java集合类学习笔记之ArrayList
1、简述
ArrayList底层的实现是使用了数组保存所有的数据,所有的操作本质上是对数组的操作,每一个ArrayList实例都有一个默认的容量(数组的大小,默认是10),随着
对ArrayList不断增加元素,默认的数组会不断的向新数组进行拷贝,由于ArrayList的内部是通过对数组的操作实现的,所以它是线程不安全的
2、实现
a、构造方法:
AyyarList一共提供了三种构造方法:
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
} /**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} /**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
在jdk1.8中,ArrayList的无参构造方法默认的是创建了一个空的数组,只有当你第一次添加是时候才会设置它的默认长度为10 ,在jdk1.6中无参构造方法默认
的就是创建一个长度为10 的空数组
b、定义内部数组:
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
关于transient关键字的说明可以参考我的另外一篇博客 java学习笔记之对象序列化
3、ArrayList的操作
增加操作:
add(E e):
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
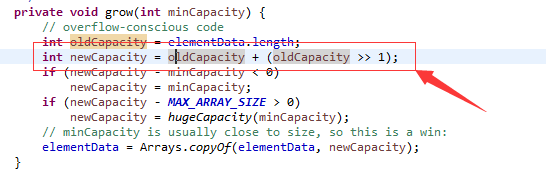
调用add(E e)方法时首先会调用ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity)去判断是否需要对集合进行扩容,然后默认的将新插入的对象放到内部数组的末尾,
当内部数组需要扩容时,每次直接将数组的长度值原来的两倍,这种操作的代价是很高的,所以在使用过程中我们尽量避免数组的扩容,当可以预知数组长度的时候
可以在构造的时候久指定其长度
add(int index, E element)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
在调用add(int index, E element)方法想ArrayList中插入一条数据时,这个方法内部先去判断传入的下表是否大于数组的长度。大于的话就会
抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常,插入的下表小于数组的长度的时候,再去判断数组是否需要扩容,最后再调用System.arraycopy方法将数组下表大于传入
的index的元素全部后移以为,并将插入的元素放到index位置
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the operation
* is in progress. (This implies that the behavior of this call is
* undefined if the specified collection is this list, and this
* list is nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
在调用addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 插入一个集合时,这个方法内部先去判断增加这个集合数组是否需要扩容,然后调用
arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos,int length)方法将新增加的集合放到数组的末尾
更新操作:
public E set(int index, E e) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e;
return oldValue;
}
在调用set(int index,E e)方法修改里面的值时,方法内部先去检查index下表是都超过数组的最大长度,然后再检查是否有其他的线程对这个对象的长度
进行修改了(所以是线程不安全的,多线程同时操作容易直接抛异常),最后是直接替换数组中下表index对应的值
删除操作:
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue;
}
在调用remove(int index)删除ArrayList中的数据时,首先校验传入的下标index是大于数组的长度,然后取出将要被删除的数并判断下标index之后是否还有元素,
如果有的话将下标之后的元素全部往前移动一位,并最终将删除的元素的值返回
java集合类学习笔记之ArrayList的更多相关文章
- java集合类学习笔记之HashMap
1.简述 HashMap是java语言中非常典型的数据结构,也是我们平常用的最多的的集合类之一.它的底层是通过一个单向链表(Node<k,v>)数组(也称之为桶bucket,数组的长度也叫 ...
- java集合类学习笔记之LinkedHashMap
1.简述 LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类,他们最大的不同是,HashMap内部维护的是一个单向的链表数组,而LinkedHashMap内部维护的是一个双向的链表数组.HashMap是 ...
- java集合类学习笔记1
一.集合的接口 java集合类库也将接口与实现相分离.首先看一下大家都熟悉的数据结构-队列是如何分离的.队列接口指出可以在队列的尾部添加元素,在队列的头部删除元素,并且可以查找队列中元素的个数.当需要 ...
- Java集合类学习笔记2
二,具体的集合 集合类型 描述 ArrayList 一种可以动态增长和缩减的索引序列 LinkedList 一种可以在任何位置进行高效地插入和删除操作的有序序列 ArrayDeque 一种用循环数组实 ...
- Java集合类学习笔记(Map集合)
Map用于保存具有映射关系的数据,因此Map集合里保存着两组数据,一组用于保存Map的key,一组用于保存key所对应的value. Map的key不允许重复. HashMap和Hashtable都是 ...
- Java集合类学习笔记(各种线性表性能分析)
ArrayList.LinkedList是线性表的两种典型实现:基于数组的线性表和基于链的线性表. Queue代表了队列,Deque代表了双端队列. 一般来说,由于数组以一块连续内存区来保存所有的数组 ...
- Java集合类学习笔记(Queue集合)
Queue集合用于模拟队列(先进先出:FIFO)这种数据类型. Queue有一个Deque接口,代表一个"双端队列",双端队列可以同时从两端来添加.删除元素,因此Deque的实现类 ...
- Java集合类学习笔记(List集合)
List集合是指一个元素有序.可重复的集合,集合中每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引. ArrayList和Vector作为List集合的两个典型实现,完全支持List接口的全部功能,并且在用法上几乎完全相 ...
- Java集合类学习笔记(Set集合)
Set集合不允许包含相同的元素,如果试图把两个相同的元素加入同一个Set集合中,则添加操作失败,add()方法返回false,且新元素不会被加入. HashSet类的特点: 不能保证元素的排列顺序,顺 ...
随机推荐
- leetcode766
本题经过一下午的思考,终于解出来了.使用的是层次遍历的思想. class Solution { public: bool isToeplitzMatrix(vector<vector<in ...
- [原创]Mybatis特殊值Enum类型转换器-ValuedEnumTypeHandler
引言 typeHandlers 阅读官方文档 typeHandlers 一节{:target="_blank"} MyBatis 在预处理语句(PreparedStatement) ...
- Vmware中的centos虚拟机克隆之后没有eth0
克隆虚拟机之后,CentOS没有eth0的解决办法 我们常常需要从一台已经安装完成的虚拟机系统克隆出来一个新系统(克隆时候必须要改变网卡物理地址,这一点无需多说),但是新系统启动之后,会发现系统网络工 ...
- cocos2d-x 初探helloWorld
cocos2d-x的main函数代码很少,把一些复杂的接口封装到AppDelegate类里了,“AppDelegate”从词意可以得出是app的代理类,而一些最早的场景都会在AppDelegate类里 ...
- Python 安装selenium
一.报错信息 No module named 'selenium' 二.系统环境 操作系统:Win10 64位 Python版本:Python 3.7.0 三.安装参考 1.使用pip安装seleni ...
- 面试题:ConcurrentHashMap实现线程安全的原理
在ConcurrentHashMap没有出现以前,jdk使用hashtable来实现线程安全,但是hashtable是将整个hash表锁住,所以效率很低下. ConcurrentHashMap将数据分 ...
- Linux 与 BSD
1)Linux 与 BSD 有什么不同? http://linux.cn/article-3186-1.html 2)BSD(Unix)家族 http://blog.csdn.net/cradmin/ ...
- Luogu 2886 [USACO07NOV]牛继电器Cow Relays
BZOJ 1706权限题. 倍增$floyd$. 首先这道题有用的点最多只有$200$个,先离散化. 设$f_{p, i, j}$表示经过$2^p$条边从$i$到$j$的最短路,那么有转移$f_{p, ...
- Luogu 3206 [HNOI2010]城市建设
BZOJ 2001 很神仙的cdq分治 先放论文的链接 顾昱洲_浅谈一类分治算法 我们考虑分治询问,用$solve(l, r)$表示询问编号在$[l, r]$时的情况,那么当$l == r$的时候 ...
- hdu 4269 Defend Jian Ge
#include <cctype> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <string> # ...
