Jun
Contents
- 数据来源
- 代码演示
- 讨论
一.数据来源
为了节省时间,我直接用了官方所给的数据,分别是雄性和雌性小鼠的肝脏芯片数据
二.代码演示
数据输入
library(WGCNA)
femData<-read.csv("LiverFemale3600.csv")
dim(femData)
names(femData)
datExpr0 = as.data.frame(t(femData[, -c(1:8)]))
names(datExpr0) = femData$substanceBXH
rownames(datExpr0) = names(femData)[-c(1:8)]
gsg = goodSamplesGenes(datExpr0, verbose = 3)##剔除不合格的基因
Step2 样本聚类
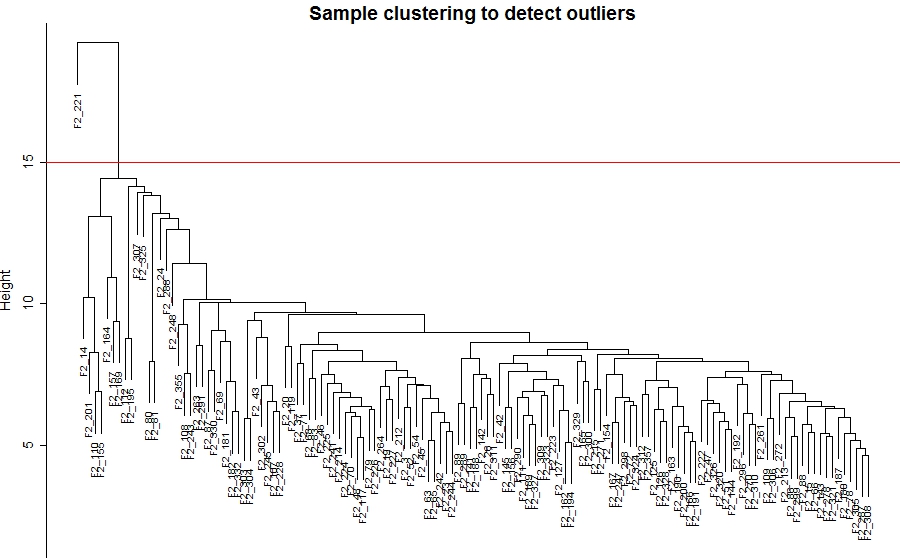
sampleTree = hclust(dist(datExpr0), method = "average")##样本聚类,可以反映样本的重 复性,也可以看出离群样本有哪些
sizeGrWindow(12,9)
par(cex = 0.6)
(mar = c(0,4,2,0))
plot(sampleTree, main = "Sample clustering to detect outliers", sub="", xlab="", cex.lab = 1.5,
cex.axis = 1.5, cex.main = 2)
abline(h = 15, col = "red")
clust = cutreeStatic(sampleTree, cutHeight = 15, minSize = 10)
table(clust)
keepSamples = (clust==1)
datExpr = datExpr0[keepSamples, ]
nGenes = ncol(datExpr)
nSamples = nrow(datExpr)
Step3 阈值计算
powers = c(c(1:10), seq(from = 12, to=20, by=2))##计算软阈值
sft = pickSoftThreshold(datExpr, powerVector = powers, verbose = 5)##sft返回的是一个列表
sizeGrWindow(9, 5)
par(mfrow = c(1,2))
cex1 = 0.9
plot(sft$fitIndices[,1], -sign(sft$fitIndices[,3])*sft$fitIndices[,2],
xlab="Soft Threshold (power)",ylab="Scale Free Topology Model Fit,signed R^2",type="n",
main = paste("Scale independence"))
text(sft$fitIndices[,1], -sign(sft$fitIndices[,3])*sft$fitIndices[,2],
labels=powers,cex=cex1,col="red")
abline(h=0.90,col="red")
plot(sft$fitIndices[,1], sft$fitIndices[,5],
xlab="Soft Threshold (power)",ylab="Mean Connectivity", type="n",
main = paste("Mean connectivity"))
text(sft$fitIndices[,1], sft$fitIndices[,5], labels=powers, cex=cex1,col="red")
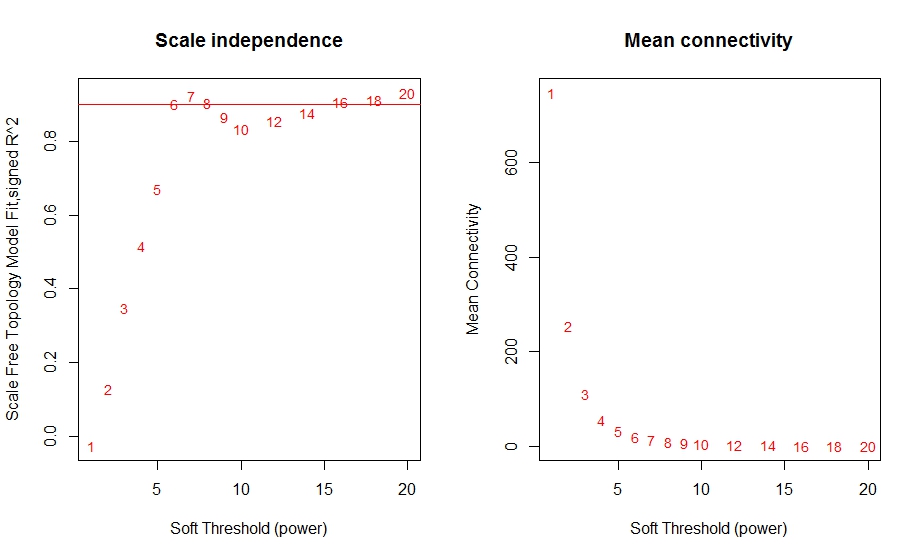
经过上面代码的运行,得出了软阈值的结果。从左图中可以看到,当阈值达到6时,整个网络就已经靠近无尺度网络的分布了,R方也达到了0.95左右的水平。sft这个列表当中的powerEstimate代表的便是最佳阈值。右图代表的是整个网络中,随着阈值的变化,整个网络中节点(Gene)间的连接度均值,符合幂率分布。
Step4 网络构建
net = blockwiseModules(datExpr, power = sft$powerEstimate,
TOMType = "unsigned", minModuleSize = 30,
reassignThreshold = 0, mergeCutHeight = 0.25,
numericLabels = TRUE, pamRespectsDendro = FALSE,
saveTOMs = TRUE,
saveTOMFileBase = "femaleMouseTOM", verbose = 3)##一步法构建网络
Step5 模块上色
sizeGrWindow(12, 9)
mergedColors = labels2colors(net$colors)
plotDendroAndColors(net$dendrograms[[1]], mergedColors[net$blockGenes[[1]]],
"Module colors",
dendroLabels = FALSE, hang = 0.03,
addGuide = TRUE, guideHang = 0.05)
moduleLabels = net$colors
moduleColors = labels2colors(net$colors)##模块上色
= net$MEs;
geneTree = net$dendrograms[[1]]
table(moduleColors)##查看模块对应的颜色及模块内的基因
moduleColors
black blue brown cyan green greenyellow grey grey60
208 456 415 79 314 102 99 47
lightcyan lightgreen magenta midnightblue pink purple red salmon
47 34 123 79 149 123 212 94
tan turquoise yellow
100 595 324
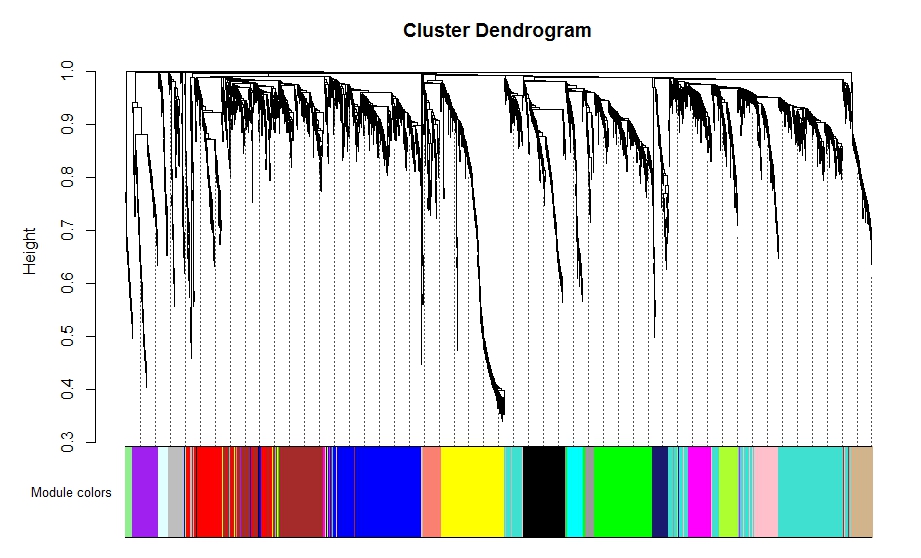
在众多模块当中,grey模块里的基因代表无法被归类到任何一个模块里的基因。同时,WGCNA也可以将距离较近的模块合并.
Step6 联系表型信息
traitData = read.csv("ClinicalTraits.csv")##引入表型信息相关数据
dim(traitData)
names(traitData)
allTraits = traitData[, -c(31, 16)]##选取部分信息
allTraits = allTraits[, c(2, 11:36) ]
dim(allTraits)
names(allTraits)
femaleSamples = rownames( 大专栏 JundatExpr);
traitRows = match(femaleSamples, allTraits$Mice)
datTraits = allTraits[traitRows, -1]
rownames(datTraits) = allTraits[traitRows, 1]
collectGarbage()
nGenes = ncol(datExpr)
nSamples = nrow(datExpr)
MEs0 = moduleEigengenes(datExpr, moduleColors)$eigengenes
MEs = orderMEs(MEs0)
moduleTraitCor = cor(MEs, datTraits, use = "p")#计算模块和表型信息的相关系数
moduleTraitPvalue = corPvalueStudent(moduleTraitCor, nSamples)
sizeGrWindow(10,6)
textMatrix = paste(signif(moduleTraitCor, 2), "n(",
signif(moduleTraitPvalue, 1), ")", sep = "")
(textMatrix) = dim(moduleTraitCor)
par(mar = c(6, 8.5, 3, 3))
#绘制表型和模块的相关性热图
labeledHeatmap(Matrix = moduleTraitCor,
xLabels = names(datTraits),
yLabels = names(MEs),
ySymbols = names(MEs),
colorLabels = FALSE,
colors = greenWhiteRed(50),
textMatrix = textMatrix,
setStdMargins = FALSE,
cex.text = 0.5,
zlim = c(-1,1),
main = paste("Module-trait relationships"))
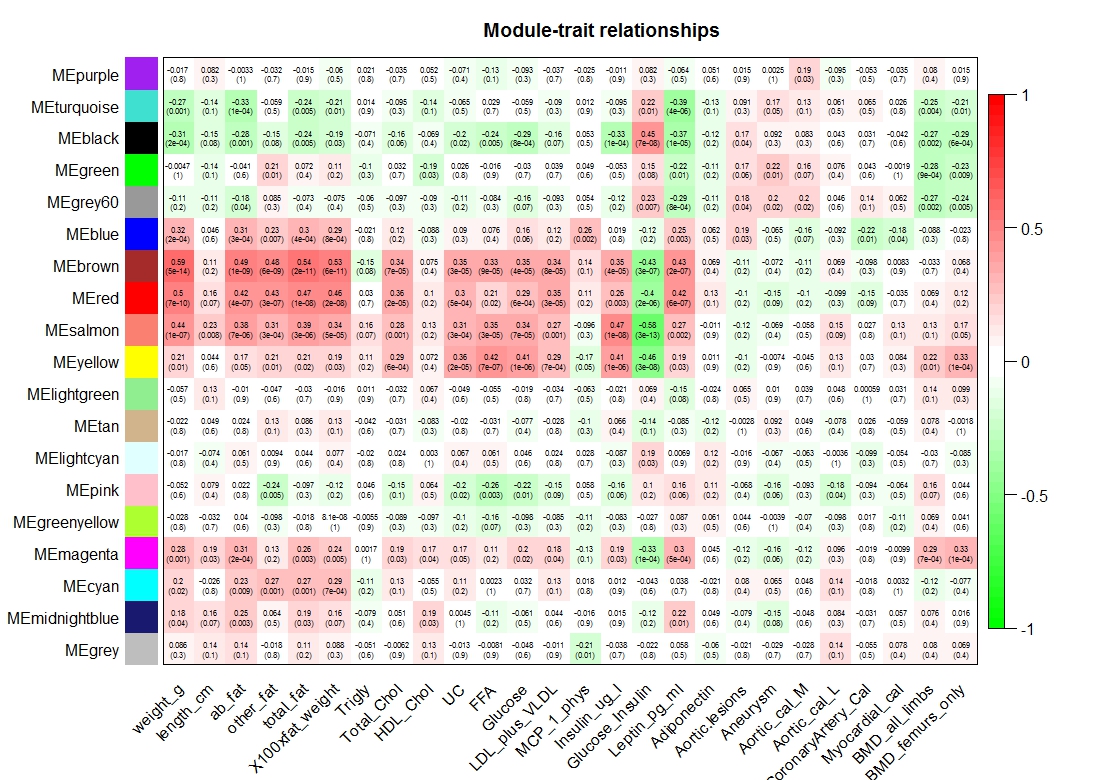
通过模块与表型相关性热图中可以看到:brown、red模块与weight有较高的相关性。研究者可以根据上述信息研究与目标表型相关联的模块,也可以研究感兴趣的模块。
比较值得注意的是,即使算出了模块与表型的相关性,一个模块里也往往存在着比较多的基因。那么具体哪些基因值得我们去做后续的分析,还需要对模块进行更深一步的细化研究。
Step7 GSvsMM
weight = as.data.frame(datTraits$weight_g)
names(weight) = "weight"
modNames = substring(names(MEs), 3)
geneModuleMembership = as.data.frame(cor(datExpr, MEs, use = "p"))##计算模块MM值与基因间的相关系数,datExpr为表达量
MMPvalue = as.data.frame(corPvalueStudent(as.matrix(geneModuleMembership), nSamples))
names(geneModuleMembership) = paste("MM", modNames, sep="")
names(MMPvalue) = paste("p.MM", modNames, sep="")
geneTraitSignificance = as.data.frame(cor(datExpr, weight, use = "p"))##计算表型weight与基因间的相关系数
GSPvalue = as.data.frame(corPvalueStudent(as.matrix(geneTraitSignificance), nSamples))
names(geneTraitSignificance) = paste("GS.", names(weight), sep="")
names(GSPvalue) = paste("p.GS.", names(weight), sep="")
在WGCNA中,定义了GS值和MM值。那么上面的代码可以简单的理解为:分别计算,ME值与基因间的相关系数,以及计算基因和表型间的相关系数。通过计算,那些不仅与模块高度相关的而且与表型也高度相关的基因就非常值得研究了。与模块高度相关的基因,往往也在这个模块中具有重要的地位或者说具有中心要素。
module = "brown"
column = match(module, modNames)
moduleGenes = moduleColors==module
sizeGrWindow(7, 7);
par(mfrow = c(1,1));
verboseScatterplot(abs(geneModuleMembership[moduleGenes, column]),
abs(geneTraitSignificance[moduleGenes, 1]),
xlab = paste("Module Membership in", module, "module"),
ylab = "Gene significance for body weight",
main = paste("Module membership vs. gene significancen"),
cex.main = 1.2, cex.lab = 1.2, cex.axis = 1.2, col = module)

Step8 导出指定模块基因名
module = "brown"
probes = names(datExpr)
inModule = (moduleColors==module)
modProbes = probes[inModule]
table(modProbes)
Step9 导出模块网络
TOM = TOMsimilarityFromExpr(datExpr, power = 6)#这一步非常消耗内存
module = "brown"
probes = names(datExpr)
inModule = (moduleColors==module)
modProbes = probes[inModule]
modTOM = TOM[inModule, inModule]
dimnames(modTOM) = list(modProbes, modProbes)
#visant格式导出
vis = exportNetworkToVisANT(modTOM,
file = paste("VisANTInput-", module, ".txt", sep=""),
weighted = TRUE,
threshold = 0,
probeToGene = data.frame(annot$substanceBXH, annot$gene_symbol))
#Cytoscape格式导出
cyt = exportNetworkToCytoscape(modTOM,
edgeFile = paste("CytoscapeInput-edges-", paste(modules, collapse="-"), ".txt", sep=""),
nodeFile = paste("CytoscapeInput-nodes-", paste(modules, collapse="-"), ".txt", sep=""),
weighted = TRUE,
threshold = 0.02,
nodeNames = modProbes,
altNodeNames = modGenes,
nodeAttr = moduleColors[inModule])
#按top值筛选,选择性导出模块基因。
nTop = 30;
IMConn = softConnectivity(datExpr[, modProbes]);
top = (rank(-IMConn) <= nTop)
上述便是用官方的雌性小鼠肝脏的芯片数据做的一个演示。其中数据包括了表达量数据、注释信息、表型数据。这里我不再用雄性小鼠的数据做演示,方法步骤一样,只是需要对代码做一些细微的修改。
三.讨论
关于WGCNA其实还是有很多问题的,比如:
批次效应的影响
计算阈值后,R方很小网络达不到无尺度分布
标准化处理的方式log2、log2(FPKM+1)、其它标准化的影响
关于这些问题我会在最后一章的内容中谈到,那么基本上WGCNA系列也就完结了。
2018/6/23 Jun
Jun的更多相关文章
- 分享吉林大学机械科学与工程学院,zhao jun 博士的Halcon学习过程及知识分享
分享吉林大学机械科学与工程学院,zhao jun 博士的Halcon学习过程及知识分享 全文转载zhao jun 博士的新浪博客,版权为zhaojun博士所有 原文地址:http://blog.sin ...
- 每日背单词 - Jun.
6月1日裸辞,计划休息到端午节后,这段时间玩的确实很开心,每天和朋友一起吹灯拔蜡:好不自在,可惜假期马上结束了,从今天开始恢复学习状态. 2018年6月1日 - 2018年6月14日 辞职休假 201 ...
- ECCV 2014 Results (16 Jun, 2014) 结果已出
Accepted Papers Title Primary Subject Area ID 3D computer vision 93 UPnP: An optimal O(n) soluti ...
- [Music] Billboard Hot 100 Singles Chart 27th Jun 2015
01 Wiz Khalifa - See You Again (Feat. Charlie P..> 30-Jul-2015 09:12 9247814 02 Taylor Swift - Ba ...
- 时间格式转换成JUN.13,2017
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("MMM.dd,yyyy", Locale.ENGLISH); String negotia ...
- [3 Jun 2015 ~ 9 Jun 2015] Deep Learning in arxiv
arXiv is an e-print service in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative bi ...
- [Fri 26 Jun 2015 ~ Thu 2 Jul 2015] Deep Learning in arxiv
Natural Neural Networks Google DeepMind又一神作 Projected Natural Gradient Descent algorithm (PRONG) bet ...
- jun引导1.04可以让N3050支持6.2
1.03引导用在3050可以安装 但是安装后找不到dsm 需要手动插拔电源才可以解决 偶尔还会死机 1.04可以引导3050安装6.2 23739 安装24922正常,但是moments传照片后会死机 ...
- QT 开发ros gui过程中遇到:error: catkin_package() include dir 'include' does not exist relative to '/home/jun/catkin_ws/src/qt_ros_test' /opt/ros/kinetic/share/catkin/cmake/catkin_package.cmake:102 (_catkin_p
这是因为在ros工作空间的包中没有include文件夹造成的,所以在该路径下创建include的文件夹,问题就解决了.
随机推荐
- AOP统一处理修改人、创建人、修改时间、创建时间
1.配置拦截 首先开启 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>代理.解释一下下面..的意思是多个 < ...
- 元组(tuple)的用途(基础)
>>>a = 123,456,'jia',['jia','xiang'] >>>a (123, 456, 'jia', ['jia', 'xiang']) 这个带括 ...
- linkage disequilibrium|linkage equilibrium
I.9 Linkage INDEPENDENCE OF GENOTYPES AT TWO LOCI:若A,B是两个独立位点:PA是基因A的概率,PB是基因B的概率.因为基因A与基因B是相互独立的位点, ...
- Datagridview 实现二维表头和行合并
借鉴别人的,改了改,没用timer using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.ComponentModel;using Sy ...
- Do jobs|permanent|secure job|Move|Look after|provide sb with sth|Move|Enjoy a good time|Learn about|Be fond of|Have a clearer idea|String quarter|Be subject to|A has little with B|Pigment
Do jobs|work jobs Long-terms|permanent Gain jobs/secure job Move|go to |stay in |live in|settle down ...
- 2013 ACM网络搜索与数据挖掘国际会议
ACM网络搜索与数据挖掘国际会议" title="2013 ACM网络搜索与数据挖掘国际会议"> 编者按:ACM网络搜索与数据挖掘国际会议(6th ACM Conf ...
- Mock测试,何去何从
2016-10-24 出处:Qtest之道 作/译者:闫耀珍 上面的情景是不是似曾相识呢?现今的业务系统已经很少是孤立存在的了,尤其对于一个大公司而言,各个部门之间的配合非常密切,我们或多或 ...
- php通过身份证判断性别
/** 已测试,百度很多写法不行的 * 1就是男性 2就是女性* 通过身份证获取性别类型* @param type $card* @return int*/function getCardSex($i ...
- HashMap、Hashtable、ConcurrentHashMap、ConcurrentSkipListMap对比及java并发包(java.util.concurrent)
一.基础普及 接口(interface) 类(class) 继承类 实现的接口 Array √ Collection √ Set √ Collection List √ Collection Map ...
- UTF虚拟对象
虚拟对象: 虚拟对象是为了让UFT识别某些不能识别的控件,把这些控件的范围定义为虚拟对象. 新建虚拟对象 管理虚拟对象 创建虚拟对象之后可通过菜单tools-Virutal Objects-Virut ...
