Protostuff序列化分析
前言
最近项目中需要将业务对象直接序列化,然后存数据库;考虑到序列化、反序列化的时间以及生产文件的大小觉得Protobuf是一个很好的选择,但是Protobuf有的问题就是需要有一个.proto的描述文件,而且由Protobuf生成的对象用来作为业务对象并不是特别友好,往往业务对象和Protobuf对象存在一个互相转换的过程;考虑到我们仅仅是将业务对象直接序列化到数据库,发现Protobuf在这种情况下并不是特别的好;
这时候发现了Protostuff,protostuff不需要依赖.proto文件,可以直接对普通的javabean进行序列化、反序列化的操作,而效率上甚至比protobuf还快,生成的二进制数据库格式和Protobuf完全相同的,可以说是一个基于Protobuf的序列化工具。
简单测试
1.先测试一下Protostuff
提供一个简单的javabean
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public class Person { private int id; private String name; private String email; // get/set方法省略} |
测试类PbStuff
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class PbStuff { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { Schema<Person> schema = RuntimeSchema.getSchema(Person.class); Person person1 = new Person(); person1.setId(1); person1.setName("zhaohui"); LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(1024); byte[] data = ProtobufIOUtil.toByteArray(person1, schema, buffer); System.out.println(data.length); }} |
序列化之后二进制的大小为29字节
2.测试Protobuf
proto文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
option java_package = "protobuf.clazz"; option java_outer_classname = "PersonX";message Person { required int32 id = 1; required string name = 2; required string email = 3;} |
PBTest类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class PBTest { public static void main(String[] args) { PersonX.Person.Builder builder = PersonX.Person.newBuilder(); builder.setId(1); builder.setName("zhaohui"); builder.setEmail("xxxxxxxx@126.com"); PersonX.Person p = builder.build(); byte[] result = p.toByteArray(); System.out.println(result.length); }} |
序列化之后二进制的大小同样也是29字节
经过简单的测试:发现Protobuf和Protostuff序列化相同的数据得到的结果是一样的
Protobuf的编码是尽其所能地将字段的元信息和字段的值压缩存储,并且字段的元信息中含有对这个字段描述的所有信息;既然Protostuff序列化之后的大小和Protobuf是一样的,那可以分析一下Protostuff的源码
源码分析
1.Schema
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
/** * Gets the schema that was either registered or lazily initialized at runtime. * <p> * Method overload for backwards compatibility. */public static <T> Schema<T> getSchema(Class<T> typeClass){ return getSchema(typeClass, ID_STRATEGY);}/** * Gets the schema that was either registered or lazily initialized at runtime. */public static <T> Schema<T> getSchema(Class<T> typeClass, IdStrategy strategy){ return strategy.getSchemaWrapper(typeClass, true).getSchema();} |
getSchema方法中指定了获取Schema的默认策略类ID_STRATEGY,ID_STRATEGY在类RuntimeEnv中进行了实例化:
|
1
|
ID_STRATEGY = new DefaultIdStrategy(); |
可以大致看一下DefaultIdStrategy类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public final class DefaultIdStrategy extends IdStrategy{ final ConcurrentHashMap<String, HasSchema<?>> pojoMapping = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); final ConcurrentHashMap<String, EnumIO<?>> enumMapping = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); final ConcurrentHashMap<String, CollectionSchema.MessageFactory> collectionMapping = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); final ConcurrentHashMap<String, MapSchema.MessageFactory> mapMapping = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); final ConcurrentHashMap<String, HasDelegate<?>> delegateMapping = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); ...} |
可以发现DefaultIdStrategy内存缓存了很多Schema信息,不难理解既然要或者业务对象的类和字段信息,必然用到反射机制,这是一个很耗时的过程,进行缓存很有必要,这样下次遇到相同的类就可以不用进行反射了
所以可以看到DefaultIdStrategy中有很多这种模式的方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public <T> HasSchema<T> getSchemaWrapper(Class<T> typeClass, boolean create) { HasSchema<T> hs = (HasSchema<T>) pojoMapping.get(typeClass.getName()); if (hs == null && create) { hs = new Lazy<>(typeClass, this); final HasSchema<T> last = (HasSchema<T>) pojoMapping.putIfAbsent( typeClass.getName(), hs); if (last != null) hs = last; } return hs; } |
先get,如果为null,就putIfAbsent
当业务对象的Schema还没被缓存,这时候就会去create,RuntimeSchema提供了createFrom方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public static <T> RuntimeSchema<T> createFrom(Class<T> typeClass, Set<String> exclusions, IdStrategy strategy){ final Map<String, java.lang.reflect.Field> fieldMap = findInstanceFields(typeClass); ...省略 final Field<T> field = RuntimeFieldFactory.getFieldFactory( f.getType(), strategy).create(fieldMapping, name, f, strategy); fields.add(field); } } return new RuntimeSchema<>(typeClass, fields, RuntimeEnv.newInstantiator(typeClass)); } |
主要就是对typeClass进行反射,然后进行封装;将字段类型封装成了RuntimeFieldFactory,最后通过RuntimeFieldFactory的create方法封装进入Field类中,RuntimeFieldFactory列举了所有支持的类型:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
static final RuntimeFieldFactory<BigDecimal> BIGDECIMAL; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<BigInteger> BIGINTEGER; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Boolean> BOOL; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Byte> BYTE; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<ByteString> BYTES; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<byte[]> BYTE_ARRAY; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Character> CHAR; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Date> DATE; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Double> DOUBLE; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Float> FLOAT; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Integer> INT32; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Long> INT64; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Short> SHORT; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<String> STRING; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Integer> ENUM; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Object> OBJECT; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Object> POJO; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Object> POLYMORPHIC_POJO; static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Collection<?>> COLLECTION = new RuntimeFieldFactory<Collection<?>>(ID_COLLECTION) |
当然还有常用的Map类型,在RuntimeMapFieldFactory中定义了
2.LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(1024);
开辟了1024字节缓存,用来存放业务对象序列化之后存放的地方,当然你可能会担心这个大小如果不够怎么办,后面的代码中可以看到,如果空间不足,会自动扩展的,所有这个大小要设置一个合适的值,设置大了浪费空间,设置小了会自动扩展浪费时间。
3.byte[] data = ProtobufIOUtil.toByteArray(person1, schema, buffer);
ProtobufIOUtil提供的就是以Protobuf编码的格式来序列化业务对象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public static <T> byte[] toByteArray(T message, Schema<T> schema, LinkedBuffer buffer){ if (buffer.start != buffer.offset) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer previously used and had not been reset."); final ProtobufOutput output = new ProtobufOutput(buffer); try { schema.writeTo(output, message); } catch (IOException e) { } return output.toByteArray();} |
schema中调用writeTo方法,将message中的消息保存到ProtobufOutput中
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public final void writeTo(Output output, T message) throws IOException{ for (Field<T> f : getFields()) f.writeTo(output, message);} |
第一步中将业务对象的字段信息都封装到了Field中了,可以看一下Field类提供的几个方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/** * Writes the value of a field to the {@code output}. */protected abstract void writeTo(Output output, T message) throws IOException;/** * Reads the field value into the {@code message}. */protected abstract void mergeFrom(Input input, T message) throws IOException;/** * Transfer the input field to the output field. */protected abstract void transfer(Pipe pipe, Input input, Output output, boolean repeated) throws IOException; |
提供了三个抽象方法,分别是写数据,读数据和转移数据
下面已int类型为实例,看看实现:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
public static final RuntimeFieldFactory<Integer> INT32 = new RuntimeFieldFactory<Integer>( ID_INT32) { @Override public <T> Field<T> create(int number, java.lang.String name, final java.lang.reflect.Field f, IdStrategy strategy) { final boolean primitive = f.getType().isPrimitive(); final long offset = us.objectFieldOffset(f); return new Field<T>(FieldType.INT32, number, name, f.getAnnotation(Tag.class)) { @Override public void mergeFrom(Input input, T message) throws IOException { if (primitive) us.putInt(message, offset, input.readInt32()); else us.putObject(message, offset, Integer.valueOf(input.readInt32())); } @Override public void writeTo(Output output, T message) throws IOException { if (primitive) output.writeInt32(number, us.getInt(message, offset), false); else { Integer value = (Integer) us.getObject(message, offset); if (value != null) output.writeInt32(number, value.intValue(), false); } } ... }; } |
上面这段代码可以在RuntimeUnsafeFieldFactory中找到,基本的数据类型都在此类中能找到,collection和map分别在RuntimeRepeatedFieldFactory和RuntimeMapFieldFactory中,writeTo方法调用了ProtobufOutput中的writeInt32方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public void writeInt32(int fieldNumber, int value, boolean repeated) throws IOException { ... tail = writeTagAndRawVarInt32( makeTag(fieldNumber, WIRETYPE_VARINT), value, this, tail); ... } |
写入field的Tag已经Value,Protobuf也是这种形式存放的,如下图所示: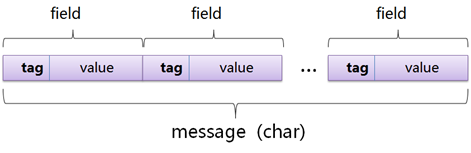
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public static LinkedBuffer writeTagAndRawVarInt32(int tag, int value, final WriteSession session, LinkedBuffer lb) { final int tagSize = computeRawVarint32Size(tag); final int size = computeRawVarint32Size(value); final int totalSize = tagSize + size; if (lb.offset + totalSize > lb.buffer.length) lb = new LinkedBuffer(session.nextBufferSize, lb); final byte[] buffer = lb.buffer; int offset = lb.offset; lb.offset += totalSize; session.size += totalSize; if (tagSize == 1) buffer[offset++] = (byte) tag; else { for (int i = 0, last = tagSize - 1; i < last; i++, tag >>>= 7) buffer[offset++] = (byte) ((tag & 0x7F) | 0x80); buffer[offset++] = (byte) tag; } if (size == 1) buffer[offset] = (byte) value; else { for (int i = 0, last = size - 1; i < last; i++, value >>>= 7) buffer[offset++] = (byte) ((value & 0x7F) | 0x80); buffer[offset] = (byte) value; } return lb; } |
tag是通过makeTag方法创建的:
|
1
2
3
4
|
public static int makeTag(final int fieldNumber, final int wireType){ return (fieldNumber << TAG_TYPE_BITS) | wireType;} |
fieldNumber每个字段的标号,wire_type是该字段的数据类型,所有如果我们改变了业务对象类中字段的顺序,或者改变了字段的类型,都会出现反序列化失败;
前面提到的数据压缩在方法computeRawVarint32Size中体现出来了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public static int computeRawVarint32Size(final int value){ if ((value & (0xffffffff << 7)) == 0) return 1; if ((value & (0xffffffff << 14)) == 0) return 2; if ((value & (0xffffffff << 21)) == 0) return 3; if ((value & (0xffffffff << 28)) == 0) return 4; return 5;} |
根据value值的范围,返回不同的字节数;接下来的代码也可以看到检查LinkedBuffer的空间是否足够,不够进行扩充;接下来的代码就是用压缩的方式将tag和Value存入缓存中。
总结
大致了解了Protostuff对业务对象序列化的过程,不管是简单的测试还是通过查看源码,都可以发现Protostuff的序列化方式是完全借鉴Protobuf来实现的。
Protostuff序列化分析的更多相关文章
- Protostuff序列化问题
最近在开发中遇到一个Protostuff序列化问题,在这记录一下问题的根源:分析一下Protostuff序列化和反序列化原理:以及怎么样避免改bug. 1. 问题描述 有一个push业务用到了mq,m ...
- Protostuff序列化
前言: Java序列化是Java技术体系当中的一个重要议题,序列化的意义在于信息的交换和存储,通常会和io.持久化.rmi技术有关(eg:一些orm框架会要求持久化的对象类型实现Serializabl ...
- java ArrayList的序列化分析
一.绪论 所谓的JAVA序列化与反序列化,序列化就是将JAVA 对象以一种的形式保持,比如存放到硬盘,或是用于传输.反序列化是序列化的一个逆过程. JAVA规定被序列化的对象必须实现java.io.S ...
- day19 Models补充+缓存+信号+序列化+分析抽屉页面
参考链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5237704.html http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5 ...
- Protostuff序列化工具类
源代码 package org.wit.ff.util; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStre ...
- protostuff序列化使用
背景 最近在做项目的时候需要使用持久化功能,1.0版本中使用的akka自带的持久化功能,使用的是akka persist支持的redis插件,在使用的过程中踩了一些坑.因此,在而2.0版本中考虑自己往 ...
- Protostuff序列化和反序列化
序列化和反序列化是在应对网络编程最常遇到的问题之一. 序列化就是将Java Object转成byte[]:反序列化就是将byte[]转成Java Object. 这里不介绍JDK serializab ...
- java protostuff 序列化反序列化工具
protostuff是由谷歌开发的一个非常优秀的序列化反序列化工具 maven导入包: <dependency> <groupId>io.protostuff</grou ...
- Protostuff序列化和反序列化使用说明
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/zhglance/article/details/56017926 google原生的protobuffer使用起来相当麻烦,首先要写.proto文件, ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode(35)-Path Sum
题目: Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up ...
- obj-c编程15[Cocoa实例02]:KVC和KVO的实际运用
我们在第16和第17篇中分别介绍了obj-c的KVC与KVO特性,当时举的例子比较fun,太抽象,貌似和实际不沾边哦.那么下面我们就用一个实际中的例子来看看KVC与KVO是如何运用的吧. 该例中用到了 ...
- JAVA_Lock
今天是毕业入职的第一个周末,一直对多线程并发方面的知识比较感兴趣,因为目前我手里的项目并没有涉及到并发方面的知识,所以怕以后遗忘,也便于以后复习和使用,所以总结了一下Lock里面的一些类的方法.具体的 ...
- Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal(根据中序遍历和后序遍历构建二叉树)
根据中序和后续遍历构建二叉树. /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * Tree ...
- plsql developer 使用 oracle instantclient的安装和配置
本文由ibyedo1贡献 1.下载 oracle instantclient basic package,在 oracle 官网下载就可以,地址如下: http://www.oracle.com/te ...
- iframe中 父页面和子页面查找元素的方法
从父页面中查找iframe子页面中对象的方法:JS: document.getElementById('iframe').contentWindow //查找iframe加载的页面的window对象 ...
- 前端技术之_CSS详解第六天--完结
前端技术之_CSS详解第六天--完结 一.复习第五天的知识 a标签的伪类4个: a:link 没有被点击过的链接 a:visited 访问过的链接 a:hover 悬停 a:active 按下鼠标不松 ...
- 手把手教你用Jenkins自动发布dotnet core程序
Jenkins部分 首先,我们要有个Jenkins咯,下载链接:https://jenkins.io/download/ 我们安装官网教程安装好jenkins,安装教程略.... 嗯?不是说好手把手么 ...
- How 5 Natural Language Processing APIs Stack Up
https://www.programmableweb.com/news/how-5-natural-language-processing-apis-stack/analysis/2014/07/2 ...
- 学习JavaScript最佳实践方法
首先要说明的是,咱现在不是高手,最多还是一个半桶水,算是入了JS的门. 谈不上经验,都是一些教训. 这个时候有人要说,“靠,你丫半桶水,凭啥教我们”.您先别急着骂,先听我说. 你叫一个大学生去教小学数 ...
