201871010101-陈来弟《面向对象程序设计(java)》第七周学习总结
201871010101-陈来弟《面向对象程序设计(java)》第七周学习总结
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
《面向对象程序设计(java)》 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11654436.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
|
实验内容和步骤
实验1:(20分)
在“System.out.println(...);”语句处按注释要求设计代码替换...,观察代码录入中IDE提示,以验证四种权限修饰符的用法。
程序代码如下:
class Parent {
private String p1 = "这是Parent的私有属性";
public String p2 = "这是Parent的公有属性";
protected String p3 = "这是Parent受保护的属性";
String p4 = "这是Parent的默认属性";
private void pMethod1() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
public void pMethod2() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void pMethod3() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void pMethod4() {
System.out.println("我是Parent无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
class Son extends Parent{
private String s1 = "这是Son的私有属性";
public String s2 = "这是Son的公有属性";
protected String s3 = "这是Son受保护的属性";
String s4 = "这是Son的默认属性";
public void sMethod1() {
System.out.println("...");//分别尝试显示Parent类的p1、p2、p3、p4值
System.out.println("我是Son用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
private void sMethod2() {
System.out.println("我是Son用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void sMethod() {
System.out.println("我是Son用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void sMethod4() {
System.out.println("我是Son无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent = new Parent();
Son son = new Son();
Parent pMethod3= new Son ();
((Son) pMethod3).sMethod1();
((Son) pMethod3).pMethod3();
((Son) pMethod3).sMethod4();
pMethod3.pMethod2();
pMethod3.pMethod3();
pMethod3.pMethod4();
System.out.println(pMethod3.p2);
System.out.println(pMethod3.p3);
System.out.println(pMethod3.p4);
}
}
运行结果:
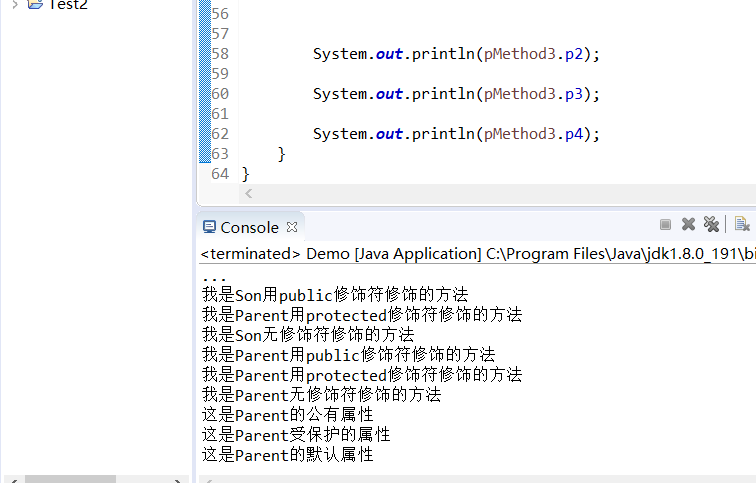
实验2:导入第5章以下示例程序,测试并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10,结合程序运行结果理解程序(教材174页-177页);
l 删除程序中Employee类、Manager类中的equals()、hasCode()、toString()方法,背录删除方法,在代码录入中理解类中重写Object父类方法的技术要点。
5-8程序代码如下:
package equals; /**
* This program demonstrates the equals method.
* @version 1.12 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EqualsTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Employee alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", , , , );
Employee alice2 = alice1;
Employee alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", , , , );
Employee bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", , , , ); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); Manager carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", , , , );
Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", , , , );
boss.setBonus();
System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss);
System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss));
System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode());
System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode());
System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode());
System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode());
}
}
5-9程序代码如下:
package equals; import java.time.*;
import java.util.Objects; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
// a quick test to see if the objects are identical
if (this == otherObject) return true; // must return false if the explicit parameter is null
if (otherObject == null) return false; // if the classes don't match, they can't be equal
if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; // now we know otherObject is a non-null Employee
var other = (Employee) otherObject; // test whether the fields have identical values
return Objects.equals(name, other.name)
&& salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay);
} public int hashCode()
{
return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay);
} public String toString()
{
return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay="
+ hireDay + "]";
}
}
5-10程序代码如下:
package equals; public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
bonus = ;
} public double getSalary()
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
return baseSalary + bonus;
} public void setBonus(double bonus)
{
this.bonus = bonus;
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false;
var other = (Manager) otherObject;
// super.equals checked that this and other belong to the same class
return bonus == other.bonus;
} public int hashCode()
{
return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus);
} public String toString()
{
return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]";
}
}
三个程序运行结果:
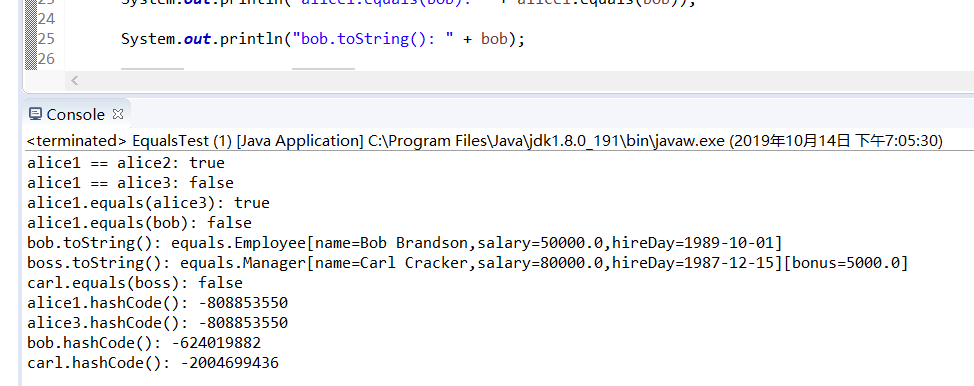
删除程序中Employee类、Manager类中的equals()、hasCode()、toString()方法,背录删除方法,在代码录入中理解类中重写Object父类方法的技术要点。
Manager:
public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus;
public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) {
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
bonus = ;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public double getSalary() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double baseSalary= super.getSalary();
return baseSalary+bonus;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object otherObject) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(!super.equals(otherObject)) return false;
Manager other=(Manager)otherObject;
return bonus==other.bonus;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.hashCode()+*new Double(bonus).hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.toString()+"[bonus="+bonus+"]";
}
}
Employee:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Employee
{
private String name; //实例域定义
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay;
public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)//构造器定义
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public LocalDate getHireDay() {
return hireDay;
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise=salary*byPercent/;
salary+=raise;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object otherObject) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(this==otherObject) return true;
if(this==null) return false;
if(getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false;
Employee other=(Employee)otherObject;
return Objects.equals(name,other.name)&&salary == other.salary&&Objects.equals(hireDay,other.hireDay);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return Objects.hash(name,salary,hireDay);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return getClass().getName()+"[name="+name+",salary="+salary+",hireday="+hireDay+"]";
}
}
运行结果:
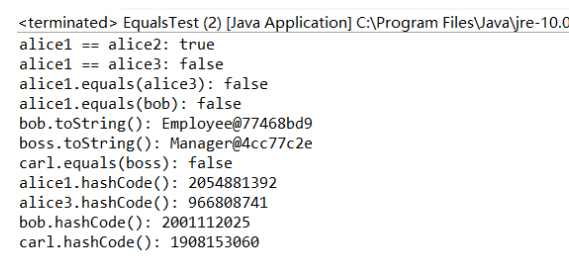
Object类存储在java.lang包中,是所有java类(Object类除外)的终极父类。当然,数组也继承了Object类。然而,接口是不继承Object类的,“Object类不作为接口的父类”。java的任何类都继承了这些函数,并且可以覆盖不被final修饰的函数。例如,没有final修饰的toString()函数可以被覆盖,但是final wait()函数就不行。Java也没有强制声明“继承Object类”。如果这样的话,就不能继承除Object类之外别的类了,因为java不支持多继承。然而,即使不声明出来,也会默认继承了Object类,
测试程序2:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行程序5-11(教材182页),结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
5-11代码:
package arrayList; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates the ArrayList class.
* @version 1.11 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ArrayListTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fill the staff array list with three Employee objects
ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<Employee>(); staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", , , , ));
staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", , , , ));
staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", , , , )); // raise everyone's salary by 5%
for (Employee e : staff)
e.raiseSalary(); // print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay="
+ e.getHireDay());
}
}
package arrayList; import java.time.*; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
}
}
运行结果:
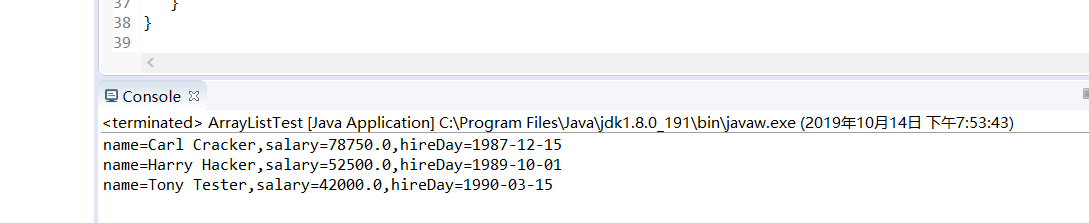
l 设计适当的代码,测试ArrayList类的set()、get()、remove()、size()等方法的用法。
package arrayList;
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates the ArrayList class.
* @version 1.11 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ArrayListTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fill the staff array list with three Employee objects
ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<Employee>(); //声明和构造一个保存Employee对象的数组列表
staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", , , , ));//使用add方法将元素添加到数组列表中
staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", , , , ));
staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", , , , ));
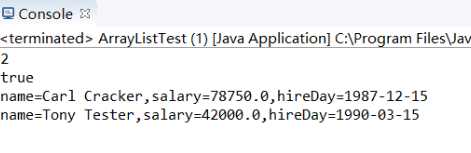
staff.remove(); //从数组列表中删除元素
int n = staff.size();
System.out.println(n);
System.out.println(staff.get()!=staff.get());
// raise everyone's salary by 5%
for (Employee e : staff)
e.raiseSalary();
// print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay="
+ e.getHireDay());
}
}
运行结果:
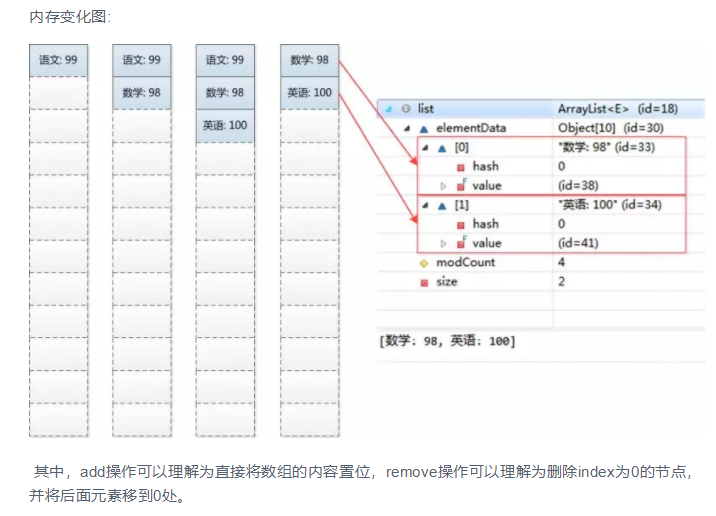
ArrayList是集合的一种实现,实现了接口List,List接口继承了Collection接口。Collection是所有集合类的父类。ArrayList使用非常广泛,不论是数据库表查询,excel导入解析,还是网站数据爬取都需要使用到,了解ArrayList原理及使用方法显得非常重要。
测试程序3:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页),结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
5-12代码:
package enums; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates enumerated types.
* @version 1.0 2004-05-24
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EnumTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);//字符串转换为大写
System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) ");
String input = in.next().toUpperCase();
Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input);//静态values方法返回枚举的所有值的数组
System.out.println("size=" + size);
System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation());
if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE)//判断语句
System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _.");
}
} enum Size
{
SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; }
public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } private String abbreviation;
}
运行结果:
l 删除程序中Size枚举类,背录删除代码,在代码录入中掌握枚举类的定义要求。
package enums; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates enumerated types.
* @version 1.0 2004-05-24
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EnumTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) ");
String input = in.next().toUpperCase();
Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input);
System.out.println("size=" + size);
System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation());
if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE)
System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _.");
}
} enum Size
{
SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; }
public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } private String abbreviation;
}
运行结果:

java.util.EnumSet和java.util.EnumMap是两个枚举集合。EnumSet保证集合中的元素不重复;EnumMap中的key是enum类型,而value则可以是任意类型。
测试程序4:录入以下代码,结合程序运行结果了解方法的可变参数用法
代码如下:
package CLD;
public class TestVarArgus {
public static void dealArray(int... intArray){
for (int i : intArray)
System.out.print(i +" ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
dealArray();
dealArray();
dealArray(, , );
}
}
运行结果:
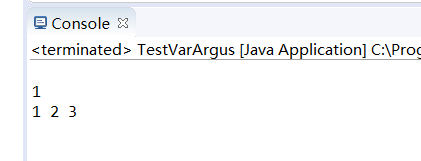
实验:3:编程练习:参照输出样例补全程序,使程序输出结果与输出样例一致。
代码:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
son.method();
}
}
class Parent {
Parent() {
System.out.println("Parent's Constructor without parameter");
}
Parent(boolean b) {
System.out.println("Parent's Constructor with a boolean parameter");
}
public void method() {
System.out.println("Parent's method()");
}
}
class Son extends Parent {
Son(){
super(false);
System.out.println("Son's Constructor without parameter");
System.out.println("Son's method()"); super.method();
}
}
运行结果:
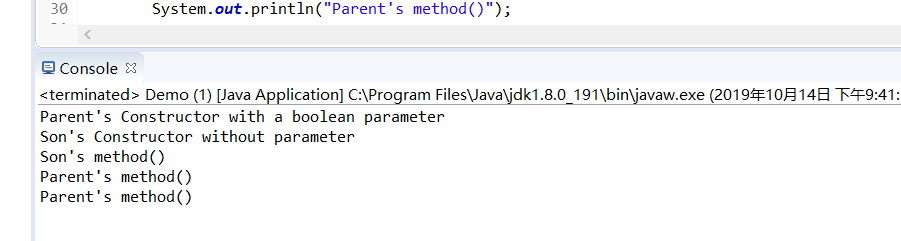
三,实验总结:
这周的 实验大多都是重复上周的实验所以也没有大的难度,让我在前一次实验的基础上对继承有了进一步的了解,但通过测试发现了很多的问题,希望通过后期的学习可以尝试着独自解决这些问题。
201871010101-陈来弟《面向对象程序设计(java)》第七周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 201521123061 《Java程序设计》第七周学习总结
201521123061 <Java程序设计>第七周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 2. 书面作业 ArrayList代码分析 1.1 解释ArrayList的contains源代码 贴上源 ...
随机推荐
- 富文本编辑器Simditor
文档地址:https://simditor.tower.im/docs/doc-usage.html 父组件: options: { placeHolder: 'this is placeHolder ...
- jQuery中的事件(七)
1. ready(fn), 当DOM载入就绪可以查询及操纵时绑定一个要执行的函数 这个方法纯粹是对向window.load事件注册事件的替代方法.通过使用这个方法,可以在DOM载入就绪能够读取并操纵时 ...
- 浅谈字符串Hash
浅谈字符串Hash 本篇随笔讲解Hash(散列表)的一个重要应用:字符串Hash. 关于Hash Hash是一种数据结构,叫做Hash表(哈希表),也叫散列表.关于Hash的实现,其实与离散化颇为类似 ...
- luoguP4094 [HEOI2016/TJOI2016]字符串
题意 考虑二分答案\(mid\),现在我们要判断\(s[c...c+mid-1]\)是否在\(s[a...b]\)出现过. 首先找到\(s[c...c+mid-1]\)所在的状态: 建出\(paren ...
- 冒泡排序法(C语言)
冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)一种计算机科学领域的较简单的排序算法.它重复地走访过要排序的元素列,依次比较两个相邻的元素,如果顺序(如从大到小.首字母从从Z到A)错误就把他们交换过来.走访元素的工 ...
- C 函数与指针(function & pointer)
C 函数与指针(function & pointer) /* * function.c * 函数在C中的使用 * */ #include <stdio.h> int noswap( ...
- vue_day05
目录 vue前后端交互: vue 分离前后端交互: vue前端发送请求: vue请求插件--axios: main.js配置: 前端朝后端请求传参方式: django后端返回数据样式: vue配置El ...
- Java文件上传的几种方式
文件上传与文件上传一样重要.在Java中,要实现文件上传,可以有两种方式: 1.通过Servlet类上传 2.通过Struts框架实现上传 这两种方式的根本还是通过Servlet进行IO流的操作. 一 ...
- Erlang语言基础总结
1.=操作符(模式匹配) 当看到一个表达式像X = 123时,它的意思看似“将整数123赋予变量X”,但这种解读是不 正确的.=不是一个赋值操作符,它实际上是一个模式匹配操作符.与其他函数式编程语言一 ...
- Java-100天知识进阶-GC种类-知识铺(六)
知识铺: 致力于打造轻知识点,持续更新每次的知识点较少,阅读不累.不占太多时间,不停的来唤醒你记忆深处的知识点. 一.GC回收器的 4个指标: 1.Throughput,非gc时间与总运行时间的比重. ...
