Java Future 和 FutureTask 源码Demo
Future 是一个接口,看源码有Future 和 FutreTask 使用Demo
package java.util.concurrent; /**
* A <tt>Future</tt> represents the result of an asynchronous
* computation. Methods are provided to check if the computation is
* complete, to wait for its completion, and to retrieve the result of
* the computation. The result can only be retrieved using method
* <tt>get</tt> when the computation has completed, blocking if
* necessary until it is ready. Cancellation is performed by the
* <tt>cancel</tt> method. Additional methods are provided to
* determine if the task completed normally or was cancelled. Once a
* computation has completed, the computation cannot be cancelled.
* If you would like to use a <tt>Future</tt> for the sake
* of cancellability but not provide a usable result, you can
* declare types of the form {@code Future<?>} and
* return <tt>null</tt> as a result of the underlying task.
*
* <p>
* <b>Sample Usage</b> (Note that the following classes are all
* made-up.) <p>
* <pre> {@code
* interface ArchiveSearcher { String search(String target); }
* class App {
* ExecutorService executor = ...
* ArchiveSearcher searcher = ...
* void showSearch(final String target)
* throws InterruptedException {
* Future<String> future
* = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() {
* public String call() {
* return searcher.search(target);
* }});
* displayOtherThings(); // do other things while searching
* try {
* displayText(future.get()); // use future
* } catch (ExecutionException ex) { cleanup(); return; }
* }
* }}</pre>
*
* The {@link FutureTask} class is an implementation of <tt>Future</tt> that
* implements <tt>Runnable</tt>, and so may be executed by an <tt>Executor</tt>.
* For example, the above construction with <tt>submit</tt> could be replaced by:
* <pre> {@code
* FutureTask<String> future =
* new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() {
* public String call() {
* return searcher.search(target);
* }});
* executor.execute(future);}</pre>
*
* <p>Memory consistency effects: Actions taken by the asynchronous computation
* <a href="package-summary.html#MemoryVisibility"> <i>happen-before</i></a>
* actions following the corresponding {@code Future.get()} in another thread.
*
* @see FutureTask
* @see Executor
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's <tt>get</tt> method
*/
public interface Future<V> {
1:测试类 App.
package com.future; import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class App {
static ExecutorService executor = null;
static ArchiveSearcher searcher = null; public static void main(String[] args) {
executor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
searcher = new ArchiveSearcherImp(); try {
showSearch("hello");
//showSearch2("world");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} static void showSearch(final String target) throws InterruptedException {
Future<String> future = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() {
return searcher.search(target);
}
});
System.out.println("displayOtherThings");
//boolean c = future.cancel(true);
// do other things while searching
try {
System.out.println("displayText(" + future.get() + ")");
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println("Future Canceled:" + future.isCancelled());
return;
}
} static void showSearch2(final String target) throws InterruptedException {
FutureTask<String> future = new FutureTask<String>(
new Callable<String>() {
public String call() {
return searcher.search(target);
}
});
executor.execute(future);
} }
2:接口类
package com.future;
public interface ArchiveSearcher {
String search(String target);
}
3:接口实现类
package com.future;
public class ArchiveSearcherImp implements ArchiveSearcher {
public String search(String target) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("ArchiveSearcherImp:" + target);
return target + "End ";
}
}
这样小Demo就跑完了,帮助我们理解,
区别:(应用来自http://blog.csdn.net/naughty610/article/details/38961675)
Future是一个接口,代表可以取消的任务,并可以获得任务的执行结果
FutureTask 是基本的实现了Future和runnable接口
实现runnable接口,说明可以把FutureTask实例传入到Thread中,在一个新的线程中执行。
实现Future接口,说明可以从FutureTask中通过get取到任务的返回结果,也可以取消任务执行(通过interreput中断)
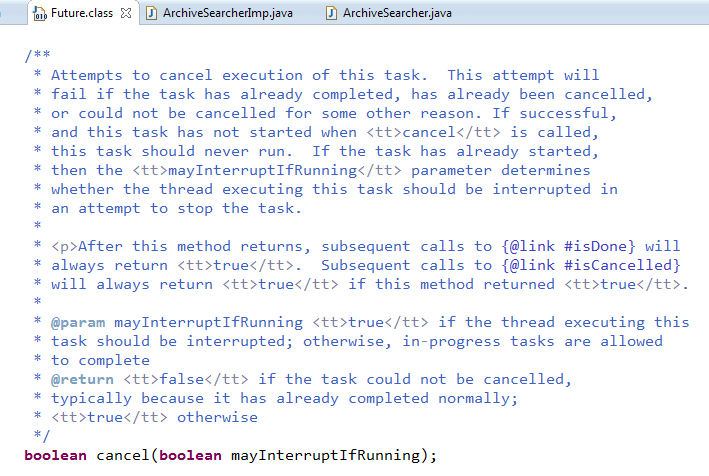
cancel方法用来取消任务,如果取消任务成功则返回true,如果取消任务失败则返回false . 参数mayInterruptIfRunning 表示是否允许取消正在执行却没有执行完毕的任务,
如果设置true,则表示可以取消正在执行过程中的任务。
如果任务已经完成,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,此方法肯定返回false,即如果取消已经完成的任务会返回false;
如果任务正在执行,若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为true,则返回true,
若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为false,则返回false;如果任务还没有执行,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,肯定返回true。
isDone
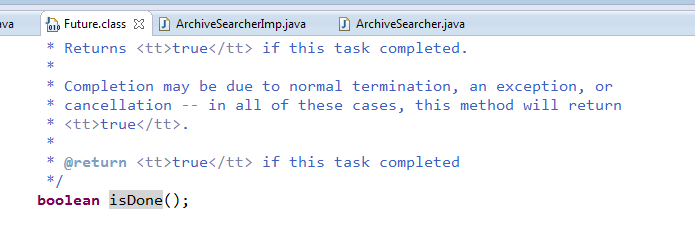
isDone方法表示任务是否已经完成,若任务完成,则返回true;
Java Future 和 FutureTask 源码Demo的更多相关文章
- Java多线程类FutureTask源码阅读以及浅析
FutureTask是一个具体的实现类,实现了RunnableFuture接口,RunnableFuture分别继承了Runnable和Future接口,因此FutureTask类既可以被线程执行,又 ...
- Java 多线程(五)—— 线程池基础 之 FutureTask源码解析
FutureTask是一个支持取消行为的异步任务执行器.该类实现了Future接口的方法. 如: 取消任务执行 查询任务是否执行完成 获取任务执行结果(”get“任务必须得执行完成才能获取结果,否则会 ...
- FutureTask源码深度剖析
FutureTask源码深度剖析 前言 在前面的文章自己动手写FutureTask当中我们已经仔细分析了FutureTask给我们提供的功能,并且深入分析了我们该如何实现它的功能,并且给出了使用Ree ...
- java 并发编程——Thread 源码重新学习
Java 并发编程系列文章 Java 并发基础——线程安全性 Java 并发编程——Callable+Future+FutureTask java 并发编程——Thread 源码重新学习 java并发 ...
- 大文件拆分问题的java实践(附源码)
引子 大文件拆分问题涉及到io处理.并发编程.生产者/消费者模式的理解,是一个很好的综合应用场景,为此,花点时间做一些实践,对相关的知识做一次梳理和集成,总结一些共性的处理方案和思路,以供后续工作中借 ...
- java Thread 类的源码阅读(oracle jdk1.8)
java线程类的源码分析阅读技巧: 首先阅读thread类重点关注一下几个问题: 1.start() ,启动一个线程是如何实现的? 2.java线程状态机的变化过程以及如何实现的? 3. 1.star ...
- SwitchButton 开关按钮 的多种实现方式 (附源码DEMO)
http://blog.csdn.net/vipzjyno1/article/details/23707149 Switch开关android源码SwitchButton 刚开始接触开关样式的按钮是在 ...
- 大文件拆分方案的java实践(附源码)
引子 大文件拆分问题涉及到io处理.并发编程.生产者/消费者模式的理解,是一个很好的综合应用场景,为此,花点时间做一些实践,对相关的知识做一次梳理和集成,总结一些共性的处理方案和思路,以供后续工作中借 ...
- java多线程----线程池源码分析
http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3509954.html 线程池示例 在分析线程池之前,先看一个简单的线程池示例. 1 import java.util.c ...
随机推荐
- VSCODE includePath 中使用系统中的变量
使用 ${env.ENVNAME} 这样只需要在 系统中加一个系统变量就可以. https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-cpptools/issues/697
- webpack 遇到报错情况及解决
webpack2 报错:optimize.OccurenceOrderPlugin is not a function. 原因:上个版本拼写错误,少写了一个字母r,新版本修正过来了.要写成这样:Occ ...
- python3 获取int最大值
python2 中获取int最大值 import sys i = sys.maxint print i 但是在python3中,报错: AttributeError: module 'sys' has ...
- c#问题(按F1或F2键时触发事件)
this.KeyPreview = true;...private void Form1_KeyDown(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.KeyEventArg ...
- 启动servlet报错:The servlets named [DemoServlet] and [main.java.com.wlf.demo.servlet.DemoServlet] are both mapped to the url-pattern [/hello] which is not permitted
先看具体错误日志: [2019-04-26 09:29:25,484] Artifact demo-servlet:war: Artifact is being deployed, please wa ...
- RDD之二:原理
RDD简介 在集群背后,有一个非常重要的分布式数据架构,即弹性分布式数据集(Resilient Distributed Dataset,RDD).RDD是Spark的最基本抽象,是对分布式内存的抽象使 ...
- phpstorm使用教程
phpstorm包含了webstorm的全部功能,更能够支持php代码.PhpStorm是一个轻量级且便捷的PHP IDE,其旨在提供用户效率,可深刻理解用户的编码,提供智能代码补全,快速导航以及即时 ...
- Java中的yield关键字的简单讲解
Thread.yield()方法作用是:暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程. yield()应该做的是让当前运行线程回到可运行状态,以允许具有相同优先级的其他线程获得运行机会.因此,使用yie ...
- Linux系统运行级与启动机制剖析
原文作者:技术成就梦想 原文链接:http://ixdba.blog.51cto.com/2895551/533740 一 系统运行级windows系统有安全运行模式和正常运行模式,这是两个不同的运行 ...
- python爬虫rp+bs4
一.开发环境 Beautiful Soup 4.4.0 文档: http://beautifulsoup.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/#id28 Requests : ht ...
