Mybatis)
- 内核:IoC(Inverse Of Control:反转控制)和 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming
- 需要核心容器IOC的支持
2、程序的耦合与解耦
- 解耦:编译器不依赖,运行时才依赖
- 步骤:反射创建对象,读取配置文件获取全限定类名
- Bean工厂
package com.itheima.factory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class BeanFactory {
//定义一个Properties对象
private static Properties props;
//使用静态代码块为Properties对象赋值
static{
try {
//实例化对象
props = new Properties();
//获取properties的流对象
InputStream in = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("Bean.properties");
props.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError("初始化properties失败");
}
}
/**
* 根据Bean的名称获取bean对象
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
public static Object getBean(String beanName){
Object bean = null;
try {
String beanPath = props.getProperty(beanName);
System.out.println(beanPath);
//反射
bean = Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
}
- 业务层
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.itheima.factory.BeanFactory;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
/**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
//业务层调用持久层
//避免写new
private IAccountDao accountDao = (IAccountDao)BeanFactory.getBean("accountDao");
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
- 工厂模式解耦,单例升级版
package com.itheima.factory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
public class BeanFactory {
//定义一个Properties对象
private static Properties props;
//定义一个map,用于存放创建的对象,我们将其称之为容器
private static Map<String,Object> beans;
//使用静态代码块为Properties对象赋值
static{
try {
//实例化对象
props = new Properties();
//获取properties的流对象
InputStream in = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("Bean.properties");
props.load(in);
//实例化容器
beans = new HashMap<>();
//取出配置文件中所有的key
Enumeration keys = props.keys();
//遍历枚举
while(keys.hasMoreElements()){
//取出每个key
String key = keys.nextElement().toString();
//根据key获取value
String beanPath = props.getProperty(key);
//反射创建对象
Object value = Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance();
//把key和value存入容器之中
beans.put(key,value);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError("初始化properties失败");
}
}
/**
* 根据Bean的名称获取bean对象
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
public static Object getBean(String beanName){
return beans.get(beanName);
}
}
- 优化版表现层调用业务层
package com.itheima.ui;
import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.factory.BeanFactory;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl; /**
* 模拟一个表现层,用于调用业务层
*/
public class Client {
private IAccountDao accountDao = (IAccountDao)BeanFactory.getBean("accountDao");
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
IAccountService as = (IAccountService)BeanFactory.getBean("accountService");
System.out.println(as);
as.saveAccount();
}
}
}
- 优化版业务层实现类
package com.itheima.service.impl; import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.itheima.factory.BeanFactory;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService; /**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
//业务层调用持久层
//避免写new
//private IAccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl();
private IAccountDao accountDao;
//private int i = 1;
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao = (IAccountDao)BeanFactory.getBean("accountDao");
int i = 1;
//如果想每次调用得到的是新值,则需要定义到方法内部
accountDao.saveAccount();
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
3、IOC的概念和Spring的IOC
- 创建对象:主动new、IOC被动接受
- 基于XML的IOC--配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--把对象的创建交给Spring管理-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
- 基于XML的IOC--获取核心容器并创建对象
package com.itheima.ui;
import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
*
*/
public class Client {
/**
* 获取Spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象---两种方式
IAccountService as = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService");
IAccountDao adao = ac.getBean("accountDao",IAccountDao.class);
System.out.println(as);
System.out.println(adao);
}
}
- 核心容器对象ApplicationContext的三个实现类
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:类路径下
- FileSystemApplicationContext:磁盘文件
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:注解创建
- BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别
- BeanFactory:延迟加载,适用于多例对象,bean.properties
- ApplicationContext:立即加载适用于单例对象,bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--把对象的创建交给Spring管理-->
<!--
Spring对Bean的管理细节
1、创建Bean的三种方式
2、Bean对象的作用范围
3、Bean对象的生命周期
-->
<!--创建Bean的三种方式-->
<!--第一种方式:使用默认构造函数创建
在Spring的配置文件中使用bean标签 ,配以id和class属性后,且没有其他属性和标签时
采用的就是默认构造函数创建Bean对象,此时如果没有构造函数,则对象无法创建
-->
<!--<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>-->
<!--jar中只有class文件,获取有些对象的返回值,则需要采用第二种或第三种创建对象-->
<!--第二种方式:使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用类中的方法创建对象,并存入Spring容器)-->
<!--<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.itheima.factory.InstancsFactory"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>--> <!--第三种方式:使用静态工厂中的静态方法创建对象,并存入Spring容器-->
<!--
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
-->
<!--bean的作用范围调整
默认是单例
通过bean标签的scope属性,调整bean的作用范围
取值:(单例和多例最常用)
singleton:单例的(默认值)
prototype:多例的
request:作用于web应用的请求范围
session:作用于web应用的会话范围
global-session:作用于集群环境的全局会话范围,当不是集群环境时,就是session
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl" scope="prototype"></bean>
-->
<!--bean对象的生命周期
区分单例对象/多例对象
单例对象
出生:当容器创建时,对象出生
存活:只要容器还在,对象就一直活着
死亡:容器销毁,对象消亡
总结:单例对象的生命周期和容器相同
多例对象
出生:当使用对象时,Spring框架为我们创建
存活:对象在使用过程中一直存活
死亡:当对象长时间不用且没有其他对象引用时,由Java的垃圾回收期回收
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl" scope="prototype"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean> </beans>
4、依赖注入:Dependency Injection
- 概念:Spring通过配置文件对依赖关系的维护,就称为依赖注入,适用于不常变化的情况,目的是降低类之间的依赖关系
- 注入方式:构造函数、set方法、注解
- 构造函数注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--构造函数注入
使用的标签:constructure-arg
标签出现的位置:bean标签的内部
标签中的属性:
type:指定要注入数据的数据类型,该数据类型也是构造函数中某个或某些参数的类型
index:用于指定要注入的数据给构造函数中指定索引位置的参数赋值。参数索引的位置从0开始
name:用于指定给构造函数中指定名称的参数赋值※常用的是名称
===================以上三个用于指定给构造函数中的哪个参数赋值=====================
value:用于提供基本类型和String类型的数据
ref:引用关联的bean对象,指定其他的bean类型数据,指的是在Spring的IOC容器中出现过的bean对象 优势:在获取bean对象时,注入数据是必须操作,否则对象无法创建成功【不需要getset方法】
弊端:改变了bean对象的实例化方式,使我们在创建对象时,如果用不到这些数据,也必须提供
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="字符串"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="now"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--配置一个日期对象-->
<bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
</beans>
- set方法注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置一个日期对象-->
<bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<!--set方法注入※更常用
涉及的标签:property
出现的位置:bean标签的内部
标签的属性:
name:指定注入时所调用的set方法名称,关心set方法去掉set和大写
===================以上三个用于指定给构造函数中的哪个参数赋值=====================
value:用于提供基本类型和String类型的数据
ref:引用关联的bean对象,指定其他的bean类型数据,指的是在Spring的IOC容器中出现过的bean对象
优势:
创建对象时没有明确的限制,可以直接使用默认构造函数
弊端:
如果有某个成员必须有值,则获取对象时,有可能set方法没有执行
即调用了AccountServiceImpl2构造,对象用完,set无法执行
-->
<bean id="accountService2" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl2">
<property name="username" value="test"></property>
<property name="age" value="21"></property>
<property name="birthday" ref="now"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 集合类型的注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- Spring中的依赖注入
依赖注入:Dependency Injection
IOC的作用:
降低/削减程序间的耦合程度(依赖关系)
依赖关系的管理
以后都交给了Spring维护
在当前类中需要用到其他类的对象,由Spring为我们提供,我们只需要在配置文件中说明
依赖关系的维护就称之为“依赖注入”
依赖注入:
能注入的数据由三类:
基本类型和String
其他bean类型(在配置文件中或者注解配置的bean)
复杂类型/集合类型
注入的方式有三种:
第一种:使用构造函数提供
第二种:使用set方法提供
第三种:使用注解提供(明天的内容)
-->
<!--构造函数注入
使用的标签:constructure-arg
标签出现的位置:bean标签的内部
标签中的属性:
type:指定要注入数据的数据类型,该数据类型也是构造函数中某个或某些参数的类型
index:用于指定要注入的数据给构造函数中指定索引位置的参数赋值。参数索引的位置从0开始
name:用于指定给构造函数中指定名称的参数赋值※常用的是名称
===================以上三个用于指定给构造函数中的哪个参数赋值=====================
value:用于提供基本类型和String类型的数据
ref:引用关联的bean对象,指定其他的bean类型数据,指的是在Spring的IOC容器中出现过的bean对象 优势:在获取bean对象时,注入数据是必须操作,否则对象无法创建成功【不需要getset方法】
弊端:改变了bean对象的实例化方式,使我们在创建对象时,如果用不到这些数据,也必须提供
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="字符串"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="now"></constructor-arg>
</bean> <!--复杂类型(集合类型)的注入(两大类)
用于给list结构集合注入的标签:list array set
用于给map结构集合注入的标签:map prop
结构相同,标签可以互换
-->
<bean id="accountService3" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl3">
<property name="myStrs">
<array>
<value>aaa</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="myList">
<list>
<value>aaa</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="mySet">
<list>
<value>aaa</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="myMap">
<map>
<entry key="testA" value="aaa"></entry>
<entry key="testB">
<value>BBB</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="myProp">
<props>
<prop key="testc">cccc</prop>
<prop key="testd">ddd</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 测试
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService; import java.util.*; /**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl3 implements IAccountService {
//如果是经常变化的数据,并不适用于注入的方式
private String[] myStrs;
private List<String> myList;
private Set<String> mySet;
private Map<String,String> myMap;
private Properties myProp; public void setMyStrs(String[] myStrs) {
this.myStrs = myStrs;
} public void setMyList(List<String> myList) {
this.myList = myList;
} public void setMySet(Set<String> mySet) {
this.mySet = mySet;
} public void setMyMap(Map<String, String> myMap) {
this.myMap = myMap;
} public void setMyProp(Properties myProp) {
this.myProp = myProp;
} public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myStrs));
System.out.println(myList);
System.out.println(mySet);
System.out.println(myMap);
System.out.println(myProp);
}
}
package com.itheima.ui;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; /**
*
*/
public class Client {
/**
* 获取Spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象---两种方式
/*IAccountService as = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService");
as.saveAccount();*/
//没有调用销毁时,容器已经消失了
//可以手动关闭容器
IAccountService as = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService3");
as.saveAccount();
}
}
六、Spring02:注解IOC、DBUtils单表CRUD、与Junit整合
1、Spring中IOC的常用注解
- 分类:创建对象、注入数据、改变作用范围、与生命周期相关
- Component注解--将当前类对象装入容器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--通过配置告知Spring在创建容器时要扫描的包,配置所需要的标签不是在beans的约束中,而是一个名称为Context的名称空间和约束中-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
package com.itheima.service.impl; import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*
* 曾经的xml配置
* <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"
* scope="" init-method="" destroy-method="">
* <property name = "" value="" ref=""></property>
* </bean>
*
* 注解分为四类:
* 用于创建对象的
* 作用与xml配置文件中编写一个bean标签<bean></bean>实现的功能相同
* @Component
* 作用:用于把当前类对象存入Spring容器中
* 属性:
* value:用于指定bean的id,当我们不写时,它的默认值是当前类名,且首字母改小写
*/
@Component(value="accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao accountDao = null;
public AccountServiceImpl(){
System.out.println("service对象创建了");
}
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
- Component的衍生注解
- @Controller:表现层
- @Service:业务层
- @Repository:持久层(相当于dao)
public class Client {
/**
* 获取Spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象---两种方式
IAccountService as = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService");
System.out.println(as);
IAccountDao adao = ac.getBean("accountDao",IAccountDao.class);
System.out.println(adao);
}
}
- 用于注入数据的注解
- @Autowired实现自动按照类型注入: 作用和xml配置文件中的bean标签写一个property标签的作用相同
- @Qualifier:按照名称注入
- @Resource:按照bean的id进行注入
- @Value:对基本类型和String类型数据进行注入,使用SPEL表达式:${表达式}
@Service(value="accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountDao1")
//@Resource(name="accountDao2")
private IAccountDao accountDao = null;
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
- 改变作用范围及生命周期注解
- 改变作用范围:@Scope,singleton prototype,默认单例singleton
- 生命周期:@PreDestroy,@PostConstruct
@Service(value="accountService")
//@Scope("single")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
//@Autowired
//@Qualifier("accountDao1")
@Resource(name="accountDao2")
private IAccountDao accountDao = null;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化方法执行了");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("销毁方法执行了");
}
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
- 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象---两种方式
IAccountService as = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService");
IAccountService as2 = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService");
/*System.out.println(as);
IAccountDao adao = ac.getBean("accountDao",IAccountDao.class);
System.out.println(adao);*/
//System.out.println(as==as2);
as.saveAccount();
ac.close();
}
}
2、使用xml方式和注解方式实现单表的CRUD操作(dbutils.QueryRunner+Spring)
- 案例必备代码
package com.itheima.dao.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private QueryRunner runner; public void setRunner(QueryRunner runner) {
this.runner = runner;
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account", new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//相当于return
}
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account where id = ?", new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//相当于return
}
}
@Override
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update("insert into account(name,money) values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//相当于return
}
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id = ?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//相当于return
}
}
@Override
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
try {
runner.update("delete from account where id = ?",accountId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//相当于return
}
}
}
- Spring的IOC配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置Service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入dao对象 -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置dao对象-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!--注入QueryRunner-->
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置QueryRunner对象-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<!--注入数据源-->
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--连接数据库的必备信息-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 案例测试
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
*/
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
List<Account> accounts = as.findAllAccount();
for (Account account : accounts) {
System.out.println(account);
}
}
@Test
public void testFindOne() {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
Account account = as.findAccountById(1);
System.out.println(account);
}
@Test
public void testSave() {
Account account = new Account();
account.setName("johann");
account.setMoney(500.0f);
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
as.saveAccount(account);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
Account account = as.findAccountById(1);
account.setMoney(256f);
as.updateAccount(account);
}
@Test
public void testDelete() {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
as.deleteAccount(4);
}
}
- 自定义类使用注解配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--告知Spring在创建容器时要扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
<!--配置QueryRunner对象-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<!--注入数据源-->
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--连接数据库的必备信息-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 业务层实现类
/**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*/
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
//唯一的对象在容器中,使用autowired实现自动注入
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao; @Override
public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
return accountDao.findAllAccount();
}
- 持久层实现类
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Autowired
private QueryRunner runner;
3、Spring的新注解
- Configuration(指定配置类)和ComponentScan(指定扫描包)
- Bean:指定存入IOC容器中的bean对象
package config;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.itheima")//类路径,内容是一个数组,可以写{xxx,xxx}或xxx
public class SpringConfiguration {
/**
* 用于创建一个QueryRunner对象
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean(name="runner")//相当于bean的id
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(DataSource dataSource){
return new QueryRunner(dataSource);
}
/**
* 创建数据源 对象
*/
@Bean(name="dataSource")
public DataSource createDataSource(){
try {
ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
ds.setDriverClass("");
ds.setJdbcUrl("");
ds.setUser("");
ds.setPassword("");
return ds;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
package com.itheima.test; import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import config.SpringConfiguration;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import java.util.List; /**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
*/
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
//1.获取容器
//ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
List<Account> accounts = as.findAllAccount();
for (Account account : accounts) {
System.out.println(account);
} }
@Test
public void testFindOne() {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
Account account = as.findAccountById(1);
System.out.println(account);
}
@Test
public void testSave() {
Account account = new Account();
account.setName("johann");
account.setMoney(500.0f);
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
as.saveAccount(account); }
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
Account account = as.findAccountById(1);
account.setMoney(256f);
as.updateAccount(account);
}
@Test
public void testDelete() {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//2.执行方法
as.deleteAccount(4);
}
}
- Import:指定是一个配置类
package config;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
/**
* Import
* 作用:用于导入其他的配置类
* 属性:
* value:用于指定其他配置类的字节码
* 当使用import注解之后,有import注解的类就是父配置类,而导入的都是子配置类
*/
//@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.itheima"})//类路径,内容是一个数组,可以写{xxx,xxx}或xxx
@Import(JdbcConfig.class)
public class SpringConfiguration {
//期望是公共配置,而不是只配置连接数据库的
}
- PropertySource
package config;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
/**
* PropertySource
* 作用:用于导入其他的配置类
* 属性:
* value:指定文件的名称和路径
* 关键字:classpath表示类路径下
* 有包:config/itheima/xxx
*
*/
//@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.itheima"})//类路径,内容是一个数组,可以写{xxx,xxx}或xxx
@Import(JdbcConfig.class)
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbcConfig.properties")
public class SpringConfiguration {
//期望是公共配置,而不是只配置连接数据库的
}
package config;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* 和Spring连接数据库相关的配置类
*/
//@Configuration
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
/**
* 用于创建一个QueryRunner对象
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean(name="runner")//相当于bean的id
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(DataSource dataSource){
return new QueryRunner(dataSource);
} /**
* 创建数据源对象
*/
@Bean(name="dataSource")
@Scope("prototype")
public DataSource createDataSource(){
try {
//希望读取配置文件
ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
ds.setDriverClass(driver);
ds.setJdbcUrl(url);
ds.setUser(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
4、Spring整合Junit
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
* Spring整合Junit的配置
* 1、导入Spring整合Junit的坐标
* 2、使用Junit提供的一个注解把原有的main方法替换成Spring提供的
* @Runwith
* 3、告知Spring的运行期,Spring和IOC创建是基于xml还是注解的,并且说明位置
* @ContextConfiguration
* locations:指定xml文件的位置,加上classpath关键字,表示在类路径下
* classes:指定注解类所在的位置
* 当使用Spring5.x版本时,要求Junit的jar包必须是4.1.2及以上
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //相当于main方法,自动调用test类
@ContextConfiguration(classes=SpringConfiguration.class) //配置文件
public class AccountServiceTest {
//private ApplicationContext ac;
@Autowired //自动注入
private IAccountService as = null;
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
//2.执行方法
List<Account> accounts = as.findAllAccount();
for (Account account : accounts) {
System.out.println(account);
}
}
配置类
package config; import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*; import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException; /**
* 该类是一个配置类,其作用和bean.xml作用相同
* Spring中的新注解
* Configuration
* 作用:指定当前类是是一个配置类
* 细节:当配置类作为AnnotationCofigApplicationContext对象创建的参数时,该注解可以不写
* ComponentScan
* 作用:用于通过注解指定spring在创建容器时要扫描的包
* value属性和basePackages的作用相同,都是用于指定创建容器时要扫描的包
* 我们使用此注解就等同于在xml中配置了
* <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
* Bean
* 作用:用于把当前方法的返回值作为bean对象存入spring的IOC容器中
* 属性:
* name:用于指定bean的id,当不写时默认值是当前方法的名称
* 细节:
* 当使用注解配置方法时,如果方法有参数,spring框架会去容器中查找有没有可用的bean对象
* 查找的方式和AutoWired是一样的,查找类型匹配,一个 ,没有,多个
*
* <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
* <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
* <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
* <property name="user" value="root"></property>
* <property name="password" value="root"></property>
* </bean>
* Import
* 作用:用于导入其他的配置类
* 属性:
* value:用于指定其他配置类的字节码
* 当使用import注解之后,有import注解的类就是父配置类,而导入的都是子配置类
* PropertySource
* 作用:用于导入其他的配置类
* 属性:
* value:指定文件的名称和路径
* 关键字:classpath表示类路径下
* 有包:config/itheima/xxx
*
*/
//@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.itheima"})//类路径,内容是一个数组,可以写{xxx,xxx}或xxx
@Import(JdbcConfig.class)
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbcConfig.properties")
public class SpringConfiguration {
//期望是公共配置,而不是只配置连接数据库的
}
七、Spring03:案例转账功能(事务问题)、动态代理解决、AOP
1、完善Account转账案例
- 演示事务问题
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置Service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入dao对象 -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置dao对象-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!--注入QueryRunner-->
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置QueryRunner对象-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<!--注入数据源-->
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--连接数据库的必备信息-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.List;
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"/bean.xml"})
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private IAccountService as;
@Test
public void testTransfer(){
as.transfer("aaa","bbb",100f);
}
}
@Override
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
try {
List<Account> accounts = runner.query("select * from account where name = ?", new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class),accountName);
if (accounts == null || accounts.size() == 0) return null;
if (accounts.size() > 1) throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一,数据存在问题");
return accounts.get(0);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//相当于return
}
} @Override
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) {
//1.根据名称查询转出账户
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
//2.根据名称查询转入账户
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
//3.转出账户金额减少
source.setMoney(source.getMoney() - money);
//4.转入账户金额增加
target.setMoney(target.getMoney() + money);
//int i = 1 / 0;
//5.更新转出账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
//6.更新转入账户
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
}
- 分析事务的问题并编写ConnectionUtils
- 线程管理工具类:获取当前线程连接池上的连接
package com.itheima.utils; import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException; /**
* 连接的工具类,用于从数据源中获取一个连接,并且实现和线程的绑定
*/
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
private DataSource dataSource; public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
} /**
* 获取当前线程上的连接
*/
public Connection getThreadConnection(){
try {
//1.先从ThreadLocal上获取
Connection conn = tl.get();
//2.判断当前线程上是否有连接
if (conn == null){
//3.从数据源中获取一个连接,并且和线程绑定,存入ThreadLocal中
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
tl.set(conn);
}
//4.返回当前线程上的连接
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
- 事务管理工具类:开启、提交、回滚、释放
package com.itheima.utils;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 和事务管理相关的工具类,包含开启事务、提交事务、回滚事务和释放连接
*/
public class TransactionManager {
//获取当前线程上的Connection
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
/**
* 开启事务
*/
public void beginTransaction(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 提交事务
*/
public void commit(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 回滚事务
*/
public void rollback(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 释放连接
*/
public void release(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();//并不是真正关闭连接,而是还回连接池中
connectionUtils.removeConnection();//进行线程的解绑
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 业务层实现类
package com.itheima.service.impl; import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.utils.TransactionManager; import java.util.List; /**
* 账户的业务层实现类
* 事务控制应当在业务层
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { private IAccountDao accountDao;
private TransactionManager txManager; public void setTxManager(TransactionManager txManager) {
this.txManager = txManager;
} public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
} @Override
public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
List<Account> accounts = accountDao.findAllAccount();
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果
return accounts;
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果
return account; } catch (Exception e) {
//回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
}finally {
//释放连接
txManager.release();
}
return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
} @Override
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
accountDao.saveAccount(account);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果 } catch (Exception e) {
//回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
}finally {
//释放连接
txManager.release();
} } @Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果 } catch (Exception e) {
//回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
}finally {
//释放连接
txManager.release();
}
} @Override
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
accountDao.deleteAccount(accountId);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果 } catch (Exception e) {
//回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
}finally {
//释放连接
txManager.release();
}
} @Override
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
//2.1根据名称查询转出账户
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
//2.2根据名称查询转入账户
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
//2.3转出账户金额减少
source.setMoney(source.getMoney() - money);
//2.4.转入账户金额增加
target.setMoney(target.getMoney() + money);
//int i = 1 / 0;
//2.5.更新转出账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
//2.6.更新转入账户
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
} finally {
//释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
}
- ConnectionUtils配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置Service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入dao对象 -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
<!--注入事务管理器-->
<property name="txManager" ref="txManager"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置dao对象-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!--注入QueryRunner-->
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
<!--注入ConnectionUtils-->
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置QueryRunner对象-->
<!--不再提供Connection对象,没有数据源,不会从数据源中获取连接-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"></bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--连接数据库的必备信息-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置Connection的工具类-ConnectionUtils-->
<bean id="connectionUtils" class="com.itheima.utils.ConnectionUtils">
<!--注入数据源的配置-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="com.itheima.utils.TransactionManager">
<!--注入ConnectionUtils-->
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2、动态代理
- 基于接口的动态代理回顾
package com.itheima.proxy; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; /**
* 模拟一个消费者
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Producer producer = new Producer();
/**
* 动态代理
* 特点:字节码随用随创建,随用随加载
* 作用:在不修改源码的基础上对方法增强
* 分类:
* 基于接口的动态代理
* 基于子类的动态代理
* 基于接口的动态代理:
* 设计的类:Proxy
* 提供者:JDK官方
* 如何创建代理对象:
* 使用Proxy类中的newProxyInstance方法
* 创建代理对象的要求:
* 被代理类至少实现一个接口,如果没有则不能使用
* newProxyInstance方法的参数:
* Classloader:类加载器
* 用于加载代理对象字节码,和被代理对象使用相同的类加载器
* Class[]:字节码数组
* 用于让代理对象和被代理对象有相同的方法
* InvocationHandler:用于提供增强的代码
* 让我们写如何代理,一般情况下写该接口的实现类,通常情况下是匿名内部类
* 此接口的实现类都是谁用谁写
*/
//不实现任何接口时,无法正常使用
IProducer proxyProducer = (IProducer)Proxy.newProxyInstance(producer.getClass().getClassLoader(),
producer.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* 作用:执行被代理对象的任何接口方法,都会经过该方法
* 方法参数
* @param proxy:代理对象的引用
* @param method:当前执行的方法
* @param args:当前执行方法所需的参数
* @return:和被代理对象有相同的返回值
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//想要增强,可以在此处提供增强的代码
Object returnValue = null;
//1.获取方法执行的参数
float money = (float) args[0];
//2.判断当前方法是不是销售
if ("saleProduct".equals(method.getName())){
returnValue = method.invoke(producer,money * 0.8f);
}
return returnValue;
}
});
proxyProducer.saleProduct(10000f);
}
}
package com.itheima.proxy;
/**
* 一个生产者
* 生产厂家需要有标准-销售和售后(接口)
*/
public class Producer implements IProducer{
/**
* 销售
* @param money
*/
//@Override
public void saleProduct(float money){
System.out.println("销售产品,并拿到"+money+"元钱");
} /**
* 售后
* @param money
*/
//@Override
public void afterService(float money){
System.out.println("提供售后服务,并拿到"+money+"元钱");
}
}
- 基于子类的动态代理--导入cglib依赖坐标
package com.itheima.cglib; import com.itheima.proxy.IProducer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; /**
* 模拟一个消费者
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Producer producer = new Producer();
/**
* 动态代理
* 特点:字节码随用随创建,随用随加载
* 作用:在不修改源码的基础上对方法增强
* 分类:
* 基于接口的动态代理
* 基于子类的动态代理
* 基于接口的动态代理:
* 设计的类:Proxy
* 提供者:第三方cglib库
* 如何创建代理对象:
* 使用Ehancer类中的create方法
* 创建代理对象的要求:
* 被代理类不能是最终类
* create方法的参数:
* Class:字节码
* 用于指定被代理对象的字节码,producer.getClass()
* Callback:用于提供增强的代码
* 让我们写如何代理,一般情况下写该接口的实现类,通常情况下是匿名内部类
* 此接口的实现类都是谁用谁写
* 一般写的都是该接口的子接口实现类:MethodIntercepter
*/
Producer cglibProducer = (Producer) Enhancer.create(producer.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() {
/**
* 执行被代理对象的任何方法都会经过该方法
* @param proxy
* @param method
* @param args
* 以上三个参数和基于接口的动态代理中invoke方法的参数相同
* @param methodProxy 当前执行方法的代理对象
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
//想要增强,可以在此处提供增强的代码
Object returnValue = null;
//1.获取方法执行的参数
float money = (float) args[0];
//2.判断当前方法是不是销售
if ("saleProduct".equals(method.getName())) {
returnValue = method.invoke(producer, money * 0.8f);
}
return returnValue;
}
});
cglibProducer.saleProduct(10000f);
}
}
- 使用动态代理实现事务控制
package com.itheima.factory;
import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.utils.TransactionManager;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; /**
* 用于创建service代理对象的工厂
*/
public class BeanFactory {
private IAccountService accountService;
private TransactionManager txManager;
public void setTxManager(TransactionManager txManager) {
this.txManager = txManager;
}
/**
* 获取service的代理对象
*
* @return
*/
public IAccountService getAccountService() {
Proxy.newProxyInstance(accountService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
accountService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* 添加事务的支持
*
* @param proxy
* @param method
* @param args
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object rtValue = null;
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
rtValue = method.invoke(accountService, args);
// 3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果
return rtValue;
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
});
return accountService;
}
public final void setAccountService(IAccountService accountService) {
this.accountService = accountService;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置代理的service对象-->
<bean id="proxyAccountService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
<!--配置beanfactory-->
<bean id="beanFactory" class="com.itheima.factory.BeanFactory">
<!--注入Service-->
<property name="accountService" ref="accountService"></property>
<!--注入事务管理器-->
<property name="txManager" ref="txManager"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置Service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入dao对象 -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property> </bean>
</beans>
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.List;
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"/bean.xml"})
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("proxyAccountService")
private IAccountService as;
@Test
public void testTransfer(){
as.transfer("aaa","bbb",100f);
}
}
3、AOP
- Aspect Oriented Programming 即:面向切面编程。
- 概念:抽取重复代码,在不修改源码的基础上,使用动态代理,对已有方法进行增强
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>day03_eesy_003springaop</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging> <properties>
<maven.compiler.source>9</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>9</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--spring的aop会用到-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--用于解析切入点表达式-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.13</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies> </project>
- 实现类
package com.itheima.service.impl; import com.itheima.service.IAccountService; /**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("执行了保存");
} @Override
public void updateAccount(int i) {
System.out.println("执行了更新"+i);
} @Override
public int deleteAccount() {
System.out.println("执行了删除");
return 0;
}
}
package com.itheima.utils; /**
* 用具记录日志的工具类,内部提供公共代码
*/
public class Logger {
/**
* 向控制台打印日志:计划在其切入点方法执行之前执行(切入点方法就是业务层方法)
*/
public void printLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的printLog方法开始记录日志了");
}
}
- 基于XML的AOP-配置步骤
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--先配置Spring的IOC,把Service对象配置进来【控制反转】-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--Spring中基于xml的aop配置步骤【面向切面编程,动态代理】
1、把通知bean(logger类)也交给Spring管理
2、使用aop:config标签表明aop的配置
3、使用aop:aspect标签表明开始配置切面
id属性用于给切面一个唯一标识
ref属性指定通知类bean的id
4、在aop:aspect标签的内部,使用对应的标签来配置通知的类型
当前示例是让printLog方法在切入点之前执行,所以是前置通知
aop:before表示配置前置通知
method属性:表示哪个方法是前置通知
pointcut属性:用于指定切入点表达式,该表达式的含义是对业务层中的哪些方法增强
切入点表达式的写法:
关键字:execution(表达式)
表达式:
访问修饰符 返回值 包名.类名.方法名 参数列表
标准写法:
public void com.itheima.service.impl.AccountService.saveAccount()
5、
-->
<!--配置logger类-->
<bean id="Logger" class="com.itheima.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!--配置aop-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="Logger">
<!--配置通知的类型,并建立通知方法和切入点方法的关联-->
<aop:before method="printLog" pointcut="execution(public void com.itheima.service.impl.AccountService.saveAccount())">
</aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- 测试类
package com.itheima.test; import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /**
* 测试AOP的配置
*/
public class AOPTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.获取对象
IAccountService as = (IAccountService)ac.getBean("accountService");
//3.执行方法
//切入点表达式只配置了对保存的增强
as.saveAccount();//查看是否实现了记录日志/日志的打印
as.updateAccount(1);
as.deleteAccount();
}
}
- 切入点表达式配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--先配置Spring的IOC,把Service对象配置进来【控制反转】-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--Spring中基于xml的aop配置步骤【面向切面编程,动态代理】
切入点表达式的写法:
关键字:execution(表达式)
表达式:
访问修饰符 返回值 包名.类名.方法名 参数列表
标准写法:
public void com.itheima.service.impl.AccountService.saveAccount()
1.访问修饰符可以省略 void com.itheima.service.impl.AccountService.saveAccount()
2.返回值可以使用通配符表示任意返回值 * com.itheima.service.impl.AccountService.saveAccount()
3.包名可以使用通配符表示任意包,但是有几级包,就需要写几个*.
3.1包名可以使用*..表示当前包及子包 * *..
4.类名和方法名都可以使用*实现通配 * *..*(*)
4.1参数列表:
可以直接写数据类型
基本类型直接写名称 int * *..*(int)
引用类型写报名.类名的方式 java.lang.String
类型可以使用通配符*表示任意类型,但必须有参数int * *..*(*)
可以使用..表示有无参数均可,有参数时表示任意类型 * *..*(..)
全通配写法:
* *..*.#(..)
实际开发中切入点表达式的通常写法:
切到业务层实现类下的所有方法
* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..)
aspectj坐标表示切入点表达式的语言联盟
-->
<!--配置logger类-->
<bean id="Logger" class="com.itheima.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!--配置aop-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="Logger">
<!--配置通知的类型,并建立通知方法和切入点方法的关联-->
<aop:before method="printLog" pointcut="execution(* *..*.*(..))"></aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- 常见的通知类型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--先配置Spring的IOC,把Service对象配置进来【控制反转】-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--配置logger类-->
<bean id="Logger" class="com.itheima.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!--配置aop-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="Logger">
<!--配置通知的类型,并建立通知方法和切入点方法的关联-->
<!--事务要么try提交,要么catch回滚-->
<!--配置前置通知:在切入点方法执行之前执行-->
<aop:before method="beforePrintLog" pointcut="execution(* *..*.*(..))"></aop:before>
<!--配置后置通知:在切入点方法正常执行之后执行,它和异常通知永远只能执行一个-->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningPrintLog" pointcut="execution(* *..*.*(..))"></aop:after-returning>
<!--配置异常通知:在切入点方法执行产生异常之后执行,它和后置通知永远只能执行一个-->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingPrintLog" pointcut="execution(* *..*.*(..))"></aop:after-throwing>
<!--配置最终通知:无论切入点方法是否正常执行,它都会在其后面执行-->
<aop:after method="afterPrintLog" pointcut="execution(* *..*.*(..))"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- 通知方法
package com.itheima.utils; /**
* 用具记录日志的工具类,内部提供公共代码
*/
public class Logger {
/**
* 前置通知
*/
public void beforePrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的beforePrintLog方法开始记录日志了");
}
/**
* 后置通知
*/
public void afterReturningPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterReturningPrintLog方法开始记录日志了");
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
public void afterThrowingPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterThrowingPrintLog方法开始记录日志了");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
public void afterPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterPrintLog方法开始记录日志了");
}
}
- 通用切入点表达式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--先配置Spring的IOC,把Service对象配置进来【控制反转】-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--配置logger类-->
<bean id="Logger" class="com.itheima.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!--配置aop-->
<aop:config>
<!--
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
-->
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="Logger">
<!--配置通知的类型,并建立通知方法和切入点方法的关联-->
<!--事务要么try提交,要么catch回滚-->
<!--配置前置通知:在切入点方法执行之前执行-->
<aop:before method="beforePrintLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:before>
<!--配置后置通知:在切入点方法正常执行之后执行,它和异常通知永远只能执行一个-->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:after-returning>
<!--配置异常通知:在切入点方法执行产生异常之后执行,它和后置通知永远只能执行一个-->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:after-throwing>
<!--配置最终通知:无论切入点方法是否正常执行,它都会在其后面执行-->
<aop:after method="afterPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:after>
<!--配置切入点表达式,id属性用于表示表达式的唯一标识,expression指定表达式内容
此标签写在aop:aspect标签内部,只能在当前切面使用
也可以写在aop:aspect标签外部(必须写在aspect标签之前),可以在所有切面使用
-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- 环绕通知
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--先配置Spring的IOC,把Service对象配置进来【控制反转】-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--配置logger类-->
<bean id="Logger" class="com.itheima.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!--配置aop-->
<aop:config>
<!--
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
--> <!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="Logger">
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<!--配置环绕通知 详细的注释请看logger类中-->
<aop:around method="aroundAroundPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- 通知代码
package com.itheima.utils;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
/**
* 用具记录日志的工具类,内部提供公共代码
*/
public class Logger {
/**
* 环绕通知
* 问题:
* 当配置了环绕通知之后,切入点方法没有执行,而通知方法执行了
* 分析:
* 通过对比动态代理中的环绕代理通知代码,发现动态代理的环绕通知有明确的切入点方法调用
*
* 动态代理的环绕通知-有明确的切入点调用
* 我们没有切入点方法
* 解决:
* Spring框架提供了一个接口:ProceedingJoinPoint,该接口有一个方法proceed,此方法就相当于明确调用切入点方法
* 该接口可以作为环绕通知的方法参数,在程序执行时,spring框架会为我们提供该接口的实现类供我们使用
* Spring中的环绕通知:
* 是Spring框架为我们提供的一种可以在代码中手动控制增强方法的实现方式
*/
public Object aroundAroundPrintLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object rtValue = null;
try {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();//得到方法执行所需的参数
System.out.println("前置通知开始记录日志了");
rtValue = pjp.proceed(args);//明确调用业务层/切入点方法
System.out.println("后置通知开始记录日志了");
return rtValue;
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("异常通知开始记录日志了");
throw new RuntimeException(throwable);
}finally {
System.out.println("最终通知开始记录日志了");
return rtValue;
}
}
}
- 基于注解的AOP配置
package com.itheima.utils; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 用具记录日志的工具类,内部提供公共代码
*/
@Component("logger")
@Aspect //表示当前类是一个切面类
public class Logger {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))")
private void pt1(){}
/**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before("pt1()")
public void beforePrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的beforePrintLog方法开始记录日志了");
}
/**
* 后置通知
*/
@AfterReturning("pt1()")
public void afterReturningPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterReturningPrintLog方法开始记录日志了");
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
@AfterThrowing("pt1()")
public void afterThrowingPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterThrowingPrintLog方法开始记录日志了");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@After("pt1()")
public void afterPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterPrintLog方法开始记录日志了");
} /**
* 环绕通知
* 问题:
* 当配置了环绕通知之后,切入点方法没有执行,而通知方法执行了
* 分析:
* 通过对比动态代理中的环绕代理通知代码,发现动态代理的环绕通知有明确的切入点方法调用
*
* 动态代理的环绕通知-有明确的切入点调用
* 我们没有切入点方法
* 解决:
* Spring框架提供了一个接口:ProceedingJoinPoint,该接口有一个方法proceed,此方法就相当于明确调用切入点方法
* 该接口可以作为环绕通知的方法参数,在程序执行时,spring框架会为我们提供该接口的实现类供我们使用
* Spring中的环绕通知:
* 是Spring框架为我们提供的一种可以在代码中手动控制增强方法的实现方式
*/
//@Around("pt1()")
public Object aroundAroundPrintLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object rtValue = null;
try {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();//得到方法执行所需的参数
System.out.println("前置通知开始记录日志了");
rtValue = pjp.proceed(args);//明确调用业务层/切入点方法
System.out.println("后置通知开始记录日志了");
return rtValue;
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("异常通知开始记录日志了");
throw new RuntimeException(throwable);
}finally {
System.out.println("最终通知开始记录日志了");
return rtValue;
}
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--配置Spring创建容器时要扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
<!--不再需要配置service-->
<!--把通知类交给Spring管理-->
<!--配置Spring开启注解AOP注解的支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<!--基于注解的aop有顺序的调用过程,而环绕通知没有调用顺序的问题※-->
</beans>
八、Spring04:JdbcTemplate及事务控制(AOP、XML、注解)
1、JdbcTemplate
- 基本用法
package com.itheima.jdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import java.sql.DriverManager; /**
* JdbcTemplate的最基本用法
*/
public class JdbcTemplateDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//准备数据源:c3p0、dbcp都可,今天介绍Spring的内置数据源
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
//1.创建JdbcTemplate对象
JdbcTemplate jt = new JdbcTemplate();//可以加带数据源的构造方法
//给jt设置数据源
jt.setDataSource(ds);
//2.执行操作
jt.execute("insert into account(name,money) values('ccc',1000)");
}
}
- 在Spring的IOC中使用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置JdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.itheima.jdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
/**
* JdbcTemplate的最基本用法
*/
public class JdbcTemplateDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.获取对象
JdbcTemplate jt = ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate",JdbcTemplate.class);
//2.执行操作
jt.execute("insert into account(name,money) values('ccc',1000)");
}
}
- CRUD操作
package com.itheima.jdbcTemplate; import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper; import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List; /**
* JdbcTemplate的CRUD操作
*/
public class JdbcTemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.获取对象
JdbcTemplate jt = ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate",JdbcTemplate.class);
//2.可带参数的执行操作(单表)
//保存
//jt.update("insert into account(name,money) values (?,?)","ssss",333f);
//更新
//jt.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?","ssss",333f,5);
//删除
//jt.update("delete from account where id=?",1);
//查询所有
//queryRunner提供的
//List<Account> accounts = jt.query("select * from account where money > ?",new AccountRowMapper(),100f);
//Spring提供的
/*List<Account> accounts1 = jt.query("select * from account where money > ?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),100f);
for (Account account : accounts1) {
System.out.println(account);
}*/
//查询一个
/*List<Account> account = jt.query("select * from account where id = ?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),1);
System.out.println(account.isEmpty()?"没有内容":account.get(0));*/
//使用聚合函数查询,返回一行一列,但不加groupby子句
//int count = jt.queryForObject("select count(*) from account where money >= ?",Integer.class,100f);
Long count = jt.queryForObject("select count(*) from account where money >= ?",Long.class,100f);
//大数据,常用long接收
System.out.println(count);
}
} /**
* 定义Account的封装策略
*/
class AccountRowMapper implements RowMapper<Account> {
/**
* 把结果集中的数据封装到Account中,然后由Spring把每个Account加入到集合中
* @param resultSet
* @param i
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public Account mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
Account account = new Account();
account.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
account.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
account.setMoney(resultSet.getFloat("money"));
return account;
}
}
- 在Dao中的使用
<!--配置账户的持久层-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置JdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
package com.itheima.dao.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import java.util.List; /**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
} @Override
public Account findAccounById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
} @Override
public Account findAccountByName(String accounName) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where name = ?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accounName);
if (accounts.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
if (accounts.size()>1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不一致");
}
return accounts.get(0);
} @Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}
package com.itheima.jdbcTemplate; import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; /**
* JdbcTemplate的最基本用法
*/
public class JdbcTemplateDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.获取对象
IAccountDao accountDao =ac.getBean("accountDao",IAccountDao.class);
Account account = accountDao.findAccounById(5);
System.out.println(account);
account.setMoney(10000f);
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
}
}
- JdbcDaoSupport与Dao的两种编写方式
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl2 implements IAccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; /*public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}*/ @Override
public Account findAccounById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
}
package com.itheima.dao.impl; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import javax.sql.DataSource; /**
* 此类用于抽取dao中的重复代码
*/
public class JdbcDaoSupport {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() {
return jdbcTemplate;
}
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
} public DataSource getDateSource() {
return dateSource;
} public void setDateSource(DataSource dateSource) {
//this.dateSource = dateSource;
if(jdbcTemplate == null){
jdbcTemplate = createJdbcTemplate(dateSource);
}
} private JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource dateSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dateSource);//支持构造函数和set方法
}
private DataSource dateSource; }
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements IAccountDao {
/*private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}*/ @Override
public Account findAccounById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accounts = getJdbcTemplate() .query("select * from account where id = ?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置账户的持久层-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dateSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2、作业:AOP实现事务控制
- 基于XML的AOP实现
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 配置Service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入dao对象 -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property> </bean>
<!--配置dao对象-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!--注入QueryRunner-->
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
<!--注入ConnectionUtils-->
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置QueryRunner对象-->
<!--不再提供Connection对象,没有数据源,不会从数据源中获取连接-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"></bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--连接数据库的必备信息-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置Connection的工具类-ConnectionUtils-->
<bean id="connectionUtils" class="com.itheima.utils.ConnectionUtils">
<!--注入数据源的配置-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="com.itheima.utils.TransactionManager">
<!--注入ConnectionUtils-->
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置AOP-->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="txAdvice" ref="txManager">
<!--配置通用的切入点表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<!--配置前置通知:开启事务-->
<aop:before method="beginTransaction" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:before>
<!--配置后置通知:提交事务-->
<aop:after-returning method="commit" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:after-returning>
<!--配置异常通知:回滚事务-->
<aop:after-throwing method="rollback" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:after-throwing>
<!--配置最终通知:释放连接-->
<aop:after method="release" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- 基于注解的AOP实现
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置Spring创建容器时要扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 配置Service --> <!--配置QueryRunner对象-->
<!--不再提供Connection对象,没有数据源,不会从数据源中获取连接-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"></bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--连接数据库的必备信息-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--开启Spring对注解aop的支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
- 连接工具类
package com.itheima.utils; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.sql.SQLException; /**
* 和事务管理相关的工具类,包含开启事务、提交事务、回滚事务和释放连接
*/
@Component("txManager")
public class TransactionManager {
//获取当前线程上的Connection
@Autowired
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.*.*(..))")
private void pt1(){}
/**
* 开启事务
*/
@Before("pt1")
public void beginTransaction(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 提交事务
*/
@AfterReturning("pt1")
public void commit(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 回滚事务
*/
@AfterThrowing("pt1")
public void rollback(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 释放连接
*/
@After("pt1")
public void release(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();//并不是真正关闭连接,而是还回连接池中
connectionUtils.removeConnection();//进行线程的解绑
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.itheima.utils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException; /**
* 连接的工具类,用于从数据源中获取一个连接,并且实现和线程的绑定
*/
@Component("connectionUtils")
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
/**
* 获取当前线程上的连接
*/
public Connection getThreadConnection(){
try {
//1.先从ThreadLocal上获取
Connection conn = tl.get();
//2.判断当前线程上是否有连接
if (conn == null){
//3.从数据源中获取一个连接,并且和线程绑定,存入ThreadLocal中
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
tl.set(conn);
}
//4.返回当前线程上的连接
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} /**
* 把连接和线程解绑
*/
public void removeConnection(){
tl.remove();
}
}
3、Spring中的事务控制
- 事务控制的一组API
- 代码准备
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置业务层-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置账户的持久层-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
import java.util.List;
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:bean.xml"})
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private IAccountService as;
@Test
public void testTransfer(){
as.transfer("aaa","bbb",100f);
}
}
- 基于XML的声明式事务控制
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--配置业务层-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置账户的持久层-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--Spring中基于XML的声明式事务配置步骤
1、配置事务管理器
2、配置事务的通知
此时需要导入事务的约束:tx名称空间和约束,同时也需要aop的
使用tx:advice标签配置事务通知
属性:
id:给事务通知起一个唯一标识
transaction-manager:给事务通知提供一个事务管理器引用
3、配置AOP中的通用切入点表达式
4、建立事务通知和切入点表达式的对应关系
5、配置事务的属性
在事务的通知tx:advice标签的内部配置
-->
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置事务通知的标签-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--配置事务的属性-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--标识transfer是业务层接口的方法,其需要一些属性
isolation="" 指定事务的隔离级别,默认是default,表示是数据库的默认隔离级别
no-rollback-for="" 用于指定一个异常,当产生该异常时,事务不会滚 ,产生其他异常时,事务回滚。没有默认值,表示任何异常都回滚
propagation="" 用于指定事务的传播行为,默认是REQUIRED,表示一定会有事务,增删改的选择,查询方法可以选择SUPPORT
read-only="" 指定事务是否只读,只有查询才能设置为true,默认为false表示读写
rollback-for="" 用于指定一个异常,当产生异常时,事务回滚。产生其他异常时,事务不回滚,没有默认值,表示任何异常都会滚
timeout="" 指定事务的超时时间,默认值是-1,表示永不超时,如果指定了数值,以秒为单位
-->
<tx:method name="*" read-only="false" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<!--指定查询方法-->
<tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"></tx:method>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--配置AOP-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.itheima.*.*(..))"/>
<!--建立切入点表达式和事务通知的对应关系-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- 基于注解的声明式事务控制
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置业务层-->
<!--配置spring创建容器时要扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
<!--配置JdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--Spring中基于注解的声明式事务配置步骤
1、配置事务管理器
2、开启Spring对注解事务的支持
3、在需要事务支持的地方使用@Transactional注解
4、建立事务通知和切入点表达式的对应关系
5、配置事务的属性
在事务的通知tx:advice标签的内部配置
-->
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--开启Spring对注解事务的支持-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
</beans>
package com.itheima.service.impl; import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; @Service("accountService")
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS,readOnly = true)//只读型事务控制
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao; @Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
}
//需要的是读写型事务控制
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false)//读写型
//xml一劳永逸
@Override
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) {
System.out.println("transfer开始执行");
//2.1根据名称查询转出账户
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
//2.2根据名称查询转入账户
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
//2.3转出账户金额减少
source.setMoney(source.getMoney() - money);
//2.4.转入账户金额增加
target.setMoney(target.getMoney() + money);
//2.5.更新转出账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
//2.6.更新转入账户
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
//int i = 1 / 0;
//3.提交事务
//txManager.commit();
}
}
- 基于纯注解的声明式事务控制
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root package config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import javax.sql.DataSource; /**
* 和连接数据库相关的配置类
*/
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
/**
* 创建JdbcTemplate对象
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
//进入容器需要bean注解
@Bean(name="jdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
} /**
* 创建一个数据源对象
* @return
*/
@Bean(name="dataSource")
public DataSource createDatasouce(){
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
}
package config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; import javax.sql.DataSource; /**
* 和事务相关的配置类
*/
public class TransactionConfig {
/**
* 用于创建事务管理器对象
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean(name="transactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager createTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
- 编程式事务控制
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置业务层-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
<property name="transactionTemplate" ref="transactionTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置账户的持久层-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<!--注入连接池数据源-->
</bean>
<!--配置事务模板对象-->
<bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
九、SpringMVC01:入门、请求参数绑定、自定义类型转换器、常见注解
1、三层架构和MVC的介绍
2、入门程序案例
3、请求参数绑定入门
4、自定义类型转换器
5、其他常用注解
十、SpringMVC02:返回值、json数据、文件上传、拦截器
1、响应返回值
2、响应JSON数据
3、文件上传
4、异常处理--友好页面
5、SpringMVC拦截器
十一、SpringMVC03:SSM整合
1、搭建整合环境
2、Spring框架代码的编写
3、Spring整合SpringMVC框架
4、Spring整合Mybatis框架
十二、Oracle01:概念、常用查询
1、简介及安装
一个数据库可以有多个实例
某某用户下有几张表,用户是数据库管理的基本单位
2、用户和表的介绍及表的操作
3、查询深入
4、复杂查询
十三、Oracle02:视图、索引、plsql、存储过程、存储函数、触发器
1、视图、索引及plsql操作
2、存储过程
3、触发器
4、使用Java调用存储过程
十四、Maven02:项目拆分聚合、私服
1、基础回顾
- 功能:依赖管理、一键构建(tomcat插件)
- 仓库:本地仓库、远程仓库(私服)、中央仓库
- 关系:默认从中央仓库下,公司中从私服中下
- 常用命令:clean、compile、test、package(打包至本地target目录)、install(放在本地仓库)、deploy(上传到私服)
2、Maven案例
- 导入jar包时的冲突解决原则(直接排除法)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>4.2.4.RELEASE</version>
<!--排除jar包的依赖包-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
- Dao配置文件编写
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.ItemsDao">
<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="items">
select * from items where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 配置文件编写
<!--dao层配置文件的编写-->
<!--dao层配置文件的开始-->
<!--配置Druid连接池(阿里巴巴提供)-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///maven"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<!--配置生产SqlSession对象的工厂-->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--扫描pojo包,给包下所有pojo对象起别名-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.itheima.domain"/>
</bean>
<!--扫描接口包路径,生成包下所有接口的代理对象,并且放入Spring容器中-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itheima.dao"/>
</bean>
<!--dao层配置文件的结束-->
</beans>
- 测试
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.dao.ItemsDao;
import com.itheima.domain.Items;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class ItemsTest {
@Test
public void findById(){
//先获取Spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 从容器中拿到所需dao的代理对象
ItemsDao itemsDao = ac.getBean(ItemsDao.class);
//调用方法
Items items = itemsDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(items.getName());
}
}
- Service层Spring配置
<!--service层配置文件开始-->
<!--开启组件扫描配置-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima.service"/>
<!--aop面向切面编程,切面就是切入点和通知的组合-->
<!--配置事务管理器aop-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--需要用到datasource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务的通知-->
<tx:advice id="advice">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<!--全局扫描-->
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="advice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
<!--service层配置文件结束-->
</beans>
- web层配置
<!--过滤器、监听器、配置文件、核心servlet-->
<!--配置编码过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>encoding</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encoding</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--配置Spring核心监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--重新制定Spring配置文件的路径-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
<!--也可以写*.do-->
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
- SpringMVC配置
<!--配置组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima.controller"/> <!--处理器映射器,处理器适配器-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/> <!--配置视图解析器-->
<bean id="internalResourceViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
<!--释放静态资源-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
</beans>
- Controller代码
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/items")
public class ItemsController {
@Autowired
private ItemsService itemsService;
@RequestMapping("/findDetail")
public String findDetail(Model model){
Items items = itemsService.findById(1);
model.addAttribute("item",items);
return "itemDetail";
}
}
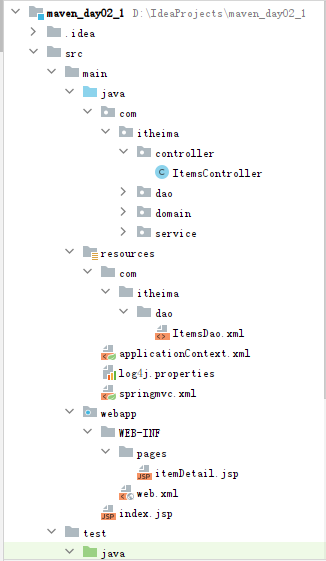
3、Maven工程的拆分与整合
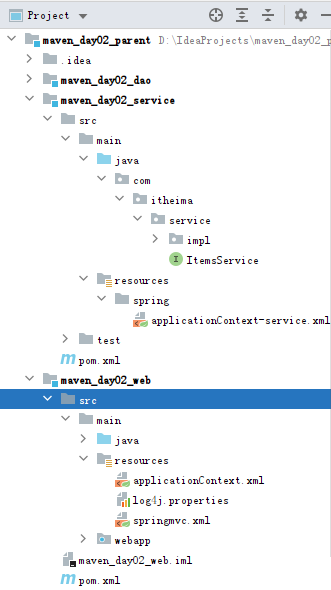
- 父工程
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>maven_day02_parent</artifactId>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!--子模块的显示-->
<modules>
<module>maven_day02_dao</module>
<module>maven_day02_service</module>
<module>maven_day02_web</module>
</modules>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>9</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>9</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!--管理子工程的jar包-->
<!--dao、service、controller-->
</project>
- 子工程
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>maven_day02_parent</artifactId>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>maven_day02_web</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
</project>
- 工程与模块:模块可以使用父工程资源,作用域不同可能会不能使用,需要重新导入
- 父工程填充
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>
<import resource="classpath:spring/applicationContext-service.xml"/>
<import resource="classpath:spring/applicationContext-dao.xml"/>
</beans>
- 启动:父工程、web模块(需要打包web项目)、本地的tomcat
4、私服
- nexus安装与启动
- 仓库介绍
- host发行版,
- 本地仓库上传到snapshot(测试)
- proxy代理
- central是中央仓库
- 3rd party是第三方插件
- releses是私服
- 应用:删除本地dao,会从私服中下载
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>maven_day02_parent</artifactId>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<!--模块的坐标com.itheima.maven_day02_dao-->
<artifactId>maven_day02_dao</artifactId> <properties>
<maven.compiler.source>9</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>9</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<id>releases</id>
<url>http://localhost:8081/nexus/content/repositories/releases/</url>
</repository>
<snapshotRepository>
<id>snapshots</id>
<url>http://localhost:8081/nexus/content/repositories/snapshots/</url>
</snapshotRepository>
</distributionManagement>
</project>
- 安装第三方jar包
@Controller@RequestMapping("/items")public class ItemsController { @Autowired private ItemsService itemsService; @RequestMapping("/findDetail") public String findDetail(Model model){ Items items = itemsService.findById(1); model.addAttribute("item",items); return "itemDetail"; }}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--把对象的创建交给Spring管理--> <!-- Spring对Bean的管理细节 1、创建Bean的三种方式 2、Bean对象的作用范围 3、Bean对象的生命周期 --> <!--创建Bean的三种方式--> <!--第一种方式:使用默认构造函数创建 在Spring的配置文件中使用bean标签 ,配以id和class属性后,且没有其他属性和标签时 采用的就是默认构造函数创建Bean对象,此时如果没有构造函数,则对象无法创建 --> <!--<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>--> <!--jar中只有class文件,获取有些对象的返回值,则需要采用第二种或第三种创建对象--> <!--第二种方式:使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用类中的方法创建对象,并存入Spring容器)--> <!--<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.itheima.factory.InstancsFactory"></bean> <bean id="accountService" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>-->
<!--第三种方式:使用静态工厂中的静态方法创建对象,并存入Spring容器--><!-- <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>--> <!--bean的作用范围调整 默认是单例 通过bean标签的scope属性,调整bean的作用范围 取值:(单例和多例最常用) singleton:单例的(默认值) prototype:多例的 request:作用于web应用的请求范围 session:作用于web应用的会话范围 global-session:作用于集群环境的全局会话范围,当不是集群环境时,就是session <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl" scope="prototype"></bean> --> <!--bean对象的生命周期 区分单例对象/多例对象 单例对象 出生:当容器创建时,对象出生 存活:只要容器还在,对象就一直活着 死亡:容器销毁,对象消亡 总结:单例对象的生命周期和容器相同 多例对象 出生:当使用对象时,Spring框架为我们创建 存活:对象在使用过程中一直存活 死亡:当对象长时间不用且没有其他对象引用时,由Java的垃圾回收期回收 --> <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl" scope="prototype" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
</beans>
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/** * 测试AOP的配置 */public class AOPTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.获取容器 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); //2.获取对象 IAccountService as = (IAccountService)ac.getBean("accountService"); //3.执行方法 //切入点表达式只配置了对保存的增强 as.saveAccount();//查看是否实现了记录日志/日志的打印 as.updateAccount(1); as.deleteAccount(); }}
Java框架--SSM&Oracle&Maven高级的更多相关文章
- JAVA 框架 / SSM / SSM SPRING+SPING MVC + MYBATIS 三大框架整合详细步骤
http://how2j.cn/k/ssm/ssm-tutorial/1137.html
- JAVA后端常用框架SSM,redis,dubbo等
JAVA后端常用框架SSM,redis,dubbo等 一.SpringMVC http://blog.csdn.net/evankaka/article/details/45501811 spri ...
- SSM 框架-04-使用maven创建web项目
SSM 框架-04-使用maven创建web项目 本篇介绍使用MAVEN来管理jar包,就不用一个一个去添加和下载jar包了,直接在maven配置文件中配置就可以了,maven可以帮助我们自动下载.本 ...
- SSM 框架-03-MyEclipse+Tomcat+MAVEN+SVN项目完整环境搭建
SSM 框架-03-MyEclipse+Tomcat+MAVEN+SVN项目完整环境搭建 如果你是使用 Eclipse 你需要先安装 MyEclipse,请参考:SSM 框架-02-MyEclipse ...
- 从零开始搭建框架SSM+Redis+Mysql(二)之MAVEN项目搭建
从零开始搭建框架SSM+Redis+Mysql(二)之MAVEN项目搭建 废话不说,直接撸步骤!!! 1.创建主项目:ncc-parent 选择maven创建项目,注意在创建项目中,packing选择 ...
- Java基于ssm框架的restful应用开发
Java基于ssm框架的restful应用开发 好几年都没写过java的应用了,这里记录下使用java ssm框架.jwt如何进行rest应用开发,文中会涉及到全局异常拦截处理.jwt校验.token ...
- maven高级笔记
Maven高级 1.maven基础知识回顾 1.1 maven介绍 maven 是一个项目管理工具,主要作用是在项目开发阶段对Java项目进行依赖管理和项目构建. 依赖管理:就是对jar包的管理.通过 ...
- Java 框架、库和软件的精选列表(awesome java)
原创翻译,原始链接 本文为awesome系列中的awesome java Awesome Java Java 框架.库和软件的精选列表 项目 Bean映射 简化 bean 映射的框架 dOOv - 为 ...
- Java Web学习系列——Maven Web项目中集成使用Spring、MyBatis实现对MySQL的数据访问
本篇内容还是建立在上一篇Java Web学习系列——Maven Web项目中集成使用Spring基础之上,对之前的Maven Web项目进行升级改造,实现对MySQL的数据访问. 添加依赖Jar包 这 ...
随机推荐
- 1.Ceph 基础篇 - 存储基础及架构介绍
文章转载自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI1MDgwNzQ1MQ==&mid=2247485232&idx=1&sn=ff0e93b9 ...
- kubeoperator 使用外部mysql
1.导出 kubeoperator 的数据库 sql 文件,然后导入到外部mysql 2.正常关闭 kubeoperator 3.关闭 kubeoperator 不会影响已经部署的 k8s 集群 4. ...
- Logstash: 启动监控及集中管理
在本篇文章里,我将详细介绍如果启动Logstash的监控及集中管理. 前提条件 安装好Logstash,设置Elasticsearch及Kibana的安全密码. 如何监控Logstash? 我们安装如 ...
- Docker容器虚拟化
Docker容器虚拟化 目录 Docker容器虚拟化 虚拟化网络 单节点容器间通信 不同节点容器间通信 虚拟化网络 Network Namespace 是 Linux 内核提供的功能,是实现网络虚拟化 ...
- .NET MAUI 社区工具包 1.3版本发布
2022 年 10 月 4 日,微软发布了 .NET MAUI 社区工具包的 1.3 版,具体参见微软官方博客:https://devblogs.microsoft.com/dotnet/announ ...
- 撸了一个简易的配置中心,顺带整合到了SpringCloud
大家好,我是三友~~ 最近突然心血来潮(就是闲的)就想着撸一个简单的配置中心,顺便也照葫芦画瓢给整合到SpringCloud. 本文大纲 配置中心的概述 随着历史的车轮不断的前进,技术不断的进步,单体 ...
- super关键字的使用
1.super理解为:父类的 2.super可以用来调用:属性.方法.构造器 3.super的使用:调用属性和方法 3.1 我们可以在子类的方法或构造器中.通过使用"super.属性&quo ...
- 齐博x1token字段,请务加在请求地址的头部header
如下图所示,你必须在请求的头部加上 token参数,主要原因有两个.第一点,这个是登录标志,因为接口访问用不了cookie,所以只能通过这个header请求标志判断用户是否已经登录.第二点,系统有时候 ...
- VMware16安装RedHat7.6步骤
1.安装准备 安装好VMware 16 下载好RedHat7.6镜像,本文为 rhel-server-7.6-x86_64-dvd.iso 2.点击"创建新的虚拟机"进入" ...
- dp优化 | 各种dp优化方式例题精选
前言 本文选题都较为基础,仅用于展示优化方式,如果是要找题单而不是看基础概念,请忽略本文. 本文包含一些常见的dp优化("√"表示下文会进行展示,没"√"表示暂 ...
