查询性能提升3倍!Apache Hudi 查询优化了解下?
从 Hudi 0.10.0版本开始,我们很高兴推出在数据库领域中称为 Z-Order 和 Hilbert 空间填充曲线的高级数据布局优化技术的支持。
1. 背景
Amazon EMR 团队最近发表了一篇很不错的文章展示了对数据进行聚簇是如何提高查询性能的,为了更好地了解发生了什么以及它与空间填充曲线的关系,让我们仔细研究该文章的设置。
文章中比较了 2 个 Apache Hudi 表(均来自 Amazon Reviews 数据集):
未聚簇的 amazon_reviews 表(即数据尚未按任何特定键重新排序)
amazon_reviews_clustered 聚簇表。当数据被聚簇后,数据按字典顺序排列(这里我们将这种排序称为线性排序),排序列为
star_rating、total_votes两列(见下图)

为了展示查询性能的改进,对这两个表执行以下查询:

这里要指出的重要考虑因素是查询指定了排序的两个列(star_rating 和 total_votes)。但不幸的是这是线性/词典排序的一个关键限制,如果添加更多列,排序的价值会会随之减少。
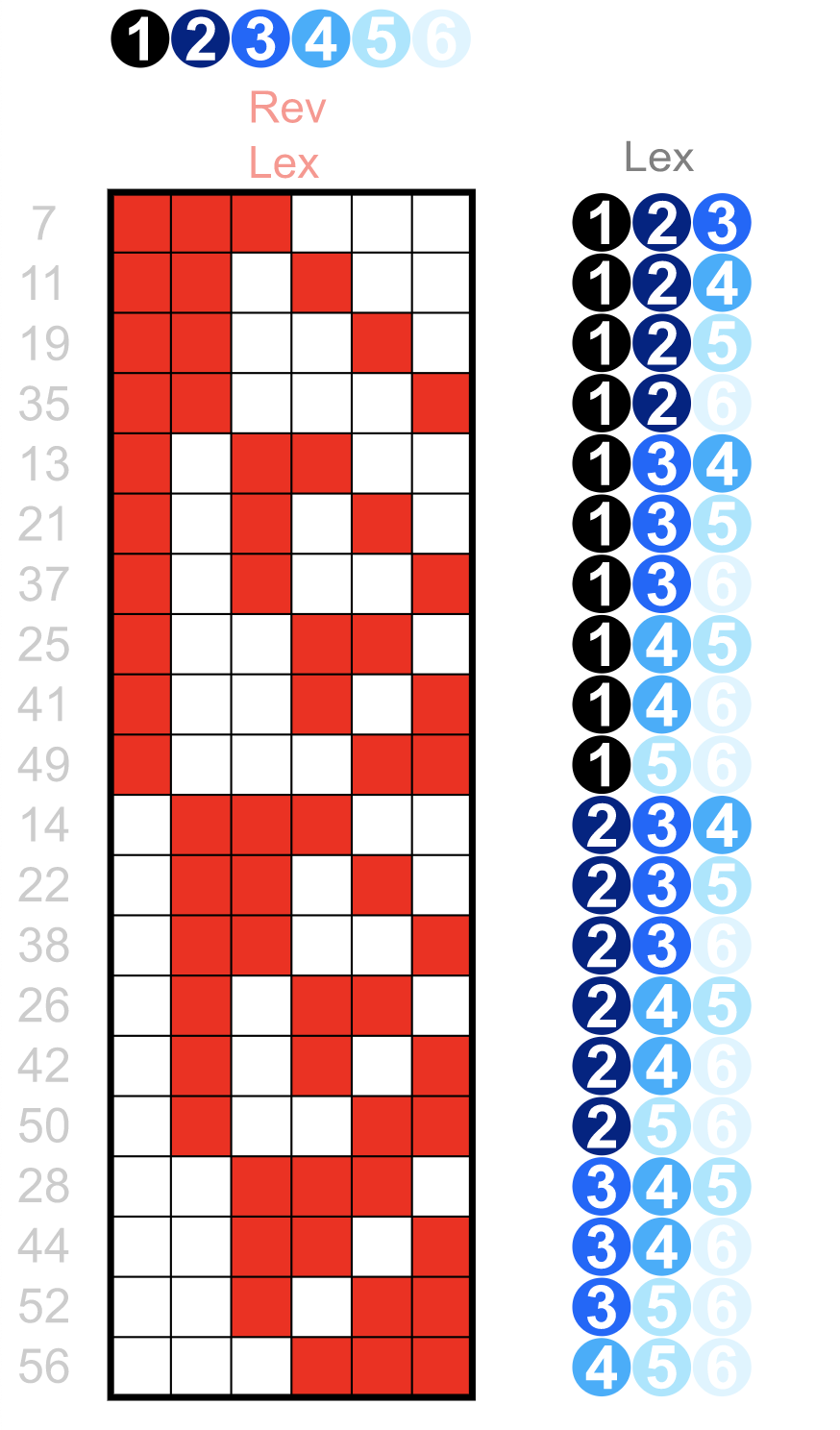
从上图可以看到,对于按字典顺序排列的 3 元组整数,只有第一列能够对所有具有相同值的记录具有关键的局部性属性:例如所有记录都具有以“开头的值” 1"、"2"、"3"(在第一列中)很好地聚簇在一起。但是如果尝试在第三列中查找所有值为"5"的值,会发现这些值现在分散在所有地方,根本没有局部性,过滤效果很差。
提高查询性能的关键因素是局部性:它使查询能够显着减少搜索空间和需要扫描、解析等的文件数量。
但是这是否意味着如果我们按表排序的列的第一个(或更准确地说是前缀)以外的任何内容进行过滤,我们的查询就注定要进行全面扫描?不完全是,局部性也是空间填充曲线在枚举多维空间时启用的属性(我们表中的记录可以表示为 N 维空间中的点,其中 N 是我们表中的列数)
那么它是如何工作的?我们以 Z 曲线为例:拟合二维平面的 Z 阶曲线如下所示:
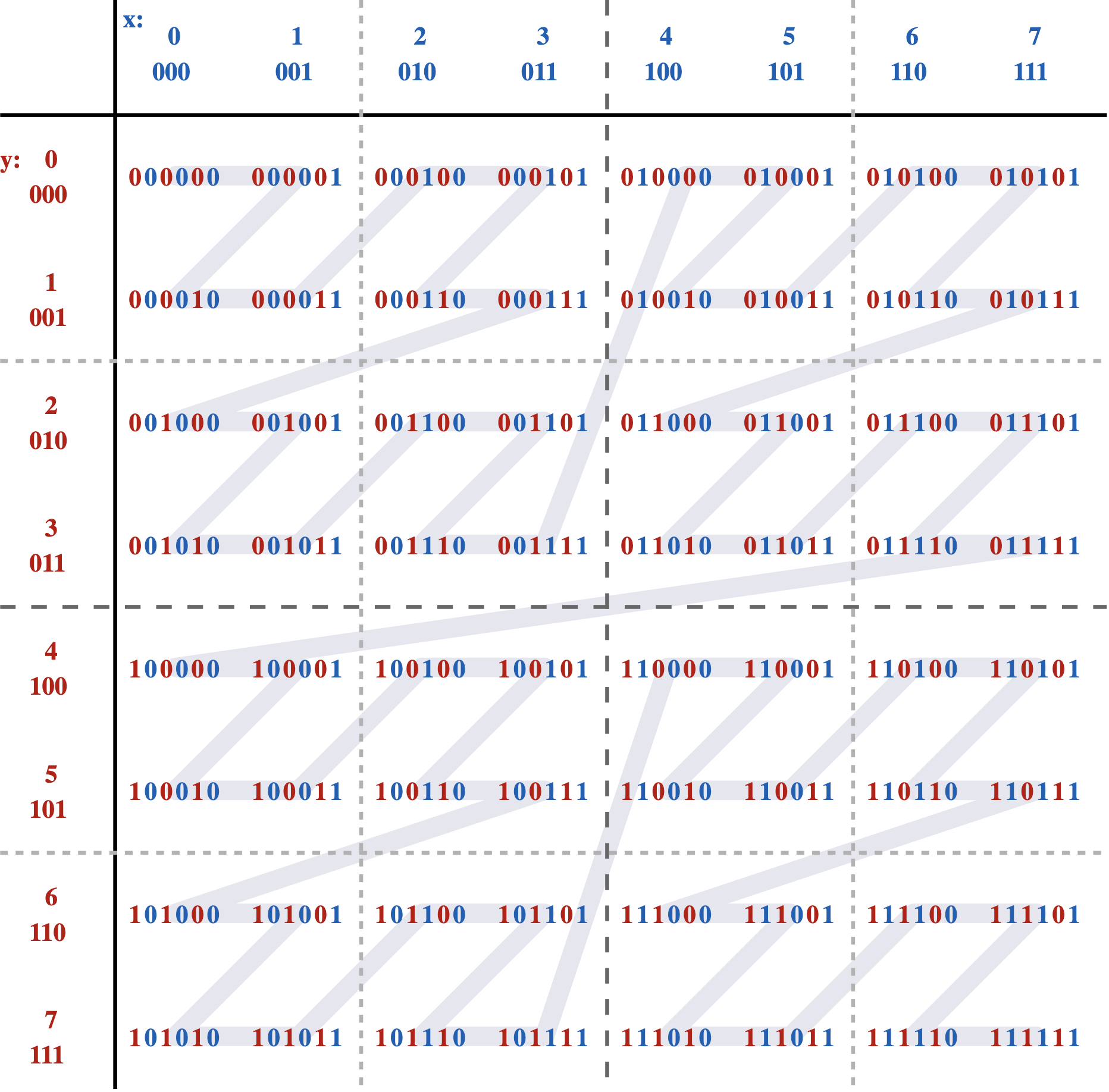
可以看到按照路径,不是简单地先按一个坐标 ("x") 排序,然后再按另一个坐标排序,它实际上是在对它们进行排序,就好像这些坐标的位已交织成单个值一样:
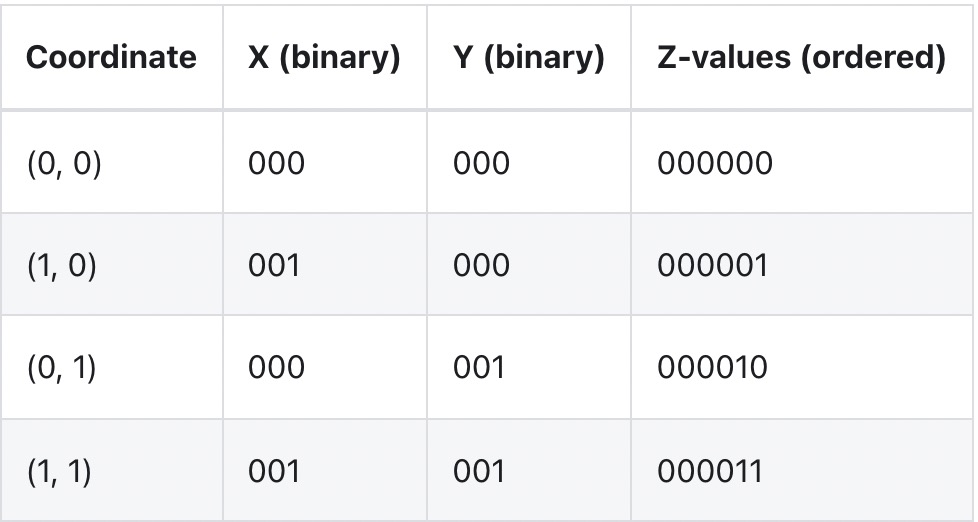
在线性排序的情况下局部性仅使用第一列相比,该方法的局部性使用到所有列。
以类似的方式,希尔伯特曲线允许将 N 维空间中的点(我们表中的行)映射到一维曲线上,基本上对它们进行排序,同时仍然保留局部性的关键属性,在此处阅读有关希尔伯特曲线的更多详细信息,到目前为止我们的实验表明,使用希尔伯特曲线对数据进行排序会有更好的聚簇和性能结果。
现在让我们来看看它的实际效果!
2. 设置
我们将再次使用 Amazon Reviews 数据集,但这次我们将使用 Hudi 按 product_id、customer_id 列元组进行 Z-Order排序,而不是聚簇或线性排序。
数据集不需要特别的准备,可以直接从 S3 中以 Parquet 格式下载并将其直接用作 Spark 将其摄取到 Hudi 表。
启动spark-shell
./bin/spark-shell --master 'local[4]' --driver-memory 8G --executor-memory 8G \
--jars ../../packaging/hudi-spark-bundle/target/hudi-spark3-bundle_2.12-0.10.0.jar \
--packages org.apache.spark:spark-avro_2.12:2.4.4 \
--conf 'spark.serializer=org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer'
导入Hudi表
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.{FileStatus, Path}
import scala.collection.JavaConversions._
import org.apache.spark.sql.SaveMode._
import org.apache.hudi.{DataSourceReadOptions, DataSourceWriteOptions}
import org.apache.hudi.DataSourceWriteOptions._
import org.apache.hudi.common.fs.FSUtils
import org.apache.hudi.common.table.HoodieTableMetaClient
import org.apache.hudi.common.util.ClusteringUtils
import org.apache.hudi.config.HoodieClusteringConfig
import org.apache.hudi.config.HoodieWriteConfig._
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import java.util.stream.Collectors
val layoutOptStrategy = "z-order"; // OR "hilbert"
val inputPath = s"file:///${System.getProperty("user.home")}/datasets/amazon_reviews_parquet"
val tableName = s"amazon_reviews_${layoutOptStrategy}"
val outputPath = s"file:///tmp/hudi/$tableName"
def safeTableName(s: String) = s.replace('-', '_')
val commonOpts =
Map(
"hoodie.compact.inline" -> "false",
"hoodie.bulk_insert.shuffle.parallelism" -> "10"
)
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Writing to Hudi
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
val df = spark.read.parquet(inputPath)
df.write.format("hudi")
.option(DataSourceWriteOptions.TABLE_TYPE.key(), COW_TABLE_TYPE_OPT_VAL)
.option("hoodie.table.name", tableName)
.option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD.key(), "review_id")
.option(RECORDKEY_FIELD.key(), "review_id")
.option(DataSourceWriteOptions.PARTITIONPATH_FIELD.key(), "product_category")
.option("hoodie.clustering.inline", "true")
.option("hoodie.clustering.inline.max.commits", "1")
// NOTE: Small file limit is intentionally kept _ABOVE_ target file-size max threshold for Clustering,
// to force re-clustering
.option("hoodie.clustering.plan.strategy.small.file.limit", String.valueOf(1024 * 1024 * 1024)) // 1Gb
.option("hoodie.clustering.plan.strategy.target.file.max.bytes", String.valueOf(128 * 1024 * 1024)) // 128Mb
// NOTE: We're increasing cap on number of file-groups produced as part of the Clustering run to be able to accommodate for the
// whole dataset (~33Gb)
.option("hoodie.clustering.plan.strategy.max.num.groups", String.valueOf(4096))
.option(HoodieClusteringConfig.LAYOUT_OPTIMIZE_ENABLE.key, "true")
.option(HoodieClusteringConfig.LAYOUT_OPTIMIZE_STRATEGY.key, layoutOptStrategy)
.option(HoodieClusteringConfig.PLAN_STRATEGY_SORT_COLUMNS.key, "product_id,customer_id")
.option(DataSourceWriteOptions.OPERATION.key(), DataSourceWriteOptions.BULK_INSERT_OPERATION_OPT_VAL)
.option(BULK_INSERT_SORT_MODE.key(), "NONE")
.options(commonOpts)
.mode(ErrorIfExists)
3. 测试
每个单独的测试请在单独的 spark-shell 中运行,以避免缓存影响测试结果。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Reading
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Temp Table w/ Data Skipping DISABLED
val readDf: DataFrame =
spark.read.option(DataSourceReadOptions.ENABLE_DATA_SKIPPING.key(), "false").format("hudi").load(outputPath)
val rawSnapshotTableName = safeTableName(s"${tableName}_sql_snapshot")
readDf.createOrReplaceTempView(rawSnapshotTableName)
// Temp Table w/ Data Skipping ENABLED
val readDfSkip: DataFrame =
spark.read.option(DataSourceReadOptions.ENABLE_DATA_SKIPPING.key(), "true").format("hudi").load(outputPath)
val dataSkippingSnapshotTableName = safeTableName(s"${tableName}_sql_snapshot_skipping")
readDfSkip.createOrReplaceTempView(dataSkippingSnapshotTableName)
// Query 1: Total votes by product_category, for 6 months
def runQuery1(tableName: String) = {
// Query 1: Total votes by product_category, for 6 months
spark.sql(s"SELECT sum(total_votes), product_category FROM $tableName WHERE review_date > '2013-12-15' AND review_date < '2014-06-01' GROUP BY product_category").show()
}
// Query 2: Average star rating by product_id, for some product
def runQuery2(tableName: String) = {
spark.sql(s"SELECT avg(star_rating), product_id FROM $tableName WHERE product_id in ('B0184XC75U') GROUP BY product_id").show()
}
// Query 3: Count number of reviews by customer_id for some 5 customers
def runQuery3(tableName: String) = {
spark.sql(s"SELECT count(*) as num_reviews, customer_id FROM $tableName WHERE customer_id in ('53096570','10046284','53096576','10000196','21700145') GROUP BY customer_id").show()
}
//
// Query 1: Is a "wide" query and hence it's expected to touch a lot of files
//
scala> runQuery1(rawSnapshotTableName)
+----------------+--------------------+
|sum(total_votes)| product_category|
+----------------+--------------------+
| 1050944| PC|
| 867794| Kitchen|
| 1167489| Home|
| 927531| Wireless|
| 6861| Video|
| 39602| Digital_Video_Games|
| 954924|Digital_Video_Dow...|
| 81876| Luggage|
| 320536| Video_Games|
| 817679| Sports|
| 11451| Mobile_Electronics|
| 228739| Home_Entertainment|
| 3769269|Digital_Ebook_Pur...|
| 252273| Baby|
| 735042| Apparel|
| 49101| Major_Appliances|
| 484732| Grocery|
| 285682| Tools|
| 459980| Electronics|
| 454258| Outdoors|
+----------------+--------------------+
only showing top 20 rows
scala> runQuery1(dataSkippingSnapshotTableName)
+----------------+--------------------+
|sum(total_votes)| product_category|
+----------------+--------------------+
| 1050944| PC|
| 867794| Kitchen|
| 1167489| Home|
| 927531| Wireless|
| 6861| Video|
| 39602| Digital_Video_Games|
| 954924|Digital_Video_Dow...|
| 81876| Luggage|
| 320536| Video_Games|
| 817679| Sports|
| 11451| Mobile_Electronics|
| 228739| Home_Entertainment|
| 3769269|Digital_Ebook_Pur...|
| 252273| Baby|
| 735042| Apparel|
| 49101| Major_Appliances|
| 484732| Grocery|
| 285682| Tools|
| 459980| Electronics|
| 454258| Outdoors|
+----------------+--------------------+
only showing top 20 rows
//
// Query 2: Is a "pointwise" query and hence it's expected that data-skipping should substantially reduce number
// of files scanned (as compared to Baseline)
//
// NOTE: That Linear Ordering (as compared to Space-curve based on) will have similar effect on performance reducing
// total # of Parquet files scanned, since we're querying on the prefix of the ordering key
//
scala> runQuery2(rawSnapshotTableName)
+----------------+----------+
|avg(star_rating)|product_id|
+----------------+----------+
| 1.0|B0184XC75U|
+----------------+----------+
scala> runQuery2(dataSkippingSnapshotTableName)
+----------------+----------+
|avg(star_rating)|product_id|
+----------------+----------+
| 1.0|B0184XC75U|
+----------------+----------+
//
// Query 3: Similar to Q2, is a "pointwise" query, but querying other part of the ordering-key (product_id, customer_id)
// and hence it's expected that data-skipping should substantially reduce number of files scanned (as compared to Baseline, Linear Ordering).
//
// NOTE: That Linear Ordering (as compared to Space-curve based on) will _NOT_ have similar effect on performance reducing
// total # of Parquet files scanned, since we're NOT querying on the prefix of the ordering key
//
scala> runQuery3(rawSnapshotTableName)
+-----------+-----------+
|num_reviews|customer_id|
+-----------+-----------+
| 50| 53096570|
| 3| 53096576|
| 25| 10046284|
| 1| 10000196|
| 14| 21700145|
+-----------+-----------+
scala> runQuery3(dataSkippingSnapshotTableName)
+-----------+-----------+
|num_reviews|customer_id|
+-----------+-----------+
| 50| 53096570|
| 3| 53096576|
| 25| 10046284|
| 1| 10000196|
| 14| 21700145|
+-----------+-----------+
4. 结果
我们总结了以下的测试结果
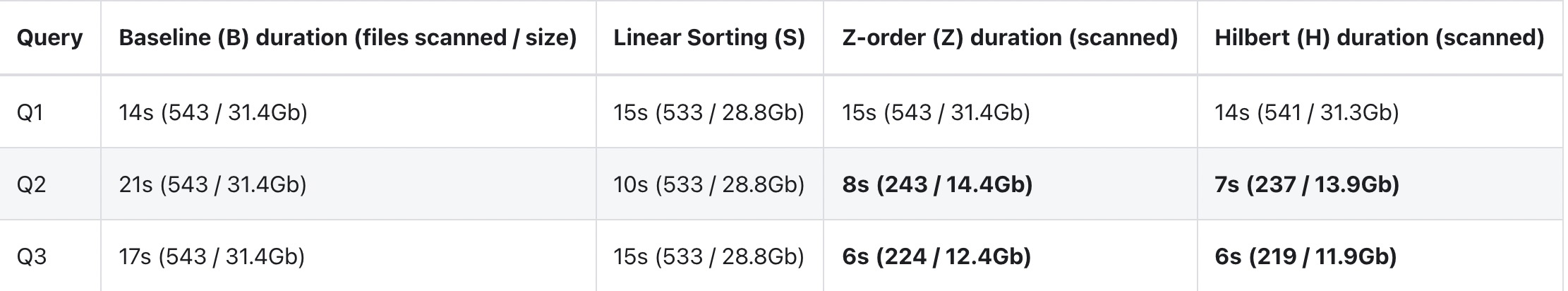
可以看到多列线性排序对于按列(Q2、Q3)以外的列进行过滤的查询不是很有效,这与空间填充曲线(Z-order 和 Hilbert)形成了非常明显的对比,后者将查询时间加快多达 3倍 。值得注意的是性能提升在很大程度上取决于基础数据和查询,在我们内部数据的基准测试中,能够实现超过 11倍 的查询性能改进!
5. 总结
Apache Hudi v0.10 为开源带来了新的布局优化功能 Z-order 和 Hilbert。 使用这些行业领先的布局优化技术可以为用户查询带来显着的性能提升和成本节约!
查询性能提升3倍!Apache Hudi 查询优化了解下?的更多相关文章
- 使用Apache Spark 对 mysql 调优 查询速度提升10倍以上
在这篇文章中我们将讨论如何利用 Apache Spark 来提升 MySQL 的查询性能. 介绍 在我的前一篇文章Apache Spark with MySQL 中介绍了如何利用 Apache Spa ...
- 重构、插件化、性能提升 20 倍,Apache DolphinScheduler 2.0 alpha 发布亮点太多!
点击上方 蓝字关注我们 社区的小伙伴们,好消息!经过 100 多位社区贡献者近 10 个月的共同努力,我们很高兴地宣布 Apache DolphinScheduler 2.0 alpha 发布.这是 ...
- Web 应用性能提升 10 倍的 10 个建议
转载自http://blog.jobbole.com/94962/ 提升 Web 应用的性能变得越来越重要.线上经济活动的份额持续增长,当前发达世界中 5 % 的经济发生在互联网上(查看下面资源的统计 ...
- 查询效率提升10倍!3种优化方案,帮你解决MySQL深分页问题
开发经常遇到分页查询的需求,但是当翻页过多的时候,就会产生深分页,导致查询效率急剧下降. 有没有什么办法,能解决深分页的问题呢? 本文总结了三种优化方案,查询效率直接提升10倍,一起学习一下. 1. ...
- 优化临时表使用,SQL语句性能提升100倍
[问题现象] 线上mysql数据库爆出一个慢查询,DBA观察发现,查询时服务器IO飙升,IO占用率达到100%, 执行时间长达7s左右.SQL语句如下:SELECT DISTINCT g.*, cp. ...
- 转--优化临时表使用,SQL语句性能提升100倍
转自:http://www.51testing.com/html/01/n-867201-2.html [问题现象] 线上mysql数据库爆出一个慢查询,DBA观察发现,查询时服务器IO飙升,IO占用 ...
- 在MongoDB中创建一个索引而性能提升1000倍的小例子
在https://www.cnblogs.com/xuliuzai/p/9965229.html的博文中我们介绍了MongoDB的常见索引的创建语法.部分同学还想看看MongoDB的威力到底有多大,所 ...
- 存算分离下写性能提升10倍以上,EMR Spark引擎是如何做到的?
引言 随着大数据技术架构的演进,存储与计算分离的架构能更好的满足用户对降低数据存储成本,按需调度计算资源的诉求,正在成为越来越多人的选择.相较 HDFS,数据存储在对象存储上可以节约存储成本,但与此 ...
- Nacos 2.0 正式发布,性能提升 10 倍!!
3月20号,Nacos 2.0.0 正式发布了! Nacos 简介: 一个更易于构建云原生应用的动态服务发现.配置管理和服务管理平台. 通俗点讲,Nacos 就是一把微服务双刃剑:注册中心 + 配置中 ...
随机推荐
- linux实时监控并实时备份数据(rsync)
目录 一:rsync实时监控备份流程 1.安装rsync(服务端 与 客服端)守护进程模式 2.修改配置文件(服务端) 3.解析配置内容 4.创建系统用户 5.创建密码文件 6.授权(必须授权为600 ...
- Elasticsearch(2) 数据搜索
本文介绍如何在Elasticsearch中对数据进行搜索. 1.简述 在Elasticsearch中的搜索中,有两类搜索: queries aggregations 区别在于:query可以进行全文搜 ...
- tmux 入门教程
tmux 本教程是基于ACWing的<Linux基础课>所做,希望大家支持ACWing 功能 分屏 当需要同时运行两个终端,并且进行比对着输入时,来回切换比较麻烦,就可以利用分屏 可以在一 ...
- 聊一聊如何用C#轻松完成一个TCC分布式事务
背景 银行跨行转账业务是一个典型分布式事务场景,假设 A 需要跨行转账给 B,那么就涉及两个银行的数据,无法通过一个数据库的本地事务保证转账的 ACID ,只能够通过分布式事务来解决. 在 聊一聊如何 ...
- ARC-124 部分题解
E 直接统计原式不好做,注意到首先我们应该知道怎样的 \(x\) 序列是合法的,那么不妨首先来统计一下合法的 \(x\) 序列数量. 令 \(b_i\) 为 \(i\) 向右给的球数,那么有(\(i ...
- Windows点击更改适配器选项出现的网络连接为空
前言:windows出现点击更改适配器选项出现的网络连接为空,一直找了很久,没有找到方法 解决方案: 1:点击状态: 2:点击网络重置 最后:电脑进行重启,即可.
- git命令log与reflog的比较
感谢原文作者:杨鲜生 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u013252047/article/details/80230781 用git命令,想看到自己的操作记录,则可以使用log ...
- JVM性能调优与实战基础理论篇-下
JVM内存管理 JVM内存分配与回收策略 对象优先在Eden分配,如果Eden内存空间不足,就会发生Minor GC.虚拟机提供了-XX:+PrintGCDetails这个收集器日志参数,告诉虚拟机在 ...
- Solution -「CF 494C」Helping People
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定序列 \(\{a_n\}\) 和 \(m\) 个操作,第 \(i\) 个操作有 \(p_i\) 的概率将 \([l_i,r_ ...
- NPM 错误、问题等汇总
一. npm的作用就是对Node.js依赖的包进行管理,也可以理解为用来安装/卸载Node.js需要装的东西 二. 1. 修改npm配置为淘宝的源下载: npm install -g cnpm --r ...
