[LeetCode] 407. Trapping Rain Water II 收集雨水 II
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
- Given the following 3x6 height map:
- [
- [1,4,3,1,3,2],
- [3,2,1,3,2,4],
- [2,3,3,2,3,1]
- ]
- Return 4.
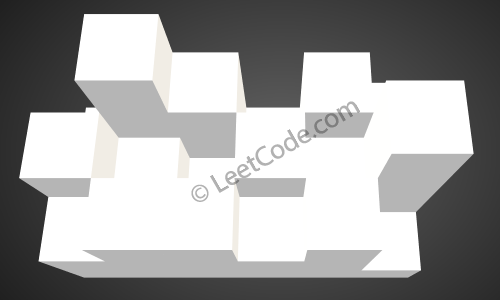
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
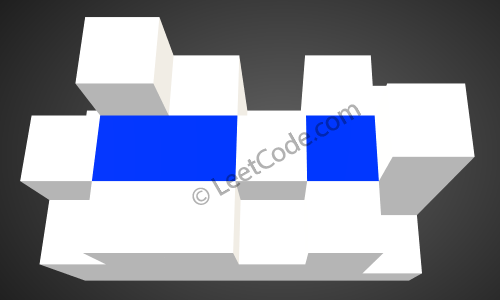
After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
42. Trapping Rain Water的拓展,由2D变3D了。解法跟之前的完全不同了,之前那道题由于是二维的,我们可以用双指针来做,而这道三维的,我们需要用BFS来做。
Java: Priority Queue
- public class Solution {
- public class Cell {
- int row;
- int col;
- int height;
- public Cell(int row, int col, int height) {
- this.row = row;
- this.col = col;
- this.height = height;
- }
- }
- public int trapRainWater(int[][] heights) {
- if (heights == null || heights.length == 0 || heights[0].length == 0)
- return 0;
- PriorityQueue<Cell> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(1, new Comparator<Cell>(){
- public int compare(Cell a, Cell b) {
- return a.height - b.height;
- }
- });
- int m = heights.length;
- int n = heights[0].length;
- boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
- // Initially, add all the Cells which are on borders to the queue.
- for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
- visited[i][0] = true;
- visited[i][n - 1] = true;
- queue.offer(new Cell(i, 0, heights[i][0]));
- queue.offer(new Cell(i, n - 1, heights[i][n - 1]));
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- visited[0][i] = true;
- visited[m - 1][i] = true;
- queue.offer(new Cell(0, i, heights[0][i]));
- queue.offer(new Cell(m - 1, i, heights[m - 1][i]));
- }
- // from the borders, pick the shortest cell visited and check its neighbors:
- // if the neighbor is shorter, collect the water it can trap and update its height as its height plus the water trapped
- // add all its neighbors to the queue.
- int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
- int res = 0;
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- Cell cell = queue.poll();
- for (int[] dir : dirs) {
- int row = cell.row + dir[0];
- int col = cell.col + dir[1];
- if (row >= 0 && row < m && col >= 0 && col < n && !visited[row][col]) {
- visited[row][col] = true;
- res += Math.max(0, cell.height - heights[row][col]);
- queue.offer(new Cell(row, col, Math.max(heights[row][col], cell.height)));
- }
- }
- }
- return res;
- }
- }
Python:
- from heapq import heappush, heappop
- class Solution(object):
- def trapRainWater(self, heightMap):
- """
- :type heightMap: List[List[int]]
- :rtype: int
- """
- m = len(heightMap)
- if not m:
- return 0
- n = len(heightMap[0])
- if not n:
- return 0
- is_visited = [[False for i in xrange(n)] for j in xrange(m)]
- heap = []
- for i in xrange(m):
- heappush(heap, [heightMap[i][0], i, 0])
- is_visited[i][0] = True
- heappush(heap, [heightMap[i][n-1], i, n-1])
- is_visited[i][n-1] = True
- for j in xrange(n):
- heappush(heap, [heightMap[0][j], 0, j])
- is_visited[0][j] = True
- heappush(heap, [heightMap[m-1][j], m-1, j])
- is_visited[m-1][j] = True
- trap = 0
- while heap:
- height, i, j = heappop(heap)
- for (dx, dy) in [(1,0), (-1,0), (0,1), (0,-1)]:
- x, y = i+dx, j+dy
- if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and not is_visited[x][y]:
- trap += max(0, height - heightMap[x][y])
- heappush(heap, [max(height, heightMap[x][y]), x, y])
- is_visited[x][y] = True
- return trap
C++:
- class Solution {
- public:
- int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
- if (heightMap.empty()) return 0;
- int m = heightMap.size(), n = heightMap[0].size(), res = 0, mx = INT_MIN;
- priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> q;
- vector<vector<bool>> visited(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
- vector<vector<int>> dir{{0,-1},{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0}};
- for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
- for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
- if (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1) {
- q.push({heightMap[i][j], i * n + j});
- visited[i][j] = true;
- }
- }
- }
- while (!q.empty()) {
- auto t = q.top(); q.pop();
- int h = t.first, r = t.second / n, c = t.second % n;
- mx = max(mx, h);
- for (int i = 0; i < dir.size(); ++i) {
- int x = r + dir[i][0], y = c + dir[i][1];
- if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || visited[x][y]) continue;
- visited[x][y] = true;
- if (heightMap[x][y] < mx) res += mx - heightMap[x][y];
- q.push({heightMap[x][y], x * n + y});
- }
- }
- return res;
- }
- };
类似题目:
[LeetCode] 42. Trapping Rain Water 收集雨水
All LeetCode Questions List 题目汇总
[LeetCode] 407. Trapping Rain Water II 收集雨水 II的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 407. Trapping Rain Water II 收集雨水之二
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevati ...
- leetCode 42.Trapping Rain Water(凹槽的雨水) 解题思路和方法
Trapping Rain Water Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of e ...
- [leetcode] 407. Trapping Rain Water II
https://leetcode.com/contest/6/problems/trapping-rain-water-ii/ 看到这题,我很高兴,因为我做过!哈哈!其实我现在也写不出来,知道大概思想 ...
- leetcode 11. Container With Most Water 、42. Trapping Rain Water 、238. Product of Array Except Self 、407. Trapping Rain Water II
11. Container With Most Water https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4455109.html 用双指针向中间滑动,较小的高度就作为当前情 ...
- leetcode#42 Trapping rain water的五种解法详解
leetcode#42 Trapping rain water 这道题十分有意思,可以用很多方法做出来,每种方法的思想都值得让人细细体会. 42. Trapping Rain WaterGiven n ...
- [array] leetcode - 42. Trapping Rain Water - Hard
leetcode - 42. Trapping Rain Water - Hard descrition Given n non-negative integers representing an e ...
- LeetCode 42. Trapping Rain Water 【两种解法】(python排序遍历,C++ STL map存索引,时间复杂度O(nlogn))
LeetCode 42. Trapping Rain Water Python解法 解题思路: 本思路需找到最高点左右遍历,时间复杂度O(nlogn),以下为向左遍历的过程. 将每一个点的高度和索引存 ...
- [LeetCode] 42. Trapping Rain Water 收集雨水
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, comput ...
- LeetCode - 42. Trapping Rain Water
42. Trapping Rain Water Problem's Link ------------------------------------------------------------- ...
随机推荐
- 题解 洛谷P1236 【算24点】
不得不说,个人认为许多大佬们把程序想复杂了,所以码量很长,但是实际上这题并不要这么复杂... 可以考虑用一个\(dfs\)维护一个状态\(f(n)[a_1,a_2--a_n]\) 接下来我们暴力枚举两 ...
- DT6.0框架留言模块漏洞修复
今天早上登入后台,留言被国外乱码注入一大堆,很烦人,得去数据库清空.所以仔细检查dt的留言模块,找到解决办法. 在:module/extend/guestbook.inc.php 大约第10行左右 i ...
- c++中关联容器set的使用
c++中set的用法 #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> #include<set ...
- rsync提权
介绍:Rsync是linux下一款数据备份工具,默认开启873端口 利用条件:rsync未授权 列出模板 rsync rsync://目标ip:873/ 列出模块src下的文件 rsync rsync ...
- AD域与信任关系
域与信任关系:信任关系分为两种,一种是林中信任关系,另一种是林之间的信任关系. 林中信任关系的特点: 注意:林中信任关系还可以分为两种:一种是父子信任,还有一种是树根信任. 父子信任:在同一个树域之中 ...
- ES6对象的个人总结
属性初始值的简写: 当一个对象的属性与本地变量同名时,不需要再写冒号和值,直接写属性名即可 let fullName = '杨三', age = 19; let obj = { fullName: f ...
- 开源项目(4-2)手势识别-Keras/Theano/OpenCV实现的CNN手势识别
https://github.com/asingh33/CNNGestureRecognizer 我提供了两种捕获模式: 二进制模式:在这里我首先将图像转换为灰度,然后应用高斯模糊效果和自适应阈值滤波 ...
- SpringBoot-设置定时任务
@Scheduled为设置定时任务的注解. 参数常用的为两种: 第一种是fixedRate,表示以一种固定频率去执行,单位为毫秒:例如@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000) 表示为 ...
- “OKR播种机”JOHN DOERR–目标是对抗纷乱思绪的一针疫苗
OKR培养出疯狂的想法,再加上对的人,奇迹就会出现 约翰·杜尔是美国最有影响力.最具创意.最不拘传统的冒险资本投资家之一.在短短10年内创造了高达1,000亿美元的经济价值.迄今为止,他已向 250家 ...
- DOM内容梳理2
JavaScript-DOM2(内容整理) 这两天新的知识有点多有点杂一时半会没有整理过来,以后不出意外会一直更行. js节点类型(NODETYPE) 查看节点类型 nodetype属性,返回的结果会 ...
