【源码解析】Flink 是如何处理迟到数据
相信会看到这篇文章的都对Flink的时间类型(事件时间、处理时间、摄入时间)和Watermark有些了解,当然不了解可以先看下官网的介绍:https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-master/dev/event_time.html
这里就会有这样一个问题:FLink 是怎么基于事件时间和Watermark处理迟到数据的呢?
在回答这个问题之前,建议大家可以看下下面的Google 的三篇论文,关于流处理的模型:
https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol8/p1792-Akidau.pdf 《The Dataflow Model: A Practical Approach to Balancing Correctness, Latency, and Cost in Massive-Scale, Unbounded, Out-of-Order Data Processing》
high-level的现代数据处理概念指引:
https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/the-world-beyond-batch-streaming-101
https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/the-world-beyond-batch-streaming-102
---------------------------进入正题--------------------------------
现在进入正题:FLink 是怎么基于事件时间和Watermark处理迟到数据的呢?
这个问题可以分成两个部分:
1. 基于事件时间创建Timestamp 和Watermark(后面会详细介绍) 2. 处理迟到数据
1. 基于事件时间创建Timestamp 和Watermark
为了方便查看,这里使用 assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(assigner: AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks[T]): DataStream[T] 重载方法基于每个事件生成水印代码如下:
val input = env.addSource(source)
.map(json => {
// json : {"id" : 0, "createTime" : "2019-08-24 11:13:14.942", "amt" : "9.8"}
val id = json.get("id").asText()
val createTime = json.get("createTime").asText()
val amt = json.get("amt").asText()
LateDataEvent("key", id, createTime, amt)
})
// assign watermarks every event
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks[LateDataEvent]() {
// check extractTimestamp emitted watermark is non-null and large than previously
override def checkAndGetNextWatermark(lastElement: LateDataEvent, extractedTimestamp: Long): Watermark = {
new Watermark(extractedTimestamp)
}
// generate next watermark
override def extractTimestamp(element: LateDataEvent, previousElementTimestamp: Long): Long = {
val eventTime = sdf.parse(element.createTime).getTime
eventTime
}
})
```
扩展:数据在算子中是以StreamRecord 对象作为流转抽象结构如下:
public final class StreamRecord<T> extends StreamElement {
/** The actual value held by this record. 具体数据*/
private T value;
/** The timestamp of the record. 该数据对应的时间戳 */
private long timestamp;
}
StreamElement 也是 Watermark 和 StreamStatus的父类,简单来说就是Flink 承载消息的基类(这里可以指定,Watermark 是和事件一个级别的抽象,而Timestamp 是Watermark和事件的成员变量,代表Watermark和事件的时间)
```
assignTimestampsAndWatermarks 是基于事件的数据(extractTimestamp 方法中返回的Timestamp),替换StreamRecord 对象中的Timestamp和发出新的Watermark(如果当前事件的Timestamp 生成的Watermark大于上一次的Watermark)
下面我们来debug这部分源码:
首先在extractTimestamp 方法中添加断点查看Timestamp 和Watermark的生成:
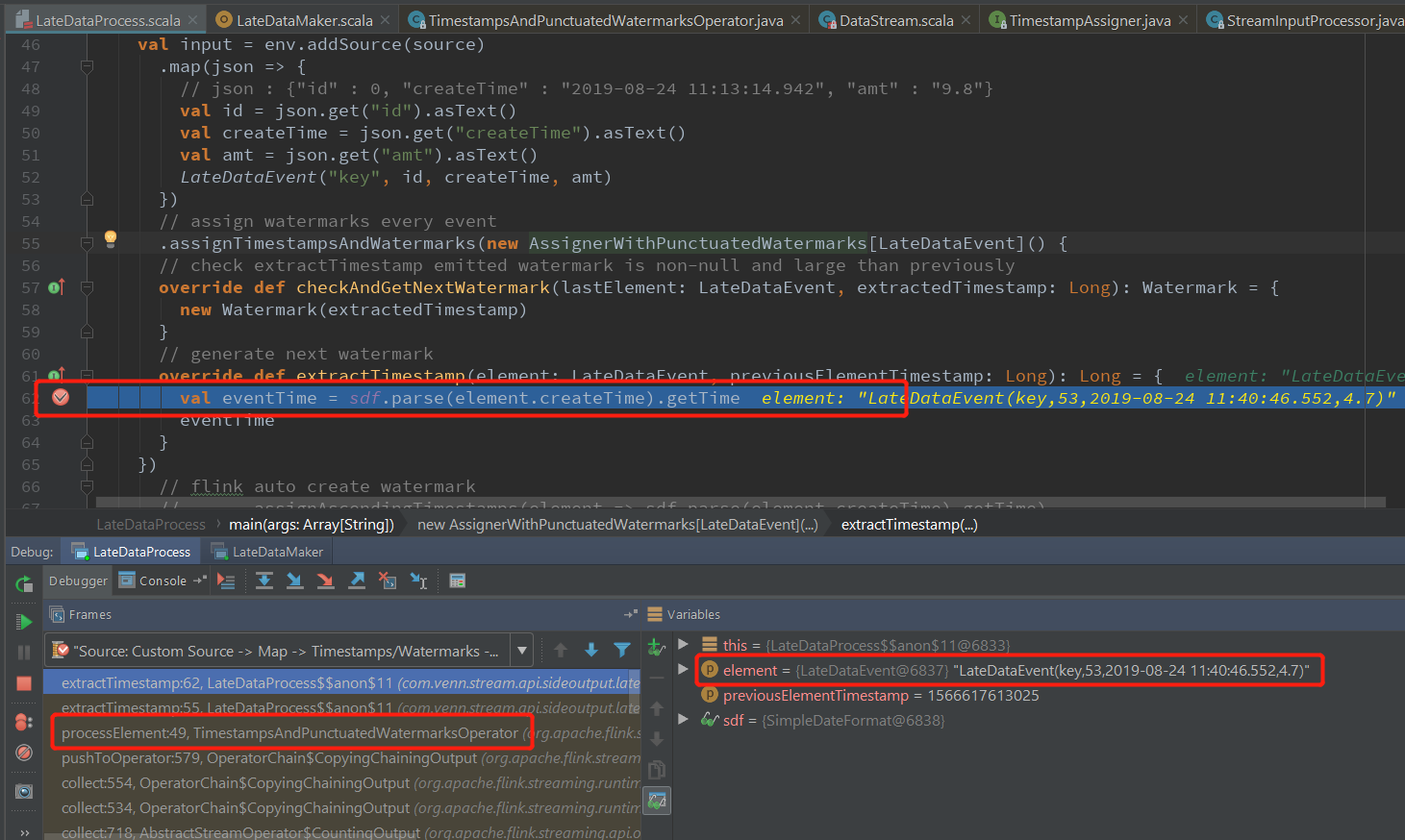
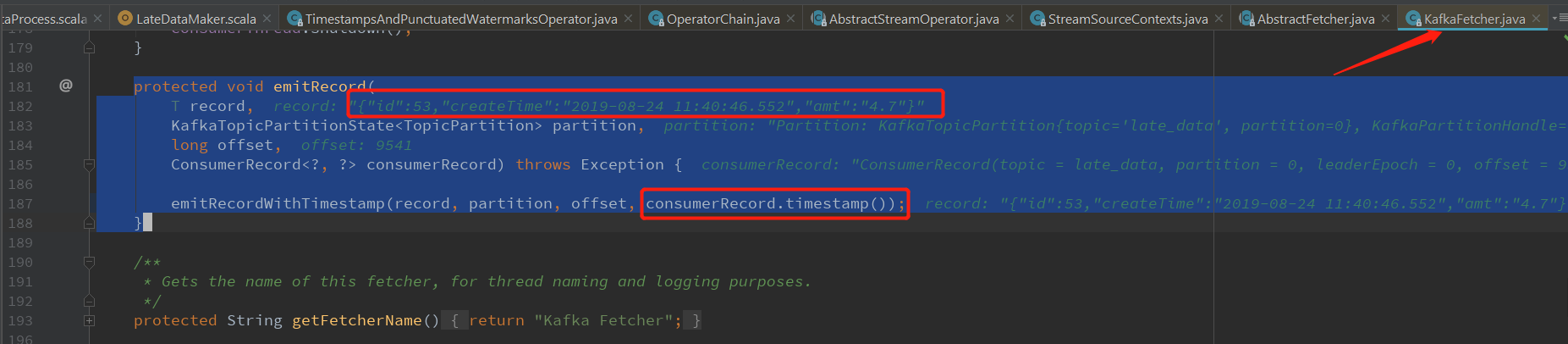
TimestampsAndPunctuatedWatermarksOperator.processElement(使用的类取决于assignTimestampsAndWatermarks 方法的参数) 中处理事件的Timestamp和对应的Watermark StreamRecord对象的创建在 StreamSourceContexts.processAndCollectWithTimestamp 中,使用的Timestamp 是数据在kafka的时间,在KafkaFetcher.emitRecord方法中从consumerRecord中获取:
KafkaFetcher.emitRecord 发出从kafka中消费到的数据:
protected void emitRecord(
T record,
KafkaTopicPartitionState<TopicPartition> partition,
long offset,
ConsumerRecord<?, ?> consumerRecord) throws Exception { emitRecordWithTimestamp(record, partition, offset, consumerRecord.timestamp());
}
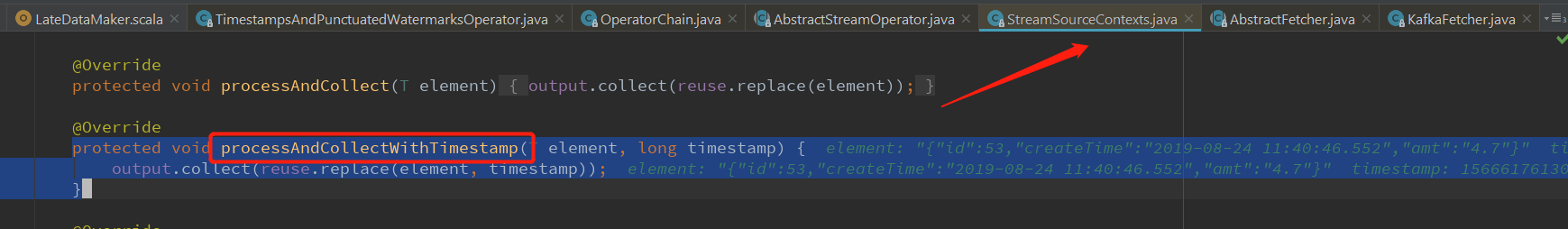
StreamSourceContexts.processAndCollectWithTimestamp 创建StreamRecord 对象
protected void processAndCollectWithTimestamp(T element, long timestamp) {
output.collect(reuse.replace(element, timestamp)); // 放入真正的事件时间戳
}
下面我们来看 TimestampsAndPunctuatedWatermarksOperator.processElement 的源码
@Override
public void processElement(StreamRecord<T> element) throws Exception {
// 获取这条数据
final T value = element.getValue();
// userFunction 就是代码里面创建的匿名类 AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks
// 调用extractTimestamp,获取新的Timestamp
// element.hasTimestamp 有的话就用,没有就给默认值long类型 的最小值
final long newTimestamp = userFunction.extractTimestamp(value,
element.hasTimestamp() ? element.getTimestamp() : Long.MIN_VALUE);
// 使用新的Timestamp 替换StreamRecord 旧的Timestamp
output.collect(element.replace(element.getValue(), newTimestamp));
// 获取下一个Watermark,调用实现的 checkAndGetNextWatermark 方法
final Watermark nextWatermark = userFunction.checkAndGetNextWatermark(value, newTimestamp);
// 如果新的Watermark 大于上一个Watermark 就发出新的
if (nextWatermark != null && nextWatermark.getTimestamp() > currentWatermark) {
currentWatermark = nextWatermark.getTimestamp();
output.emitWatermark(nextWatermark);
}
}
至此Timestamp和Watermark的创建(或者说生成)就好了
2. Flink 处理迟到数据
为了演示这个功能,在上面的程序中添加了window算子和迟到数据侧边输出的方法 sideOutputLateData,为了方便查看,这里再添加一次全部代码
val source = new FlinkKafkaConsumer[ObjectNode]("late_data", new JsonNodeDeserializationSchema(), Common.getProp)
// 侧边输出的tag
val late = new OutputTag[LateDataEvent]("late")
val input = env.addSource(source)
.map(json => {
// json : {"id" : 0, "createTime" : "2019-08-24 11:13:14.942", "amt" : "9.8"}
val id = json.get("id").asText()
val createTime = json.get("createTime").asText()
val amt = json.get("amt").asText()
LateDataEvent("key", id, createTime, amt)
})
// assign watermarks every event
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks[LateDataEvent]() {
// check extractTimestamp emitted watermark is non-null and large than previously
override def checkAndGetNextWatermark(lastElement: LateDataEvent, extractedTimestamp: Long): Watermark = {
new Watermark(extractedTimestamp)
}
// generate next watermark
override def extractTimestamp(element: LateDataEvent, previousElementTimestamp: Long): Long = {
val eventTime = sdf.parse(element.createTime).getTime
eventTime
}
})
// after keyBy will have window number of different key
.keyBy("key")
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.minutes(1)))
// get lateData
.sideOutputLateData(late)
.process(new ProcessWindowFunction[LateDataEvent, LateDataEvent, Tuple, TimeWindow] {
// just for debug window process late data
override def process(key: Tuple, context: Context, elements: Iterable[LateDataEvent], out: Collector[LateDataEvent]): Unit = {
// print window start timestamp & end timestamp & current watermark time
println("window:" + context.window.getStart + "-" + context.window.getEnd + ", currentWatermark : " + context.currentWatermark)
val it = elements.toIterator
while (it.hasNext) {
val current = it.next()
out.collect(current)
}
}
})
// print late data
input.getSideOutput(late).print("late:")
input.print("apply:")
env.execute("LateDataProcess")
代码逻辑很简单,主要是为了加入window算子,process算子是为了方便debug到window算子中
下面开始debug源码:
在process 方法中添加断点:

这次直接从window算子接收上游发过来的数据开始看起:
StreamInputProcessor.processInput方法负责将接收到的事件(数据、Watermark、StreamStatus、LatencyMarker),反序列化为 StreamElement(上文已经说得了,是事件抽象的基类),判断具体是那种消息,分别进行处理
public boolean processInput() throws Exception {
while (true) {
if (currentRecordDeserializer != null) {
DeserializationResult result = currentRecordDeserializer.getNextRecord(deserializationDelegate);
if (result.isBufferConsumed()) {
currentRecordDeserializer.getCurrentBuffer().recycleBuffer();
currentRecordDeserializer = null;
}
if (result.isFullRecord()) {
StreamElement recordOrMark = deserializationDelegate.getInstance();
if (recordOrMark.isWatermark()) {
// handle watermark
statusWatermarkValve.inputWatermark(recordOrMark.asWatermark(), currentChannel);
continue;
} else if (recordOrMark.isStreamStatus()) {
// handle stream status
statusWatermarkValve.inputStreamStatus(recordOrMark.asStreamStatus(), currentChannel);
continue;
} else if (recordOrMark.isLatencyMarker()) {
// handle latency marker
synchronized (lock) {
streamOperator.processLatencyMarker(recordOrMark.asLatencyMarker());
}
continue;
} else {
// now we can do the actual processing
StreamRecord<IN> record = recordOrMark.asRecord();
synchronized (lock) {
numRecordsIn.inc();
streamOperator.setKeyContextElement1(record);
streamOperator.processElement(record);
}
return true;
}
}
}
}
注:代码比较长,挑选了跟这次主题相关的部分
Watermark:

数据:

这里我们主要看数据的处理逻辑:
// now we can do the actual processing
StreamRecord<IN> record = recordOrMark.asRecord();
synchronized (lock) {
// metric 的Counter,统计有多少条数据进来
numRecordsIn.inc();
// 选择当前的key(类似与数据分区,每个key一个,里面存储自己的states)
streamOperator.setKeyContextElement1(record);
// 真正在进到WindowOperator 中处理数据了
streamOperator.processElement(record);
}
就到了 WindowOperator.processElement 方法(主要判断逻辑都在这里)
// 判断windowAssigner 是不是MergingWindowAssigner
if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner)
区分开会话窗口和滑动、跳动窗口的处理逻辑,会话窗口的各个key的窗口是不对齐的
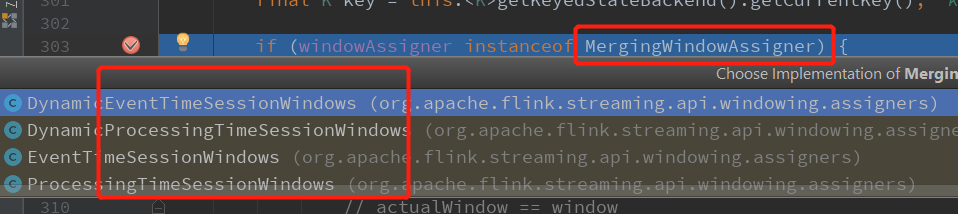
直接到 else部分:
} else {
for (W window: elementWindows) {
// drop if the window is already late 判断窗口数据是否迟到
// 是,就直接跳过这条数据,重新处理下一条数据
if (isWindowLate(window)) {
continue;
}
PS: 写了这么久,终于到迟到数据处理的地方了 -_-
下面看下 isWindowLate 部分的处理逻辑:
/**
* Returns {@code true} if the watermark is after the end timestamp plus the allowed lateness
* of the given window.
*/
protected boolean isWindowLate(W window) {
// 只有事件时间下,并且 窗口元素的最大时间 + 允许迟到时间 <= 当前Watermark 的时候为true(即当前窗口元素迟到了)
return (windowAssigner.isEventTime() && (cleanupTime(window) <= internalTimerService.currentWatermark()));
} /**
* Returns the cleanup time for a window, which is
* {@code window.maxTimestamp + allowedLateness}. In
* case this leads to a value greater than {@link Long#MAX_VALUE}
* then a cleanup time of {@link Long#MAX_VALUE} is
* returned.
* 返回窗口的cleanup 时间, 窗口的最大时间 + 允许延迟的时间
* @param window the window whose cleanup time we are computing.
*/
private long cleanupTime(W window) {
if (windowAssigner.isEventTime()) {
long cleanupTime = window.maxTimestamp() + allowedLateness;
return cleanupTime >= window.maxTimestamp() ? cleanupTime : Long.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
return window.maxTimestamp();
}
}
看一条正常到达的数据:
{"id" : 891, "createTime" : "2019-08-24 17:51:44.152", "amt" : "5.6"}
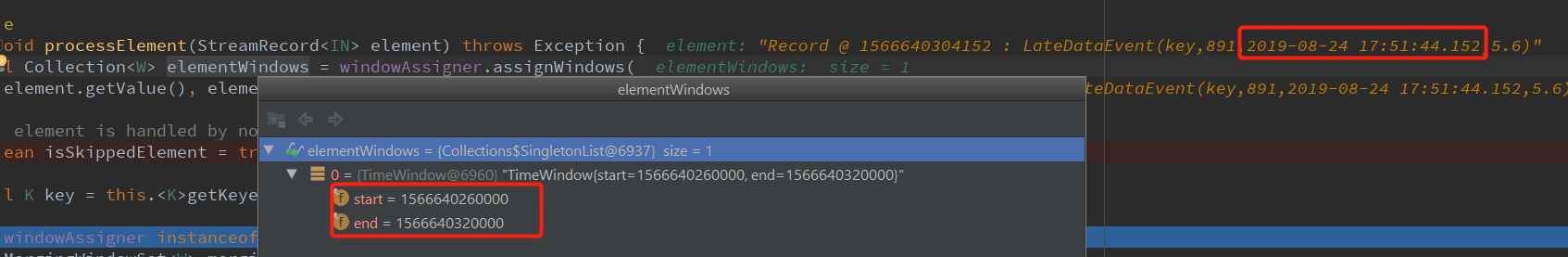

891 这条数据的事件时间是:2019-08-24 17:51:44.152 ,1 分钟的整分窗口,这条数据对应的窗口就是: [2019-08-24 17:51:00.000, 2019-08-24 17:52:000) ,对应的时间戳是 : [1566640260000, 1566640320000) ,当前的Watermark 是 : 1566640294102,窗口数据的最大时间戳大于 当前的Watermark, 不是迟到数据,不跳过。
现在在来看一条迟到的数据:
{"id" : 892, "createTime" : "2019-08-24 17:51:54.152", "amt" : "3.6"}
892 这条数据的事件时间是:2019-08-24 17:51:54.152 ,1 分钟的整分窗口,这条数据对应的窗口就是: [2019-08-24 17:51:00.000, 2019-08-24 17:52:000) ,对应的时间戳是 : [1566640260000, 1566640320000) ,当前的Watermark 是 : 1566652224102 ,窗口数据的最大时间戳小于 当前的Watermark, 数据是迟到数据,跳过。
上面就是窗口对迟到数据的处理源码dubug了,到这里就已经讲完Flink 处理迟到数据的两个部分:
1. 基于事件时间创建Timestamp 和Watermark(后面会详细介绍) 2. 窗口处理迟到数据
注: 这里加上“窗口”,明确是window 算子做的这些事情
下面在来看下窗口迟到输出的SideOutput ,源码在:WindowOperator.processElement 方法的最后一段:
// side output input event if 事件时间
// element not handled by any window 没有window处理过这条数据,上面isSkippedElement 默认值为true,如果上面判断为迟到数据,isSkippedElement就会为false
// late arriving tag has been set
// windowAssigner is event time and current timestamp + allowed lateness no less than element timestamp
if (isSkippedElement && isElementLate(element)) {
// 设置了 lateDataOutputTag 即window 算子后面的 .sideOutputLateData(late)
if (lateDataOutputTag != null){
sideOutput(element);
} else {
this.numLateRecordsDropped.inc();
}
} /**
* Decide if a record is currently late, based on current watermark and allowed lateness.
* 事件时间,并且 元素的时间戳 + 允许延迟的时间 <= 当前watermark 是为true
* @param element The element to check
* @return The element for which should be considered when sideoutputs
*/
protected boolean isElementLate(StreamRecord<IN> element){
return (windowAssigner.isEventTime()) &&
(element.getTimestamp() + allowedLateness <= internalTimerService.currentWatermark());
} /**
* Write skipped late arriving element to SideOutput.
*
* @param element skipped late arriving element to side output
*/
protected void sideOutput(StreamRecord<IN> element){
output.collect(lateDataOutputTag, element);
}
搞定
欢迎关注Flink菜鸟公众号,会不定期更新Flink(开发技术)相关的推文

【源码解析】Flink 是如何处理迟到数据的更多相关文章
- [源码解析] Flink UDAF 背后做了什么
[源码解析] Flink UDAF 背后做了什么 目录 [源码解析] Flink UDAF 背后做了什么 0x00 摘要 0x01 概念 1.1 概念 1.2 疑问 1.3 UDAF示例代码 0x02 ...
- Flink 源码解析 —— Flink JobManager 有什么作用?
JobManager 的作用 https://t.zsxq.com/2VRrbuf 博客 1.Flink 从0到1学习 -- Apache Flink 介绍 2.Flink 从0到1学习 -- Mac ...
- Flink 源码解析 —— Flink TaskManager 有什么作用?
TaskManager 有什么作用 https://t.zsxq.com/RZbu7yN 博客 1.Flink 从0到1学习 -- Apache Flink 介绍 2.Flink 从0到1学习 -- ...
- [源码解析] Flink的groupBy和reduce究竟做了什么
[源码解析] Flink的groupBy和reduce究竟做了什么 目录 [源码解析] Flink的groupBy和reduce究竟做了什么 0x00 摘要 0x01 问题和概括 1.1 问题 1.2 ...
- [源码解析] Flink的Slot究竟是什么?(1)
[源码解析] Flink的Slot究竟是什么?(1) 目录 [源码解析] Flink的Slot究竟是什么?(1) 0x00 摘要 0x01 概述 & 问题 1.1 Fllink工作原理 1.2 ...
- [源码解析] Flink的Slot究竟是什么?(2)
[源码解析] Flink 的slot究竟是什么?(2) 目录 [源码解析] Flink 的slot究竟是什么?(2) 0x00 摘要 0x01 前文回顾 0x02 注册/更新Slot 2.1 Task ...
- Hadoop源码解析之: TextInputFormat如何处理跨split的行
我们知道hadoop将数据给到map进行处理前会使用InputFormat对数据进行两方面的预处理: 对输入数据进行切分,生成一组split,一个split会分发给一个mapper进行处理. 针对每个 ...
- [源码解析] GroupReduce,GroupCombine 和 Flink SQL group by
[源码解析] GroupReduce,GroupCombine和Flink SQL group by 目录 [源码解析] GroupReduce,GroupCombine和Flink SQL grou ...
- Flink 源码解析 —— 源码编译运行
更新一篇知识星球里面的源码分析文章,去年写的,周末自己录了个视频,大家看下效果好吗?如果好的话,后面补录发在知识星球里面的其他源码解析文章. 前言 之前自己本地 clone 了 Flink 的源码,编 ...
随机推荐
- 3-html块-语义化的标签
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title> ...
- P4357 [CQOI2016]K远点对
题意:给定平面中的 \(n\) 个点,求第 \(K\) 远的点对之间的距离,\(n\leq 1e5,K\leq min(100,\frac{n\times (n-1)}{2})\) 题解:kd-tre ...
- 洛谷 P3375 【模板】KMP字符串匹配 题解
KMP模板,就不解释了 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algo ...
- 在新浪SAE上搭建微信公众号的python应用
微信公众平台的开发者文档https://www.w3cschool.cn/weixinkaifawendang/ python,flask,SAE(新浪云),搭建开发微信公众账号http://www. ...
- PHP-FPM参数详情
pid = run/php-fpm.pid #pid设置,默认在安装目录中的var/run/php-fpm.pid,建议开启 error_log = log/php-fpm.log #错误日志,默认在 ...
- 洛谷 P2661 信息传递 题解
P2661 信息传递 题目描述 有 \(n\) 个同学(编号为 \(1\) 到 \(n\) )正在玩一个信息传递的游戏.在游戏里每人都有一个固定的信息传递对象,其中,编号为 \(i\) 的同学的信息传 ...
- Python常量类
class _const: class ConstError(TypeError): pass class ConstCaseError(ConstError): pass def __setattr ...
- python反射hasattr getattr setattr delattr
反射 : 是用字符串类型的名字 去操作 变量 相比于用eval('print(name)') 留有 安全隐患 反射 就没有安全问题 hasattr 语法: hasattr(object, name)o ...
- 01_tf和numpy的区别
import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tf # 这里是为了演示numpy和tf的区别.np.random.seed(43) x_data = np.random ...
- openssl从内存中读取私钥进行签名
麻痹的找了好久,真恶心! #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #ifdef WIN32 #include <windows.h& ...
