DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
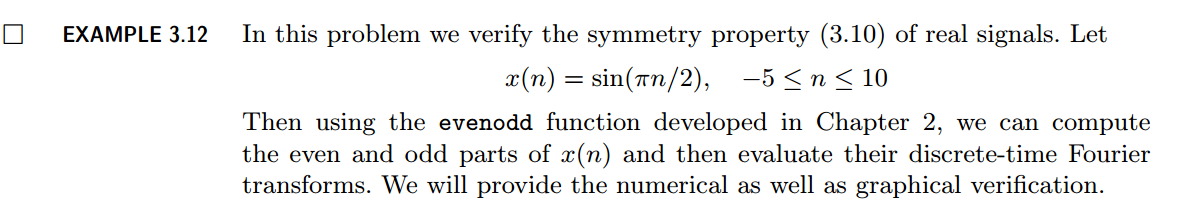
用到的性质
代码:
n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2);
k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , [0,pi] axis divided into 101 points.
X = x * (exp(-j*pi/100)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of x % signal decomposition
[xe,xo,m] = evenodd(x,n); % even and odd parts
XE = xe * (exp(-j*pi/100)) .^ (m'*k); % DTFT of xe
XO = xo * (exp(-j*pi/100)) .^ (m'*k); % DTFT of xo magXE = abs(XE); angXE = angle(XE); realXE = real(XE); imagXE = imag(XE);
magXO = abs(XO); angXO = angle(XO); realXO = real(XO); imagXO = imag(XO);
magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X); %verification
XR = real(X); % real part of X
error1 = max(abs(XE-XR)); % Difference
XI = imag(X); % imag part of X
error2 = max(abs(XO-j*XI)); % Difference figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'x sequence')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n,x); title('x sequence'); xlabel('n'); ylabel('x(n)'); grid on; figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'xe & xo sequence')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); stem(m,xe); title('xe sequence '); xlabel('m'); ylabel('xe(m)'); grid on;
subplot(2,1,2); stem(m,xo); title('xo sequence '); xlabel('m'); ylabel('xo(m)'); grid on; %% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%% START X's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'X its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX); grid on; axis([-1,1,0,9]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X's mag ang real imag
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START XE's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
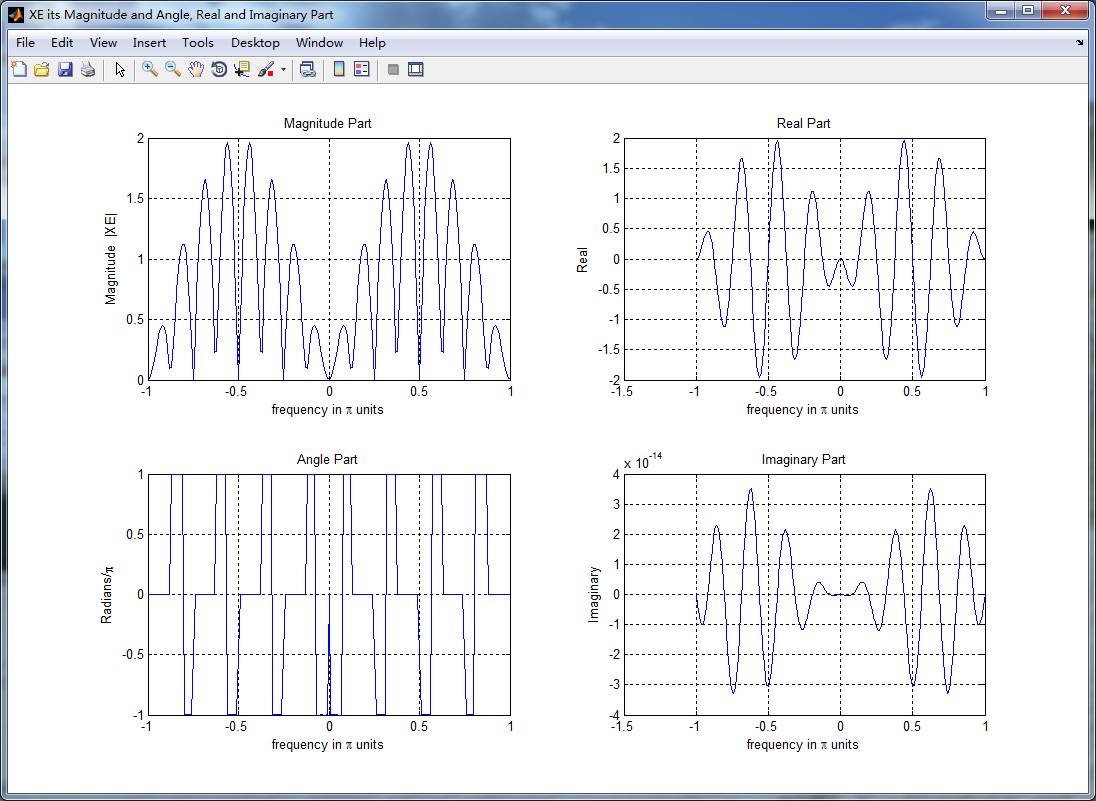
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'XE its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magXE); grid on; axis([-1,1,0,2]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |XE|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angXE/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realXE); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagXE); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END XE's mag ang real imag
%% -------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START XO's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
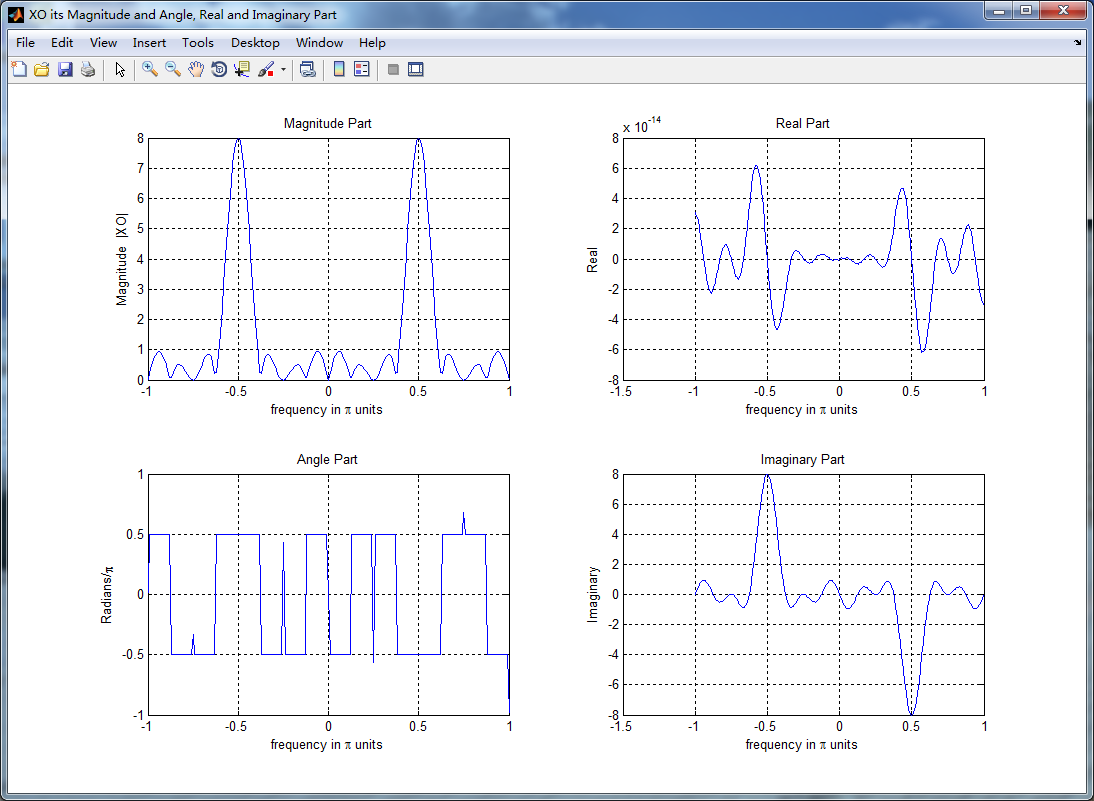
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'XO its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magXO); grid on; axis([-1,1,0,8]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |XO|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angXO/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realXO); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagXO); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END XO's mag ang real imag
%% -------------------------------------------------------------- %% ----------------------------------------------------------------
%% START Graphical verification
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------
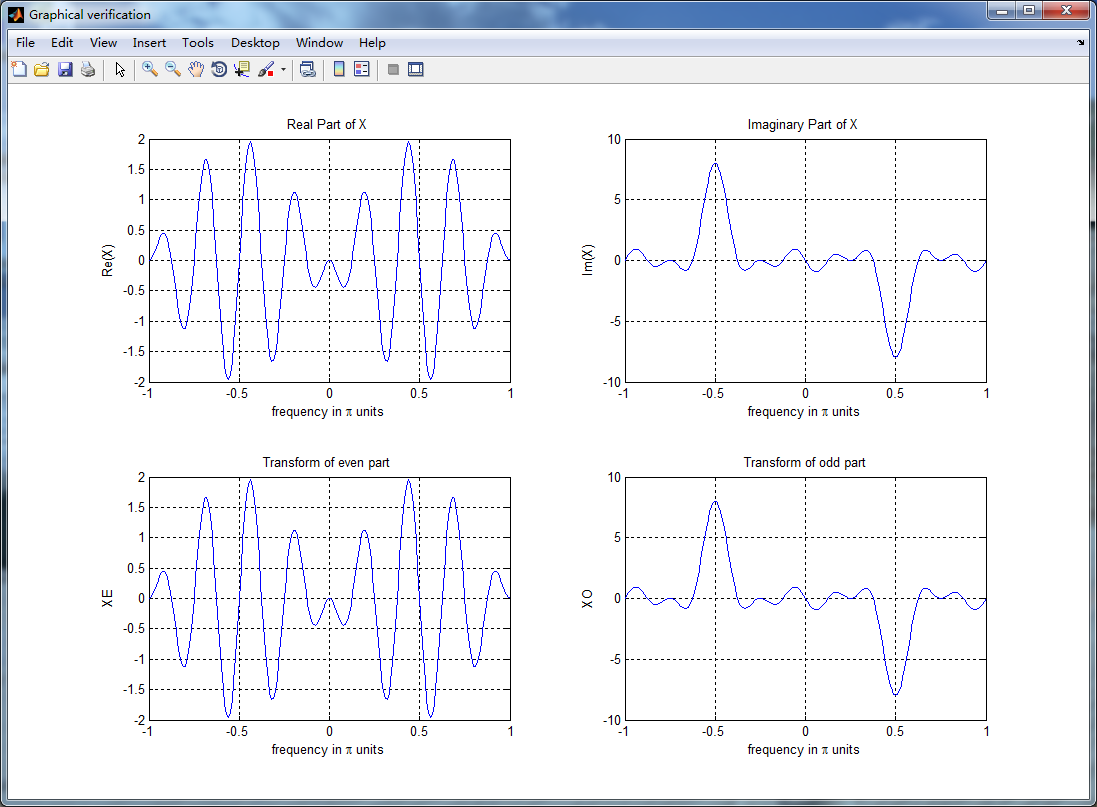
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Graphical verification');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,XR); grid on; axis([-1,1,-2,2]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Re(X)'); title('Real Part of X ');
subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi,XI); grid on; axis([-1,1,-10,10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Im(X)'); title('Imaginary Part of X '); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi,realXE); grid on; axis([-1,1,-2,2]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('XE'); title('Transform of even part ');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi,imagXO); grid on; axis([-1,1,-10,10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('XO'); title('Transform of odd part'); %% ----------------------------------------------------------------
%% END Graphical verification
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果:



DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.11
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi an ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.10
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)) + j * rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
随机推荐
- HTML 表单 选择器
表单元素 每个表单都对应一个<form></form>标签 表单内所有元素都写在 <form></form>里面: 1.最重要的属性 <fo ...
- EF没有同步更新(转)
不知道这算不算一个bug,当你新建一个从数据库生成的edmx时,他能正确的生成所有的tt文件,但是当你从数据库更新表结构时,他不能正确的更新tt文件,以建立Model1.edmx为例,在解决方案中展开 ...
- js生成验证码并验证
前台代码: <%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="Default.as ...
- objective-c可变字典
1 #pragma mark *****************************字典******************************** 2 // 字典:通过ke ...
- supersr--图片轮播逻辑
// // ViewController.m // 图片轮播 // // Created by apple on 14-5-18. // Copyright (c) 2014年 All rig ...
- nyoj1007(euler 函数)
euler(x)公式能计算小于等于x的并且和x互质的数的个数: 我们再看一下如何求小于等于n的和n互质的数的和, 我们用sum(n)表示: 若gcd(x, a)=1,则有gcd(x, x-a)=1: ...
- LoadRunner函数
一.基础函数简介 在VU左边导航栏中,有三个LoadRunner框架函数,分别是vuser_init().Action().vuser_end().这三个函数存在于任何Vuser类型的脚本中. vus ...
- JAVA基础学习之流的简述及演示案例、用缓冲区方法buffer读写文件、File类对象的使用、Serializable标记接口(6)
1.流的简述及演示案例输入流和输出流相对于内存设备而言.将外设中的数据读取到内存中:输入将内存的数写入到外设中:输出.字符流的由来:其实就是:字节流读取文字字节数据后,不直接操作而是先查指定的编码表. ...
- ListView优化中ViewHolder要不要定义为static静态内部类?
给学生讲课的时候,发现存在这个问题,下来百度了下,发现很纠结,涉及到了内部类对外部类的引用,静态类的生命周期等java知识,现总结如下: static class ViewHolder { //定义l ...
- 【翻译十七】java-并发之高性能对象
High Level Concurrency Objects So far, this lesson has focused on the low-level APIs that have been ...
