c# 窗体开发3 文件处理技术
以字节形式向磁盘写入数据通常称为字节流(比特流)
常常使用System.Io
常用的类
|
类
|
说明
|
|
File
|
提供用于创建、复制、删除、移动和打开文件的静态方法,并协助创建 FileStream 对象。
|
|
FileInfo
|
提供创建、复制、删除、移动和打开文件的实例方法,并且帮助创建 FileStream 对象。无法继承此类。
|
|
FileStream
|
公开以文件为主的 Stream,既支持同步读写操作,也支持异步读写操作。
|
|
BinaryReader
|
用特定的编码将基元数据类型读作二进制值。
|
|
BinaryWriter
|
以二进制形式将基元类型写入流,并支持用特定的编码写入字符串。
|
|
BufferedStream
|
给另一流上的读写操作添加一个缓冲层。无法继承此类。
|
|
Directory
|
公开用于创建、移动和枚举通过目录和子目录的静态方法。无法继承此类。
|
|
DirectoryInfo
|
公开用于创建、移动和枚举目录和子目录的实例方法。无法继承此类。
|
|
Path
|
对包含文件或目录路径信息的 String 实例执行操作。这些操作是以跨平台的方式执行的。
|
|
StreamReader
|
实现一个 TextReader,使其以一种特定的编码从字节流中读取字符。
|
|
StreamWriter
|
实现一个 TextWriter,使其以一种特定的编码向流中写入字符。
|
|
FileSysWatcher
|
侦听文件系统更改通知,并在目录或目录中的文件发生更改时引发事件。
|
基本使用类的介绍
1.1File
常用方法
类File提供用于创建、复制、删除、移动和打开文件的静态方法
|
方法
|
说明
|
|
Move
|
将指定文件移到新位置,并提供指定新文件名的选项。
|
|
Delete
|
删除指定的文件。如果指定的文件不存在,则不引发异常。
|
|
Copy
|
已重载。 将现有文件复制到新文件。
|
|
CreateText
|
创建或打开一个文件用于写入 UTF-8 编码的文本。
|
|
OpenText
|
打开现有 UTF-8 编码文本文件以进行读取。
|
|
Open
|
已重载。 打开指定路径上的 FileStream。
|
eg
using System;
using System.IO;
class Test
{
public static void Main()
{
string path = @"c:\temp\123.txt";
if (!File.Exists(path))
{
// 创建文件以便写入内容。
using (StreamWriter sw = File.CreateText(path))
{
sw.WriteLine("Hello");
sw.WriteLine("And");
sw.WriteLine("Welcome");
}
}
// 打开文件从里面读数据。
using (StreamReader sr = File.OpenText(path))
{
string s = "";
while ((s = sr.ReadLine()) != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
}
try
{
string path2 = path + "temp";
// 确认将要拷贝成的文件是否已经有同名的文件存在。
File.Delete(path2);
// 拷贝文件。
File.Copy(path, path2);
Console.WriteLine("{0} was copied to {1}.", path, path2);
// 删除新生成的文件。
File.Delete(path2);
Console.WriteLine("{0} was successfully deleted.", path2);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("The process failed: {0}", e.ToString());
}
}
}
File 使用
1.2FileInfo
类FileInfo提供创建、复制、删除、移动和打开文件的实例方法,并且帮助创建 FileStream 对象。无法继承此类
|
属性
|
说明
|
|
Attributes
|
获取或设置当前 FileSystemInfo 的 FileAttributes。(从 FileSystemInfo 继承。)
|
|
CreationTime
|
获取或设置当前 FileSystemInfo 对象的创建时间。(从 FileSystemInfo 继承。)
|
|
Directory
|
获取父目录的实例。
|
|
DirectoryName
|
获取表示目录的完整路径的字符串。
|
|
Exists
|
已重写。获取指示文件是否存在的值。
|
|
Extension
|
获取表示文件扩展名部分的字符串。(从 FileSystemInfo 继承。)
|
获取目录名
using System;
using System.IO;
class Test
{
public static void Main()
{
string fileName = "C:\\autoexec.bat";
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(fileName);
if (!fileInfo.Exists)
{
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0} has a directoryName of {1}",fileName,fileInfo.DirectoryName);
/* 下面是代码的处理结果,
* 实际的结果因机器不同:
*
* C:\autoexec.bat has a directoryName of C:\
*/
}
}
代码
同磁盘下文件复制问题:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 复制文本文件
/// </summary>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string somefile = @"C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\SQL Server2000安装故障.txt";
string target = @"c:\2.txt";
if (!File.Exists(somefile))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件不存在!");
}
else
{
if (File.Exists(target))
{
File.Delete(target);
}
File.Copy(somefile, target);
MessageBox.Show("文件复制成功!");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 创建文本文件
/// </summary>
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string target = @"c:\2.txt";
if (File.Exists(target))
{
File.Delete(target);
}
File.CreateText(target);
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除文本文件
/// </summary>
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string target = @"c:\2.txt";
if (File.Exists(target))
{
File.Delete(target);
MessageBox.Show("文件删除成功!");
}
}
}
} ------------------通过FileInfo类执行同样的复制 private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string path = @"C:\WINDOWS\IE4 Error Log.txt";
string target = @"c:\1.txt";
FileInfo myfile = new FileInfo(path);
if (!myfile.Exists)
{
MessageBox.Show("对不起,未发现路径文件!");
}
else
{
myfile.CopyTo(target);
MessageBox.Show("复制成功!");
}
}
code
获取文件的基本信息
向一个Form窗体上拖拽三个Lable控件和一个Button控件,Button控件的text属性设置为“获取文件信息”
代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取文件信息单击事件
/// </summary>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string somefile = @"C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\SQL Server2000安装故障.txt";
FileInfo myfile = new FileInfo(somefile);
if (myfile.Exists)
{
MessageBox.Show("文件已经存在");
label1.Text = "文件创建时间:" + myfile.CreationTime.ToString();
label2.Text = "文件夹:" + myfile.Directory.ToString();
label3.Text = "文件夹名称:" + myfile.DirectoryName.ToString() + ",文件扩展名:" + myfile.Extension.ToString();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("文件并不存在");
}
}
}
}
代码
1.3 Directory公开用于创建、移动和枚举通过目录和子目录的静态方法
常用的方法
|
方法
|
说明
|
|
Move
|
将文件或目录及其内容移到新位置。
|
|
Delete
|
已重载。 删除指定的目录。
|
|
CreateDirectory
|
已重载。 创建指定路径中的所有目录
|
|
GetCreationTime
|
获取目录的创建日期和时间。
|
|
GetCurrentDirectory
|
获取应用程序的当前工作目录。
|
|
GetFiles
|
已重载。 返回指定目录中的文件的名称
|
目录创建了多少天
using System;
using System.IO; class Test
{
public static void Main()
{
try
{
// 获取当前目录的创建时间.
DateTime dt = Directory.GetCreationTime(Environment.CurrentDirectory);
// 给用户反馈信息.
if (DateTime.Now.Subtract(dt).TotalDays > )
{
Console.WriteLine("This directory is over a year old.");
}
else if (DateTime.Now.Subtract(dt).TotalDays > )
{
Console.WriteLine("This directory is over a month old.");
}
else if (DateTime.Now.Subtract(dt).TotalDays <= )
{
Console.WriteLine("This directory is less than a day old.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("This directory was created on {0}", dt);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("The process failed: {0}", e.ToString());
}
}
}
c_code
目录的相关操作
向一个Form窗体上拖拽五个Button控件,Button控件的text属性设置为“创建目录”、“删除目录”、“移动目录”、“目录创建时间”、“返回指定目录文件”
在类Form3里添加二个静态字段directory_path、directory_otherpath,都为string类型,分别代表工作目录路径和其他目录路径;双击“创建目录”、“删除目录”、“移动目录”、“目录创建时间”、“返回指定目录文件”
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form3 : Form
{
public Form3()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private static string directory_path = "c:\\qs250";
private static string directory_otherpath = "c:\\qqqq";
/// <summary>
/// 删除目录鼠标单击事件
/// </summary>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(directory_path);
button2.Enabled = true;
button1.Enabled = false;
button3.Enabled = true;
button4.Enabled = true;
button5.Enabled = true;
MessageBox.Show("文件夹成功建立。", "警报");
}
catch (Exception mm)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert.ToString(mm), "警报");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除目录鼠标单击事件
/// </summary>
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
Directory.Delete(directory_path);
button2.Enabled = false;
button1.Enabled = true;
button3.Enabled = false;
button4.Enabled = false;
button5.Enabled = false;
MessageBox.Show("文件夹删除建立。", "警报");
}
catch (Exception mm)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert.ToString(mm), "警报");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 移动目录鼠标单击事件
/// </summary>
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
Directory.Move(directory_path, directory_otherpath);
MessageBox.Show("文件夹移动成功。", "警报");
//举例来讲,如果您尝试将c:\mydir 移到c:\public,并且c:\public 已存在,
//则此方法引发IOException。您必须将“c:\\public\\mydir”指定为destDirName 参数,或者指定新目录名,例如“c:\\newdir”。
}
catch (Exception mm)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert.ToString(mm), "警报");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 目录创建时间鼠标单击事件
/// </summary>
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
MessageBox.Show(string.Format("{0:G}",Directory.GetCreationTime(directory_path)), "提示");
//获取时间格式参见DateTimeFormatInfo
}
catch (Exception mm)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert.ToString(mm), "警报");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回指定目录文件鼠标单击事件
/// </summary>
private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
string[] fileEntries = Directory.GetFiles(directory_path);
if (fileEntries.Length != )
{
foreach (string s in fileEntries)
{
if (File.Exists(s))
{
MessageBox.Show("内有文件信息:" + s, "提示");
}
}
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("空文件夹", "提示");
}
//获取时间格式参见DateTimeFormatInfo
}
catch (Exception mm)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert.ToString(mm), "警报");
}
}
}
}
文件夹的相关操作
1.4 file类读取文本文件的方法
|
方法
|
说明
|
|
CreateText(string FilePath)
|
创建或打开一个文件用于写入 UTF-8 编码的文本。
|
|
OpenText(string FilePath)
|
打开现有 UTF-8 编码文本文件以进行读取。
|
|
Open(string FilePath, FileMode)
|
打开指定路径上的 FileStream,具有读/写访问权限。
|
|
Create(string FilePath)
|
在指定路径中创建文件。
|
|
OpenRead(string FilePath)
|
打开现有文件以进行读取。
|
|
AppendText(string FilePath)
|
创建一个 StreamWriter,它将 UTF-8 编码文本追加到现有文件。
|
案例写一个记事本
向一个Form窗体上拖拽两个GroupBox控件,text属性分别设置为“写入文本”、“命名文本文件:”;向两个GroupBox控件里拖拽一个RichTextBox控件和一个TextBox控件;向第一个GroupBox控件里拖拽二个Button控件,属性分别设置为“保存编辑文件”、“打开文本文件”;向第二个GroupBox控件里拖拽一个Button控件,text属性设置为“创建文本文件”

在案例中添加一个静态字段directory_path,string类型,代表工作目录路径;双击“保存编辑文件”、“打开文本文件”、“创建文本文件”,在click事件处理方法里分别添加代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form4 : Form
{
public Form4()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private static string directory_path = "c:\\";
/// <summary>
/// 创建文本文件
/// </summary>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (textBox1.Text.Length == )
{
MessageBox.Show("文件名禁止为空!", "警报");
}
else
{
directory_path = directory_path + textBox1.Text.Trim() + ".txt";
//File.CreateText(..)返回的是一个StreamWriter
StreamWriter sw = File.CreateText(directory_path);
button2.Enabled = true;
button3.Enabled = true;
button1.Enabled = false;
richTextBox1.Enabled = true;
MessageBox.Show("文件文件成功建立。", "消息");
sw.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception mm)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert.ToString(mm), "警报");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 打开文本文件
/// </summary>
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
OpenFileDialog open = new OpenFileDialog();//创建一个打开的对话框
open.Title = "打开文本文件";
open.FileName = "";
open.AddExtension = true;//设置是否自动在文件中添加扩展名
open.CheckFileExists = true;//检查文件是否存在
open.CheckPathExists = true;//验证路径有效性
open.Filter = "文本文件(*.txt)|*.txt";//设置将打开文件的类型
open.ValidateNames = true;
//文件有效性验证ValidateNames,验证用户输入是否是一个有效的Windows文件名
if (open.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(open.FileName, System.Text.Encoding.Default);
this.richTextBox1.Text = sr.ReadToEnd();
}
MessageBox.Show("文件打开成功。", "消息");
}
catch (Exception mm)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert.ToString(mm), "警报");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 保存编辑文件
/// </summary>
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
FileStream textfile = File.Open(directory_path, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(textfile, Encoding.GetEncoding("GB2312"));
sw.Write(richTextBox1.Text.ToString());
MessageBox.Show("文件写成功。", "警报");
}
catch (Exception mm)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert.ToString(mm), "警报");
}
}
}
}
记事本
1.5FileStream 文件流
用File类提供的方法在创建或打开文件时,总是会产生一个FileStream对象。
(1)使用File对象的Create方法
FileStream mikecatstream;
mikecatstream = File.Create("c:\\mikecat.txt");
//本段代码的含义:
//利用类File的Create()方法在C:根目录下创建文件mikecat.txt,并把文件流赋给mikecatstream
方法
(2) 使用File对象的Open方法,‘
FileStream mikecatstream;
mikecatstream = File.Open("c:\\mikecat.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
//本段代码的含义:
//利用类File的Open()方法打开在C:根目录下的文件mikecat.txt,打开的模式为打开或创建,对文件的访问形式为只写,并把文件流赋给mikecatstream。
方法2
(3) 使用类FileStream的构造函数
FileStream mikecatstream;
mikecatstream = new FileStream("c:\\mikecat.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
//本段代码的含义:
//利用类FileStream的构造函数打开在C:根目录下的文件mikecat.txt,打开的模式为打开或创建,对文件的访问形式为只写,并把文件流赋给mikecatstream。
方法3
最常用的构造函数
|
名称
|
说明
|
|
FileStream(string FilePath, FileMode)
|
使用指定的路径和创建模式初始化 FileStream 类的新实例。
|
|
FileStream(string FilePath, FileMode, FileAccess)
|
使用指定的路径、创建模式和读/写权限初始化 FileStream 类的新实例。
|
|
FileStream(string FilePath, FileMode, FileAccess, FileShare)
|
使用指定的路径、创建模式、读/写权限和共享权限创建 FileStream 类的新实例。
|
构造函数中使用的枚举类型
|
名称
|
取值
|
说明
|
|
FileMode
|
Append、Create、CreateNew、Open、OpenOrCreate和Truncate
|
指定操作系统打开文件的方式。
|
|
FileAccess
|
Read、ReadWrite和Write
|
定义用于控制对文件的读访问、写访问或读/写访问的常数。
|
|
FileShare
|
Inheritable、None、Read、ReadWrite和Write
|
包含用于控制其他 FileStream 对象对同一文件可以具有的访问类型的常数。
|
实例
FileStream fstream = new FileStream("Test.cs", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.ReadWrite, FileShare.None);
//本段代码的含义:
//利用类FileStream的构造函数打开当前目录下的文件Test.cs,打开的模式为打开或创建,对文/的访问形式为读写,共享模式为拒绝共享,并把文件流赋给fstream。
代码
关于FileMode和FileAccess,FileShare这三个枚举类型值
|
成员名称
|
说明
|
|
Append
|
打开现有文件并查找到文件尾,或创建新文件。FileMode.Append 只能同 FileAccess.Write 一起使用。任何读尝试都将失败并引发 ArgumentException。
|
|
Create
|
指定操作系统应创建新文件。如果文件已存在,它将被改写。这要求 FileIOPermissionAccess.Write。System.IO.FileMode.Create 等效于这样的请求:如果文件不存在,则使用 CreateNew;否则使用 Truncate。
|
|
CreateNew
|
指定操作系统应创建新文件。此操作需要 FileIOPermissionAccess.Write。如果文件已存在,则将引发 IOException。
|
|
Open
|
指定操作系统应打开现有文件。打开文件的能力取决于 FileAccess 所指定的值。如果该文件不存在,则引发 System.IO.FileNotFoundException。
|
|
OpenOrCreate
|
指定操作系统应打开文件(如果文件存在);否则,应创建新文件。如果用 FileAccess.Read 打开文件,则需要 FileIOPermissionAccess.Read。如果文件访问为FileAccess.Write 或 FileAccess.ReadWrite,则需要 FileIOPermissionAccess.Write。如果文件访问为 FileAccess.Append,则需要 FileIOPermissionAccess.Append。
|
|
Truncate
|
指定操作系统应打开现有文件。文件一旦打开,就将被截断为零字节大小。此操作需要 FileIOPermissionAccess.Write。试图从使用 Truncate 打开的文件中进行读取将导致异常。
|
|
成员名称
|
说明
|
|
Read
|
对文件的读访问。可从文件中读取数据。同 Write 组合即构成读写访问权。
|
|
ReadWrite
|
对文件的读访问和写访问。可从文件读取数据和将数据写入文件。
|
|
Write
|
文件的写访问。可将数据写入文件。同 Read 组合即构成读/写访问权。
|
|
成员名称
|
说明
|
|
Delete
|
允许随后删除文件。
|
|
Inheritable
|
使文件句柄可由子进程继承。Win32 不直接支持此功能。
|
|
None
|
谢绝共享当前文件。文件关闭前,打开该文件的任何请求(由此进程或另一进程发出的请求)都将失败。
|
|
Read
|
允许随后打开文件读取。如果未指定此标志,则文件关闭前,任何打开该文件以进行读取的请求(由此进程或另一进程发出的请求)都将失败。但是,即使指定了此标志,仍可能需要附加权限才能够访问该文件。
|
|
ReadWrite
|
允许随后打开文件读取或写入。如果未指定此标志,则文件关闭前,任何打开该文件以进行读取或写入的请求(由此进程或另一进程发出)都将失败。但是,即使指定了此标志,仍可能需要附加权限才能够访问该文件。
|
|
Write
|
允许随后打开文件写入。如果未指定此标志,则文件关闭前,任何打开该文件以进行写入的请求(由此进程或另一进过程发出的请求)都将失败。但是,即使指定了此标志,仍可能需要附加权限才能够访问该文件。
|
|
对于FileMode,如果要求的模式与文件的现有状态不一致,就会抛出一个异常。如果文件不存在,Append、Open和Truncate会抛出一个异常,如果文件存在,CreateNew会抛出一个异常。Create和OpenOrCreate可以处理这两种情况,但Create会删除现有的文件,创建一个新的空文件。FileAccess 和FileShare枚举是按位标志,所以这些值可以与C#的按位OR运算符|合并使用。
|
1****2 文件的读写
通过一个窗体,如图3-7所示,在点击相应按钮控件时,可以完成对文件的读写操作、磁盘操作以及对目录的管理操作。通过本案例使读者快速掌握操作文件、目录的技术方法及类FileStream的应用。
从工具箱之中拖拽五个GroupBox控件到Form窗体上,text属性分别设置为:“文件管理”、“读写文件操作”、“文件磁盘操作”、“设置文件属性”、“目录管理”;向第一个GroupBox控件拖拽一个RichTextBox控件;再向第一个GroupBox控件拖拽一个Button控件,text属性设置为“关闭”;向第二个GroupBox控件拖拽一个ComboBox控件,text属性设置为“写入类型选择:”,Items属性中添加“创建空文本文件”、“添加入文本文件”、“新写入文本文件”;再向第二个GroupBox控件拖拽二个Button控件,text属性分别设置为“写入文件”、“读出文件”;向第三个GroupBox控件拖拽一个ComboBox控件,text属性设置为“文件磁盘操作选择:”,Items属性中添加“文件创建”、“文件删除”、“文件复制”、“文件移动”;再向第三个GroupBox控件拖拽一个Button控件,text属性设置为“文件磁盘操作”;向第四个GroupBox控件拖拽二个CheckBox控件,text属性分别设置为“只读”、“隐藏”;再向第四个GroupBox控件拖拽一个Button控件,text属性设置为“属性确认”;向第五个GroupBox控件拖拽一个ComboBox控件,text属性分别设置为“文件目录操作选择:”,Items属性中添加“创建文件夹”、“文件夹删除”、“文件夹移动”、“获取子文件信息”;再向第五个GroupBox控件拖拽一个Button控件,text属性设置为“文件目录操作”。
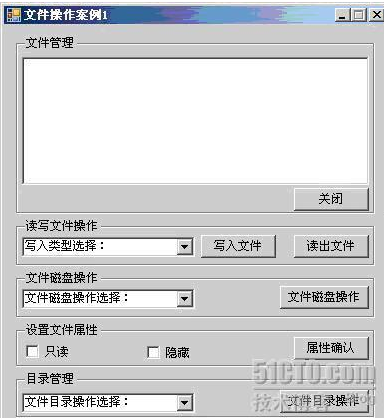
代码
//=========================第一部分:主界面功能设计=============================
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form6 : Form
{
public Form6()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 读写文件操作
/// </summary>
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int p = comboBox1.SelectedIndex;
if (p == -)
{
MessageBox.Show("请您选择文件写入方式", "警告信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
else
{
string filecontent = richTextBox1.Text.Trim();
MyFileOption myoption = new MyFileOption();
string filepath = @"c:\1.txt";
bool i = myoption.WriteTextFile(filepath, filecontent, Convert.ToInt16(comboBox1.SelectedIndex));
if (i == true)
{
MessageBox.Show("保存成功", "保存信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("写入文件时出错", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 文件磁盘操作
/// </summary>
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Int16 p = Convert.ToInt16(comboBox2.SelectedIndex);
if (p == -)
{
MessageBox.Show("请您选择磁盘文件操作方式", "警告信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
else
{
string sourcepath = "c:\\1.txt";
string targetpath = "c:\\2.txt";
MyFileOption myoption = new MyFileOption();
bool i = myoption.DiskFileOption(sourcepath, targetpath, p);
if (i == true)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘文件操作成功", "保存信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘文件操作时出错", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Text = null;
richTextBox1.Focus();
}
/// <summary>
/// 读出文本文件内容
/// </summary>
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MyFileOption myoption = new MyFileOption();
string filepath = @"c:\1.txt";
Int16 i = ;
string filecontent = "";
myoption.ReadTextFile(filepath, out i, out filecontent);
if (i == )
{
MessageBox.Show(filecontent, "错误信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
richTextBox1.Text = filecontent;
}
else if (i == )
{
richTextBox1.Text = filecontent;
MessageBox.Show("读取文件成功", "成功", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
else if (i == )
{
richTextBox1.Text = filecontent;
MessageBox.Show(filecontent, "错误信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 文件基本属性设置
/// </summary>
private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string filepath = @"c:\1.txt";
if (checkBox1.Checked && checkBox2.Checked)
{
File.SetAttributes(filepath, FileAttributes.ReadOnly | FileAttributes.Hidden);
MessageBox.Show("文件已经改为只读且隐藏", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
else
{
if (!checkBox1.Checked && !checkBox2.Checked)
{
File.SetAttributes(filepath, FileAttributes.Archive);
MessageBox.Show("文件已经改为正常", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
else
{
if (checkBox2.Checked)
{
File.SetAttributes(filepath, FileAttributes.ReadOnly);
MessageBox.Show("文件已经改为只读", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
if (checkBox1.Checked)
{
File.SetAttributes(filepath, FileAttributes.Hidden);
MessageBox.Show("文件已经改为隐藏", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 文件夹操作
/// </summary>
private void button6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Int16 p = Convert.ToInt16(comboBox3.SelectedIndex);
if (p == -)
{
MessageBox.Show("请您选择文件夹操作方式", "警告信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
else
{
string sourcepath = @"c:\1";
string targetpath = @"c:\2";
MyFileOption myoption = new MyFileOption();
string[] filesname = null;
bool i = myoption.DirectoryOption(sourcepath, targetpath, p, out filesname);
if (i == true)
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘文件夹操作成功", "保存信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
if (filesname != null)
{
foreach (string somestring in filesname)
{
richTextBox1.Text += somestring + "\r\n";
}
}
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("磁盘文件夹操作时出错", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
}
}
}
}
代码

向FileOption.cs文件中添加代码如下:
//==============================第二部分:类设计============================
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
class MyFileOption
{
/// <summary>
/*******************************************************
**方法 名:WriteTextFile
**输入参数:filepath:文件路径;
** filecontent:写入文件的内容
** WriteMethord:写入方法(0:打开并创建文件;1:添加文本;2:新建文本)
**输出参数:逻辑类型参数
**返 回 值:bool
**创建 人:钱哨
**创建日期:09-7-9
**描 述:打开存放在某目录下名称为filepath文件,并在该文件中写入filecontent。
*******************************************************/
public bool WriteTextFile(string filepath, string filecontent, Int16 WriteMethord)
{
bool i = true;
try
{
if (WriteMethord == )
{
FileStream textfile = File.Open(filepath, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(textfile, Encoding.Default);
sw.Write(filecontent);
i = true;
sw.Close();
textfile.Close();
}
else if (WriteMethord == )
{
FileStream textfile = File.Open(filepath, FileMode.Append, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(textfile, Encoding.Default);
sw.Write(filecontent);
i = true;
sw.Close();
textfile.Close();
}
else if (WriteMethord == )
{
FileStream textfile = File.Open(filepath, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(textfile, Encoding.Default);
sw.Write(filecontent);
i = true;
sw.Close();
textfile.Close();
}
return i;
}
catch
{
i = false;
return i;
}
}
/// <summary>
/*******************************************************
**方法 名:DiskFileOption
**输入参数:SourcePath:源文件路径;
** TargetPath:目的文件路径;
** OptionMethord:操作类别;0:文件创建;1:文件删除;2:文件复制;3:文件移动
**输出参数:逻辑类型参数
**返 回 值:bool
**创 建 人:钱哨
**创建日期:09-7-9
**描 述:对磁盘文件实施基本操作。
*******************************************************/
public bool DiskFileOption(string SourcePath, string TargetPath, Int16 OptionMethord)
{
bool i = true;
try
{
if (OptionMethord == )
{
//文件创建
FileStream textfile = File.Create(SourcePath);
textfile.Close();
}
else if (OptionMethord == )
{
//文件删除
File.Delete(SourcePath);
}
else if (OptionMethord == )
{
//文件复制
File.Copy(SourcePath, TargetPath, true);
}
else if (OptionMethord == )
{
//文件移动
File.Move(SourcePath,TargetPath);
}
return i;
}
catch
{
i = false;
return i;
}
} /// <summary>
/*******************************************************
**方法 名:ReadTextFile
**输入参数:filepath:文件路径;
**输出参数:i:读取类型(1:正常;2:文件读取错误;3:文件或路径无效);
** filecontent:返回内容
**返 回 值:逻辑类型参数
**创 建 人:钱哨
**创建日期:09-7-9
**描 述:读取存放在某目录下名称为filepath文件内容。
*******************************************************/
public void ReadTextFile(string filepath, out Int16 i, out string filecontent)
{
if (File.Exists(filepath))
{
try
{
StreamReader textreader = new StreamReader(filepath, System.Text.Encoding.Default);
filecontent = textreader.ReadToEnd();
textreader.Close();
i = ;
}
catch
{
i = ;
filecontent = "文件读取错误!";
}
}
else
{
i = ;
filecontent = "文件或路径无效!";
}
}
/// <summary>
/*******************************************************
**方法 名:DirectoryOption
**输入参数:filepath:文件路径;
**输出参数:i:读取类型 (0:创建文件夹;1:文件夹删除;2:文件夹移动;3:获取文件夹下面所有的子文件信息) filecontent:返回内容
**返 回 值:逻辑类型参数
**创 建 人:钱哨
**创建日期:09-7-9
**描 述:读取存放在某目录下名称为filepath文件内容。
*******************************************************/
/// <summary>
public bool DirectoryOption(string Directorypath, string TargetDirectorypath, Int16 OptionMethord, out string[] filesname)
{
bool k = true;
filesname = null;
if (Directory.Exists(Directorypath))
{
try
{
if (OptionMethord == )
{
//创建文件夹
Directory.CreateDirectory(Directorypath);
}
else if (OptionMethord == )
{
//文件夹删除
Directory.Delete(Directorypath, true);
}
else if (OptionMethord == )
{
//文件夹移动
Directory.Move(Directorypath, TargetDirectorypath);
}
else if (OptionMethord == )
{
//获取文件夹下面所有的子文件信息
filesname = Directory.GetFiles(Directorypath);
}
}
catch
{
k = false;
}
}
else
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(Directorypath);
k = true;
}
return k;
}
}
}
代码1
文件流FileStream综合案例
从工具箱之中拖拽三个GroupBox控件到Form窗体上,text属性分别设置为:“添加物理路径”、“打开文本文件”、“文本编辑区”;向第一个GroupBox控件拖拽一个TextBox控件;再向第一个GroupBox控件拖拽一个Button控件,text属性设置为“选定文件夹”;向第二个GroupBox控件拖拽一个TextBox控件;再向第二个GroupBox控件拖拽一个Button控件,text属性设置为“选定文件”;向第三个GroupBox控件拖拽一个richTextBox控件;再向窗体上非GroupBox区域拖拽一个Button控件,text属性设置为“保存文本文件”。
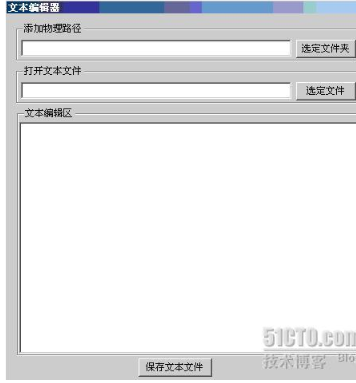
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form11 : Form
{
public Form11()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//添加变量TypeW,int类型,0为默认,1为打开文件夹并建立new.txt文件,2为打开文本文件
int TypeW = ;
/// <summary>
/// 选定某个文件夹
/// </summary>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//新建文件夹
FolderBrowserDialog openfolder = new FolderBrowserDialog();
if (openfolder.ShowDialog ()== DialogResult.OK)
{
textBox1.Text = Convert.ToString(openfolder.SelectedPath);
TypeW = ;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 选定某个文件夹下面的文本文件
/// </summary>
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog openfile = new OpenFileDialog();
openfile.Filter = "文本文件|*.txt";
if (openfile.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
FileStream OpenFileStream = new FileStream(openfile.FileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(OpenFileStream, Encoding.Default);
richTextBox1.Text = sr.ReadToEnd();
textBox2.Text = Convert.ToString(openfile.FileName);
OpenFileStream.Close();
sr.Close();
TypeW = ;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 保存文本文件
/// </summary>
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (richTextBox1.Text == string.Empty)
{
MessageBox.Show("编辑文本文件内容禁止为空!", "提示信息");
return;
}
else
{
if (TypeW == )
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(textBox1.Text+@"\\new.txt",FileMode.Create,FileAccess.ReadWrite);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fs,Encoding.Default);
sw.Write(richTextBox1.Text);
TypeW = ;
MessageBox.Show("已经成功的将文本文件写入" + textBox1.Text + "\\new.txt之中", "提示信息");
//注意:此处顺序绝不可调换,为什么?【另外,为什么必须关闭线程资源?】
sw.Close();
fs.Close();
}
else if(TypeW==)
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(textBox2.Text, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.ReadWrite);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fs, Encoding.Default);
sw.Write(richTextBox1.Text);
TypeW = ;
MessageBox.Show("已经成功的将文本文件写入" + textBox2.Text + "之中", "提示信息");
//注意:此处顺序绝不可调换,为什么?
sw.Close();
fs.Close();
}
}
}
}
}
代码2
4 读取二进制
|
FileStream filestream = new FileStream(Filename, FileMode.Create);
BinaryWriter objBinaryWriter = new BinaryWriter(filestream);
|
常用方法:
|
方法
|
说明
|
|
Close()
|
关闭当前阅读器及基础流。
|
|
Read()
|
已重载。 从基础流中读取字符,并提升流的当前位置。
|
|
ReadDecimal()
|
从当前流中读取十进制数值,并将该流的当前位置提升十六个字节。
|
|
ReadByte()
|
从当前流中读取下一个字节,并使流的当前位置提升1个字节。
|
|
ReadInt16()
|
从当前流中读取2字节有符号整数,并使流的当前位置提升2个字节。
|
|
ReadInt32()
|
从当前流中读取4字节有符号整数,并使流的当前位置提升4个字节。
|
|
ReadString()
|
从当前流中读取一个字符串。字符串有长度前缀,一次7位地被编码为整数。
|
实例:建立一个BinaryReader类的一些主要方法
using System;
using System.IO; class BinaryRW
{
static void Main()
{
int i = ;
char[] invalidPathChars = Path.InvalidPathChars;
MemoryStream memStream = new MemoryStream();
BinaryWriter binWriter = new BinaryWriter(memStream);
// 写入内存
binWriter.Write("Invalid file path characters are: ");
for (i = ; i < invalidPathChars.Length; i++)
{
binWriter.Write(invalidPathChars[i]);
}
// 用作生成编写器的内存流同样作为生成读取器的内存流
BinaryReader binReader = new BinaryReader(memStream);
// 设置流的起点
memStream.Position = ;
// 从内存中读取数据,并把数据写入控制台
Console.Write(binReader.ReadString());
char[] memoryData = new char[memStream.Length - memStream.Position];
for (i = ; i < memoryData.Length; i++)
{
memoryData[i] = Convert.ToChar(binReader.Read());
}
Console.WriteLine(memoryData);
}
}
代码
类BinaryWriter以二进制形式将基元类型写入流,并支持用特定的编码写入字符串。
|
方法
|
说明
|
|
Close()
|
关闭当前的 BinaryWriter 和基础流。
|
|
Flush()
|
清理当前编写器的所有缓冲区,使所有缓冲数据写入基础设备。
|
|
Write()
|
已重载。 将值写入当前流。
|
建立一个BinaryWriter类方法
using System;
using System.IO; class BinaryRW
{
static void Main()
{
using (BinaryWriter binWriter = new BinaryWriter(File.Open(fileName, FileMode.Create)))
{
binWriter.Write(aspectRatio);
binWriter.Write(lookupDir);
binWriter.Write(autoSaveTime);
binWriter.Write(showStatusBar);
}
}
}
code Reader
4.2 写二进制文件
从工具箱之中拖拽MainMenu控件、SaveFileDialog控件、GroupBox控件、PictureBox控件各一个到Form窗体上;Form窗体的text属性设置为“图片处理器”;GroupBox控件的text属性设置为“图片显示区”;PictureBox控件的sizemode属性设置为zoom;MainMenu控件添加菜单项及子项:
|
菜单项
|
子项
|
其他属性
|
|
图片(&P)
|
打开图片(&O)
|
快捷键等其他属性根据自己设计定(下同)
|
|
复制图片(&C)
|
|
|
|
关闭(&Q)
|
|
|

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form12 : Form
{
public Form12()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/*******************************************************
**方 法 名:GetFileBytes
**输 入参数:Filename:文件名称;
**输 出参数:比特流类型
**返 回 值:byte[]二进制流
**创 建 人:钱哨
**创 建日期:09-7-9
**描 述:将读取的文件转化成为二进制流。
*******************************************************/
/// <summary>
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Filename">打开的图片具体路径及文件名称</param>
/// <returns>比特流类型</returns>
public byte[] GetFileBytes(string Filename)
{
if (Filename == "")
return null;
try
{
FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(Filename, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
BinaryReader binaryReader = new BinaryReader(fileStream);
byte[] fileBytes = binaryReader.ReadBytes((int)fileStream.Length);
binaryReader.Close();
fileStream.Close();
return fileBytes;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
/*******************************************************
**方 法 名:WriteFileBytes
**输 入参数:TargetFilename:目标文件名称;
**输 出参数:布尔类型:是否写成功
**返 回 值:byte[]二进制流
**创 建 人:钱哨
**创 建日期:09-7-9
**描 述:将读取的文件转化成为二进制流。
*******************************************************/
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TargetFilename">目标文件</param>
/// <param name="fileBytes">文件比特流</param>
/// <returns>布尔类型:是否写成功</returns>
public bool WriteFileBytes(string TargetFilename, byte[] fileBytes)
{
bool k = true;
if (TargetFilename != "" && fileBytes.Length != )
{
try
{
FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(TargetFilename, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
BinaryWriter binaryWriter = new BinaryWriter(fileStream);
binaryWriter.Write(fileBytes);
binaryWriter.Flush();
binaryWriter.Close();
fileStream.Close();
}
catch
{
k = false;
}
}
else
{
k = false;
}
return k;
}
/// <summary>
/// 菜单:打开图片
/// </summary>
private void toolStripMenuItem3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
OpenFileDialog openfile = new OpenFileDialog();
openfile.Filter = "jpg类型图片(*.jpg)|*.jpg|BMP类型图片(*.bmp)|*.bmp";
if (openfile.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
byte[] picbinary = GetFileBytes(openfile.FileName);
//第一步:打开图片文件,获得比特流
MemoryStream mempicstream = new MemoryStream(picbinary);
//第二步:将比特流还存在内存工作流中。
pictureBox1.Image = Image.FromStream(mempicstream);
//第三步:加载内存流到图片控件
mempicstream.Dispose();
mempicstream.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception m)
{
MessageBox.Show("读取图片出错,可能的问题是:"+Convert.ToString(m) ,"错误提示");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 将打开的图片进行复制
/// </summary>
private void toolStripMenuItem4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (pictureBox1.Image == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("禁止图片为空时候另存信息。", "错误提示");
}
else
{
saveFileDialog1.Filter = "jpg类型图片(*.jpg)|*.jpg";
DialogResult result = saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog();
if (result == DialogResult.OK)
{
MemoryStream ms=new MemoryStream();
Bitmap bm = new Bitmap(pictureBox1.Image);
bm.Save(ms, System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Jpeg);
byte[] bytes = ms.ToArray();
WriteFileBytes(saveFileDialog1.FileName, bytes);
MessageBox.Show("另存图片成功", "提示");
ms.Dispose();
ms.Close();
bm.Dispose();
}
}
}
catch (Exception m)
{
MessageBox.Show("读取图片出错,可能的问题是:" + Convert.ToString(m), "错误提示");
}
}
}
}
代码
成功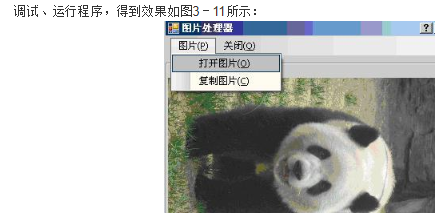
3.5读写内存流
5-1 读写内存流 ——MemoryStream类
|
名称
|
说明
|
|
MemoryStream ()
|
使用初始化为零的可扩展容量初始化 MemoryStream 类的新实例。
|
|
MemoryStream (byte[])
|
基于指定的字节数组初始化 MemoryStream 类的无法调整大小的新实例。
|
|
MemoryStream (byte[], Boolean)
|
使用按指定要求设置的 CanWrite 属性基于指定的字节数组初始化 MemoryStream 类的无法调整大小的新实例。
|
|
MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(buffer);
//这时,无法再设置Capacity属性的大小。
|
|
MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(buffer, false);
//这时,CanWrite属性就被设置为false 。
|
案例学习:MemoryStream类案例
从工具箱之中拖拽五个Label控件到Form窗体上,拖拽一个Button控件。

eg.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form14 : Form
{
public Form14()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//建立字节数组
byte[] buffer = new byte[];
/// <summary>
/// 获取测试性数据
/// </summary>
private void GetTestData()
{
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
buffer[i] = (byte)(i % );
//byte类型的数最大不能超过255,用256取模实现
}
}
/// <summary>
/// button1按钮的鼠标单击Click事件
/// </summary>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//创建测试数据
GetTestData();
//创建内存流对象,初始分配50字节的缓冲区
MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream();
//向内存流中写入字节数组的所有数据
mem.Write(buffer,,buffer.GetLength());
//使用从缓冲区读取的数据将字节块写入当前流。
//参数:
//1、buffer从中写入数据的缓冲区。
//2、offset buffer中的字节偏移量,从此处开始写入。
//3、count最多写入的字节数。
//GetLength(0) 为 GetLength 的一个示例,它返回 Array 的第一维中的元素个数。
label1.Text = "写入数据后的内存流长度是:"+mem.Length.ToString();
label2.Text = "分配给内存流的缓冲区大小:"+mem.Capacity.ToString();
mem.SetLength();
label3.Text = "调用SetLength方法后的内存流长度:" + mem.Length.ToString();
mem.Capacity = ;//注意:此值不能小于Length属性
label4.Text = "调用Capacity方法后缓冲区大小:" + mem.Capacity.ToString();
//将读写指针移到距流开头10个字节的位置
mem.Seek(, SeekOrigin.Begin);
label5.Text = "内存中的信息是:"+mem.ReadByte().ToString();
}
}
}
code

5-3 读写缓存流 ——BufferedStream类
|
名称
|
说明
|
|
使用默认的缓冲区大小 4096 字节初始化 BufferedStream 类的新实例。
|
|
|
使用指定的缓冲区大小初始化 BufferedStream 类的新实例。
|
BufferedStream类案例学习
1. 案例学习:通过缓冲区交换数据
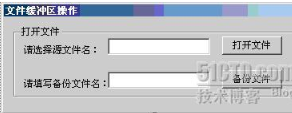
从工具箱之中拖拽一个GroupBox,text属性设置为“打开文件”;拖拽二个Label控件到GroupBox上,text属性分别设置为“请选择源文件名:”、“请填写备份文件名:”;拖拽二个TextBox控件到GroupBox上,其中第一TextBox控件的Enabled属性为false;拖拽二个Button控件到GroupBox上,text属性分别设置为“打开文件”、“备份文件”。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form16 : Form
{
public Form16()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 打开原始文件
/// </summary>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog openfile = new OpenFileDialog();
openfile.Filter = "文本文件(*.txt)|*.txt";
if (openfile.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
textBox1.Text = openfile.FileName.ToString();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 备份目标文件;Stream 和 BufferedStream 的实例
/// </summary>
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string targetpath = @"c:\" + textBox2.Text + ".txt";
FileStream fs =File.Create(targetpath);
fs.Dispose();
fs.Close();
string sourcepath = textBox1.Text;
Stream outputStream= File.OpenWrite(targetpath);
Stream inputStream = File.OpenRead(sourcepath);
BufferedStream bufferedInput = new BufferedStream(inputStream);
BufferedStream bufferedOutput = new BufferedStream(outputStream);
byte[] buffer = new Byte[];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead =bufferedInput.Read(buffer, ,)) > )
{
bufferedOutput.Write(buffer, , bytesRead);
}
//通过缓冲区进行读写
MessageBox.Show("给定备份的文件已创建", "提示");
bufferedOutput.Flush();
bufferedInput.Close();
bufferedOutput.Close();
//刷新并关闭 BufferStream
}
}
}
代码
文件流FileStream 上机实验
文本编辑器
mainMenu TextBox OpenFileDialog SaveFileDialog FontDialog colorDialog
代碼
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace FileOptionApplication
{
public partial class Form16 : Form
{
public Form16()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 打开原始文件
/// </summary>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog openfile = new OpenFileDialog();
openfile.Filter = "文本文件(*.txt)|*.txt";
if (openfile.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
textBox1.Text = openfile.FileName.ToString();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 备份目标文件;Stream 和 BufferedStream 的实例
/// </summary>
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string targetpath = @"c:\" + textBox2.Text + ".txt";
FileStream fs =File.Create(targetpath);
fs.Dispose();
fs.Close();
string sourcepath = textBox1.Text;
Stream outputStream= File.OpenWrite(targetpath);
Stream inputStream = File.OpenRead(sourcepath);
BufferedStream bufferedInput = new BufferedStream(inputStream);
BufferedStream bufferedOutput = new BufferedStream(outputStream);
byte[] buffer = new Byte[];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead =bufferedInput.Read(buffer, ,)) > )
{
bufferedOutput.Write(buffer, , bytesRead);
}
//通过缓冲区进行读写
MessageBox.Show("给定备份的文件已创建", "提示");
bufferedOutput.Flush();
bufferedInput.Close();
bufferedOutput.Close();
//刷新并关闭 BufferStream
}
}
} ————————————————————————————————
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms; namespace WindowsApplication1
{
public partial class Form9 : Form
{
public Form8 mainForm;
public Form9()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 点击查询下一个后
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnFindNext_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
mainForm.findKey = txtContent.Text;
mainForm.isToDown = radToDown.Checked;
mainForm.mathingStyle = checkBox1.Checked;
string source; //被查找的文本
string finding; //查找的关键字 //当不区分大小写时,将内容都转换为小写
if (this.checkBox1.Checked == false)
{
source = this.mainForm.textBox1.Text.ToLower();
finding = this.txtContent.Text.ToLower();
}
else
{
source = this.mainForm.textBox1.Text;
finding = this.txtContent.Text;
} //向下查找
if (this.radToDown.Checked)
{
//SelectionStart能获取光标起始点
int temp = source.IndexOf(finding, mainForm.textBox1.SelectionStart + mainForm.textBox1.SelectedText.Length);
if (temp >= )
{
this.mainForm.textBox1.Select(temp, finding.Length);
mainForm.textBox1.ScrollToCaret();//当屏幕显示不了时,实现滚动
this.mainForm.Focus();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("没有找到" + "'" + txtContent.Text + "'");
}
}
//向上查找
else
{
int temp = -;
try
{
temp = source.LastIndexOf(finding, mainForm.textBox1.SelectionStart - );
}
catch { }
if (temp >= )
{
this.mainForm.textBox1.Select(temp, finding.Length);
mainForm.textBox1.ScrollToCaret();//当屏幕显示不了时,实现滚动
this.mainForm.Focus();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("没有找到" + "'" + txtContent.Text + "'");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 点击取消后
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnCancel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
/// <summary>
/// 当查询文本框文本内容发生变化后
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void txtContent_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (txtContent.Text.Length > )
{
btnFindNext.Enabled = true;
}
else
{
btnFindNext.Enabled = false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 表单初始化事件
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void Form9_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
txtContent.Text = mainForm.textBox1.SelectedText;
} }
}
————————————————————————————————— using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms; namespace WindowsApplication1
{
public partial class Form10 : Form
{
public Form8 mainForm;
public Form10()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 取消
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnCancel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
/// <summary>
/// 查找下一个
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnFindNext_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string source;
string finding;
if (this.checkBox1.Checked == false)
{
source = this.mainForm.textBox1.Text.ToLower();
finding = this.txtFindContent.Text.ToLower();
}
else
{
source = this.mainForm.textBox1.Text;
finding = this.txtFindContent.Text;
} int temp = source.IndexOf(finding, mainForm.textBox1.SelectionStart + mainForm.textBox1.SelectedText.Length);
if (temp >= )
{
this.mainForm.textBox1.Select(temp, finding.Length);
mainForm.textBox1.ScrollToCaret();
this.mainForm.Focus();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("没有找到" + "'" + txtFindContent.Text + "'");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 替换
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnReplace_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (txtFindContent.Text == mainForm.textBox1.SelectedText)
{
mainForm.textBox1.SelectedText = txtReplace.Text;
}
else
{
btnFindNext.PerformClick();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 全部替换
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnReplaceAll_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int count = ;
int position;
string source;
string finding;
while (true)
{
//下面为查找代码
if (this.checkBox1.Checked == false)
{
source = this.mainForm.textBox1.Text.ToLower();
finding = this.txtFindContent.Text.ToLower();
}
else
{
source = this.mainForm.textBox1.Text;
finding = this.txtFindContent.Text;
} if (count == )
{
position = source.IndexOf(finding, );
}
else
{
position = source.IndexOf(finding, mainForm.textBox1.SelectionStart + mainForm.textBox1.SelectedText.Length);
} if (position >= )
{
this.mainForm.textBox1.Select(position, finding.Length);
mainForm.textBox1.ScrollToCaret();
this.mainForm.Focus();
count++;
} //下面为替换代码
if (mainForm.textBox1.SelectedText.Length > )
{
btnReplace.PerformClick();
}
else
{
break;
}
}
MessageBox.Show("替换了" + count + "个地方");
}
/// <summary>
/// 表单初始化
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void Form10_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
txtFindContent.Text = mainForm.textBox1.SelectedText;
}
}
}
ccode
二进制和内存流文件操作上机实验
往数据库放图片
school Myphoto
Pid id 自动增长类型 主码
Photo Image
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO; namespace WindowsApplication1
{
public partial class Form13 : Form
{
public Form13()
{
InitializeComponent();
} SqlConnection connection;
/// <summary>
/// 打开数据库
/// </summary>
private void open()
{
string connstring = "Data Source=(local);Initial Catalog=school;User ID=sa";
connection = new SqlConnection(connstring);
connection.Open();
}
/// <summary>
/// 关闭数据库
/// </summary>
private void close()
{
connection.Dispose();
connection.Close();
connection = null;
} /// <summary>
/// 输入SQL命令,得到DataReader对象
/// </summary>
public SqlDataReader GetDataReader(string sqlstring)
{
open();
SqlCommand mycom = new SqlCommand(sqlstring, connection);
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter();
adapter.SelectCommand = mycom;
SqlDataReader Dr = mycom.ExecuteReader();
return Dr; } /// <summary>
/*******************************************************
**方 法 名:GetFileBytes
**输 入参数:Filename:文件名称;
**
**输 出参数:
**返 回 值:byte[]二进制流
**创 建 人:钱哨
**创 建日期:08-7-9
**描 述:将读取的文件转化成为二进制流。
*******************************************************/
/// <summary>
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Filename">打开的图片具体路径及文件名称</param>
/// <returns>比特流类型</returns>
public byte[] GetFileBytes(string Filename)
{
if (Filename == "")
return null;
try
{
FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(Filename, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
BinaryReader binaryReader = new BinaryReader(fileStream); byte[] fileBytes = binaryReader.ReadBytes((int)fileStream.Length);
binaryReader.Close();
fileStream.Close(); return fileBytes;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 加载并刷新当前的combobox对象控件
/// </summary>
private void loadcombobox()
{
comboBox1.Items.Clear();
SqlDataReader dr = GetDataReader("select * from Myphoto");
while (dr.Read())
{
comboBox1.Items.Add(dr[].ToString());
}
close();
} /// <summary>
/// 初始化事件,加载combobox对象控件的列表信息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void Form13_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
loadcombobox();
} /// <summary>
/// 打开图片
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
OpenFileDialog openfile = new OpenFileDialog();
openfile.Filter = "jpg类型图片(*.jpg)|*.jpg|BMP类型图片(*.bmp)|*.bmp";
if (openfile.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
byte[] picbinary = GetFileBytes(openfile.FileName);//第一步:打开图片文件,获得比特流
MemoryStream mempicstream = new MemoryStream(picbinary);//第二步:将比特流还存在内存工作流中。
pictureBox1.Image = Image.FromStream(mempicstream);//第三步:加载内存流到图片控件
textBox1.Text = openfile.FileName.ToString();
mempicstream.Dispose();
mempicstream.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception m)
{
MessageBox.Show("读取图片出错,可能的问题是:" + Convert.ToString(m), "错误提示");
}
} private void comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (comboBox1.SelectedIndex > -)
{
string sqlstring = string.Format("select photo from Myphoto where pid="+comboBox1.Text);
SqlDataReader dr = GetDataReader(sqlstring);
if (dr.Read())
{
byte[] b = (byte[])dr["photo"];
MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(b);
//Image img = Image.FromStream(ms);
Image imge = new Bitmap(ms);
pictureBox1.Image = imge;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 将打开的文件保存到数据库之中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (pictureBox1.Image == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("禁止图片为空时候存储信息。", "错误提示");
}
else
{ MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream();
Bitmap bm = new Bitmap(pictureBox1.Image);
bm.Save(ms, System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Jpeg);
byte[] bytes = ms.ToArray();
//开始向数据库写信息
string insert = "INSERT INTO Myphoto(Photo) VALUES (@Photo)";
//sql命令参数
open();
SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(insert, connection);
//此句特别重要:指定SQL操作的参数性质!
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add("@Photo", SqlDbType.Binary).Value = bytes; sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
close(); MessageBox.Show("另存图片成功", "提示"); ms.Dispose();
ms.Close();
bm.Dispose();
loadcombobox();
} }
catch (Exception m)
{
MessageBox.Show("读取图片出错,可能的问题是:" + Convert.ToString(m), "错误提示");
}
} }
}
code
c# 窗体开发3 文件处理技术的更多相关文章
- c# 窗体开发4 数据库访问技术
ADO.NET的名称起源于ADO(ACTIVEX DATA OBJECTS) USING SYSTEM; USING SYSTEM.COLLECTIONS.GENERIC; USING SYSTEM. ...
- 【基于WinForm+Access局域网共享数据库的项目总结】之篇一:WinForm开发总体概述与技术实现
篇一:WinForm开发总体概述与技术实现 篇二:WinForm开发扇形图统计和Excel数据导出 篇三:Access远程连接数据库和窗体打包部署 [小记]:最近基于WinForm+Access数据库 ...
- 移动端IM开发需要面对的技术问题
1.前言 这两年多一直从事网易云信 iOS 端 IM SDK的开发,期间不断有兄弟部门的同事和合作伙伴过来问各种技术细节,干脆统一介绍下一个IM APP的方方面面,包括技术选型(包括通讯方式,网络连接 ...
- C#进行Visio二次开发之文件导出及另存Web页面
在我前面很多关于Visio的开发过程中,介绍了各种Visio的C#开发应用场景,包括对Visio的文档.模具文档.形状.属性数据.各种事件等相关的基础处理,以及Visio本身的整体项目应用,虽然时间过 ...
- Windows 窗体的.Net 框架绘图技术
当编写一个典型的Windows 窗体程序时,窗体和控件的绘制.效果等操作是不需要特别加以考虑的.这是为什么呢?因为通过使用 .Net 框架,开发人员可以拖动一系列的控件到窗体上,并书写一些简单的与事件 ...
- 从无到有开发连麦直播技术<转>
转贴地址:http://blog.csdn.net/heisedelangzi/article/details/52400333 从无到有开发连麦直播技术点整理-AnyRTC 直播关键字 采集.前处理 ...
- Java和.NET(C#)的开发用到的技术对比总结
前言 声明:我指的是一般的Java和.NET(C#)的后台开发用到的技术总结 最近一直在应聘ing,楼主的项目还是.NET(C#)项目居多,Java项目相对少,在这也吐槽下,招.NET(C#)的公司实 ...
- 安卓开发_数据存储技术_sqlite
一.SQLite SQLite第一个Alpha版本诞生于2000年5月,它是一款轻量级数据库,它的设计目标是嵌入式的,占用资源非常的低,只需要几百K的内存就够了.SQLite已经被多种软件和产品使用 ...
- 安卓开发_数据存储技术_SharedPreferences类
SharedPreferences类 供开发人员保存和获取基本数据类型的键值对. 该类主要用于基本类型,例如:booleans,ints,longs,strings.在应用程序结束后,数据仍旧会保存. ...
随机推荐
- 从比特币、以太坊、libra的不同特点认识move语言
关于比特币.以太坊.libra,我们知道他们是不同的区块链应用,那么他们的根本差别在哪里呢. 其实,单从白皮书的标题,就可以大概看出三个项目在设计目标上的差异. 比特币的目标是 -- 可编程货币(Pr ...
- [2018-01-12] laravel中的MVC
路由里面可以做所有事情,但是真正的项目当中,路由只用来接收请求,并转发给控制器的方法进行处理 首先我们先了解一下 一.app/Http/routes路由的用法: 方法一. 这种方法写完后在控制器创建方 ...
- bzoj1004 card
明知是burnside然而根本不会然后无耻地颓了题解后一脸傻气的我: 直接套公式???为啥方案数==等价类数量啊??? skyh:显然啊(狂笑)(hey wxy!他问为啥方案书等于等价类数量!) wx ...
- 零基础小白入门IT开发指南
先自我介绍以下,本人是一枚刚毕业不到两年的某一线城市的程序员,本科阶段专业是计算机科学与技术.从大四开始出去实习到现在的编码经验也有快2年半了,两年半的时间包括实习在内任职过有4家公司,包括一家互联网 ...
- 使用Typescript重构axios(三十二)——写在最后面(总结)
0. 系列文章 1.使用Typescript重构axios(一)--写在最前面 2.使用Typescript重构axios(二)--项目起手,跑通流程 3.使用Typescript重构axios(三) ...
- Scrapy进阶知识点总结(一)——基本命令与基本类(spider,request,response)
一.常见命令 scrapy全局命令可以在任何地方用,项目命令只能在项目路径下用 全局命令: 项目命令: startproject crawl genspider check settings list ...
- 平滑启动shell脚本
# 平滑关闭和启动 Spring Boot 程序#设置端口SERVER_PORT="8090"#当前时间time=`date +%Y-%m-%d`#设置应用名称JAR_NAME=& ...
- 用大写字母输入 Linux 命令,实现以 sudo 用户权限运行
我们知道,一些 Linux 命令是要通过 sudo 权限才能运行的,这需要我们每次使用这些命令时在前面加一个 sudo ,十分繁琐.今天给大家介绍一个好用的工具 SUDO ,它只需要我们用大写字母键入 ...
- nyoj 21-三个水杯(BFS)
21-三个水杯 内存限制:64MB 时间限制:1000ms Special Judge: No accepted:7 submit:18 题目描述: 给出三个水杯,大小不一,并且只有最大的水杯的水是装 ...
- mysql基础之数据类型
一.整型 分为:tinyint .smallint .mediumint .int .bigint 常用的 分为以下三项: tinyint. smallint.int 数据类型 存储范围 字节 tin ...
