python(36)- 测试题
1、8<<2等于?
32
- “<<”位运算
- 264 132 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
- 原始位置 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
- 想左位移2位 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2、通过内置函数计算5除以2的余数
- a=divmod(5,2)
- print(a)
- --->(2,1) #2为商,1有余数
- print(a[1])
- --->1
3、s=[1,"h",2,"e",[1,2,3],"l",(4,5),"l",{1:"111"},"o"],将s中的5个字符提取出来并拼接成字符串。
- s = [1, "h", 2, "e", [1, 2, 3], "l", (4, 5), "l", {1: "111"}, "o"]
- str_s=""
- for i in s:
- if type(i)==str:
- str_s+="".join(i)
- print(str_s)
- --->hello
- str_s="".join([i for i in s if type(i)==str])
- print(str_s)
- --->hello
4、判断"yuan"是否在[123,(1,"yuan"),{"yuan":"handsome"},"yuanhao"],如何判断以及对应结果?
- s=[123, (1, "yuan"), {"yuan": "handsome"}, "yuanhao"]
- if "yuan" in s:
- print('"yuan"在列表s中')
- else:
- print('"yuan"不在列表s中')
- --->"yuan"不在列表s中
5、l=[1,2,3]
l2=l.insert(3,"hello")
print(l2)
执行结果并解释为什么?
- l=[1,2,3]
- l2=l.insert(3,"hello")
- print(l)
- --->[1, 2, 3, 'hello']
- print(l2)
- --->None #因为l.insert(3,'hello')的执行结果是没有返回值的,所以打印l2什么也得不到
6、 a=[1,2,[3,"hello"],{"egon":"aigan"}]
b=a[:]
a[0]=5
a[2][0]=666
print(a)
print(b)
计算结果以及为什么?
- [5, 2, [666, 'hello'], {'egon': 'aigan'}]
- [1, 2, [666, 'hello'], {'egon': 'aigan'}]
- b相当于a的浅拷贝,当拷贝a中[3,"hello"]相当于只拷贝了一个内存地址,当劣列表里的元素改变时,
- b指向的内存地址并未发生改变,所以列表元素跟着一起改变
7 使用文件读取,找出文件中最长的行的长度(用一行代码解决)?
- print(max([line for line in open("a.txt","r",encoding="utf8")]))
8.
def add(s, x):
return s + x
def generator():
for i in range(4):
yield i
base = generator()
for n in [1, 11]:
base = (add(i, n) for i in base)
print list(base)
- --->[22, 23, 24, 25]
- base=[0,1,2,3]
- base1=(add(i, n) for i in [0,1,2,3])
- --->[11,12,13,14]
- base2=(add(i, n) for i in [11,12,13,14])
- --->[22,23,24,25]
9
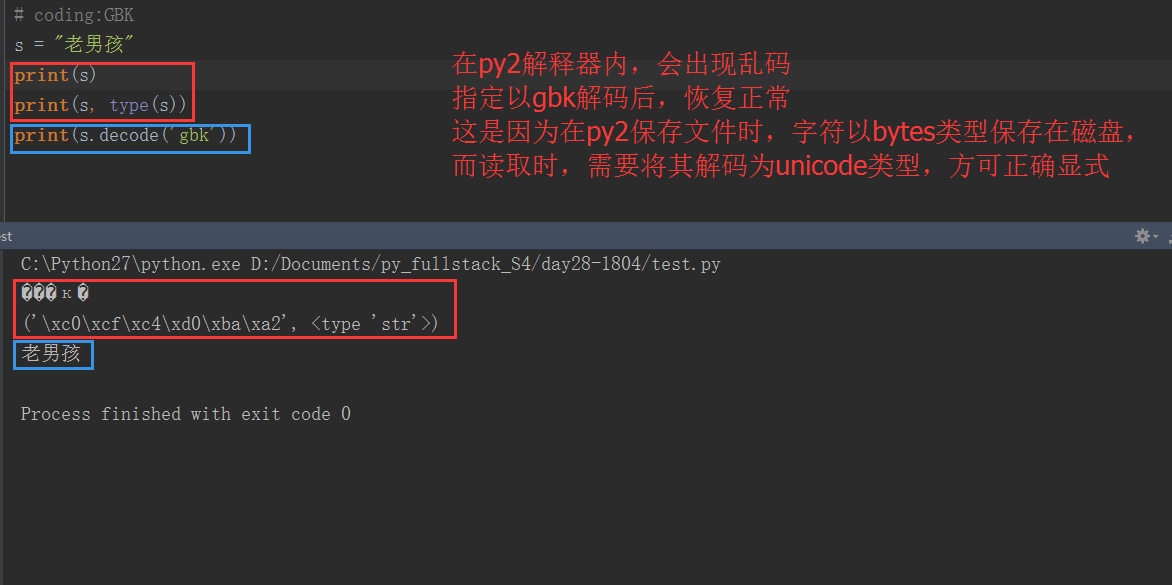
hello.py(gbk方式保存):
#coding:GBK
print(“老男孩”)
如果用py2,py3下在cmd下运行回报错吗?为什么并提出解决方案? (编码)
- 均不会报错,因为cmd默认编码方式为GBK,所以在python2和python3中都不会报错

- 但在python2解释器中会报错,需要gbk模式解码。python3解释器中不会报错
10 通过函数化编程实现5的阶乘
- def func(n):
- if n == 1:
- return 1
- else:
- return n * func(n-1)
- obj = func(3)
- print(obj)
11 打印如下图案:
- *
- ***
- *****
- *******
- *****
- ***
- *
- def func(number):
- for i in range(1,number,2):
- print(("*" * i).center(number))
- for i in range(number,0,-2):
- print(("*" * i).center(number))
- func(7)
12 求s=a+aa+aaa+aaaa+aa...a的值,其中a是一个数字。例如2+22+222+2222+22222,几个数相加以及a的值由键盘控制。
- def func(a,n):
- sum=0
- a=str(a)
- for i in range(1,n+1):
- x=int(a*i)
- sum+=x
- return sum
- print(func(2,2))
13
def foo():
print('hello foo')
return()
def bar():
print('hello bar')
(1)为这些基础函数加一个装饰器,执行对应函数内容后,将当前时间写入一个文件做一个日志记录。
- def timer(func):
- def wrapper():
- import time
- res = func()
- f = open('log', 'a+') #以追加的方式打开文件,没有则会创建
- s = time.asctime() #获取当前时间:Tue Apr 18 21:46:18 2017
- f.write(s + '\n') #将当前时间写入log文件,并换行
- f.close() #关闭log文件
- return res
- return wrapper
- @timer
- def foo():
- print('hello foo')
- return ()
- @timer
- def bar():
- print('hello bar')
- foo()
- bar()
(2)改成参数装饰器,即可以根据调用时传的参数决定是否记录时间,比如@logger(True)
- def logger(choice):
- def timmer(func):
- def wrapper():
- import time
- if choice == True:
- res = func()
- f = open('log', 'a+') #以追加的方式打开文件,没有则会创建
- s = time.asctime() #获取当前时间:Tue Apr 18 21:46:18 2017
- f.write(s + '\n') #将当前时间写入log文件,并换行
- f.close() #关闭log文件
- return res
- else:
- pass
- return wrapper
- return timmer
- @logger(True)
- def foo():
- print('hello foo')
- return ()
- @logger(True)
- def bar():
- print('hello bar')
- foo()
- bar()
18 三次登陆锁定:要求一个用户名密码输入密码错误次数超过三次锁定?
- #读取注册用户的信息,用户名,密码,输错次数,写入字典中
- user={}
- with open("DB1",encoding="utf8") as f:
- for line in f:
- username_list=line.strip().split("|") #username_list--->['egon', '123', '2']
- user[username_list[0]]={"name":username_list[0],
- "pwd":username_list[1],
- "times":username_list[2]}
- # print(user) #-->{'egon': {'name': 'egon', 'pwd': '123', 'times': '2'}, 'xuyaping': {'name': 'xuyaping', 'pwd': '123', 'times': '0'}, 'xyy': {'name': 'xyy', 'pwd': '123', 'times': '1'}}
- #读取黑名单用户,将黑名单用户加入列表中
- with open("black_lockname",encoding="utf8") as f1:
- black_list=[]
- for line in f1:
- black_list.append(line.strip())
- # print(black_list)
- while True:
- username = input("please input your username:").strip()
- passwd = input("please input your passwd:").strip()
- #用户在黑名单中
- if username in black_list:
- print("该用户为黑名单用户,请滚")
- break
- # 用户为注册用户
- elif username in user:
- user[username]["times"]=int(user[username]["times"])
- if user[username]["times"]<3 and passwd==user[username]["pwd"]:
- print("登录成功")
- user[username]["times"]=0
- #将修改后的信息重新写入DB1中
- with open("DB1","w",encoding="utf8") as f3:
- for i in user:
- f3.write(i + "|" + user[i]["pwd"] + "|" + str(user[i]["times"]) + "\n")
- break
- else:
- user[username]["times"]+=1
- print("登录错误")
- # 将修改后的信息重新写入DB1中
- with open("DB1", "w", encoding="utf8") as f3:
- for i in user:
- f3.write(i + "|" + user[i]["pwd"] + "|" + str(user[i]["times"]) + "\n")
- if user[username]["times"]==3:
- black_list.append(username)
- print("账户被锁定")
- # 将修改后的信息重新写入black_lockname中
- with open("black_lockname","w",encoding="utf8") as f4:
- for j in black_list:
- f4.write(j+ "\n")
- break
- #用户不是注册用户
- else:
- print("该用户没有注册")
- break
参考博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuyaping/p/6679305.html
python(36)- 测试题的更多相关文章
- [Leetcode][Python]36: Valid Sudoku
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-'''__author__ = 'dabay.wang@gmail.com' 36: Valid Sudokuhttps://oj.leetcode.com ...
- Python基础测试题
1,执行Python脚本的两种方式 答:一种是 交互式,命令行shell启动Python,输入相应代码得出结果,无保存,另一种是 脚本式,例如:python 脚本文件.py,脚本文件一直存在,可编辑, ...
- Python 36 死锁现象和递归锁、信号量、Event事件、线程queue
一:死锁现象和递归锁 所谓死锁: 是指两个或两个以上的进程或线程在执行过程中,因争夺资源而造成的一种互相等待的现象,若无外力作用,它们都将无法推进下去.此时称系统处于死锁状态或系统产生了死锁,这些永远 ...
- Python 36 GIL全局解释器锁 、vs自定义互斥锁
一:GIL全局解释器锁介绍 在CPython中,全局解释器锁(或GIL)是一个互斥锁, 它阻止多个本机线程同时执行Python字节码.译文:之所以需要这个锁, 主要是因为CPython的内存管理不是线 ...
- python 36 进程池、线程池
目录 1. 死锁与递归锁 2. 信号量Semaphor 3. GIL全局解释器锁:(Cpython) 4. IO.计算密集型对比 4.1 计算密集型: 4.2 IO密集型 5. GIL与Lock锁的区 ...
- python.36的特性新定义初学者必看课程
一.Python3.6新特性 1.新的格局化字符串办法 <p "="">新的格局化字符串办法,即在一般字符串前增加 f 或 F 前缀,其效果相似于str.fo ...
- python+selenium 自动化测试实战
一.前言: 之前的文章说过, 要写一篇自动化实战的文章, 这段时间比较忙再加回家过11一直没有更新博客,今天整理一下实战项目的代码共大家学习.(注:项目是针对我们公司内部系统的测试,只能内部网络访问, ...
- 零基础学Python--------入门篇 第1章 初始Python
入门篇 第1章 初始Python 1.1 Pyhton 概述 1.1.1 了解 Python Python,本义是指“蟒蛇”.1989年,荷兰人Guido van Rossum发明了一种面向对象的 ...
- Python面试常见的问题
So if you are looking forward to a Python Interview, here are some most probable questions to be ask ...
- 用 Python 和 OpenCV 检测图片上的条形码(转载)
原文地址:http://python.jobbole.com/80448/ 假设我们要检测下图中的条形码: # load the image and convert it to grayscale 1 ...
随机推荐
- Leetcode 423.从英文中重建数字
从英文中重建数字 给定一个非空字符串,其中包含字母顺序打乱的英文单词表示的数字0-9.按升序输出原始的数字. 注意: 输入只包含小写英文字母. 输入保证合法并可以转换为原始的数字,这意味着像 &quo ...
- Django模板(filter过滤器{{ }}与tag标签{% %}应用)
模板里面过滤器与标签的应用 templates模板里面的应用参考(主要应用在这里面) <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> & ...
- Balanced Lineup(ST)
描述 For the daily milking, Farmer John's N cows (1 ≤ N ≤ 50,000) always line up in the same order. On ...
- [译]pycache是什么?
原回答: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/16869024/what-is-pycache 当你用python运行一个程序时,解释器首先将它编译成字节码(这是一 ...
- Linux 终端操作之「I/O Redirection」
I/O 重定向是在终端运行程序时很常用的技巧,但是我对它所知甚少.今天我在 DigitalOcean 上发现了一篇很好的 tutorial.这篇随笔记录一下我的心得体会和发现的一个问题. I/O re ...
- 刷题总结——开车旅行(NOIP2012 set+倍增)
题目: 题目描述 小 A 和小 B 决定利用假期外出旅行,他们将想去的城市从 1 到 N 编号,且编号较小的城市在编号较大的城市的西边,已知各个城市的海拔高度互不相同,记城市 i 的海拔高度为Hi,城 ...
- windows下 maven+selenium+testng项目搭建(七)
Selenium2.47.1 + Maven3.3.9 + TestNG6.8.8 windows准备好以下环境 1. Jdk,环境变量配置 2. maven环境3. eclipse 开发工具 ,ec ...
- cf671B Robin Hood
We all know the impressive story of Robin Hood. Robin Hood uses his archery skills and his wits to s ...
- C语言第四题
今天就一道题 阅读printf代码的具体实现,要求在阅读过程中要做下列的事 1.至少列出十个c标准库的方法,并且说明他们方法的含义,以及参数的含义 2.至少列出2个c标准库的引入(或者是依赖),并且说 ...
- 什么是GOP(转)
所谓GOP,意思是画面组,MPEG格中的帧序列,分为I.P.B三种,如排成IBBPBBPBBPBBPBBP...样式,这种连续的帧图片组合即为GOP(画面群,GROUP OF PICTURE),是MP ...
