MachO文件详解--逆向开发
今天是逆向开发的第5天内容--MachO文件(Mac 和 iOS 平台可执行的文件),在逆向开发中是比较重要的,下面我们着重讲解一下MachO文件的基本内容和使用。
一、MachO概述
1. 概述
Mach-O是Mach Object文件格式的缩写,iOS以及Mac上可执行的文件格式,类似Window的exe格式,Linux上的elf格式。Mach-O是一个可执行文件、动态库以及目标代码的文件格式,是a.out格式的替代,提供了更高更强的扩展性。
2.常见格式
Mach-O常见格式如下:
- 目标文件 .o
- 库文件
- .a
- .dylib
- .framework
- 可执行文件
- dyld
- .dsym
通过file文件路径查看文件类型
我们通过部分实例代码来简单研究一下。
2.1目标文件.o
通过test.c 文件,可以使用clang命令将其编译成目标文件.o

我们再通过file命令(如下)查看文件类型
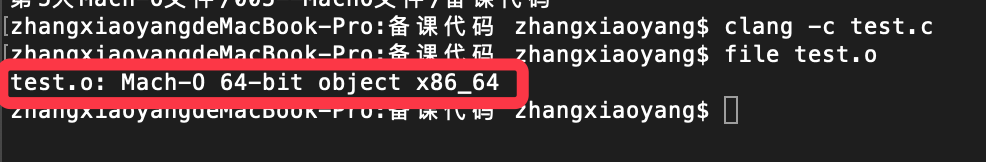
是个Mach-O文件。
2.2 dylib
通过cd /usr/lib命令查看dylib

通过file命令查看文件类型
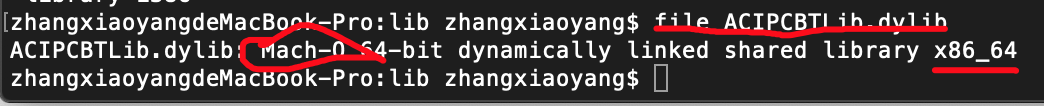
2.3 .dsym
下面是一个截图来说明.dsym是也是Mach-O文件格式

以上只是Mach-O常见格式的某一种,大家可以通过命令来尝试。
3. 通用二进制文件
希望大家在了解App二进制架构的时候,可以先读一下本人写的另一篇博客关于armv7,armv7s以及arm64等的介绍。https://www.cnblogs.com/guohai-stronger/p/9447364.html
通用二进制文件是苹果自身发明的,基本内容如下

下面通过指令查看Macho文件来看下通用二进制文件
然后通过file指令查看文件类型
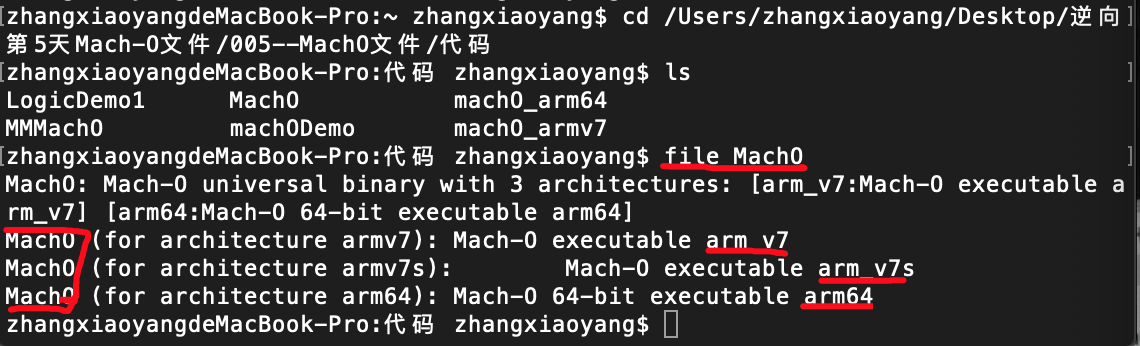
上面该MachO文件包含了3个架构分别是arm v7,arm v7s 以及arm 64 。
针对该MachO文件我们做几个操作,利用lipo命令拆分合并架构
3.1 利用lipo-info查看MachO文件架构

3.2 瘦身MachO文件,拆分
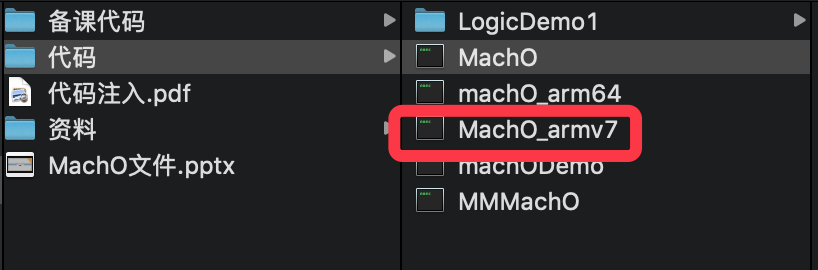
利用lipo-thin瘦身架构

查看一下结果如下,多出来一个新建的MachO_armv7
3.3 增加架构,合并
利用lipo -create 合并多种架构
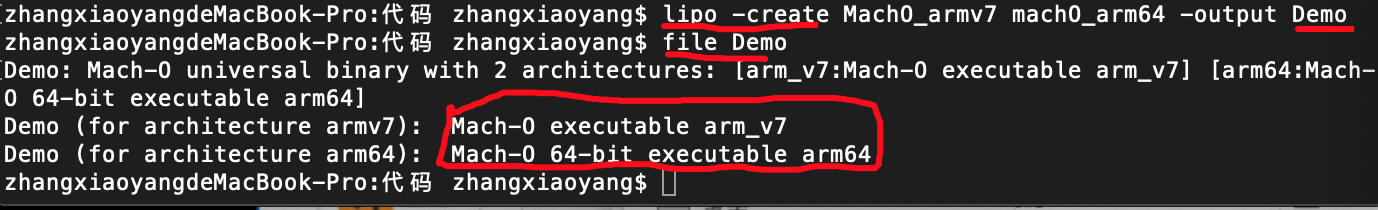
发现多出一种框架,合并成功多出Demo可执行文件。结果如下:

整理出lipo命令如下:

二、MachO文件
2.1 文件结构
下面是苹果官方图解释MachO文件结构图
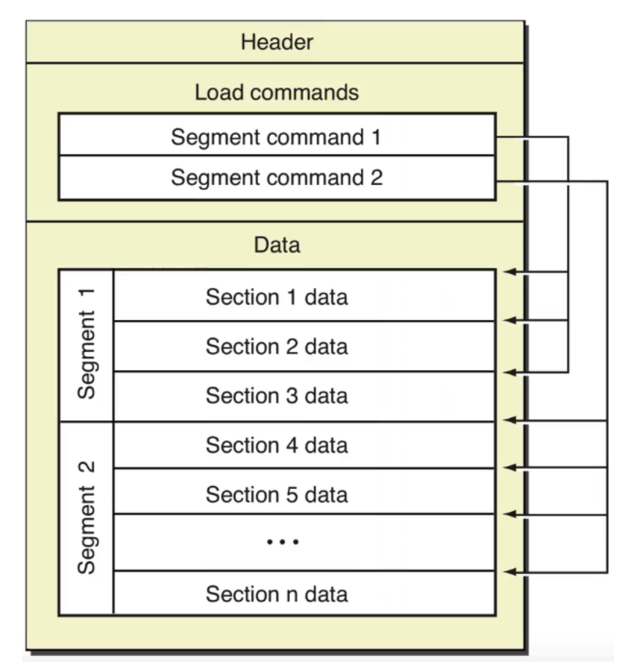
MachO文件的组成结构如上,看包括了三个部分
- Header包含了该二进制文件的一般信息,信息如下:
- 字节顺序、加载指令的数量以及架构类型
- 快速的确定一些信息,比如当前文件是32位或者64位,对应的文件类型和处理器是什么
- Load commands 包含很多内容的表
- 包括区域的位置、动态符号表以及符号表等
- Data一般是对象文件的最大部分
- 一般包含Segement具体数据
2.2 Header的数据结构
在项目代码中,按下Command+ 空格,然后输入loader.h
然后查看loader.h文件,找到mach_header
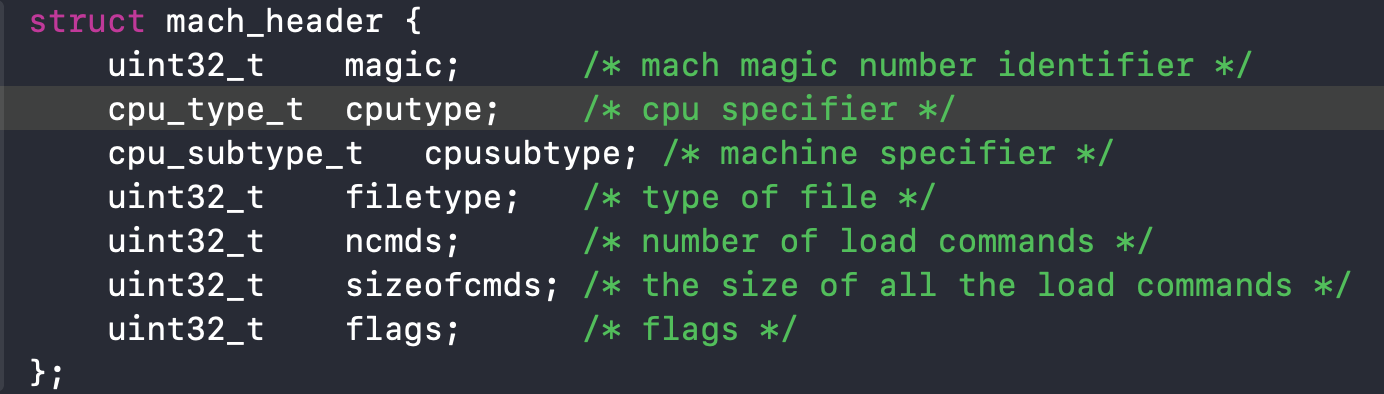
上面是mach_header,对应结构体的意义如下:

通过MachOView查看Mach64 Header头部信息
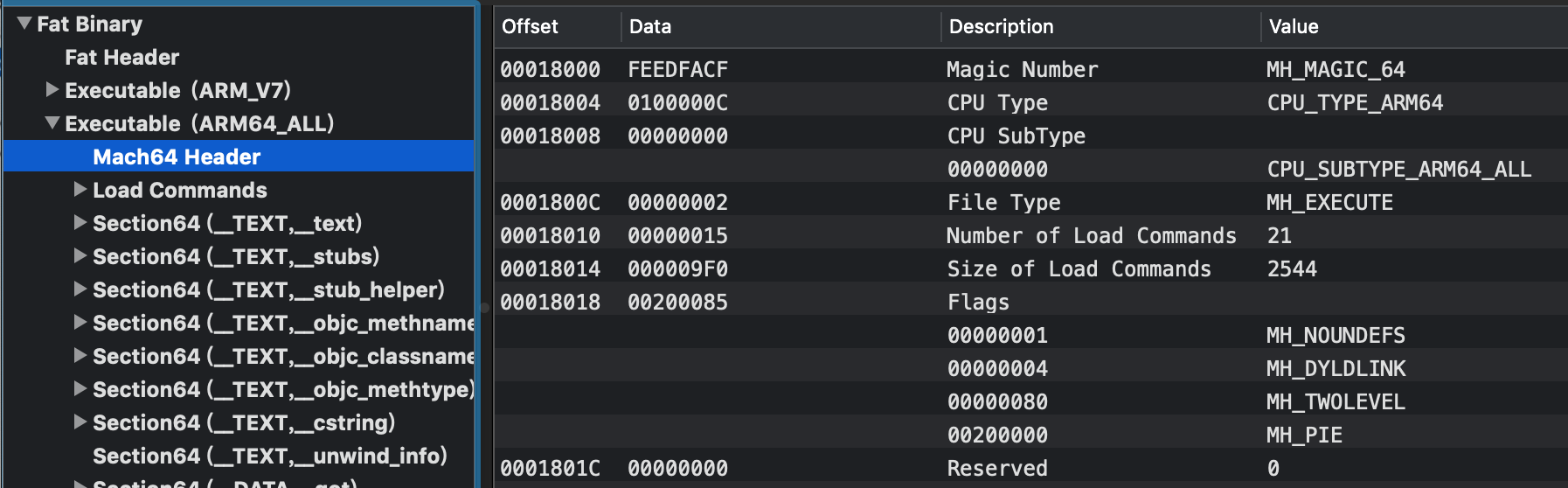
2.3 LoadCommands
LoadCommand包含了很多内容的表,通过MachOView查看LoadCommand的信息,图如下:
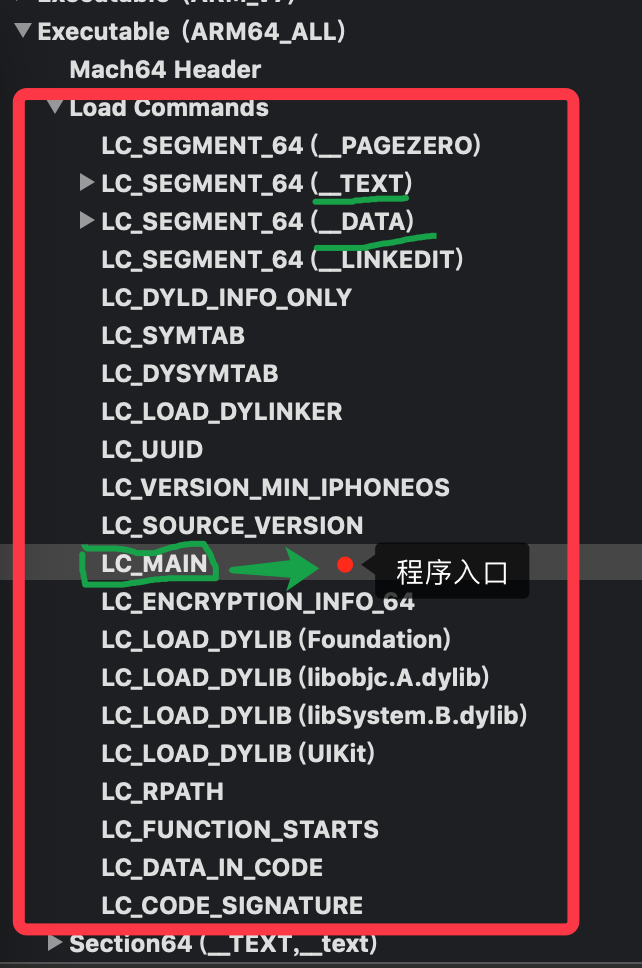
但是大家看的可能并不了解内容,下面有图进行注解,可以看下主要的意思

2.4 Data
Data包含Segement,存储具体数据,通过MachOView查看,地址映射内容
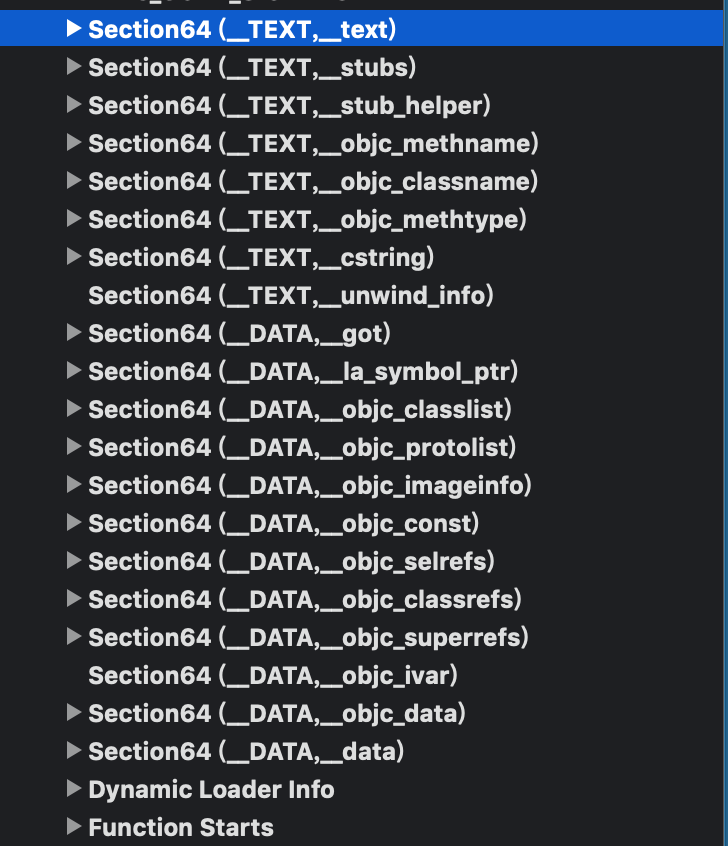
三、DYLD
3.1 dyld概述
dyld(the dynamic link editor)是苹果动态链接器,是苹果系统一个重要的组成部分,系统内核做好准备工作之后,剩下的就会交给了dyld。
3.2 dyld加载过程
程序的入口一般都是在main函数中,但是比较少的人关心main()函数之前发生了什么?这次我们先探索dyld的加载过程。(但是比在main函数之前,load方法就在main函数之前)
3.2.1 新建项目,在main函数下断

main()之前有个libdyld.dylib start入口,但是不是我们想要的,根据dyld源码找到__dyld_start函数
3.2.2 dyld main()函数
dyld main()函数是关键函数,下面是函数实现内容。(此时的main实现函数和程序App的main 函数是不一样的,因为dyld也是一个可执行文件,也是具有main函数的)
//
// Entry point for dyld. The kernel loads dyld and jumps to __dyld_start which
// sets up some registers and call this function.
//
// Returns address of main() in target program which __dyld_start jumps to
//
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
// Grab the cdHash of the main executable from the environment
// 第一步,设置运行环境
uint8_t mainExecutableCDHashBuffer[];
const uint8_t* mainExecutableCDHash = nullptr;
if ( hexToBytes(_simple_getenv(apple, "executable_cdhash"), , mainExecutableCDHashBuffer) )
// 获取主程序的hash
mainExecutableCDHash = mainExecutableCDHashBuffer; // Trace dyld's load
notifyKernelAboutImage((macho_header*)&__dso_handle, _simple_getenv(apple, "dyld_file"));
#if !TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// Trace the main executable's load
notifyKernelAboutImage(mainExecutableMH, _simple_getenv(apple, "executable_file"));
#endif uintptr_t result = ;
// 获取主程序的macho_header结构
sMainExecutableMachHeader = mainExecutableMH;
// 获取主程序的slide值
sMainExecutableSlide = mainExecutableSlide; CRSetCrashLogMessage("dyld: launch started");
// 设置上下文信息
setContext(mainExecutableMH, argc, argv, envp, apple); // Pickup the pointer to the exec path.
// 获取主程序路径
sExecPath = _simple_getenv(apple, "executable_path"); // <rdar://problem/13868260> Remove interim apple[0] transition code from dyld
if (!sExecPath) sExecPath = apple[]; if ( sExecPath[] != '/' ) {
// have relative path, use cwd to make absolute
char cwdbuff[MAXPATHLEN];
if ( getcwd(cwdbuff, MAXPATHLEN) != NULL ) {
// maybe use static buffer to avoid calling malloc so early...
char* s = new char[strlen(cwdbuff) + strlen(sExecPath) + ];
strcpy(s, cwdbuff);
strcat(s, "/");
strcat(s, sExecPath);
sExecPath = s;
}
} // Remember short name of process for later logging
// 获取进程名称
sExecShortName = ::strrchr(sExecPath, '/');
if ( sExecShortName != NULL )
++sExecShortName;
else
sExecShortName = sExecPath; // 配置进程受限模式
configureProcessRestrictions(mainExecutableMH); // 检测环境变量
checkEnvironmentVariables(envp);
defaultUninitializedFallbackPaths(envp); // 如果设置了DYLD_PRINT_OPTS则调用printOptions()打印参数
if ( sEnv.DYLD_PRINT_OPTS )
printOptions(argv);
// 如果设置了DYLD_PRINT_ENV则调用printEnvironmentVariables()打印环境变量
if ( sEnv.DYLD_PRINT_ENV )
printEnvironmentVariables(envp);
// 获取当前程序架构
getHostInfo(mainExecutableMH, mainExecutableSlide);
//-------------第一步结束------------- // load shared cache
// 第二步,加载共享缓存
// 检查共享缓存是否开启,iOS必须开启
checkSharedRegionDisable((mach_header*)mainExecutableMH);
if ( gLinkContext.sharedRegionMode != ImageLoader::kDontUseSharedRegion ) {
mapSharedCache();
}
... try {
// add dyld itself to UUID list
addDyldImageToUUIDList(); // instantiate ImageLoader for main executable
// 第三步 实例化主程序
sMainExecutable = instantiateFromLoadedImage(mainExecutableMH, mainExecutableSlide, sExecPath);
gLinkContext.mainExecutable = sMainExecutable;
gLinkContext.mainExecutableCodeSigned = hasCodeSignatureLoadCommand(mainExecutableMH); // Now that shared cache is loaded, setup an versioned dylib overrides
#if SUPPORT_VERSIONED_PATHS
checkVersionedPaths();
#endif // dyld_all_image_infos image list does not contain dyld
// add it as dyldPath field in dyld_all_image_infos
// for simulator, dyld_sim is in image list, need host dyld added
#if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// get path of host dyld from table of syscall vectors in host dyld
void* addressInDyld = gSyscallHelpers;
#else
// get path of dyld itself
void* addressInDyld = (void*)&__dso_handle;
#endif
char dyldPathBuffer[MAXPATHLEN+];
int len = proc_regionfilename(getpid(), (uint64_t)(long)addressInDyld, dyldPathBuffer, MAXPATHLEN);
if ( len > ) {
dyldPathBuffer[len] = '\0'; // proc_regionfilename() does not zero terminate returned string
if ( strcmp(dyldPathBuffer, gProcessInfo->dyldPath) != )
gProcessInfo->dyldPath = strdup(dyldPathBuffer);
} // load any inserted libraries
// 第四步 加载插入的动态库
if ( sEnv.DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES != NULL ) {
for (const char* const* lib = sEnv.DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES; *lib != NULL; ++lib)
loadInsertedDylib(*lib);
}
// record count of inserted libraries so that a flat search will look at
// inserted libraries, then main, then others.
// 记录插入的动态库数量
sInsertedDylibCount = sAllImages.size()-; // link main executable
// 第五步 链接主程序
gLinkContext.linkingMainExecutable = true;
#if SUPPORT_ACCELERATE_TABLES
if ( mainExcutableAlreadyRebased ) {
// previous link() on main executable has already adjusted its internal pointers for ASLR
// work around that by rebasing by inverse amount
sMainExecutable->rebase(gLinkContext, -mainExecutableSlide);
}
#endif
link(sMainExecutable, sEnv.DYLD_BIND_AT_LAUNCH, true, ImageLoader::RPathChain(NULL, NULL), -);
sMainExecutable->setNeverUnloadRecursive();
if ( sMainExecutable->forceFlat() ) {
gLinkContext.bindFlat = true;
gLinkContext.prebindUsage = ImageLoader::kUseNoPrebinding;
} // link any inserted libraries
// do this after linking main executable so that any dylibs pulled in by inserted
// dylibs (e.g. libSystem) will not be in front of dylibs the program uses
// 第六步 链接插入的动态库
if ( sInsertedDylibCount > ) {
for(unsigned int i=; i < sInsertedDylibCount; ++i) {
ImageLoader* image = sAllImages[i+];
link(image, sEnv.DYLD_BIND_AT_LAUNCH, true, ImageLoader::RPathChain(NULL, NULL), -);
image->setNeverUnloadRecursive();
}
// only INSERTED libraries can interpose
// register interposing info after all inserted libraries are bound so chaining works
for(unsigned int i=; i < sInsertedDylibCount; ++i) {
ImageLoader* image = sAllImages[i+];
image->registerInterposing();
}
} // <rdar://problem/19315404> dyld should support interposition even without DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES
for (long i=sInsertedDylibCount+; i < sAllImages.size(); ++i) {
ImageLoader* image = sAllImages[i];
if ( image->inSharedCache() )
continue;
image->registerInterposing();
}
... // apply interposing to initial set of images
for(int i=; i < sImageRoots.size(); ++i) {
sImageRoots[i]->applyInterposing(gLinkContext);
}
gLinkContext.linkingMainExecutable = false; // <rdar://problem/12186933> do weak binding only after all inserted images linked
// 第七步 执行弱符号绑定
sMainExecutable->weakBind(gLinkContext); // If cache has branch island dylibs, tell debugger about them
if ( (sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress != NULL) && (sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress->header.mappingOffset >= 0x78) && (sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress->header.branchPoolsOffset != ) ) {
uint32_t count = sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress->header.branchPoolsCount;
dyld_image_info info[count];
const uint64_t* poolAddress = (uint64_t*)((char*)sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress + sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress->header.branchPoolsOffset);
// <rdar://problem/20799203> empty branch pools can be in development cache
if ( ((mach_header*)poolAddress)->magic == sMainExecutableMachHeader->magic ) {
for (int poolIndex=; poolIndex < count; ++poolIndex) {
uint64_t poolAddr = poolAddress[poolIndex] + sSharedCacheLoadInfo.slide;
info[poolIndex].imageLoadAddress = (mach_header*)(long)poolAddr;
info[poolIndex].imageFilePath = "dyld_shared_cache_branch_islands";
info[poolIndex].imageFileModDate = ;
}
// add to all_images list
addImagesToAllImages(count, info);
// tell gdb about new branch island images
gProcessInfo->notification(dyld_image_adding, count, info);
}
} CRSetCrashLogMessage("dyld: launch, running initializers");
...
// run all initializers
// 第八步 执行初始化方法
initializeMainExecutable(); // notify any montoring proccesses that this process is about to enter main()
dyld3::kdebug_trace_dyld_signpost(DBG_DYLD_SIGNPOST_START_MAIN_DYLD2, , );
notifyMonitoringDyldMain(); // find entry point for main executable
// 第九步 查找入口点并返回
result = (uintptr_t)sMainExecutable->getThreadPC();
if ( result != ) {
// main executable uses LC_MAIN, needs to return to glue in libdyld.dylib
if ( (gLibSystemHelpers != NULL) && (gLibSystemHelpers->version >= ) )
*startGlue = (uintptr_t)gLibSystemHelpers->startGlueToCallExit;
else
halt("libdyld.dylib support not present for LC_MAIN");
}
else {
// main executable uses LC_UNIXTHREAD, dyld needs to let "start" in program set up for main()
result = (uintptr_t)sMainExecutable->getMain();
*startGlue = ;
}
}
catch(const char* message) {
syncAllImages();
halt(message);
}
catch(...) {
dyld::log("dyld: launch failed\n");
}
... return result;
}
折叠开dyld main函数,步骤总结如下

对待dyld的讲述,是非常不易的,因为本身过程是比较复杂的,上面仅仅是自身的抽出来的。下面再画一张流程图,帮助大家理解。

四、总结
MachO文件对于逆向开发是非常重要的,通过本次讲解,希望对大家理解逆向开发有所帮助,也希望大家真正可以提高技术,应对iOS市场的大环境,下一篇我们将讲述Hook原理--逆向开发。谢谢!!!
MachO文件详解--逆向开发的更多相关文章
- LLDB调试详解--逆向开发
前言 今天讲述在苹果日常开发中一个装逼神器LLDB,是Xcode内置的动态调试工具. 在iOS系统程序开发中,会经常需要代码调试的追踪, 最常用的也是LLDB(low level debugger) ...
- [转]AndroidManifest.xml文件详解
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/greatverve/archive/2012/05/08/AndroidManifest-xml.html AndroidManifest.xml ...
- 详解LUA开发工具及其环境配置
LUA开发工具及其环境配置是本文要介绍的内容,主要是来了解并学习lua开发工具的使用和环境的配置,第一次接触LUA的话,就跟本人一起学习吧.看我能不能忽悠到你. LUA是语言,那么一定有编写的工具.第 ...
- Maven pom.xml文件详解
Maven pom.xml文件详解 一.简介 POM全称是Project Object Model,即项目对象模型. pom.xml是maven的项目描述文件,它类似与antx的project.xml ...
- javaweb web.xml文件详解
web.xml文件详解 前言:一般的web工程中都会用到web.xml,web.xml主要用来配置,可以方便的开发web工程.web.xml主要用来配置Filter.Listener.Servlet等 ...
- /etc/fstab文件详解【转】
******************************************************************************* 有很多人经常修改/etc/fstab文件 ...
- Angular Npm Package.Json文件详解
Angular7 Npm Package.Json文件详解 近期时间比较充裕,正好想了解下Angular Project相关内容.于是将Npm官网上关于Package.json的官方说明文档进行了 ...
- 史上最全的maven的pom.xml文件详解(转载)
此文出处:史上最全的maven的pom.xml文件详解——阿豪聊干货 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" x ...
- vue-cli生成的模板各个文件详解(转)
vue-cli脚手架中webpack配置基础文件详解 一.前言 原文:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000014804826 vue-cli是构建vue单页应用的脚手架 ...
随机推荐
- C# 关于config文件中的usersettings
在调整app.config的时候遇到了一点问题,把这个问题记录下来,可能我只是没有找到解决方案,问题本身也许并不复杂. 在VS中通过Properties中的Settings.settings来设置作用 ...
- CSAPP: 位操作实现基本运算
目录 实验要求 实现代码 1.pow2plus1 2.pow2plus4 3.bitXor 4.tmin 5.isTmax 6.allOddBits 7.negate 8.isAsciiDigit 9 ...
- vue-cli3 搭建 vue 项目
vue-cli3 搭建 vue 项目 项目是在mac的环境下配置的 win的同学请移步[https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaomeizi/p/8483597.html] 安装 nod ...
- vue实现rsa加密,数字签名,md5加密等
一.使用jsencrypt进行rsa加密 原文链接:Js参数RSA加密传输,jsencrypt.js的使用 - CSDN博客 *(原文处有一个地方不对,不需要转换+,rsa已经做过base64转码了) ...
- BrickerBot
BrickerBot 概况 <大华(Dahua)安防监控设备弱口令问题报告 >主要提到是Telnet弱口令 root/vizxv 相关链接:(发布时间:2015年4月1日) 通过Telne ...
- 详解k8s中的liveness和readiness的原理和区别
liveness与readiness的探针工作方式源码解析 liveness和readiness作为k8s的探针,可以对应用进行健康探测. 二者支持的探测方式相同.主要的探测方式支持http探测,执行 ...
- Element-ui-安装
1.node环境安装 1.1.根据自己电脑位数,下载最新版node.js并安装https://nodejs.org/en/ 1.2.下载git并安装https://gitforwindows.org/ ...
- 基本的sql 语句
1,登陆数据库:mysql -u root -p2,退出数据库:exit quit ctr+d3,创建数据库:create database 数据库名 charset=utf84,使用数据库:use ...
- android studio ndk 环境配置成eclipse模式
gradle.properties: android.useDeprecatedNdk=true build.gradle: android { ... sourceSets.main { jni.s ...
- Nginx 的请求处理流程,你了解吗?
之前我们已经讲解了 Nginx 的基础内容,接下来我们开始介绍 Nginx 的架构基础. 为什么我们要讨论 Nginx 的架构基础? 因为 Nginx 运行在企业内网的最外层也就是边缘节点,那么他处理 ...
