【JAVA多线程中使用的方法】
一、sleep和wait的区别。
1.wait可以指定时间,也可以不指定。
而sleep必须制定。
2.在同步的时候,对于CPU的执行权和以及锁的处理不同。
wait:释放执行权,释放锁。
sleep:释放执行权,不释放锁。
二、线程是否安全?
class Test implements Runnable
{
public synchronized void show()
{
try
{
wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
}
public synchronized void method()
{
notifyAll();
}
}
假设有四个线程0123,其中有三个线程012全部挂在wait上了,另外一个线3程则调用了notifyAll方法,这样在同步代码块中就有了三个线程,这和“在同步代码块中只能有一个线程”的原则相违背,线程变得不安全了。这话乍听起来没有错,事实上是有问题的。实际上,当线程3调用了notifyAll方法的时候,CPU执行权还在自己手里,而被唤醒的三个线程虽然拥有了执行资格,但是仅仅是执行资格,他们将会加入堵塞队列,等待执行权;等到线程三释放了执行权以及锁(method方法结束),在堵塞队列中的012线程中的一个将会获得执行权,任务结束后,释放锁以及执行权并交给下一个线程。。
验证代码:
class Test implements Runnable
{
public boolean flag=true;
public void run()
{
if(this.flag==true)
show();
else
method();
}
public synchronized void show()
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":将会等待");
try
{
wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(50);
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":正在执行"+i);
}
}
public synchronized void method()
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":将会唤醒所有线程");
notifyAll();
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(50);
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":正在执行"+i);
}
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Test t=new Test();
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t);
Thread t3=new Thread(t);
Thread t4=new Thread(t);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start(); try
{
Thread.sleep(20);
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
t.flag=false;
t4.start(); }
}
其运行结果和预想的结果相同。
三、怎么结束线程
1.使用stop方法:已过时,不推荐使用。
2.控制run方法结束。
可以使用标志变量的方法。
/*
能控制线程停止的情况。
*/
class Test implements Runnable
{
private boolean flag=true;
public void run()
{
while(flag)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++++++++++++++");
}
public void setFlag()
{
this.flag=false;
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Test t=new Test();
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t);
t1.start();
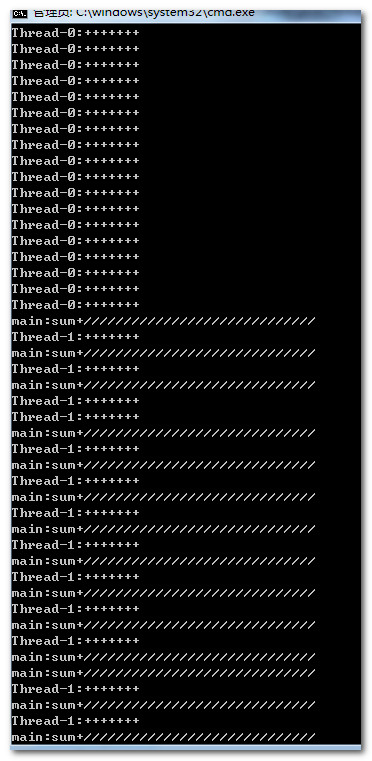
t2.start(); int sum=0;
while(true)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////");
if(++sum==20)
{
t.setFlag();
System.out.println("over");
break;
}
}
}
}
这是在未加同步的时候。若是加上同步,有的时候就不管用了。
/*
不能控制线程停止的情况。
*/
class Test implements Runnable
{
private boolean flag=true;
public void run()
{
while(flag)
{
synchronized(this)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行");
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++++++++++++++");
}
}
}
}
public void setFlag()
{
this.flag=false;
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Test t=new Test();
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t);
t1.start();
t2.start(); int sum=0;
while(true)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////");
if(++sum==20)
{
t.setFlag();
System.out.println("over");
break;
}
}
}
}
由于线程0、1均进入了冻结状态,所以不再判断flag标记,线程也就不会结束了。
3.使用interrupt方法结束线程。
此方法带有强制性,因此会抛出异常,需要捕获。
interrupt方法的功能是将处于冻结状态的线程强制性唤醒,使其具有CPU执行资格。
/*
使用interrupt方法控制线程停止的情况。
*/
class Test implements Runnable
{
private boolean flag=true;
public void run()
{
while(flag)
{
synchronized(this)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行");
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++++++++++++++");
}
}
}
}
public void setFlag()
{
this.flag=false;
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Test t=new Test();
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t);
t1.start();
t2.start(); int sum=0;
while(true)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////");
if(++sum==20)
{
t.setFlag();
t1.interrupt();
t2.interrupt();
System.out.println("over");
break;
}
}
}
}
4、使用守护线程
setDaemon方法:设置线程为守护线程或者用户线程、后台线程。
守护线程具有依附性,一旦所依附的线程结束,自己也将会消失,所以要“守护”,所以叫“用户线程”(这是和系统线程相对应的叫法)。
JAVA中规定,一旦程序中线程全部为守护线程,则JAVA虚拟机将会自动退出,所有线程都将会结束。
将t2设置成守护线程,一旦t1线程和main线程全部结束,t2线程将成为唯一一个线程而且是守护线程,JAVA虚拟机将会自动退出,t2线程也会跟着结束。
/*
守护线程举例。
*/
class Test implements Runnable
{
private boolean flag=true;
public void run()
{
while(flag)
{
synchronized(this)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行");
try
{
this.wait();
}
catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++++++++++++++");
}
}
}
}
public void setFlag()
{
this.flag=false;
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Test t=new Test();
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t);
t1.start();
//要在t2线程开启之前设置。
t2.setDaemon(true); t2.start(); int sum=0;
while(true)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////");
if(++sum==20)
{
t.setFlag();
t1.interrupt();
//t2.interrupt();
System.out.println("over");
break;
}
}
}
}
设置守护线程要在线程启动之前设置。
四.join方法。
join方法的功能:加入当前线程,当前线程会释放执行权,一直等到新加入的线程执行完任务之后才执行自己的任务。
/*
join方法使用
*/
class Test implements Runnable
{
private boolean flag=true;
public void run()
{
int sum=1;
while(++sum<21)
{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++");
}
}
public void setFlag()
{
this.flag=false;
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
Test t=new Test();
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t);
t1.start();
t1.join(); t2.start(); int sum=0;
while(true)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////");
if(++sum==20)
{
t.setFlag();
t1.interrupt();
t2.interrupt();
System.out.println("over");
break;
}
}
}
}
五、线程优先级
toString方法:返回字符串包括线程名称、线程优先级、线程所属的线程组。
线程有10个优先级1-10,且数字越大,优先级越大。为了便于使用,将优先级划分为三级:
Thread.MAX_PRIORITY:最大优先级,相当于10
Thread.MIN_PRIORITY:最小优先级,相当于1
Thread.MAX_PRIORITY:默认优先级,相当于5
设置优先级的方法是setPriority();
/*
验证优先级,其实没什么效果
*/
class Test implements Runnable
{
private boolean flag=true;
public void run()
{
int sum=1;
while(++sum<21)
{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
}
}
public void setFlag()
{
this.flag=false;
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
Test t=new Test();
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t); t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
t2.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); t1.start();
t2.start(); int sum=0;
while(true)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
if(++sum==20)
{
t.setFlag();
t1.interrupt();
t2.interrupt();
System.out.println("over");
break;
}
}
}
}
应当注意的是,设置优先级的高低只是增加或者减小CPU切换到的概率,实际上仍然要争夺CPU执行权。
六、yied方法
yield方法是静态方法,使用Thread类名直接调用,作用是释放当前线程的执行权。给别的线程更多的机会执行任务。
/*
验证yield方法,是Thread类的静态方法。
*/
class Test implements Runnable
{
private boolean flag=true;
public void run()
{
int sum=1;
while(sum<20)
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(10);
}
catch(InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":"+sum);
Thread.yield();
sum++;
}
}
public void setFlag()
{
this.flag=false;
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Test t=new Test();
Thread t1=new Thread(t);
Thread t2=new Thread(t);
t1.start();
t2.start(); }
}
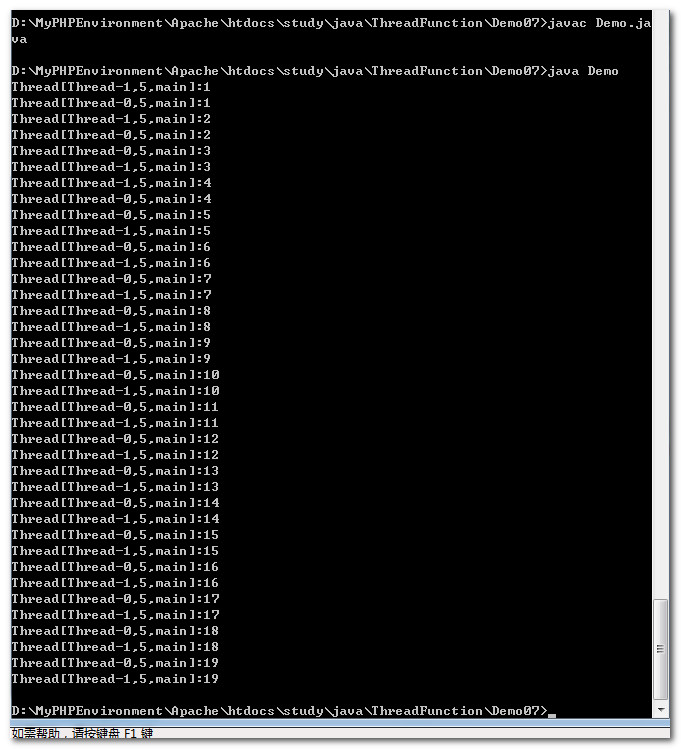
我们可以观察到两个线程任务的执行进度高度同步,这是由于yied方法强制放弃CPU执行权造成的。
【JAVA多线程中使用的方法】的更多相关文章
- java 多线程中的wait方法的详解
java多线程中的实现方式存在两种: 方式一:使用继承方式 例如: PersonTest extends Thread{ String name; public PersonTest(String n ...
- Java多线程中的join()方法
一.join()方法介绍 join() 定义在Thread.java中.join()方法把指定的线程加入到当前线程,可以将两个交替执行的线程合并为顺序执行的线程.比如在线程B中调用了线程A的join( ...
- 浅谈Java多线程中的join方法
先上代码 新建一个Thread,代码如下: package com.thread.test; public class MyThread extends Thread { private String ...
- Java多线程中的join方法
新建一个Thread,代码如下: package com.thread.test; public class MyThread extends Thread { private String name ...
- java多线程中关于join方法的使用
Thread的非静态方法join()让一个线程B"加入"到另外一个线程A的尾部.在A执行完毕之前,B不能工作.例如: Thread t = new MyThread ...
- Java并发编程--多线程中的join方法详解
Java Thread中, join()方法主要是让调用该方法的thread在完成run方法里面的部分后, 再执行join()方法后面的代码 例如:定义一个People类,run方法是输出姓名年龄. ...
- java多线程中的三种特性
java多线程中的三种特性 原子性(Atomicity) 原子性是指在一个操作中就是cpu不可以在中途暂停然后再调度,既不被中断操作,要不执行完成,要不就不执行. 如果一个操作时原子性的,那么多线程并 ...
- Java多线程中的常用方法
本文将带你讲诉Java多线程中的常用方法 Java多线程中的常用方法有如下几个 start,run,sleep,wait,notify,notifyAll,join,isAlive,current ...
- Java多线程中的竞争条件、锁以及同步的概念
竞争条件 1.竞争条件: 在java多线程中,当两个或以上的线程对同一个数据进行操作的时候,可能会产生“竞争条件”的现象.这种现象产生的根本原因是因为多个线程在对同一个数据进行操作,此时对该数据的操作 ...
随机推荐
- Tunna内网转发
Tunna和reduh原理一样.. 使用方法: 上传源码包中文件夹webshell下的脚本至网站目录 然后本地进行连接上传的webshell即可 python proxy.py -u http://1 ...
- jtable插件api
官网2016-03-15 事例图: 一.客户端配置 1. paging boolean default:false 配置是否分页,果断改为true. 2. pageList string defaul ...
- zabbix安装报某些模块未安装上
执行下 make clean /usr/local/php5/bin/phpize ./configure --with-curl --with-php-config=/usr/local/php5/ ...
- centos 设置永久dns
最近在折腾一个问题. 由于服务器的带宽是联通5M, 不稳定.而且所处的网络的dns解析貌似老出问题,每隔一定周期解析时间特别长. 于是乎,想在本地做一个dns,这样可以减少dns解析时间,并做些静态配 ...
- C++ 输出调试的一些技巧
主要利用了宏和stderr... #define enable_debug #ifdef enable_debug FILL some macros/functions here #else /// ...
- POJ 1088
http://poj.org/problem?id=1088 一道中文题,这道题如果不限时的话,是个简单的搜索,但限时的话,就要用记忆化搜索 所谓记忆化搜索就是对每一次搜索的结果进行记录,然后之后的如 ...
- 【转】关于Class.getResource和ClassLoader.getResource的路径问题
Java中取资源时,经常用到Class.getResource和ClassLoader.getResource,这里来看看他们在取资源文件时候的路径问题. Class.getResource(Stri ...
- echo 单引号和双引号
echo输出 $key=value echo "$key" echo 后面带双引号的话,双引号里面的内容会翻译,输出value echo '$key' echo后面带单引号的话,双 ...
- 6.js模式-中介者模式
1. 中介者模式 所有对象通过中介者进行通信 var playDirector = (function(){ var players = []; var options = {}; options.a ...
- FFmpeg-20160506-snapshot-bin
ESC 退出 0 进度条开关 1 屏幕原始大小 2 屏幕1/2大小 3 屏幕1/3大小 4 屏幕1/4大小 S 下一帧 [ -2秒 ] +2秒 ; -1秒 ' +1秒 下一个帧 -> -5秒 F ...
