制作mysql大数据表验证覆盖索引
昨天跟同事聊起数据表性能的问题,能不能仅用覆盖索引实现数据的汇总统计。找了一个开发环境已有的数据表进行测试,通过explain命令,能看到mysql通过覆盖索引就能实现sum的需求,而无须去读取实际行数据。
但开发环境数据量太小,对执行时间的优化,没有直观感受,于是决定做一个数据量能到千万级的数据表,方便测试。写个java程序来填充随机数据是第一选择,但还要动用IDE太麻烦,尝试直接使用mysql的函数来实现。
1 数据表设计
目的是演示如何生成千万级数据,只设计了一个最简单常用的数据表:user。
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`user_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`account` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(128) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL,
`mobile` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin;
2 编写函数/过程
mysql的rand()函数,返回的是一个随机浮点数。为了实现随机插入数据,将基于这个函数实现。
2.1 获取随机整数
CREATE FUNCTION `getRandomInt`(`maxValue` int) RETURNS int(11)
BEGIN
DECLARE randomInt int default 0;
SET randomInt = FLOOR(rand() * `maxValue`);
RETURN randomInt;
END
2.2 获取随机字符串
CREATE FUNCTION `getRandomString`(`length` int) RETURNS varchar(128) CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin
BEGIN
DECLARE result VARCHAR(128) default '';
DECLARE chars varchar(30) default 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'; #全小写字母
DECLARE charIndex int default 0;
WHILE length > 0 DO
SET charIndex = getRandomInt(26);
SET result = concat(result, SUBSTRING(chars, charIndex + 1, 1));
SET length = length - 1;
END WHILE;
RETURN result;
END
2.3 获取随机手机号
11位手机号,必须1开始,后续10位只要是数字就行,有点不符合现在的手机号规则。
CREATE FUNCTION `getRandomMobile`() RETURNS varchar(128) CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin
BEGIN
DECLARE result VARCHAR(128) default '';
DECLARE chars varchar(30) default '';
DECLARE charIndex int default 0;
DECLARE length int DEFAULT 10;
WHILE length > 0 DO
SET charIndex = getRandomInt(9);
SET result = concat(result, SUBSTRING(chars, charIndex + 1, 1));
SET length = length - 1;
END WHILE;
RETURN result;
END
2.4 获取随机汉字
中文汉字的unicode,是从0X4E00(19968)开始的,写个函数随机从前2000个汉字中读出一个。这儿要注意的是char的方法,想生成汉字要使用 using utf16。实测生成的数据存入到 utf8 编码的数据表字段中,能正确显示。
CREATE FUNCTION `getRandomChineseChar`() RETURNS varchar(2) CHARSET utf8
BEGIN
DECLARE charValue int DEFAULT 19968;
SET charValue = charValue + getRandomInt(2000);
RETURN char(charValue using utf16);
END
2.5 获取随机姓名
姓名还不能完全使用随机汉字,“姓”我决定从百家姓里取前两百个。贴出来的代码中字符串不完整,感兴趣的自己上网查下来补一下就行。
CREATE FUNCTION `getRandomChineseName`() RETURNS varchar(20) CHARSET utf8
BEGIN
DECLARE LAST_NAMES VARCHAR(300) DEFAULT '赵钱孙李周吴郑王...';
DECLARE chineseName varchar(20) default '';
SET chineseName = SUBSTRING(LAST_NAMES, getRandomInt(200) + 1, 1);
SET chineseName = concat(chineseName, getRandomChineseChar());
SET chineseName = concat(chineseName, getRandomChineseChar());
RETURN chineseName;
END
2.6 插入随机用户数据
在这个过程中实现真正插入用户数据。
CREATE PROCEDURE `createRandomUser`(IN `count` int)
BEGIN
DECLARE userCount DECIMAL(10) default 0; DECLARE account VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT '';
DECLARE thePassword VARCHAR(128) DEFAULT '';
DECLARE theName VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT '';
DECLARE email VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT '';
DECLARE mobile VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT '';
DECLARE age int DEFAULT 0; WHILE userCount < `count` DO
SET account = getRandomString(10);
SET thePassword = getRandomString(20);
SET theName = getRandomChineseName();
SET email = concat(account, '@codestory.tech');
SET mobile = getRandomMobile();
SET age = 10 + getRandomInt(50); #年龄10-60岁 insert into user values(null, account, thePassword, theName, email, mobile, age);
SET userCount = userCount + 1;
END WHILE;
END
3 生成数据
执行过程,就可以生成相应的数据。如下代码生成100行
[SQL] call createRandomUser(100);
受影响的行: 100
时间: 1.004s
我电脑上这个表的数据行数
mysql> select count(*) from user\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(*): 10001102
1 row in set (5.70 sec)
如下是我生成的部分数据
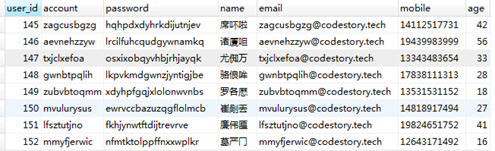
4 索引对查询性能的影响
设计一个简单的查询:所有赵姓用户且手机号139开头,平均年龄是多少?
测试SQL,以及查看执行情况
select count(user_id), avg(age) from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
explain select count(user_id), avg(age) from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
4.1 只有主键的情况
我们前面创建数据表时,只设置了主键,没有创建任何索引。这时候执行情况
mysql> select count(user_id), avg(age) from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(user_id): 682
avg(age): 34.4296
1 row in set (7.03 sec)
执行耗时7.03秒
mysql> explain select count(user_id), avg(age) from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: user
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 9928072
Extra: Using where
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
可以看到,查询使用的是全表查询,读了所有的数据行。
4.2 单字段索引-name
首先在name字段创建一个单字段索引
mysql>ALTER TABLE `user` ADD INDEX `idx_user_name` (`name`) USING BTREE ;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 34.35 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
执行SQL
mysql> select count(user_id), avg(age) from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(user_id): 682
avg(age): 34.4296
1 row in set (3.52 sec)
耗时3.52秒
mysql> explain select count(user_id), avg(age) from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: user
type: range
possible_keys: idx_user_name
key: idx_user_name
key_len: 98
ref: NULL
rows: 100634
Extra: Using index condition; Using where
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
使用索引进行检索,读取的数据减少到 10万行。
4.3 单字段索引-mobile
为了测试方便,先删除name字段的索引,再创建一个mobile字段索引
mysql> ALTER TABLE `user` DROP INDEX `idx_user_name`;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql>ALTER TABLE `user` ADD INDEX `idx_user_mobile` (`mobile`) USING BTREE ;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 27.50 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
执行SQL
mysql> select count(user_id), avg(age) from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(user_id): 682
avg(age): 34.4296
1 row in set (9.93 sec)
耗时9.93秒
mysql> explain select count(user_id), avg(age) from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: user
type: range
possible_keys: idx_user_mobile
key: idx_user_mobile
key_len: 63
ref: NULL
rows: 233936
Extra: Using index condition; Using where
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
尽管我们的SQL语句将mobile字段作为第二个查询条件,mysql仍然使用了mobile上的索引进行检索。mobile索引过滤出来的数据有23万行,比基于name的更多,所以耗时也就更长。
4.4 双字段索引-name & mobile
这次我们将两个字段建成一个联合索引。
mysql> ALTER TABLE `user` DROP INDEX `idx_user_mobile`;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> ALTER TABLE `user` ADD INDEX `idx_user_name_mobile` (`name`, `mobile`) USING BTREE ;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 54.81 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
执行SQL
mysql> select avg(age) as age_avg from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
age_avg: 34.4296
1 row in set (0.06 sec)
执行时间大大缩短,只需要0.06秒
mysql> explain select avg(age) as age_avg from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: user
type: range
possible_keys: idx_user_name_mobile
key: idx_user_name_mobile
key_len: 161
ref: NULL
rows: 100764
Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
读取的行数还是10万行,但时间大大缩短。从这个时间,我们应该能够猜出mysql的过滤数据的过程。mysql执行where过滤时仅仅通过索引即可完成,然后根据索引中的user_id去数据页面读取相应的age值出来做平均。
4.5 终极版-覆盖索引
前面的分析可以看到,为了计算平均值,mysql还需要读取行数据。如果age字段也在这个索引中,查询性能会进一步提升吗?因为不再读行数据。
调整索引
mysql> ALTER TABLE `user` DROP INDEX `idx_user_name_mobile`;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> ALTER TABLE `user` ADD INDEX `idx_user_name_mobile_age` (`name`, `mobile`, `age`) USING BTREE ;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 55.32 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
执行SQL
mysql> select avg(age) as age_avg from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
age_avg: 34.4296
1 row in set (0.04 sec)
执行时间更短,仅为0.04秒。数据量可能还不够大,同上一个执行的区别不是太大。
mysql> explain select avg(age) as age_avg from user where name like '赵%' and mobile like '139%'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: user
type: range
possible_keys: idx_user_name_mobile_age
key: idx_user_name_mobile_age
key_len: 161
ref: NULL
rows: 103688
Extra: Using where; Using index
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
最重要的变化是Extra信息:Using index condition 变成 Using index。Using index condition 表示使用了索引作为查询过滤的条件;Using index表示整个SQL只使用了索引。
制作mysql大数据表验证覆盖索引的更多相关文章
- Mysql大数据表优化处理
原文链接: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000006158186 当MySQL单表记录数过大时,增删改查性能都会急剧下降,可以参考以下步骤来优化: 单表优化 除非单表 ...
- mysql大数据表优化
1.应尽量避免在 where 子句中使用!=或<>操作符,否则将引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描. 2.对查询进行优化,应尽量避免全表扫描,首先应考虑在 where 及 order by 涉 ...
- mysql大数据表删除操作锁表,导致其他线程等待锁超时(Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction;)
背景: 1.有一个定时任务,每10分钟入一批统计数据: 2.另一个定时任务,每天定时清理7天前数据,此定时任务每天01:18:00执行: 现象: 每天01:20:00的统计数据入库失败,异常信息如下, ...
- mysql大数据表改表结构方案
有一个表有上千W数据, 用什么方法给这个表加一个字段最快?1. alert2. 建一个表和第一个表一样,只是多了要加的字段,然后用多个INSERT INTO SELECT语句limit写入3. 就是导 ...
- MySQL大数据表水平分区优化的详细步骤
将运行中的大表修改为分区表 本文章代码仅限于以数据时间按月水平分区,其他需求可自行修改代码实现 1. 创建一张分区表 这张表的表字段和原表的字段一摸一样,附带分区 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ...
- MySql数据表设计,索引优化,SQL优化,其他数据库
MySql数据表设计,索引优化,SQL优化,其他数据库 1.数据表设计 1.1数据类型 1.2避免空值 1.3text类型优化 2.索引优化 2.1索引分类 2.2索引优化 3.SQL优化 3.1分批 ...
- MySQL大数据分页的优化思路和索引延迟关联
之前上次在部门的分享会上,听了关于MySQL大数据的分页,即怎样使用limit offset,N来进行大数据的分页,现在做一个记录: 首先我们知道,limit offset,N的时候,MySQL的查询 ...
- MySQL中大数据表增加字段,增加索引实现
MySQL中大数据表增加字段,通过增加索引实现 普通的添加字段sql ALTER TABLE `table_name` ADD COLUMN `num` int(10) NOT NULL DEFAUL ...
- mysql 大数据分页优化
一.mysql大数据量使用limit分页,随着页码的增大,查询效率越低下. 1. 直接用limit start, count分页语句, 也是我程序中用的方法: select * from prod ...
随机推荐
- 关于 .Net Core runtimeconfig 文件说明
在项目的bin\debug\netcoreapp${Version}下面能够找到这个${AppName}.runtimeconfig.json文件,简单来说,它就是用来定义用用程序所用的共享框架(.N ...
- SpringBoot电商项目实战 — Redis实现分布式锁
最近有小伙伴发消息说,在Springboot系列文第二篇,zookeeper是不是漏掉了?关于这个问题,其实我在写第二篇的时候已经考虑过,但基于本次系列文章是实战练习,在项目里你能看到Zookeepe ...
- 《NVM-Express-1_4-2019.06.10-Ratified》学习笔记(8)
8 Feature(特性) 8.1 固件升级过程 固件升级通过重启激活的过程是: 1. 主机发一个Firmware Image Download命令,下载固件映像版本到controller.可能有多个 ...
- keras+ ctpn 原理流程图
- springBoot项目配置日志打印管理(log4j2)
1.修改pom文件引用log4j2相关jar包 依赖代码: <!-- log4j2 start --><!-- Spring Boot log4j2依赖 --><depe ...
- 关于GIS中Scale和Resolution的那些事儿
在ArcMap或各类前端地图框架(Leaflet.js.OpenLayers.js.ArcGIS Javascript等)中都需要加载WMTS或ArcGIS Rest服务,但所有的地图显示的原理基本上 ...
- 关于Springboot+thymeleaf +MybatisPlus 报错Error resolving template [index], template might not exist的问题解决
这个问题困扰了我整整一上午,各种方式,什么返回路径 ,静态资源啊 什么的,能想到的都去搞了,可是问题还是解决不了!!!我查看了一下编译文件的[target]文件夹!发现了问题所在!根本就没有编译进去! ...
- 关于Socket、TCP/IP、HTTP、FTP及网络编程
来源:陶邦仁 链接:http://blog.jobbole.com/99694/ 既然是网络传输,涉及几个系统之间的交互,那么首先要考虑的是如何准确的定位到网络上的一台或几台主机,再者如何进行可靠高效 ...
- 你真的了解MyBatis中${}和#{}的区别吗?
动态sql是mybatis的主要特性之一.在mapper中定义的参数传到xml中之后,在查询之前mybatis会对其进行动态解析. mybatis提供了两种支持动态sql的语法:#{} 和 ${}. ...
- 安装python的第三方库pillow
参考:http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/ff42efa929e6c8c19f220254.html 用Python做图像处理时,需要用到PIL(图像处理库).但是PIL ...
