JavaScript中的递归
译者按: 程序员应该知道递归,但是你真的知道是怎么回事么?
为了保证可读性,本文采用意译而非直译。
递归简介
一个过程或函数在其定义或说明中有直接或间接调用自身的一种方法,它通常把一个大型复杂的问题层层转化为一个与原问题相似的规模较小的问题来求解,递归策略只需少量的程序就可描述出解题过程所需要的多次重复计算,大大地减少了程序的代码量。
我们来举个例子,我们可以用4的阶乘乘以4来定义5的阶乘,3的阶乘乘以4来定义4的阶乘,以此类推。
factorial(5) = factorial(4) * 5factorial(5) = factorial(3) * 4 * 5factorial(5) = factorial(2) * 3 * 4 * 5factorial(5) = factorial(1) * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5factorial(5) = factorial(0) * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5factorial(5) = 1 * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5
用Haskell的Pattern matching 可以很直观的定义factorial函数:
factorial n = factorial (n-1) * nfactorial 0 = 1
在递归的例子中,从第一个调用factorial(5)开始,一直递归调用factorial函数自身直到参数的值为0。下面是一个形象的图例:
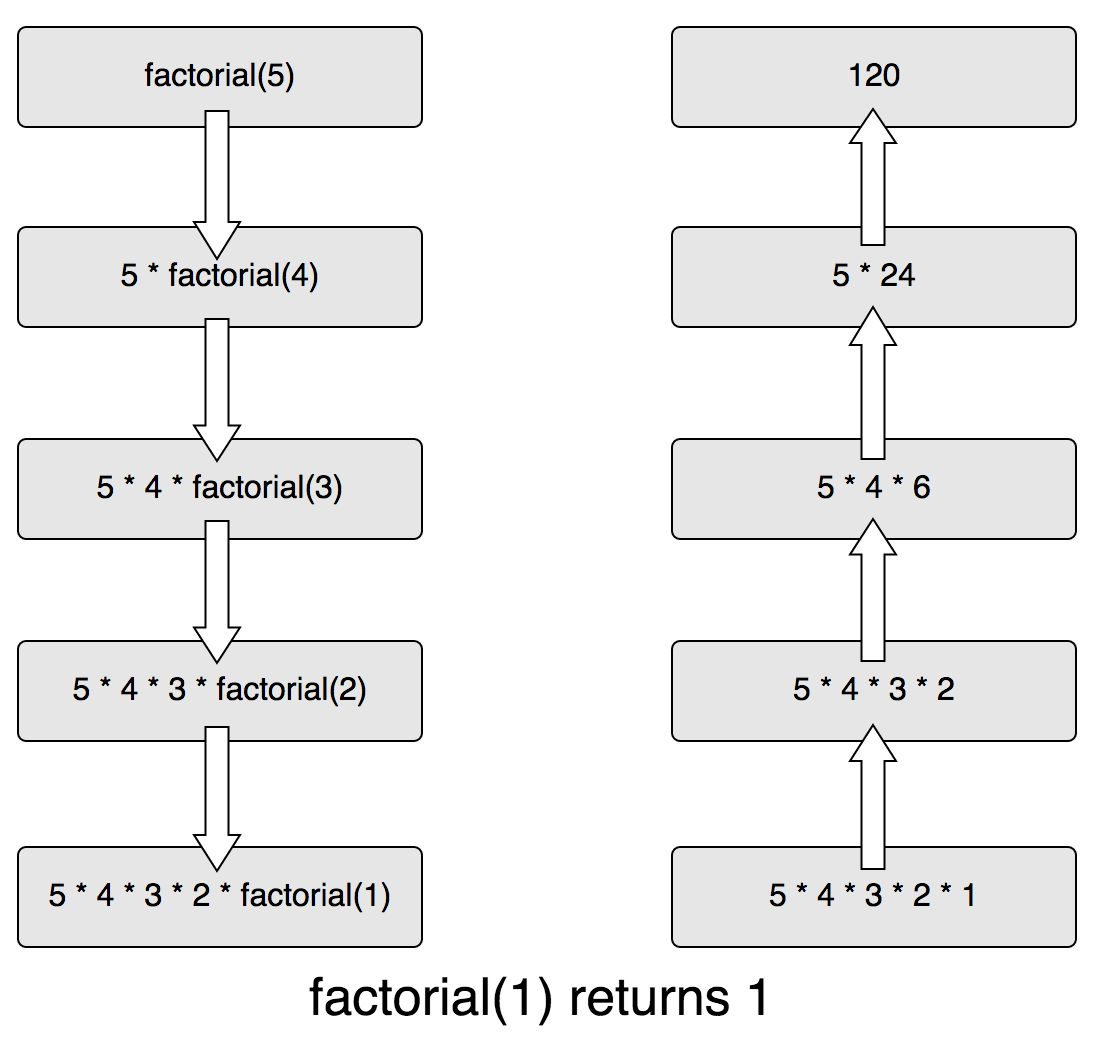
递归的调用栈
为了理解调用栈,我们回到factorial函数的例子。
function factorial(n) {if (n === 0) {return 1}return n * factorial(n - 1)}
如果我们传入参数3,将会递归调用factorial(2)、factorial(1)和factorial(0),因此会额外再调用factorial三次。
每次函数调用都会压入调用栈,整个调用栈如下:
factorial(0) // 0的阶乘为1factorial(1) // 该调用依赖factorial(0)factorial(2) // 该调用依赖factorial(1)factorial(3) // 该掉用依赖factorial(2)
现在我们修改代码,插入console.trace()来查看每一次当前的调用栈的状态:
function factorial(n) {console.trace()if (n === 0) {return 1}return n * factorial(n - 1)}factorial(3)
接下来我们看看调用栈是怎样的。
第一个:
Traceat factorial (repl:2:9)at repl:1:1 // 请忽略以下底层实现细节代码at realRunInThisContextScript (vm.js:22:35)at sigintHandlersWrap (vm.js:98:12)at ContextifyScript.Script.runInThisContext (vm.js:24:12)at REPLServer.defaultEval (repl.js:313:29)at bound (domain.js:280:14)at REPLServer.runBound [as eval] (domain.js:293:12)at REPLServer.onLine (repl.js:513:10)at emitOne (events.js:101:20)
你会发现,该调用栈包含一个对factorial函数的调用,这里是factorial(3)。接下来就更加有趣了,我们来看第二次打印出来的调用栈:
Traceat factorial (repl:2:9)at factorial (repl:7:12)at repl:1:1 // 请忽略以下底层实现细节代码at realRunInThisContextScript (vm.js:22:35)at sigintHandlersWrap (vm.js:98:12)at ContextifyScript.Script.runInThisContext (vm.js:24:12)at REPLServer.defaultEval (repl.js:313:29)at bound (domain.js:280:14)at REPLServer.runBound [as eval] (domain.js:293:12)at REPLServer.onLine (repl.js:513:10)
现在我们有两个对factorial函数的调用。
第三次:
Traceat factorial (repl:2:9)at factorial (repl:7:12)at factorial (repl:7:12)at repl:1:1at realRunInThisContextScript (vm.js:22:35)at sigintHandlersWrap (vm.js:98:12)at ContextifyScript.Script.runInThisContext (vm.js:24:12)at REPLServer.defaultEval (repl.js:313:29)at bound (domain.js:280:14)at REPLServer.runBound [as eval] (domain.js:293:12)
第四次:
Traceat factorial (repl:2:9)at factorial (repl:7:12)at factorial (repl:7:12)at factorial (repl:7:12)at repl:1:1at realRunInThisContextScript (vm.js:22:35)at sigintHandlersWrap (vm.js:98:12)at ContextifyScript.Script.runInThisContext (vm.js:24:12)at REPLServer.defaultEval (repl.js:313:29)at bound (domain.js:280:14)
设想,如果传入的参数值特别大,那么这个调用栈将会非常之大,最终可能超出调用栈的缓存大小而崩溃导致程序执行失败。那么如何解决这个问题呢?使用尾递归。
尾递归
尾递归是一种递归的写法,可以避免不断的将函数压栈最终导致堆栈溢出。通过设置一个累加参数,并且每一次都将当前的值累加上去,然后递归调用。
我们来看如何改写之前定义factorial函数为尾递归:
function factorial(n, total = 1) {if (n === 0) {return total}return factorial(n - 1, n * total)}
factorial(3)的执行步骤如下:
factorial(3, 1)factorial(2, 3)factorial(1, 6)factorial(0, 6)
调用栈不再需要多次对factorial进行压栈处理,因为每一个递归调用都不在依赖于上一个递归调用的值。因此,空间的复杂度为o(1)而不是0(n)。
接下来,通过console.trace()函数将调用栈打印出来。
function factorial(n, total = 1) {console.trace()if (n === 0) {return total}return factorial(n - 1, n * total)}factorial(3)
很惊讶的发现,依然有很多压栈!
// ...// 下面是最后两次对factorial的调用Traceat factorial (repl:2:9) // 3次压栈at factorial (repl:7:8)at factorial (repl:7:8)at repl:1:1 // 请忽略以下底层实现细节代码at realRunInThisContextScript (vm.js:22:35)at sigintHandlersWrap (vm.js:98:12)at ContextifyScript.Script.runInThisContext (vm.js:24:12)at REPLServer.defaultEval (repl.js:313:29)at bound (domain.js:280:14)at REPLServer.runBound [as eval] (domain.js:293:12)Traceat factorial (repl:2:9) // 最后第一调用再次压栈at factorial (repl:7:8)at factorial (repl:7:8)at factorial (repl:7:8)at repl:1:1 // 请忽略以下底层实现细节代码at realRunInThisContextScript (vm.js:22:35)at sigintHandlersWrap (vm.js:98:12)at ContextifyScript.Script.runInThisContext (vm.js:24:12)at REPLServer.defaultEval (repl.js:313:29)at bound (domain.js:280:14)
这是为什么呢?
在Nodejs下面,我们可以通过开启strict mode, 并且使用--harmony_tailcalls来开启尾递归(proper tail call)。
'use strict'function factorial(n, total = 1) {console.trace()if (n === 0) {return total}return factorial(n - 1, n * total)}factorial(3)
使用如下命令:
node --harmony_tailcalls factorial.js
调用栈信息如下:
Traceat factorial (/Users/stefanzan/factorial.js:3:13)at Object.<anonymous> (/Users/stefanzan/factorial.js:9:1)at Module._compile (module.js:570:32)at Object.Module._extensions..js (module.js:579:10)at Module.load (module.js:487:32)at tryModuleLoad (module.js:446:12)at Function.Module._load (module.js:438:3)at Module.runMain (module.js:604:10)at run (bootstrap_node.js:394:7)at startup (bootstrap_node.js:149:9)Traceat factorial (/Users/stefanzan/factorial.js:3:13)at Object.<anonymous> (/Users/stefanzan/factorial.js:9:1)at Module._compile (module.js:570:32)at Object.Module._extensions..js (module.js:579:10)at Module.load (module.js:487:32)at tryModuleLoad (module.js:446:12)at Function.Module._load (module.js:438:3)at Module.runMain (module.js:604:10)at run (bootstrap_node.js:394:7)at startup (bootstrap_node.js:149:9)Traceat factorial (/Users/stefanzan/factorial.js:3:13)at Object.<anonymous> (/Users/stefanzan/factorial.js:9:1)at Module._compile (module.js:570:32)at Object.Module._extensions..js (module.js:579:10)at Module.load (module.js:487:32)at tryModuleLoad (module.js:446:12)at Function.Module._load (module.js:438:3)at Module.runMain (module.js:604:10)at run (bootstrap_node.js:394:7)at startup (bootstrap_node.js:149:9)Traceat factorial (/Users/stefanzan/factorial.js:3:13)at Object.<anonymous> (/Users/stefanzan/factorial.js:9:1)at Module._compile (module.js:570:32)at Object.Module._extensions..js (module.js:579:10)at Module.load (module.js:487:32)at tryModuleLoad (module.js:446:12)at Function.Module._load (module.js:438:3)at Module.runMain (module.js:604:10)at run (bootstrap_node.js:394:7)at startup (bootstrap_node.js:149:9)
你会发现,不会在每次调用的时候压栈,只有一个factorial。
注意:尾递归不一定会将你的代码执行速度提高;相反,可能会变慢。不过,尾递归可以让你使用更少的内存,使你的递归函数更加安全 (前提是你要开启harmony模式)。
那么,博主这里就疑问了:为什么尾递归一定要开启harmony模式才可以呢?
关于Fundebug:
Fundebug专注于JavaScript、微信小程序、微信小游戏、支付宝小程序、React Native、Node.js和Java实时BUG监控。 自从2016年双十一正式上线,Fundebug累计处理了7亿+错误事件,得到了Google、360、金山软件、百姓网等众多知名用户的认可。欢迎免费试用!

版权声明
转载时请注明作者Fundebug以及本文地址:
https://blog.fundebug.com/2017/06/14/all-about-recursions/
JavaScript中的递归的更多相关文章
- 浅谈javascript中的递归和闭包
递归和闭包作为js中很重要的一环,几乎在前端的面试中都会涉及,特别闭包.今天前端组的组长冷不丁的问了我一下,粗略的回答了一下,感觉不太满足,于是重新学习了一下,写下本篇. 在说这个两个概念之前,我们先 ...
- Javascript中递归造成的堆栈溢出及解决方案
关于堆栈的溢出问题,在Javascript日常开发中很常见,Google了下,相关问题还是比较多的.本文旨在描述如何解决此类问题. 首先看一个实例(当然你可以使用更容易的方式实现,这里我们仅探讨递归) ...
- javascript中的Array对象 —— 数组的合并、转换、迭代、排序、堆栈
Array 是javascript中经常用到的数据类型.javascript 的数组其他语言中数组的最大的区别是其每个数组项都可以保存任何类型的数据.本文主要讨论javascript中数组的声明.转换 ...
- JavaScript中‘this’关键词的优雅解释
本文转载自:众成翻译 译者:MinweiShen 链接:http://www.zcfy.cc/article/901 原文:https://rainsoft.io/gentle-explanation ...
- 【跟着子迟品 underscore】JavaScript 中如何判断两个元素是否 "相同"
Why underscore 最近开始看 underscore.js 源码,并将 underscore.js 源码解读 放在了我的 2016 计划中. 阅读一些著名框架类库的源码,就好像和一个个大师对 ...
- javascript 中继承实现方式归纳
转载自:http://sentsin.com/web/1109.html 不同于基于类的编程语言,如 C++ 和 Java,javascript 中的继承方式是基于原型的.同时由于 javascrip ...
- JavaScript中reduce()方法
原文 http://aotu.io/notes/2016/04/15/2016-04-14-js-reduce/ JavaScript中reduce()方法不完全指南 reduce() 方法接收 ...
- JavaScript中的arguments,callee,caller
在提到上述的概念之前,首先想说说javascript中函数的隐含参数: arguments: arguments 该对象代表正在执行的函数和调用它的函数的参数. [function.]argument ...
- 理解JavaScript中的原型继承(2)
两年前在我学习JavaScript的时候我就写过两篇关于原型继承的博客: 理解JavaScript中原型继承 JavaScript中的原型继承 这两篇博客讲的都是原型的使用,其中一篇还有我学习时的错误 ...
随机推荐
- 第二周Access课总结
一.问;这节课你学到了什么知识? 答:回忆上周主要学了关于Access的基础知识和基本操作,一转眼,这周也学到了很多,主要学Access的数据类型的表的建立和管理相关的操作! 收获多少在于学了多少,正 ...
- 背水一战 Windows 10 (91) - 文件系统: Application Data 中的文件操作, Application Data 中的“设置”操作, 通过 uri 引用 Application Data 中的媒体
[源码下载] 背水一战 Windows 10 (91) - 文件系统: Application Data 中的文件操作, Application Data 中的“设置”操作, 通过 uri 引用 Ap ...
- hdoj6483 A Sequence Game(ST预处理RMQ+莫队)
传送:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6483 题意:有长度为$n$的数组,对于一个子区间$[l,r]$内,存在最大值$mx$与最小值$mi$,有$ ...
- WannaCry勒索病毒全解读,权威修复指南大集合
多地的出入境.派出所等公安网络疑似遭遇了勒索蠕虫病毒袭击,已暂时停办出入境业务:加油站突然断网,不能支持支付宝.微信.银联卡等联网支付:大批高校师生电脑中的文件被蠕虫病毒加密,需要支付相应的赎金方可解 ...
- 什么是CDN及CDN加速原理
目录 CDN是什么? CDN的相关技术 负载均衡技术 动态内容分发与复制技术 缓存技术 谁需要CDN? CDN的不足 随着互联网的发展,用户在使用网络时对网站的浏览速度和效果愈加重视,但由于网民数量激 ...
- 锚接口(下)——html5的history api
概述 虽然html5的history api是H5专门用来解决记录历史记录和单页面的方法,但是很多老式的浏览器并不支持它,所以一般遇到老式的浏览器会做一个polyfill使用之前的hashchange ...
- LabVIEW(十二):VI本地化-控件标题内容的修改
一.对于一般LabVIEW的学习,很少遇到本地化的问题但是我们经常会遇到界面控件标题的显示问题.由于各个技术领域的专业性,往往用户对VI界面的显示有自己的要求,其中就包括控件的标题问题,这可以理解成本 ...
- Statement与PreparedStatement的区别
Statement与PreparedStatement的区别 PreparedStatement预编译SQL语句,性能好. PreparedStatement无序拼接SQL语句,编程更简单. Pr ...
- Linux - 查看命令所属的软件包
这里以查看netstat命令所属的软件包为例. CentOS:利用yum provides命令 netstat命令所属的软件包为net-tools [root@CentOS7 ~]# yum prov ...
- 测试工具之RobotFramework安装
Robot Framework很多公司再用,图形化界面,类表格填写关键字和参数,几乎不需要编码知识,上手很快 最近看到某满公司使用的就是这个工具,特地看了下,确实很简单,对于初入测试行业的人来说是个很 ...
