深入理解spring中的各种注解(转)
Spring中的注解大概可以分为两大类:
1)spring的bean容器相关的注解,或者说bean工厂相关的注解;
2)springmvc相关的注解。
spring的bean容器相关的注解,先后有:@Required, @Autowired, @PostConstruct, @PreDestory,还有Spring3.0开始支持的JSR-330标准javax.inject.*中的注解(@Inject, @Named, @Qualifier, @Provider, @Scope, @Singleton).
springmvc相关的注解有:@Controller, @RequestMapping, @RequestParam, @ResponseBody等等。
要理解Spring中的注解,先要理解Java中的注解。
1. Java中的注解
Java中1.5中开始引入注解,我们最熟悉的应该是:@Override, 它的定义如下:

/**
* Indicates that a method declaration is intended to override a
* method declaration in a supertype. If a method is annotated with
* this annotation type compilers are required to generate an error
* message unless at least one of the following conditions hold:
* The method does override or implement a method declared in a
* supertype.
* The method has a signature that is override-equivalent to that of
* any public method declared in Object.
*
* @author Peter von der Ahé
* @author Joshua Bloch
* @jls 9.6.1.4 @Override
* @since 1.5
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Override {
}

从注释,我们可以看出,@Override的作用是,提示编译器,使用了@Override注解的方法必须override父类或者java.lang.Object中的一个同名方法。我们看到@Override的定义中使用到了 @Target, @Retention,它们就是所谓的“元注解”——就是定义注解的注解,或者说注解注解的注解(晕了...)。我们看下@Retention

/**
* Indicates how long annotations with the annotated type are to
* be retained. If no Retention annotation is present on
* an annotation type declaration, the retention policy defaults to
* RetentionPolicy.CLASS.
*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Retention {
/**
* Returns the retention policy.
* @return the retention policy
*/
RetentionPolicy value();
}

@Retention用于提示注解被保留多长时间,有三种取值:

public enum RetentionPolicy {
/**
* Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler.
*/
SOURCE,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler
* but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default
* behavior.
*/
CLASS,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and
* retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively.
*
* @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
*/
RUNTIME
}

RetentionPolicy.SOURCE 保留在源码级别,被编译器抛弃(@Override就是此类); RetentionPolicy.CLASS被编译器保留在编译后的类文件级别,但是被虚拟机丢弃;
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME保留至运行时,可以被反射读取。
再看 @Target:

package java.lang.annotation; /**
* Indicates the contexts in which an annotation type is applicable. The
* declaration contexts and type contexts in which an annotation type may be
* applicable are specified in JLS 9.6.4.1, and denoted in source code by enum
* constants of java.lang.annotation.ElementType
* @since 1.5
* @jls 9.6.4.1 @Target
* @jls 9.7.4 Where Annotations May Appear
*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Target {
/**
* Returns an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type
* can be applied to.
* @return an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type
* can be applied to
*/
ElementType[] value();
}

@Target用于提示该注解使用的地方,取值有:

public enum ElementType {
/** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */
TYPE,
/** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */
FIELD,
/** Method declaration */
METHOD,
/** Formal parameter declaration */
PARAMETER,
/** Constructor declaration */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** Local variable declaration */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Annotation type declaration */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/** Package declaration */
PACKAGE,
/**
* Type parameter declaration
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/**
* Use of a type
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_USE
}

分别表示该注解可以被使用的地方:1)类,接口,注解,enum; 2)属性域;3)方法;4)参数;5)构造函数;6)局部变量;7)注解类型;8)包
所以:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Override {
}
表示 @Override 只能使用在方法上,保留在源码级别,被编译器处理,然后抛弃掉。
还有一个经常使用的元注解 @Documented :

/**
* Indicates that annotations with a type are to be documented by javadoc
* and similar tools by default. This type should be used to annotate the
* declarations of types whose annotations affect the use of annotated
* elements by their clients. If a type declaration is annotated with
* Documented, its annotations become part of the public API
* of the annotated elements.
*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Documented {
}

表示注解是否能被 javadoc 处理并保留在文档中。
2. 使用 元注解 来自定义注解 和 处理自定义注解
有了元注解,那么我就可以使用它来自定义我们需要的注解。结合自定义注解和AOP或者过滤器,是一种十分强大的武器。比如可以使用注解来实现权限的细粒度的控制——在类或者方法上使用权限注解,然后在AOP或者过滤器中进行拦截处理。下面是一个关于登录的权限的注解的实现:

/**
* 不需要登录注解
*/
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface NoLogin {
}

我们自定义了一个注解 @NoLogin, 可以被用于 方法 和 类 上,注解一直保留到运行期,可以被反射读取到。该注解的含义是:被 @NoLogin 注解的类或者方法,即使用户没有登录,也是可以访问的。下面就是对注解进行处理了:

/**
* 检查登录拦截器
* 如不需要检查登录可在方法或者controller上加上@NoLogin
*/
public class CheckLoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(CheckLoginInterceptor.class); @Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
if (!(handler instanceof HandlerMethod)) {
logger.warn("当前操作handler不为HandlerMethod=" + handler.getClass().getName() + ",req="
+ request.getQueryString());
return true;
}
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
String methodName = handlerMethod.getMethod().getName();
// 判断是否需要检查登录
NoLogin noLogin = handlerMethod.getMethod().getAnnotation(NoLogin.class);
if (null != noLogin) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("当前操作methodName=" + methodName + "不需要检查登录情况");
}
return true;
}
noLogin = handlerMethod.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getAnnotation(NoLogin.class);
if (null != noLogin) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("当前操作methodName=" + methodName + "不需要检查登录情况");
}
return true;
}
if (null == request.getSession().getAttribute(CommonConstants.SESSION_KEY_USER)) {
logger.warn("当前操作" + methodName + "用户未登录,ip=" + request.getRemoteAddr());
response.getWriter().write(JsonConvertor.convertFailResult(ErrorCodeEnum.NOT_LOGIN).toString()); // 返回错误信息
return false;
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}

上面我们定义了一个登录拦截器,首先使用反射来判断方法上是否被 @NoLogin 注解:
NoLogin noLogin = handlerMethod.getMethod().getAnnotation(NoLogin.class);
然后判断类是否被 @NoLogin 注解:
noLogin = handlerMethod.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getAnnotation(NoLogin.class);
如果被注解了,就返回 true,如果没有被注解,就判断是否已经登录,没有登录则返回错误信息给前台和false. 这是一个简单的使用 注解 和 过滤器 来进行权限处理的例子。扩展开来,那么我们就可以使用注解,来表示某方法或者类,只能被具有某种角色,或者具有某种权限的用户所访问,然后在过滤器中进行判断处理。
3. spring的bean容器相关的注解
1)@Autowired 是我们使用得最多的注解,其实就是 autowire=byType 就是根据类型的自动注入依赖(基于注解的依赖注入),可以被使用再属性域,方法,构造函数上。
2)@Qualifier 就是 autowire=byName, @Autowired注解判断多个bean类型相同时,就需要使用 @Qualifier("xxBean") 来指定依赖的bean的id:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userService")
private UserService userService;
3)@Resource 属于JSR250标准,用于属性域额和方法上。也是 byName 类型的依赖注入。使用方式:@Resource(name="xxBean"). 不带参数的 @Resource 默认值类名首字母小写。
4)JSR-330标准javax.inject.*中的注解(@Inject, @Named, @Qualifier, @Provider, @Scope, @Singleton)。@Inject就相当于@Autowired, @Named 就相当于 @Qualifier, 另外 @Named 用在类上还有 @Component的功能。
5)@Component, @Controller, @Service, @Repository, 这几个注解不同于上面的注解,上面的注解都是将被依赖的bean注入进入,而这几个注解的作用都是生产bean, 这些注解都是注解在类上,将类注解成spring的bean工厂中一个一个的bean。@Controller, @Service, @Repository基本就是语义更加细化的@Component。
6)@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 不是用于依赖注入,而是bean 的生命周期。类似于 init-method(InitializeingBean) destory-method(DisposableBean)
4. spring中注解的处理
spring中注解的处理基本都是通过实现接口 BeanPostProcessor 来进行的:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
相关的处理类有: AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor, RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
这些处理类,可以通过 <context:annotation-config/> 配置隐式的配置进spring容器。这些都是依赖注入的处理,还有生产bean的注解(@Component, @Controller, @Service, @Repository)的处理:
<context:component-scan base-package="net.aazj.service,net.aazj.aop" />
这些都是通过指定扫描的基包路径来进行的,将他们扫描进spring的bean容器。注意 context:component-scan 也会默认将 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 配置进来。所以<context:annotation-config/>是可以省略的。另外context:component-scan也可以扫描@Aspect风格的AOP注解,但是需要在配置文件中加入 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> 进行配合。
5. Spring注解和JSR-330标准注解的区别:
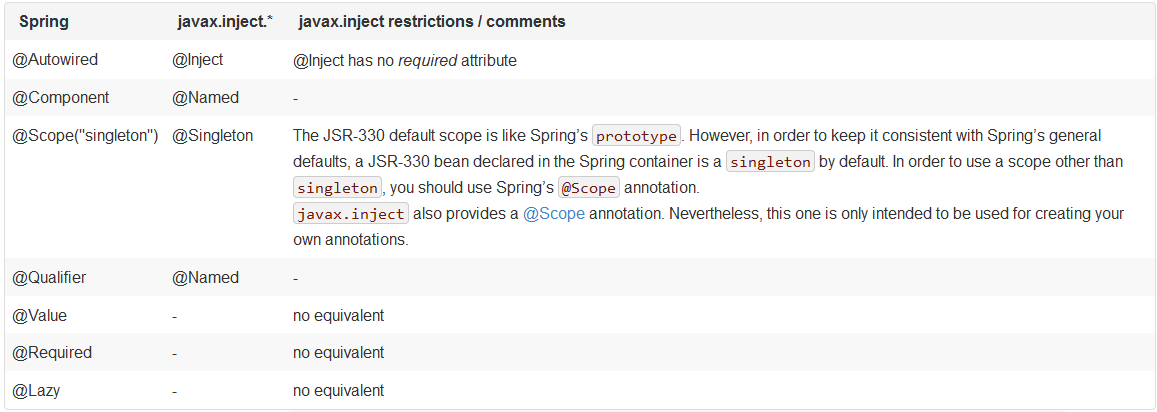
深入理解spring中的各种注解(转)的更多相关文章
- 深入理解spring中的各种注解
Spring中的注解大概可以分为两大类: 1)spring的bean容器相关的注解,或者说bean工厂相关的注解: 2)springmvc相关的注解. spring的bean容器相关的注解,先后有:@ ...
- Spring 中aop切面注解实现
spring中aop的注解实现方式简单实例 上篇中我们讲到spring的xml实现,这里我们讲讲使用注解如何实现aop呢.前面已经讲过aop的简单理解了,这里就不在赘述了. 注解方式实现aop我们 ...
- 通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期
通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期及AOP原理 Spring源码解析(十一)Spring扩展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProces ...
- 第5章—构建Spring Web应用程序—关于spring中的validate注解后台校验的解析
关于spring中的validate注解后台校验的解析 在后台开发过程中,对参数的校验成为开发环境不可缺少的一个环节.比如参数不能为null,email那么必须符合email的格式,如果手动进行if判 ...
- Spring中的常用注解
Spring中的常用注解 1.@Controller 标识一个该类是Spring MVC controller处理器,用来创建处理http请求的对象.
- JavaEE开发之Spring中的条件注解组合注解与元注解
上篇博客我们详细的聊了<JavaEE开发之Spring中的多线程编程以及任务定时器详解>,本篇博客我们就来聊聊条件注解@Conditional以及组合条件.条件注解说简单点就是根据特定的条 ...
- spring中aop的注解实现方式简单实例
上篇中我们讲到spring的xml实现,这里我们讲讲使用注解如何实现aop呢.前面已经讲过aop的简单理解了,这里就不在赘述了. 注解方式实现aop我们主要分为如下几个步骤(自己整理的,有更好的方法的 ...
- JavaEE开发之Spring中的条件注解、组合注解与元注解
上篇博客我们详细的聊了<JavaEE开发之Spring中的多线程编程以及任务定时器详解>,本篇博客我们就来聊聊条件注解@Conditional以及组合条件.条件注解说简单点就是根据特定的条 ...
- 浅谈spring中AOP以及spring中AOP的注解方式
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming):AOP的专业术语是"面向切面编程" 什么是面向切面编程,我的理解就是:在不修改源代码的情况下增强功能.好了,下面在 ...
随机推荐
- Xcode 4.6.2 运行次数为偶数程序崩溃问题
如果你的MAC 系统升级到10.8.4 Xcode升级到4.6.2,在工程运行第二次.第四次.第六次 ... 的时候程序就会崩溃 无论是新建的模板工程也会这样,这个属于系统BUG,在stackove ...
- nginx 源码安装
安装环境: 操作系统:Ubuntu 12.04 Nginx: V1.4.2 PCRE: V8.33 zlib: V1.2.8 下载上述源包到当前用户主目录(本机:/hom ...
- 《sql---教学反馈系统-阶段项目2》
/* a) 创建数据库 使用T-SQL创建数据库feedback,要求:①一个主要文件(存放在第一个硬盘分区C:\project文件夹下),初始大小为10M,最大为200M,文件自动增长率为15% ② ...
- winXP JDK由1.8改为1.6
(1)直接在环境变量中删除配置的相关路径 path的值: C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>path PATH=C:\Documents and S ...
- Unobtrusive Ajax
ASP.NET MVC之Unobtrusive Ajax(五) 前言 这一节我们来讲讲Unobtrusive中的Ajax提交,大部分情况下我们是利用JQuery来进行Ajax请求,当然利用JQue ...
- c++对象指针-01(转载)
1.指向对像的指针在建立对像时,编译系统会为每一个对像分配一定的存储空间,以存放其成员,对像空间的起始地址就是对像的指针.可以定义一个指针变量,用来存和对像的指针.如果有一个类:class Time{ ...
- SWT的选择文件和文件夹的函数
org.eclipse.swt.widgets.DirectoryDialog//选择目录org.eclipse.swt.widgets.FileDialog//SWT.OPEN打开文件 SWT.SA ...
- poj 2010 Moo University - Financial Aid (贪心+线段树)
转载请注明出处,谢谢http://blog.csdn.net/ACM_cxlove?viewmode=contents by---cxlove 骗一下访问量.... 题意大概是:从c个中选出n个 ...
- OCP读书笔记(19) - 数据库空间管理
传输表空间:将linux下的数据库中的test表空间传输到windows平台下的数据库 在传输表空间前,先确定一下源库与目标数据库字符集一致: select * from nls_database_p ...
- Effective C++规定45 附加代码
这部分是额外的代码的博客.键45条款想法已经实现. #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T> c ...
