LeetCode树专题
LeetCode树专题
98. 验证二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树,每个结点的值都有一个范围

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root,INT_MIN,INT_MAX);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* root,long long l,long long r){
if(!root) return true;
//判断当前结点
if(root->val < l || root->val > r) return false;
//递归判断左右子节点
return dfs(root->left,l,root->val - 1ll) && dfs(root->right,root->val+1ll,r);
}
};
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
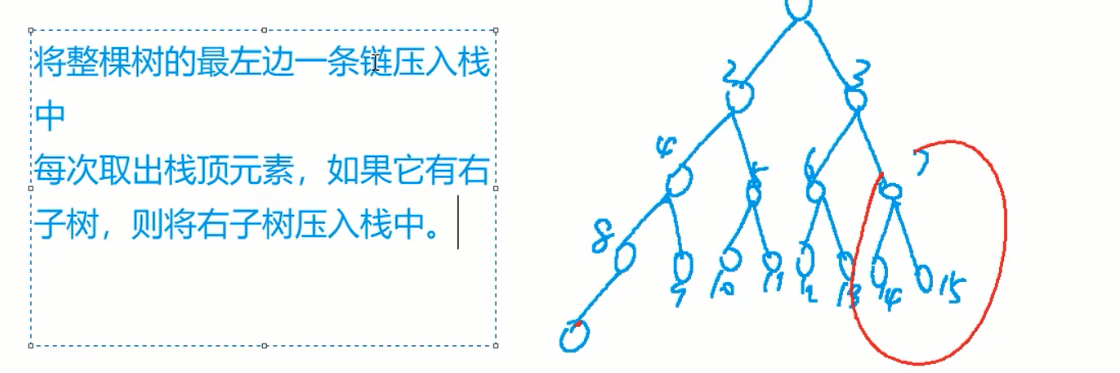
二叉树中序遍历的迭代写法
模拟中序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
auto p = root;
while(p || stk.size()){
while(p){ //1.把左子树全部加入栈中
stk.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
p = stk.top(); //2.取栈首 输出栈首
stk.pop();
result.push_back(p->val);
p = p->right; //3.转到右子树
}
return result;
}
};
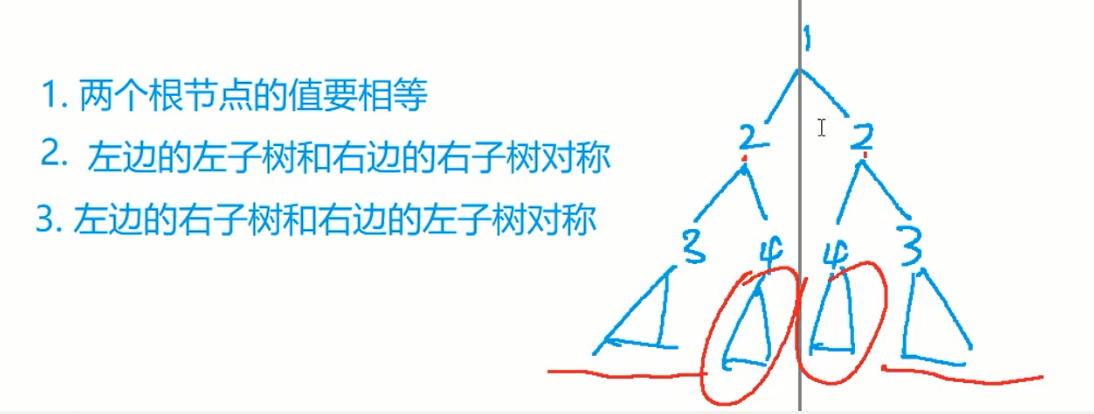
101. 对称二叉树
用递归和迭代两种做法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return true;
return dfs(root->left,root->right);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* p,TreeNode* q){
if(!p || !q) return !p && !q; //左右不能一空一不空
//1.比较当前两结点的值
//2.比较p结点左子树和q结点右子树
//3.比较p结点右子树和q结点左子树
return p->val == q->val &&
dfs(p->left,q->right) && dfs(p->right,q->left);
}
};
迭代:左边左中右,右边右中左;每次遍历对应两个结点比较值是否相等
类似LeetCode94的迭代遍历二叉树的思路
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
假设树中没有重复的元素。
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树。

前序序列确定根
在中序序列中找到根的值,那么根左边为左子树序列,右边为右子树序列
前序序列下一个结点是左子树的根;
前序序列当前位置加上左子树的大小的下一个原始就是右子树的根;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int,int> mp;
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int n = preorder.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) mp[inorder[i]] = i; //哈希表预统计中序各元素所在下标
return dfs(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& preorder,vector<int>& inorder,int pl,int pr,int il,int ir){
if(pl > pr) return NULL;
int value = preorder[pl];
int pos = mp[value]; //找到根在中序序列中的位置
int len = pos-il; //左子树元素个数
auto root = new TreeNode(value); //建立根
root->left = dfs(preorder,inorder,pl+1,pl+len,il,pos-1); //建左子树
root->right = dfs(preorder,inorder,pl+len+1,pr,pos+1,ir); //建右子树
return root;
}
};
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
以层为单位
bfs分别统计每一层
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(!root) return result; //边界判断 特判root为空
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(q.size()){
vector<int> levelList;
int len = q.size(); //循环刚进来 代表上一层的元素个数
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++){
//把当前层每一个元素分别出队 并把左右结点入队
auto top = q.front();
q.pop();
levelList.push_back(top->val);
if(top->left) q.push(top->left);
if(top->right) q.push(top->right);
}
result.push_back(levelList);
}
return result;
}
};
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
思路:来源leetcode题解

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
//递归出口
if(root == NULL || root == p || root == q) return root;
//递归统计左右结点
auto left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
auto right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
//只在一个子树上
if(left == NULL) return right;
if(right == NULL) return left;
//否则left和right都非空
//说明一个结点在其左子树 另一个结点在右子树那么当前结点就是最近公共祖先
return root;
}
};
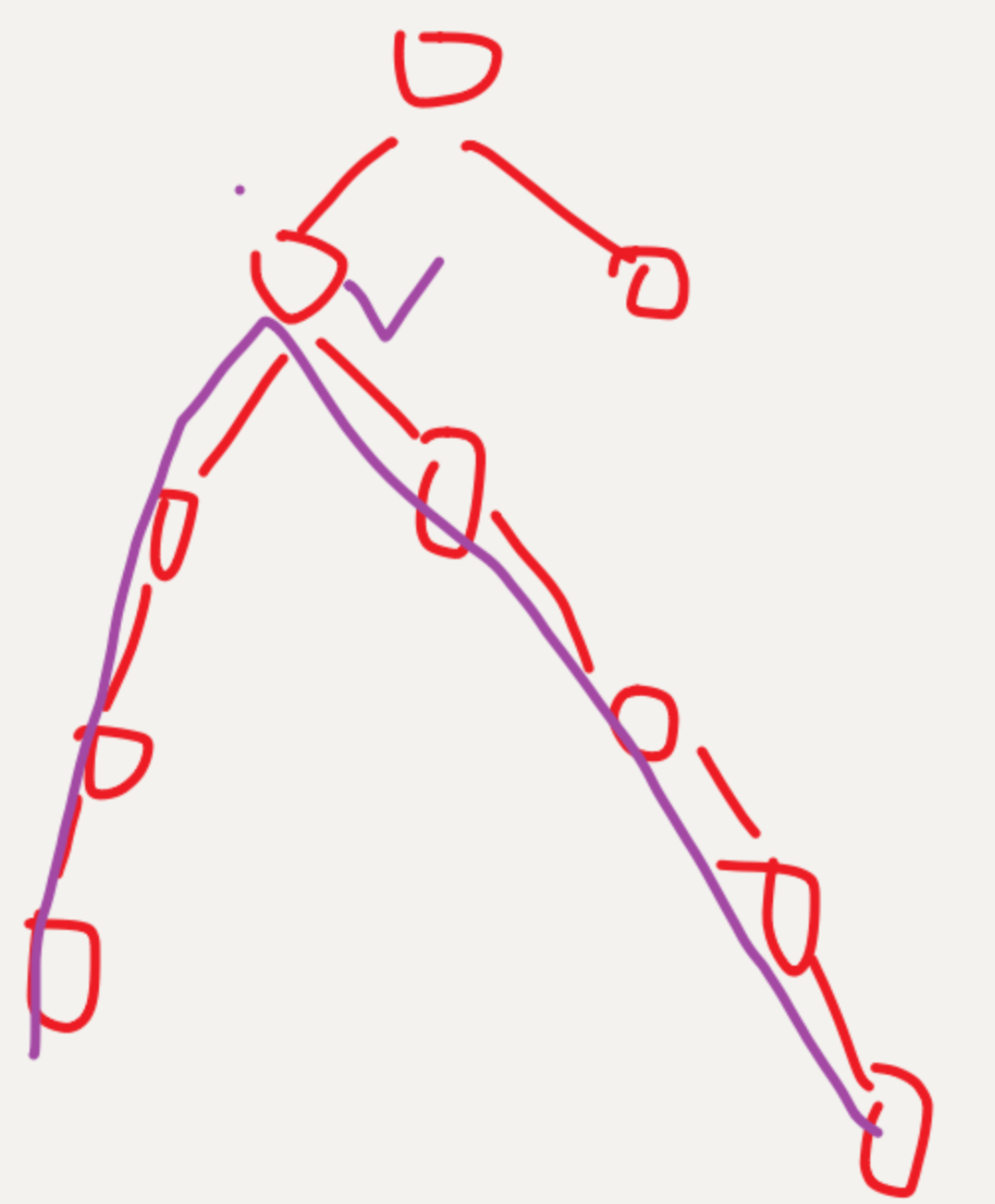
543. 二叉树的直径
直径:树中最长的路径(从一点到另一点)


注意:因为一开始不确定最高点是哪个,根节点不一定是最高点,比如下图样例
所以在dfs的过程上枚举最高点,就是计算当前结点下ans的最大值
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans = 0; //最优值
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return 0;
int left = dfs(root->left);
int right = dfs(root->right);
//加入当前结点后的最优值: 左子树深度 + 右子树深度
ans = max(ans,left+right); //更新当前节点下 最长直径长度
return max(left,right); //返回当前树上 左右子树的最大值
}
};
其它做法:
先找到一个深度最深的端点(最高点),再把最高点作为根dfs找到新的最深距离
https://www.cnblogs.com/fisherss/p/10914820.html
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
从树中任意节点出发,达到任意节点的序列的最大路径和
和LeetCode543思路一样,dfs的过程中枚举最优点(最高点),即最优点下路径和最大,其对应所在的一条路径上权值和最大,所在的路径为左子树路径+本身+右子树

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans = INT_MIN;
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
//从当前结点root向下走的最大值
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return 0;
int left = dfs(root->left);
int right = dfs(root->right);
//dfs枚举到最优点下 更新加入当前结点后的最优值
ans = max(ans,left+root->val+right); //左边最大值 + 自己 + 右边最大值
/*
//下面三行都可以省略替代为上一行
//因为dfs左右子树后 左右子树已达最优 只要再加入当前结点的值就行
ans = max(ans,root->val);
ans = max(ans,left+root->val);
ans = max(ans,right+root->val);
*/
//三种情况和0比较
return max(0,max(root->val,max(left+root->val,right+root->val)));
}
};
173. 二叉搜索树迭代器
题目描述:
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器。你将使用二叉搜索树的根节点初始化迭代器。
调用 next() 将返回二叉搜索树中的下一个最小的数。
题目要求:
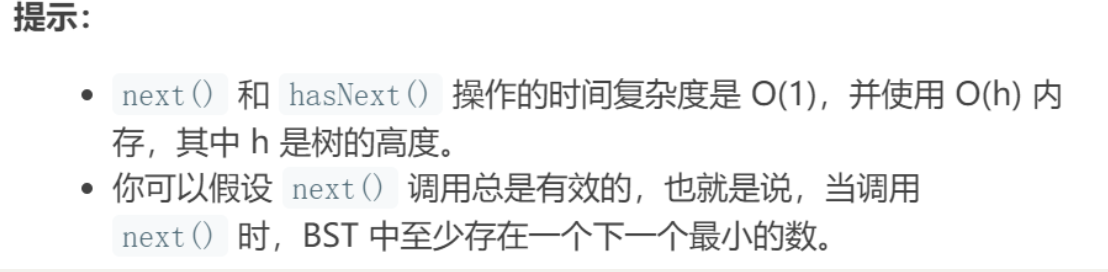
思路:
二叉搜索树每次返回一个最小的数,就相当于对二叉搜索树进行中序遍历
因为二叉搜索树的左子树都比根小,右子树都比根大;即左、中、右的值依次增大
递归方式(不满足空间要求):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class BSTIterator {
public:
vector<int> v;
int pos = 0;
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return;
dfs(root->left);
v.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->right);
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
int next() {
return v[pos++];
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
bool hasNext() {
if(pos < v.size()) return true;
return false;
}
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator* obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj->next();
* bool param_2 = obj->hasNext();
*/
迭代方式(用栈来模拟中序遍历):
参考LeetCode94,只不过是把迭代拆开写了
满足next函数内存是O(h),即栈中最多加入了一列深度下的节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class BSTIterator {
public:
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
while(root){ //初始加入左子树入栈
stk.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
int next() { //O(h)
auto p = stk.top(); //二叉搜索树中序的栈顶一定是最小的
stk.pop();
int result = p->val;
p = p->right; //左子树遍历完了 根也遍历完了 就移向右子树
while(p){
stk.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
return result;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
bool hasNext() {
return !stk.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator* obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj->next();
* bool param_2 = obj->hasNext();
*/
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
序列化相当于先序遍历序列,NULL值用#代替;
反序列化相当于用带#表示空值的先序序列来建树(本来只用先序序列无法建树,但是这里使用了#来代表叶节点孩子的值为空,就可以用先序建树了)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
string data;
dfs1(root,data);
return data;
}
void dfs1(TreeNode* root,string &data){
if(!root){
data += "#,";
return;
}
data += to_string(root->val) + ','; //先序遍历
dfs1(root->left,data);
dfs1(root->right,data);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
int index = 0;
return dfs2(data,index);
}
TreeNode* dfs2(string &data,int &index){
if(data[index] == '#'){ //遇到#号 要消耗一个,和一个#
index+=2;
return NULL;
}
bool is_minus = false;
if(data[index] == '-') { //判断是否是负数
is_minus = true;
index++;
}
int value = 0;
while(data[index] != ','){ //求这个数的值 到下一个逗号结束
value = value * 10 + (data[index] - '0');
index++;
}
index++;
if(is_minus) value = -value; //负数
auto root = new TreeNode(value); //建立根节点
root->left = dfs2(data,index); //递归求左右子树
root->right = dfs2(data,index);
return root;
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec;
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));
LeetCode树专题的更多相关文章
- leetcode树专题894.897,919,951
满二叉树是一类二叉树,其中每个结点恰好有 0 或 2 个子结点. 返回包含 N 个结点的所有可能满二叉树的列表. 答案的每个元素都是一个可能树的根结点. 答案中每个树的每个结点都必须有 node.va ...
- LeetCode:树专题
树专题 参考了力扣加加对与树专题的讲解,刷了些 leetcode 题,在此做一些记录,不然没几天就没印象了 力扣加加-树专题 总结 树的定义 // Definition for a binary tr ...
- LeetCode刷题 树专题
树专题 关于树的几个基本概念 1 树的节点定义 2 关于二叉树的遍历方法 2.1 前序遍历 2.2 中序遍历 2.3 后序遍历 2.4 层序遍历 3 几种常见的树介绍 3.1 完全二叉树 3.2 二叉 ...
- LeetCode 字符串专题(一)
目录 LeetCode 字符串专题 <c++> \([5]\) Longest Palindromic Substring \([28]\) Implement strStr() [\(4 ...
- zkw线段树专题
题目来自大神博客的线段树专题 http://www.notonlysuccess.com/index.php/segment-tree-complete/ hdu1166 敌兵布阵题意:O(-1)思路 ...
- vj线段树专题
vj线段树专题题解 单点更新模板 void build(int x,int l,int r){//sum[x]控制l-r区域 if(l==r){Sum[x]=num[l];return ;} int ...
- leetcode 树类型题
树的测试框架: // leetcodeTree.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream& ...
- leetcode: 树
1. sum-root-to-leaf-numbers Given a binary tree containing digits from0-9only, each root-to-leaf pat ...
- 《剑指offer》树专题 (牛客10.25)
考察的知识点主要在于树的数据结构(BST,AVL).遍历方式(前序,中序,后序,层次).遍历算法(DFS,BFS,回溯)以及遍历时借助的数据结构如队列和栈.由于树本身就是一个递归定义的结构,所以在递归 ...
随机推荐
- 再砸4.35亿美元,LG疯狂扩建太阳能电池生产线
LG在收缩高分辨率电视和其他消费电子产品业务的同时,在太阳能面板业务上却很明显一直在进行扩张.LG公司表示,他们将斥资4.35亿美元在韩国工厂增加超过6条生产线,使其太阳能电池生产量能够在2018年达 ...
- C语言编程入门题目--No.15
题目:利用条件运算符的嵌套来完成此题:学习成绩>=90分的同学用A表示,60-89分之间的用B表示, 60分以下的用C表示. 1.程序分析:(a>b)?a:b这是条件运算符的基本例子. 2 ...
- 图论--边双连通V-DCC缩点
// tarjan算法求无向图的割点.点双连通分量并缩点 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> ...
- PyCharm 集成 SVN,检出、提交代码
1.安装 SVN,解决 SVN 目录中没有 svn.exe 问题 重新打开 TortoiseSVN 安装文件 选择 Modify 后在command line client tools 选项修改为 W ...
- JWT的浅谈
在实际工作过程中,运行jmeter脚本的时候,开发给了一个jwt的授权信息,到底是做什么用的呢,翻阅了一些资料,整理如下: 一.JWT(Json Web Token)是什么 JWT是一串格式为xxxx ...
- 绕WAF文章收集
在看了bypassword的<在HTTP协议层面绕过WAF>之后,想起了之前做过的一些研究,所以写个简单的短文来补充一下文章里“分块传输”部分没提到的两个技巧. 技巧1 使用注释扰乱分块数 ...
- async与await----js的异步处理
async与await----js的异步处理 博客说明 文章所涉及的资料来自互联网整理和个人总结,意在于个人学习和经验汇总,如有什么地方侵权,请联系本人删除,谢谢! 说明 之前写代码遇到一个问题,返回 ...
- 前端【JS】,深拷贝与浅拷贝的区别及详解!
我是前端小白一枚,为了巩固知识和增强记忆,开始整理相关的知识,方便以后复习和面试的时候看看.OK,让我们进入正题~ 先说说浅拷贝和深拷贝的理解吧,个人是这样理解的:两个对象A.B, A有数据B为空,B ...
- spring内嵌jetty容器,实现main方法启动web项目
Jetty 是一个开源的servlet容器,它为基于Java的web容器,例如JSP和servlet提供运行环境.Jetty是使用Java语言编写的,它的API以一组JAR包的形式发布.开发人员可以将 ...
- boost在Qt中的使用
一.说明 理论上,Qt和boost是同等级别的C++库,如果使用Qt,一般不会需要再用boost,但是偶尔也会有特殊情况,比如,第三方库依赖等等.本文主要介绍boost在windows Qt(MinG ...
