基于谷歌开源的TensorFlow Object Detection API视频物体识别系统搭建自己的应用(四)
本章主要内容是利用mqtt、多线程、队列实现模型一次加载,批量图片识别分类功能
目录结构如下:
mqtt连接及多线程队列管理
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
import images_detect
MQTTHOST = "192.168.3.202"
MQTTPORT = 1883
mqttClient = mqtt.Client()
q = Queue()
# 连接MQTT服务器
def on_mqtt_connect():
mqttClient.connect(MQTTHOST, MQTTPORT, 60)
mqttClient.loop_start()
# 消息处理函数
def on_message_come(mqttClient, userdata, msg):
q.put(msg.payload.decode("utf-8")) # 放入队列
print("产生消息", msg.payload.decode("utf-8"))
def consumer(q, pid):
print("开启消费序列进程", pid)
# 多进程中发布消息需要重新初始化mqttClient
ImagesDetect = images_detect.ImagesDetect()
ImagesDetect.detect(q)
# subscribe 消息订阅
def on_subscribe():
mqttClient.subscribe("test", 1) # 主题为"test"
mqttClient.on_message = on_message_come # 消息到来处理函数
# publish 消息发布
def on_publish(topic, msg, qos):
mqttClient.publish(topic, msg, qos);
def main():
on_mqtt_connect()
on_subscribe()
for i in range(1, 3):
c1 = Process(target=consumer, args=(q, i))
c1.start()
while True:
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
图片识别
images_detect.py
# coding: utf-8
import numpy as np
import os
import sys
import tarfile
import tensorflow as tf
from object_detection.utils import label_map_util
from object_detection.utils import visualization_utils as vis_util
import cv2
import decimal
import MyUtil
context = decimal.getcontext()
context.rounding = decimal.ROUND_05UP
class ImagesDetect():
def __init__(self):
sys.path.append("..")
MODEL_NAME = 'faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28'
MODEL_FILE = MODEL_NAME + '.tar.gz'
# Path to frozen detection graph. This is the actual model that is used for the object detection.
PATH_TO_CKPT = MODEL_NAME + '/frozen_inference_graph.pb'
# List of the strings that is used to add correct label for each box.
PATH_TO_LABELS = os.path.join('data', 'mscoco_label_map.pbtxt')
NUM_CLASSES = 90
tar_file = tarfile.open(MODEL_FILE)
for file in tar_file.getmembers():
file_name = os.path.basename(file.name)
if 'frozen_inference_graph.pb' in file_name:
tar_file.extract(file, os.getcwd())
# ## Load a (frozen) Tensorflow model into memory.
self.detection_graph = tf.Graph()
with self.detection_graph.as_default():
od_graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
with tf.gfile.GFile(PATH_TO_CKPT, 'rb') as fid:
serialized_graph = fid.read()
od_graph_def.ParseFromString(serialized_graph)
tf.import_graph_def(od_graph_def, name='')
# ## Loading label map
# Label maps map indices to category names, so that when our convolution network predicts `5`, we know that this corresponds to `airplane`. Here we use internal utility functions, but anything that returns a dictionary mapping integers to appropriate string labels would be fine
label_map = label_map_util.load_labelmap(PATH_TO_LABELS)
categories = label_map_util.convert_label_map_to_categories(label_map, max_num_classes=NUM_CLASSES, use_display_name=True)
self.category_index = label_map_util.create_category_index(categories)
self.image_tensor = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('image_tensor:0')
# 每个框代表一个物体被侦测到
self.boxes = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_boxes:0')
# 每个分值代表侦测到物体的可信度.
self.scores = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_scores:0')
self.classes = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_classes:0')
self.num_detections = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('num_detections:0')
def detect(self, q):
with self.detection_graph.as_default():
config = tf.ConfigProto()
# config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
config.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.2
with tf.Session(graph=self.detection_graph, config=config) as sess:
while True:
img_src = q.get()
print('------------start------------' + MyUtil.get_time_stamp())
image_np = cv2.imread(img_src)
# 扩展维度,应为模型期待: [1, None, None, 3]
image_np_expanded = np.expand_dims(image_np, axis=0)
# 执行侦测任务.
(boxes, scores, classes, num_detections) = sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes, self.num_detections],
feed_dict={self.image_tensor: image_np_expanded})
# 检测结果的可视化
vis_util.visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
image_np,
np.squeeze(boxes),
np.squeeze(classes).astype(np.int32),
np.squeeze(scores),
self.category_index,
use_normalized_coordinates=True,
line_thickness=8)
print('------------end------------' + MyUtil.get_time_stamp())
# cv2.imshow('object detection', cv2.resize(image_np, (800, 600)))
if cv2.waitKey(25) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
break
import time
def get_time_stamp():
ct = time.time()
local_time = time.localtime(ct)
data_head = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", local_time)
data_secs = (ct - int(ct)) * 1000
time_stamp = "%s.%03d" % (data_head, data_secs)
return time_stamp
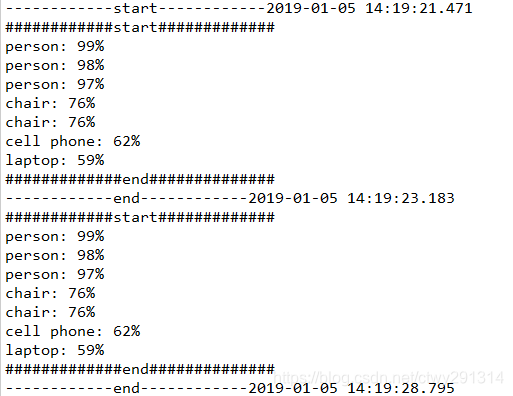
效果:
基于谷歌开源的TensorFlow Object Detection API视频物体识别系统搭建自己的应用(四)的更多相关文章
- 对于谷歌开源的TensorFlow Object Detection API视频物体识别系统实现教程
本教程针对Windows10实现谷歌近期公布的TensorFlow Object Detection API视频物体识别系统,其他平台也可借鉴. 本教程将网络上相关资料筛选整合(文末附上参考资料链接) ...
- 谷歌开源的TensorFlow Object Detection API视频物体识别系统实现教程
视频中的物体识别 摘要 物体识别(Object Recognition)在计算机视觉领域里指的是在一张图像或一组视频序列中找到给定的物体.本文主要是利用谷歌开源TensorFlow Object De ...
- 谷歌开源的TensorFlow Object Detection API视频物体识别系统实现(二)[超详细教程] ubuntu16.04版本
本节对应谷歌开源Tensorflow Object Detection API物体识别系统 Quick Start步骤(一): Quick Start: Jupyter notebook for of ...
- 谷歌开源的TensorFlow Object Detection API视频物体识别系统实现(一)[超详细教程] ubuntu16.04版本
谷歌宣布开源其内部使用的 TensorFlow Object Detection API 物体识别系统.本教程针对ubuntu16.04系统,快速搭建环境以及实现视频物体识别系统功能. 本节首先介绍安 ...
- 安装运行谷歌开源的TensorFlow Object Detection API视频物体识别系统
Linux安装 参照官方文档:https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/object_detection/g3doc/inst ...
- 使用Tensorflow object detection API——训练模型(Window10系统)
[数据标注处理] 1.先将下载好的图片训练数据放在models-master/research/images文件夹下,并分别为训练数据和测试数据创建train.test两个文件夹.文件夹目录如下 2. ...
- 基于TensorFlow Object Detection API进行迁移学习训练自己的人脸检测模型(二)
前言 已完成数据预处理工作,具体参照: 基于TensorFlow Object Detection API进行迁移学习训练自己的人脸检测模型(一) 设置配置文件 新建目录face_faster_rcn ...
- 基于TensorFlow Object Detection API进行相关开发的步骤
*以下二/三.四步骤确保你当前的文件目录是以research文件夹为相对目录. 一/安装或升级protoc 查看protoc版本命令: protoc --version 如果发现版本低于2.6.0或运 ...
- 使用TensorFlow Object Detection API+Google ML Engine训练自己的手掌识别器
上次使用Google ML Engine跑了一下TensorFlow Object Detection API中的Quick Start(http://www.cnblogs.com/take-fet ...
随机推荐
- Java——容器(Interator)
[Interator接口] <1> 所有实现了Collection接口的容器类都有一个interator方法用以返回一个实现了Interaor接口的对象. <2> Inte ...
- 【bzoj3566】 [SHOI2014]概率充电器
*题目描述: 著名的电子产品品牌 SHOI 刚刚发布了引领世界潮流的下一代电子产品——概率充电器: “采用全新纳米级加工技术,实现元件与导线能否通电完全由真随机数决定!SHOI 概率充电器,您生活不可 ...
- 笨办法学Python(learn python the hard way)--练习程序42
下面是练习42,基于python3 #ex42.py 1 class TheThing(object): 2 #__init__为class设置内部变量的方式,正常情况下函数内的变量与外部没有关联,但 ...
- 电脑配置Java环境变量之后,在cmd中仍然无法识别
在电脑上配置了Java的环境变量,但是在cmd框中仍然无法识别: 解决方法:cmd.exe右键---以管理员身份运行,即可识别
- optistruct如何将多个约束置于一个约束集合中
建立load_col,卡片设置SPCADD.
- WebRtc 源码下载
项目需要用到WebRtc,记录下基本下载的步骤: 1.下载depot_tools,利用depot_tools 下载WebRtc源码 git clone https://chromium.googles ...
- HTML - form 表单提交
form 表单提交 数据发送 disabled:不发送 display_none:发送 type_hidden:发送 readonly:发送 测试 html: <!DOCTYPE html> ...
- Vue知识整理4:v-html标签
可以在数据绑定中使用html标签,这样在变量里可以使用html标签输出结果,如下所示:
- 使用spring配置类代替xml配置文件注册bean类
spring配置类,即在类上加@Configuration注解,使用这种配置类来注册bean,效果与xml文件是完全一样的,只是创建springIOC容器的方式不同: //通过xml文件创建sprin ...
- try...catch语句
程序的异常:Throwable 严重问题Error我们不处理,这种问题一般都是很严重的,比如内存溢出 问题Exception 编译期问题不是RuntimeException的异常必须进行处理,如果不处 ...
