OptiX8入门(一)optixHello
本人初学者,如有错误和更好的表述,请指出
环境:CLion+VS2022+CUDA Toolkit 12.0.1+OptiX8
下载好后打开SDK就可以看到OptiX官方提供的许多例子,CMake配置好后点开自己想看的内容直接开始看。推荐先把GAMES101看完之后再学API。可以看看文档,但是是英文的
OptiX8是一个基于硬件的光追,主要分为三块进行理解,管线(Pipeline),加速结构,shader binding table(sbt)(资源组织)。
GPU和CPU之间的区别只需记住,device表示GPU端,host表示CPU端。
管线就是配置整个光追流程,包括硬件部分的函数入口等。
加速结构,一般是BVH或KD-Tree,不懂的话当成黑盒使用即可,暂时不用去管,只要知道是提升光线的遍历速度的就好。
shader binding table表示里记录所有shader的绑定信息。
光追中主要存在这么几个函数:
Ray generation,可以理解为函数入口(main函数),对每个pixel都执行一遍,一般在这里进行写下TraceRay(发出光线)相关函数,具体是optixTrace()。Intersection,这个是光线和几何体的碰撞,但据说很少用,因为三角形和box的光线交是内置的,一般用于自己定义的可以解析的曲面,例如球。Any hit,射线在任意碰到的交点都会触发,但是不保证交点的触发顺序(应该是用加速结构的原因),也不保证一条线上所有的交点都会触发,比如碰到某些点,会更新光线的TMin和TMax,而在[TMin,TMax]之外的点就不会触发。Closest hit,一条射线上最早碰到的点,可以理解为直射,一般在这里进行计算信息,或者可以再发出射线。Miss,没碰到场景,可以在这里计算天空信息,或者再发出射线。
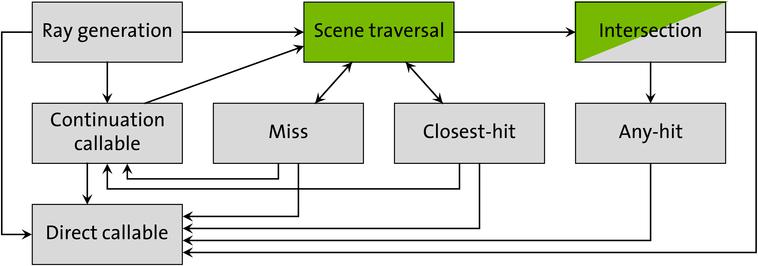
不懂没关系,看看代码,在这里介绍下基础的optixHello,这部分主要结果是生成一个带颜色的画面。
三个文件,optixHello.h、draw_solid_color.cu、optixHello.cpp
cpp和h文件就不说了,cu文件用于GPU,编译成ptx文件后绑定到程序中进行执行,.cu文件是可以printf进行调试的。
看下optixHello.h内容,对比一下draw_solid_color.cu,两个都是在GPU和CPU通信的参数。
struct Params
{
uchar4* image; //一维数组,其中rgb皆为char型,用于填充画面
unsigned int image_width; //只保存width就够了,对于(x,y)的数据用x*width+y就可以定位
};
struct RayGenData
{
float r,g,b; //在cu文件中作为填充色
};
看下draw_solid_color.cu文件,这里的所有函数都要类似__raygen__开头的命名
extern "C" {
__constant__ Params params; //记录结果
}
extern "C"
__global__ void __raygen__draw_solid_color()
{
uint3 launch_index = optixGetLaunchIndex(); //获取当前的pixel坐标
RayGenData* rtData = (RayGenData*)optixGetSbtDataPointer(); //获取sbt记录的数据,在这里是颜色,当然这个程序里直接记录在params也可以
params.image[launch_index.y * params.image_width + launch_index.x] =
make_color( make_float3( rtData->r, rtData->g, rtData->b ) ); //在image数据中记录颜色
}
看下optixHello.cpp
创建context
// Initialize CUDA and create OptiX context
OptixDeviceContext context = nullptr;
{
// Initialize CUDA
CUDA_CHECK( cudaFree( 0 ) );
CUcontext cuCtx = 0; // zero means take the current context
OPTIX_CHECK( optixInit() );
OptixDeviceContextOptions options = {};
options.logCallbackFunction = &context_log_cb;
options.logCallbackLevel = 4;
OPTIX_CHECK( optixDeviceContextCreate( cuCtx, &options, &context ) );
}
创建module,在这里绑定变量和cu文件
// Create module
OptixModule module = nullptr;
OptixPipelineCompileOptions pipeline_compile_options = {};
{
OptixModuleCompileOptions module_compile_options = {};
#if !defined(NDEBUG)
module_compile_options.optLevel = OPTIX_COMPILE_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL_0;
module_compile_options.debugLevel = OPTIX_COMPILE_DEBUG_LEVEL_FULL;
#endif
pipeline_compile_options.usesMotionBlur = false;
pipeline_compile_options.traversableGraphFlags = OPTIX_TRAVERSABLE_GRAPH_FLAG_ALLOW_SINGLE_LEVEL_INSTANCING;
pipeline_compile_options.numPayloadValues = 2;
pipeline_compile_options.numAttributeValues = 2;
pipeline_compile_options.exceptionFlags = OPTIX_EXCEPTION_FLAG_NONE; // TODO: should be OPTIX_EXCEPTION_FLAG_STACK_OVERFLOW;
pipeline_compile_options.pipelineLaunchParamsVariableName = "params"; //这里绑定cu文件的params变量
size_t inputSize = 0;
const char* input = sutil::getInputData( OPTIX_SAMPLE_NAME, OPTIX_SAMPLE_DIR, "draw_solid_color.cu", inputSize ); //这里绑定cu文件
OPTIX_CHECK_LOG( optixModuleCreate(
context,
&module_compile_options,
&pipeline_compile_options,
input,
inputSize,
LOG, &LOG_SIZE,
&module
) );
}
创建program groups,在这里绑定函数
// Create program groups, including NULL miss and hitgroups
OptixProgramGroup raygen_prog_group = nullptr;
OptixProgramGroup miss_prog_group = nullptr;
{
OptixProgramGroupOptions program_group_options = {}; // Initialize to zeros
OptixProgramGroupDesc raygen_prog_group_desc = {}; //
raygen_prog_group_desc.kind = OPTIX_PROGRAM_GROUP_KIND_RAYGEN;
raygen_prog_group_desc.raygen.module = module;
raygen_prog_group_desc.raygen.entryFunctionName = "__raygen__draw_solid_color"; //看这里绑定入口函数
OPTIX_CHECK_LOG( optixProgramGroupCreate(
context,
&raygen_prog_group_desc,
1, // num program groups
&program_group_options,
LOG, &LOG_SIZE,
&raygen_prog_group
) );
// Leave miss group's module and entryfunc name null
OptixProgramGroupDesc miss_prog_group_desc = {}; //这个是miss相关的,在这个程序里暂时没用
miss_prog_group_desc.kind = OPTIX_PROGRAM_GROUP_KIND_MISS;
OPTIX_CHECK_LOG( optixProgramGroupCreate(
context,
&miss_prog_group_desc,
1, // num program groups
&program_group_options,
LOG, &LOG_SIZE,
&miss_prog_group
) );
}
创建pipeline,这里绑定program group
// Link pipeline
OptixPipeline pipeline = nullptr;
{
const uint32_t max_trace_depth = 0;
OptixProgramGroup program_groups[] = { raygen_prog_group };
OptixPipelineLinkOptions pipeline_link_options = {};
pipeline_link_options.maxTraceDepth = max_trace_depth;
OPTIX_CHECK_LOG( optixPipelineCreate( //创建pipeline,绑定program group
context,
&pipeline_compile_options,
&pipeline_link_options,
program_groups,
sizeof( program_groups ) / sizeof( program_groups[0] ),
LOG, &LOG_SIZE,
&pipeline
) );
OptixStackSizes stack_sizes = {};
for( auto& prog_group : program_groups )
{
OPTIX_CHECK( optixUtilAccumulateStackSizes( prog_group, &stack_sizes, pipeline ) );
}
uint32_t direct_callable_stack_size_from_traversal;
uint32_t direct_callable_stack_size_from_state;
uint32_t continuation_stack_size;
OPTIX_CHECK( optixUtilComputeStackSizes( &stack_sizes, max_trace_depth,
0, // maxCCDepth
0, // maxDCDEpth
&direct_callable_stack_size_from_traversal,
&direct_callable_stack_size_from_state, &continuation_stack_size ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixPipelineSetStackSize( pipeline, direct_callable_stack_size_from_traversal,
direct_callable_stack_size_from_state, continuation_stack_size,
2 // maxTraversableDepth
) );
}
创建sbt,在这里设置record和传进去的data,在这里就是生成的颜色
// Set up shader binding table
OptixShaderBindingTable sbt = {};
{
CUdeviceptr raygen_record;
const size_t raygen_record_size = sizeof( RayGenSbtRecord );
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMalloc( reinterpret_cast<void**>( &raygen_record ), raygen_record_size ) );
RayGenSbtRecord rg_sbt;
OPTIX_CHECK( optixSbtRecordPackHeader( raygen_prog_group, &rg_sbt ) );
rg_sbt.data = {0.462f, 0.725f, 0.f};
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMemcpy(
reinterpret_cast<void*>( raygen_record ),
&rg_sbt,
raygen_record_size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice
) );
CUdeviceptr miss_record;
size_t miss_record_size = sizeof( MissSbtRecord );
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMalloc( reinterpret_cast<void**>( &miss_record ), miss_record_size ) );
RayGenSbtRecord ms_sbt;
OPTIX_CHECK( optixSbtRecordPackHeader( miss_prog_group, &ms_sbt ) );
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMemcpy(
reinterpret_cast<void*>( miss_record ),
&ms_sbt,
miss_record_size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice
) );
sbt.raygenRecord = raygen_record;
sbt.missRecordBase = miss_record;
sbt.missRecordStrideInBytes = sizeof( MissSbtRecord );
sbt.missRecordCount = 1;
}
创建outputbuffer用于接收结果,然后launch,这个launch会在每个pixel中执行一次
sutil::CUDAOutputBuffer<uchar4> output_buffer( sutil::CUDAOutputBufferType::CUDA_DEVICE, width, height );
// launch
{
CUstream stream;
CUDA_CHECK( cudaStreamCreate( &stream ) );
Params params;
params.image = output_buffer.map(); //对应到outputbuffer
params.image_width = width;
CUdeviceptr d_param; //创建一个GPU指针
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMalloc( reinterpret_cast<void**>( &d_param ), sizeof( Params ) ) ); //malloc一个GPU空间存放Params
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMemcpy(
reinterpret_cast<void*>( d_param ),
¶ms, sizeof( params ),
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice
) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixLaunch( pipeline, stream, d_param, sizeof( Params ), &sbt, width, height, /*depth=*/1 ) );
CUDA_SYNC_CHECK();
output_buffer.unmap();
CUDA_CHECK( cudaFree( reinterpret_cast<void*>( d_param ) ) );
}
显示图像
//// Display results
{
sutil::ImageBuffer buffer;
buffer.data = output_buffer.getHostPointer(); //这里要在CPU端展示,因此要转为CPU端的数据
buffer.width = width;
buffer.height = height;
buffer.pixel_format = sutil::BufferImageFormat::UNSIGNED_BYTE4; //对应uchar4
if( outfile.empty() )
sutil::displayBufferWindow( argv[0], buffer );
else
sutil::saveImage( outfile.c_str(), buffer, false );
}
清理资源,注意正序生成,倒序清理
// Cleanup
{
CUDA_CHECK( cudaFree( reinterpret_cast<void*>( sbt.raygenRecord ) ) );
CUDA_CHECK( cudaFree( reinterpret_cast<void*>( sbt.missRecordBase ) ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixPipelineDestroy( pipeline ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixProgramGroupDestroy( miss_prog_group ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixProgramGroupDestroy( raygen_prog_group ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixModuleDestroy( module ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixDeviceContextDestroy( context ) );
}
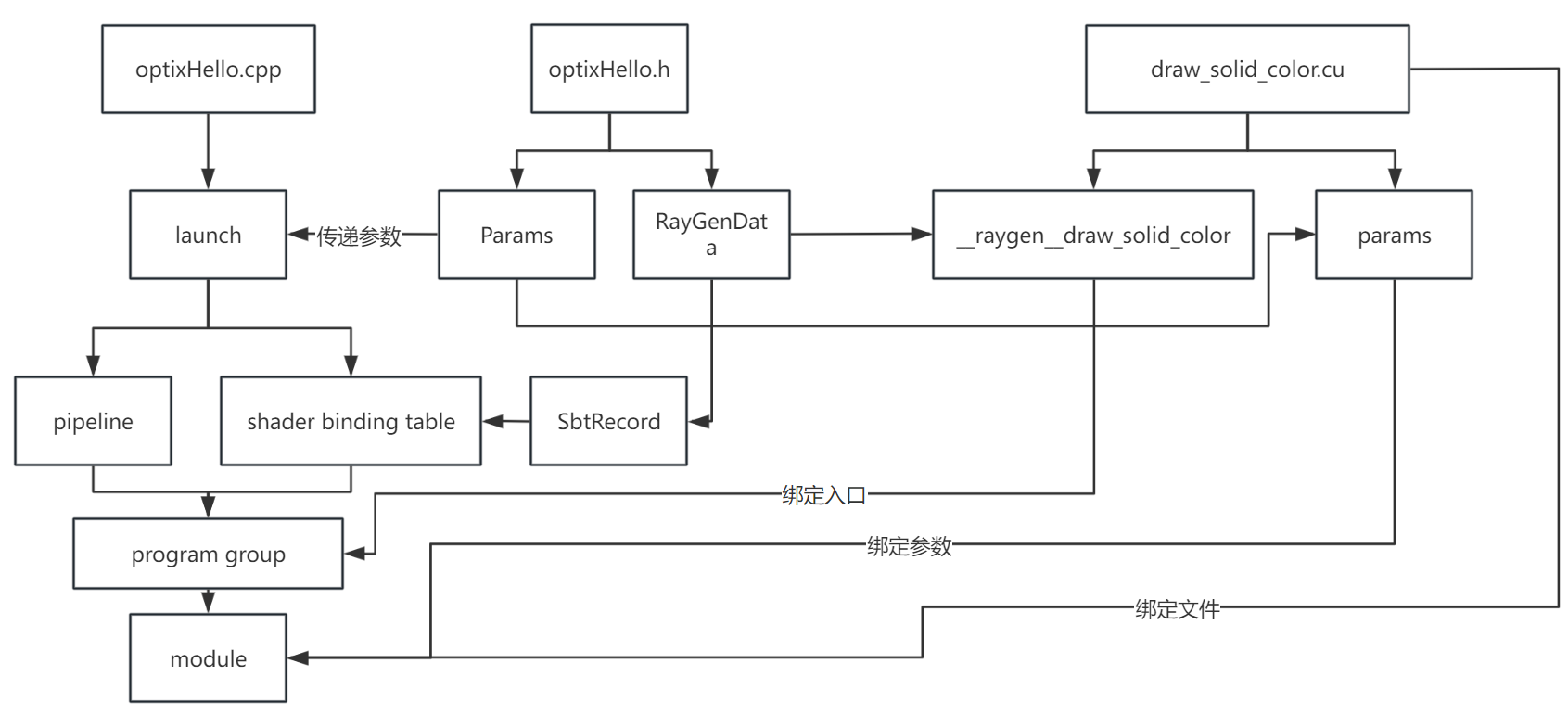
整个程序的大致结构如图(不保证正确)
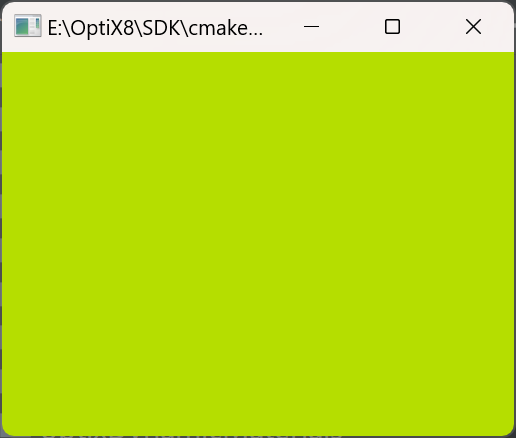
执行结果:
码字不易,点个赞吧
总结
整个程序流程大致就是:
- 创建加速结构(在这里没有)
- 创建
module、program group - 创建
pipeline、sbt launch,显示图像
每个pixel中执行launch,在这里就是每个pixel执行__raygen__draw_solid_color函数设置颜色,传递形成一个outbuffer一维数组,形成图像。
OptiX8入门(一)optixHello的更多相关文章
- Angular2入门系列教程7-HTTP(一)-使用Angular2自带的http进行网络请求
上一篇:Angular2入门系列教程6-路由(二)-使用多层级路由并在在路由中传递复杂参数 感觉这篇不是很好写,因为涉及到网络请求,如果采用真实的网络请求,这个例子大家拿到手估计还要自己写一个web ...
- ABP入门系列(1)——学习Abp框架之实操演练
作为.Net工地搬砖长工一名,一直致力于挖坑(Bug)填坑(Debug),但技术却不见长进.也曾热情于新技术的学习,憧憬过成为技术大拿.从前端到后端,从bootstrap到javascript,从py ...
- Oracle分析函数入门
一.Oracle分析函数入门 分析函数是什么?分析函数是Oracle专门用于解决复杂报表统计需求的功能强大的函数,它可以在数据中进行分组然后计算基于组的某种统计值,并且每一组的每一行都可以返回一个统计 ...
- Angular2入门系列教程6-路由(二)-使用多层级路由并在在路由中传递复杂参数
上一篇:Angular2入门系列教程5-路由(一)-使用简单的路由并在在路由中传递参数 之前介绍了简单的路由以及传参,这篇文章我们将要学习复杂一些的路由以及传递其他附加参数.一个好的路由系统可以使我们 ...
- Angular2入门系列教程5-路由(一)-使用简单的路由并在在路由中传递参数
上一篇:Angular2入门系列教程-服务 上一篇文章我们将Angular2的数据服务分离出来,学习了Angular2的依赖注入,这篇文章我们将要学习Angualr2的路由 为了编写样式方便,我们这篇 ...
- Angular2入门系列教程4-服务
上一篇文章 Angular2入门系列教程-多个组件,主从关系 在编程中,我们通常会将数据提供单独分离出来,以免在编写程序的过程中反复复制粘贴数据请求的代码 Angular2中提供了依赖注入的概念,使得 ...
- wepack+sass+vue 入门教程(三)
十一.安装sass文件转换为css需要的相关依赖包 npm install --save-dev sass-loader style-loader css-loader loader的作用是辅助web ...
- wepack+sass+vue 入门教程(二)
六.新建webpack配置文件 webpack.config.js 文件整体框架内容如下,后续会详细说明每个配置项的配置 webpack.config.js直接放在项目demo目录下 module.e ...
- wepack+sass+vue 入门教程(一)
一.安装node.js node.js是基础,必须先安装.而且最新版的node.js,已经集成了npm. 下载地址 node安装,一路按默认即可. 二.全局安装webpack npm install ...
- js学习笔记:webpack基础入门(一)
之前听说过webpack,今天想正式的接触一下,先跟着webpack的官方用户指南走: 在这里有: 如何安装webpack 如何使用webpack 如何使用loader 如何使用webpack的开发者 ...
随机推荐
- lec-1-Deep Reinforcement Learning, Decision Making, and Control
What is RL 基于学习的决策的数学形式 从经验中学习决策和控制的方法 Why should we study this now 深度神经网络特征方法 强化学习的提升 计算能力的提升 我们还需要 ...
- Python对两个Excel操作
简介 现在有个需求,我们根据需要 data.xlsx 中某些单元格的内容来查找 find.xlsx 中的某些內容. 数据内容(为了数据安全,所有数据均已模糊处理) data.xlsx内容: find. ...
- 【Java】连接MySQL问题总结
前言 最近在学习Java的数据库相关操作,在看视频时自己找资源而产生的一些问题,在此做个总结. 正文 在刚开始学习的时候,你可能跟着老师这样写代码,虽然某些地方已经冒出了红色的波浪线,但你半信半疑的继 ...
- 【HDU】1312 Red andBlack (DFS&BFS经典好题)
Red and Black 题目 我是题目链接 题解 找出所能到达的所有黑色的数量,用DFS和BFS均可. BFS: #include <iostream> #include <qu ...
- LLM探索:环境搭建与模型本地部署
前言 最近一直在炼丹(搞AIGC这块),突然发现业务代码都索然无味了- 上次发了篇AI画图的文章,ChatGPT虽然没法自己部署,但现在开源的LLM还是不少的,只要有一块差不多的显卡,要搞个LLM本地 ...
- Part2: DDPM as Example of Variational Inference
很多次翻看DDPM,始终不太能理解论文中提到的\(\text{Variational Inference}\)到底是如何在这个工作中起到作用.五一假期在家,无意间又刷到徐亦达老师早些年录制的理论视频, ...
- 第一章 Rust基本知识 -- tour of rust
第一章 基础知识 将探讨函数.变量和最基本的类型等基本知识. 变量 变量使用let关键字来声明. 在赋值时,Rust能够在99%的情况下推断变量类型.如果不能,也可以将类型添加到变量声明中. 注意 如 ...
- SRE 的工作介绍
哈喽大家好,我是咸鱼 今天看到了一篇很不错的文章,作者是一名 SRE 工程师,在 Shopee 工作,base 新加坡 分享出来给大家看看 作者:卡瓦邦噶 原文链接:https://www.kawab ...
- HTTP请求:requests的进阶使用方法浅析
1 背景 上篇文章讲解了requests模块的基础使用,其中有get.put.post等多种请求方式,使用data.json等格式做为请求参数,在请求体中添加请求头部信息的常见信息,如:headers ...
- Elastaticsearch 集群部署
系统Ubuntu 16.04 Elastaticsearch 5.6.9 Kibana 5.6.9 官网地址 https://www.elastic.co/products/elasticsearch ...
