Spring全家桶之spring boot(五)
Thymeleaf简介
Thymeleaf是一个流行的模板引擎,该模板引擎采用Java语言开发,模板引擎是一个技术名词,是跨领域跨平台的概念,在Java语言体系下有模板引擎,在C#、PHP语言体系下也有模板引擎。除了thymeleaf之外还有Velocity、FreeMarker等模板引擎,功能类似。
Thymeleaf的主要目标在于提供一种可被浏览器正确显示的、格式良好的模板创建方式,因此也可以用作静态建模。你可以使用它创建经过验证的XML与HTML模板。使用thymeleaf创建的html模板可以在浏览器里面直接打开(展示静态数据),这有利于前后端分离。需要注意的是thymeleaf不是spring旗下的。这里我们使用thymeleaf 3版本。
thymeleaf官方网址:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
thymeleaf官方在线文档网址:https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
第一个thymeleaf程序
1、要想使用thymeleaf,首先需要添加thymeleaf依赖,这里与之前不一样的是我们需要勾选thymeleaf模板引擎依赖,其他的几个依赖我们之前已经说过,这里就不再进行讲解了。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、修改spring boot配置文件添加如下代码,在开发阶段建议关闭thymeleaf缓存,因为我们需要对开发项目进行实时修改,所以在这里我们先将缓存关闭。
#关闭thymeleaf缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
3、thymeleaf会对html中的标签进行严格的校验,如果标签缺少结束的话thymeleaf会报错,比如之前我们在html中写的<input>标签,如果缺少</input>则会报错。类似于这种错误不容易发现所以我们可以通过下面的方式去除thymeleaf的严格校验,首先添加依赖(需要手动添加,无法自动生成):
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.nekohtml</groupId>
<artifactId>nekohtml</artifactId>
<version>1.9.22</version>
</dependency>
pom.xml中添加完依赖之后,在spring boot配置文件中添加如下内容(完成以上两步之后就可以关闭thymeleaf的严格校验了):
spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGANCYHTML5
4、创建controller,通过Model向html中传递数据,这里我们需要跳转html,不需要转换Json数据所以不需要使用RestController,Controller即可。thymeleaf默认的视图解析器为html,所以controller跳转时不需要再加html后缀,直接写"index"。
package com.scm.thymeleaf.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller
public class ThymeleafController {
@RequestMapping("/firstThymeleaf")
public String thymeleafTest(Model model){
model.addAttribute("info","This is my first thymeleaf!");
return "index";
}
}
5、在resources/templates里面创建一个index.html,填写下面内容。
注意:这里我们使用了thymeleaf,所以我们在<html>标签中添加 xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Spring boot集成 Thymeleaf</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="${info}">Spring boot集成 Thymeleaf</p>
</body>
</html>
在html中我们通过th:text属性接收controller的"info"参数。并且将动态数据替换掉静态数据"Spring boot集成 Thymeleaf";
Springboot使用thymeleaf作为视图展示的时候,我们将模板文件放置在resource/templates目录下,静态资源放置在resource/static目录下。
Thymeleaf表达式
标准变量表达式
先创建一个controller用于向html传递数据,这里我们创建了一个User类。
package com.scm.thymeleaf.bean; import lombok.Data; @Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String Name;
private String Phone;
public User(){}
public User(int id,String Name,String Phone){
this.id = id;
this.Name = Name;
this.Phone = Phone;
}
}
Controller
package com.scm.thymeleaf.controller; import com.scm.thymeleaf.bean.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller
public class userInfo {
@RequestMapping("/userInfo")
public String userInfos(Model model){
User user = new User(1000,"scm","188888888");
model.addAttribute("u",user);
model.addAttribute("hello","Hello World");
return "user";
}
}
user.html
html中我们接收了controller中传递的User对象,html中的${对象名.属性},对象名是addAttribute("键",“值”)方法中的键,而不是我们创建的User类。
在<td></td>标签中我们写入了静态数据,这些静态数据会被动态数据所取代,但是如果我们找到html本地路径,在本地直接打开user.html的话会显示静态资源,而不显示动态资源。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body> <table>
<tr>
<td th:text="${u.id}">1</td>
<td th:text="${u.name}">a</td>
<td th:text="${u.phone}">137</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
选择变量表达式
在标准变量表达式中我们通过${对象名.属性}的方式接收controller传递的参数。如果User类中有几十个属性甚至更多,那么岂不是要写几十次对象名,这样就显得麻烦。而使用选择变量表达式之后我们只需要声明一次对象名就可以了。代码如下:
<table>
<tr th:object="${u}">
<td th:text="*{id}">1</td>
<td th:text="*{name}">a</td>
<td th:text="*{phone}">137</td>
</tr>
</table>
在<tr></tr>标签中我们声明了一个th:object获取了controller中的User对象,那么在这个<tr>标签中,我们就可以直接用*{属性名}的方式。这样如果User中的属性多的话我们只需要写属性名即可。
url表达式
将后台传入的数据拼接到url中,通过url表达式可以动态的拼接url。这里使用th:href属性,前两个为非Restful风格的get请求,后两个为Restful风格请求。
<a href="info.html" th:href="@{/user/info(id=${u.id})}">参数拼接</a>
<a href="info.html" th:href="@{/user/info(id=${u.id},phone=${u.phone})}">多参数拼接</a>
<a href="info.html" th:href="@{/user/info/{uid}(uid=${u.id})}">restful风格</a>
<a href="info.html" th:href="@{/user/info/{uid}/abc(uid=${u.id})}">restful风格</a>



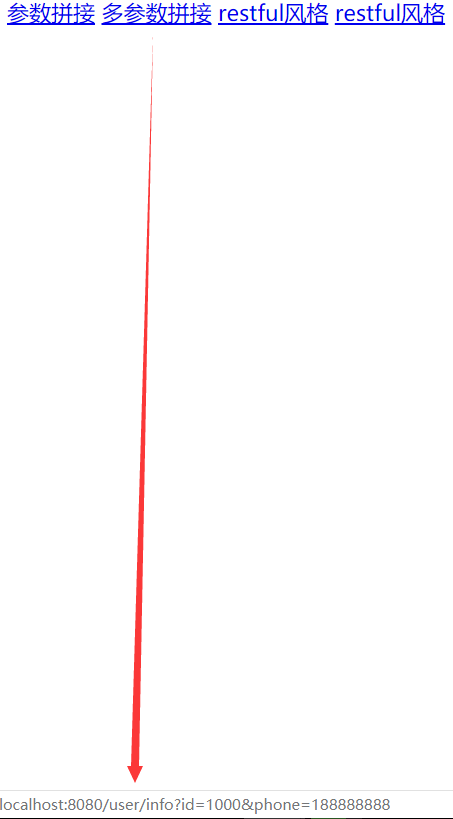
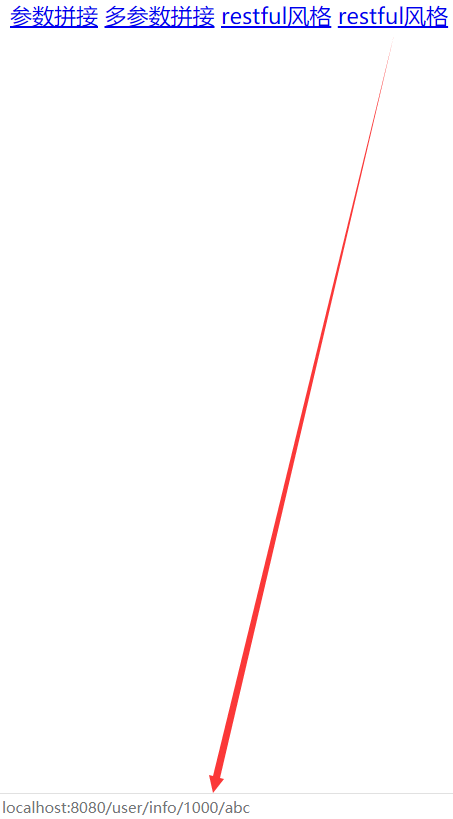
从图中看出我们将鼠标悬浮在超链接上,在下方我们可以看到动态拼接的url,这些url中的动态数据都是从controller中传递到url中的。
Thymeleaf运算符和表达式
重新创建一个controller,先在这里设置一些我们将要用到的参数。
package com.scm.thymeleaf.controller; import com.scm.thymeleaf.bean.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.Date; @Controller
public class userInfo {
@RequestMapping("/userInfo1")
public String userInfos1(Model model, HttpSession seesion){
model.addAttribute("page",5);//字符串拼接
model.addAttribute("sex",1);//三目运算符
seesion.setAttribute("phone","16666666666");//session内置对象
model.addAttribute("myDate",new Date());//#Date类
return "user";
}
}
字符串拼接(两种方式)
方式一:这种方式与java中字符串拼接类似。
<span th:text="'当前是第'+${page}+'页 ,共'+${page}+'页'"></span>
方式二:使用“|”减少了字符串的拼接,在| |之间thymeleaf可以自动识别 ${}表达式。
<span th:text="|当前是第${page}页,共${page}页|"></span>
三目运算符
<span th:text="${sex eq 0} ? '男' : '女'">未知</span>
基本运算和关系判断
算术运算:+ , - , * , / , % 关系比较: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le ) 相等判断:== , != ( eq , ne )
thymeleaf内置对象
模板引擎提供了一组内置的对象,这些内置的对象可以直接在模板中使用,这些对象由#号开始引用。
1、#request:相当于是HttpServletRequest对象
<span th:text="${#request.getContextPath()}"></span><br>
2、#session: 相当于是HttpSession对象
<span th:text="${#session.getAttribute('phone')}"></span><br>
除了上面的对象之外,工作中常使用的数据类型,如集合,时间,数值,thymeleaf的专门提供了功能性对象来处理它们,下面列举一部分。
1、#dates: java.util.Date对象的实用方法,可以调用里面的方法。#后边都多加一个s,例如#dates就是Date类。myDate参数是在controller创建的一个new Date();
<span th:text="${#dates.format(myDate, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}"></span>
2、#numbers: 格式化数字对象的实用方法;(Number类)
3、#strings: 字符串对象的实用方法;(String类)
4、#objects: 对objects操作的实用方法;(Object类)
5、#lists: list的实用方法,比如<span th:text="${#lists.size(datas)}">(List类)
6、#aggregates: 对数组或集合创建聚合的实用方法;(Aggregate类)
Thymeleaf常用属性
th:each
该属性较为常用,比如从后台传来一个对象集合那么就可以使用此属性遍历输出,它与JSTL中的<c: forEach>类似,此属性既可以循环遍历集合,也可以循环遍历数组及Map。
1、循环list集合
先创建controller构建list数据,这里我们还使用上边的User类。
package com.scm.thymeleaf.controller; import com.scm.thymeleaf.bean.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date; @Controller
public class userInfo {
@RequestMapping("/userInfo2")
public String userInfo3(Model model){
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){
User user = new User(i,"scm"+i,"1666666666"+i);
al.add(user);
}
model.addAttribute("list",al);
return "user";
}
}
user.html
<table>
<tr th:each="user, interStat : ${list}">
<td th:text="${interStat.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.phone}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
让我们来分析一下html中的代码。首先我们通过${list}接收到了controller传递的ArrayList集合。那么引号中的user和interStat又分别是什么呢?其实这两个都是我们其的一个别名,在list集合中存入了User对象,注意不要将html中的user和User对象混淆,html中的user是可以随意命名的,比如这里我们可以把html中的user换成u,那么在td中的${}我们就要改为u.id、u.name和u.phone。通俗的讲我们就是把集合中的对象起了一个别名,然后通过别名去遍历获取集合中的值。interStat同样是我们起的一个别名,这里的interStat类似于jstl里面foreach的varStatus,可以获取到当前的迭代信息。
这里有另一种写法就是将interStat省略,这样thymeleaf会自动为我们起一个名字,命名规则为对象别名+Stat。本例我们对象别名为user,所以当我们省略interStat时,thymeleaf为我们自动起一个userStat的名字,然后通过userStat.index可以达到同样的效果。再比如我们将别名改为u,这时自动生成的就是uStat。如下的代码与上边的代码是等效的。
<tr th:each="user:${list}">
<td th:text="${userStat.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.phone}"></td>
</tr>
总结两种写法,第一种写法我们手动起了两个别名,一个用于调用对象属性,另一个用于查看迭代信息。第二种写法只需要我们起一个别名,另外一个别名是thymeleaf根据我们起的对象别名自动生成的。下面是interStat里面一些属性的含义:
index: 当前迭代对象的index(从0开始计算)
count: 当前迭代对象的个数(从1开始计算)
size: 被迭代对象的大小
current: 当前迭代变量
even/odd: 布尔值,当前循环是否是偶数/奇数(从0开始计算)
first: 布尔值,当前循环是否是第一个
last: 布尔值,当前循环是否是最后一个
2、遍历map集合
controller构建map数据
@RequestMapping("/userInfo3")
public String userInfo3(Model model){
HashMap<String, User> userMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setName("scm" + i);
user.setPhone("13"+i+"11111111");
userMap.put(String.valueOf(i), user);
}
model.addAttribute("userMap", userMap);
return "user";
}
html,myMapVal.key相当于map的键,myMapVal.value相当于map中的值。
<div th:each="myMapVal : ${userMap}">
<span th:text="${myMapValStat.count}"></span>
<span th:text="${myMapVal.key}"></span>
<span th:text="${myMapVal.value.name}"></span>
<span th:text="${myMapVal.value.phone}"></span>
<br/>
</div>
遍历map与遍历list集合原理类似,只不过map是以键值对的形式存在的,所以我们需要通过别名.key方式获取键,别名.value获取值。
3、遍历循环数组
controller构建数组数据
@RequestMapping(value="/usersArray")
public String selectAllUserArray (Model model) {
User[] userArray = new User[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setName("scm" + i);
user.setPhone("13"+i+"11111111");
userArray[i] = user;
}
model.addAttribute("userArray", userArray);
return "user";
}
user.html
<div th:each="myArrayVal : ${userArray}">
<div th:text="${myArrayVal.id}"></div>
<div th:text="${myArrayVal.name}"></div>
<div th:text="${myArrayVal.phone}"></div>
</div>
th:id
动态设置html标签中的id属性,比如:我们从后台传入一个字符串hello,那么就可以将${hello)的值作为span标签的id。
<span th:id="${hello}">good</span>
th:if
条件判断,比如后台传来一个变量,判断该变量的值,0为男,1为女:
<span th:if="${sex} == 0" >
男:<input type="radio" name="sex" th:value="男" />
</span>
<span th:if="${sex} == 1">
女:<input type="radio" name="sex" th:value="女" />
</span>
th:switch/th:case
switch,case判断语句,比如:
<div th:switch="${sex}">
<p th:case="0">性别:男</p>
<p th:case="1">性别:女</p>
<p th:case="*">性别:未知</p>
</div>
这里的*表示默认,当上面的case都是false的时候,会执行默认的内容。
th:value
类似html标签中的value属性,能对某元素的value属性进行赋值,比如:
<input type="hidden" id="userId" name="userId" th:value="${userId}">
th:inline
th:inline 有三个取值类型
- text(从后台取出数据展示)
<span th:inline="text">Hello, [[${name}]]</span>
等同于:
<span>Hello, <span th:text="${name}"></span></span>
类似于第二行代码中的例子。我们需要在第一个span中的Hello,后动态获取数据,这时需要再写一个span标签然后使用th:text属性。但是我们可以使用th:inline="text"直接实现等同的效果。
- none(有时候希望在html中直接显示[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]],此时可以使用none)
在th:inline="text"中使用[[${ }]]的方式获取controller的数据。那么当我们想直接输出[[1,2,3]]这样的字符串类型的怎么办呢。如果我们直接<div>[[1,2,3]]</div>发现会报错,因为thymeleaf自动将[[ ]]识别为获取传递的数据。这时就要用到th:linline="none"了。
<p th:inline="none"> [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]!</p>
使用none之后就相当于告诉thymeleaf这个双中括号内的内容不是传递的参数,你不需要去识别。这样thymeleaf就会知道了。
- javascript(如果希望在JavaScript中获取后台相应的数据,可以使用下面内容:)
创建controller构建数据
@RequestMapping("/userInfo4")
public String userInfo4(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","scm");
return "javascript";
}
javascript.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body> </body>
<script th:inline="javascript" type="text/javascript">
var msg = "Hello," + [[${name}]];
alert(msg);
</script>
</html>
可以看到在th:inline="javascript"可以让我们在javascript中获取controller传递的数据,同样是[[${ }]]的格式接收数据。
到这里为止thymeleaf的第一个程序和thymeleaf相关的常用表达式和相关属性就讲完了,一些不太常用的这里就不做讲解了。如果发现错误或有疑问的地方请及时评论,谢谢。
Spring全家桶之spring boot(五)的更多相关文章
- Spring全家桶之spring boot(三)
spring boot集成mybatis 众所周知,spring与springmvc可以无缝集成,而mybatis不是spring旗下的框架,因此需要进行配置,当然,这里的配置也是非常简单的. 1.首 ...
- Spring全家桶之spring boot(二)
spring boot的两种配置文件: 虽然spring boot可以帮助我们进行一些配置项,但是有些内容还是需要开发者自己进行配置,因此spring boot提供了配置文件以供开发者配置.sprin ...
- Spring全家桶之spring boot(一)
spring boot框架抛弃了繁琐的xml配置过程,采用大量的默认配置简化我们的开发过程.使用spring boot之后就不用像以前使用ssm的时候添加那么多配置文件了,spring boot除了支 ...
- Spring全家桶之spring boot(四)
spring boot拦截器.过滤器.servlet和健康检查机制 spring boot拦截器 spring boot配置拦截器与原来大致相同,只是需要在拦截器的配置类上添加@Configurat ...
- 10分钟详解Spring全家桶7大知识点
Spring框架自2002年诞生以来一直备受开发者青睐,它包括SpringMVC.SpringBoot.Spring Cloud.Spring Cloud Dataflow等解决方案.有人亲切的称之为 ...
- Java秋招面试复习大纲(二):Spring全家桶+MyBatis+MongDB+微服务
前言 对于那些想面试高级 Java 岗位的同学来说,除了算法属于比较「天方夜谭」的题目外,剩下针对实际工作的题目就属于真正的本事了,热门技术的细节和难点成为了面试时主要考察的内容. 这里说「天方夜谭」 ...
- 一文解读Spring全家桶 (转)
Spring框架自2002年诞生以来一直备受开发者青睐,它包括SpringMVC.SpringBoot.Spring Cloud.Spring Cloud Dataflow等解决方案.有人亲切的称之为 ...
- 【转】Spring全家桶
Spring框架自诞生以来一直备受开发者青睐,有人亲切的称之为:Spring 全家桶.它包括SpringMVC.SpringBoot.Spring Cloud.Spring Cloud Dataflo ...
- Spring全家桶–SpringBoot Rest API
Spring Boot通过提供开箱即用的默认依赖或者转换来补充Spring REST支持.在Spring Boot中编写RESTful服务与SpringMVC没有什么不同.总而言之,基于Spring ...
随机推荐
- [WPF] 考古Expression Web:微软当年最漂亮的WPF软件
1. 什么是Expression Web Expression Studio是微软在2007年推出的一套针对设计师的套件,其中包含专业的设计工具和新技术,可以弹性且自由地将设计方案转为实际--无论设计 ...
- javascript-数组简单的认识
一起组团(什么是数组) 我们知道变量用来存储数据,一个变量只能存储一个内容.假设你想存储10个人的姓名或者存储20个人的数学成绩,就需要10个或20个变量来存储,如果需要存储更多数据,那就会变的更麻烦 ...
- Inno Setup打包之先卸载再安装
使用Inno Setup打包程序之后,如果想要在安装前先卸载,那么需要加下面代码,需要注意的是红色标注的改为你们自己的.网上看到有些说_is1前面用AppName,但是我这边验证不行. [Setup] ...
- 初入React源码(一)
导语 React是我接触的第二个框架,我最初开始接触的是vue,但是并没有深入的理解过vue,然后在工作过程中,我开始使用了React,现在已经觉得React会比vue更加实用,但是这只是个人观点,可 ...
- ACM卡常处理办法(虽然我到现在没遇到)
今天做预流推送,一样的代码.别人500MS(OI选手)而我5S,百思不得其解,然后我知道了还有卡常这一说. 我们今天就来看一看吧: 1.循环展开: 在缓存和寄存器允许的情况下一条语句内大量的展开运算会 ...
- P2024 食物链(种类并查集)
P2024 [NOI2001]食物链 题目描述 动物王国中有三类动物 A,B,C,这三类动物的食物链构成了有趣的环形.A 吃 B,B吃 C,C 吃 A. 现有 N 个动物,以 1 - N 编号.每个动 ...
- MySQL 8.0.20 源码安装数据库软件
官方支持的平台: https://www.mysql.com/support/supportedplatforms/database.html
- 《Docker从入门到跑路》之镜像和容器的基本操作
一.获取镜像 官方提供了一个公共镜像仓库Docker Hub,默认是从这上面获取镜像的. 搜素镜像使用docker search 命令: # docker search --help Usage: d ...
- libevent(九)bufferevent
bufferevent,带buffer的event struct bufferevent { struct event_base *ev_base; const struct bufferevent_ ...
- 【认证与授权】Spring Security自定义页面
在前面的篇幅中,我们对认证和授权流程大致梳理了一遍.在这个过程中我们一直都是使用系统生成的默认页面,登录成功后也是直接调转到根路径页面.而在实际的开发过程中,我们是需要自定义登录页面的,有时还会添加各 ...
