MIPS汇编学习
MIPS汇编学习
mips汇编不同于x86汇编,属于精简指令集,常见于路由器等一些嵌入式设备中。
mips汇编没有对堆栈的直接操作,也就是没有push和pop指令,mips汇编中保留了32个通用寄存器,但是不同于x86汇编,mips汇编中没有ebp/rbp寄存器。
mips每条指令都用固定的长度,每条指令都是四个字节,所以内存数据的访问必须以32位严格对齐,这一点也不同于x86汇编。
通过一个demo,用mips-linux-gnu-gcc编译,通过IDA远程调试,来理解mips汇编中的一些概念。
#include<stdio.h>
int sum(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
int main()
{
int a=1,b=2,c;
c=sum(a,b);
printf("%d\n",c);
return 0;
}
32个通用寄存器的功能和使用约定定义如下:
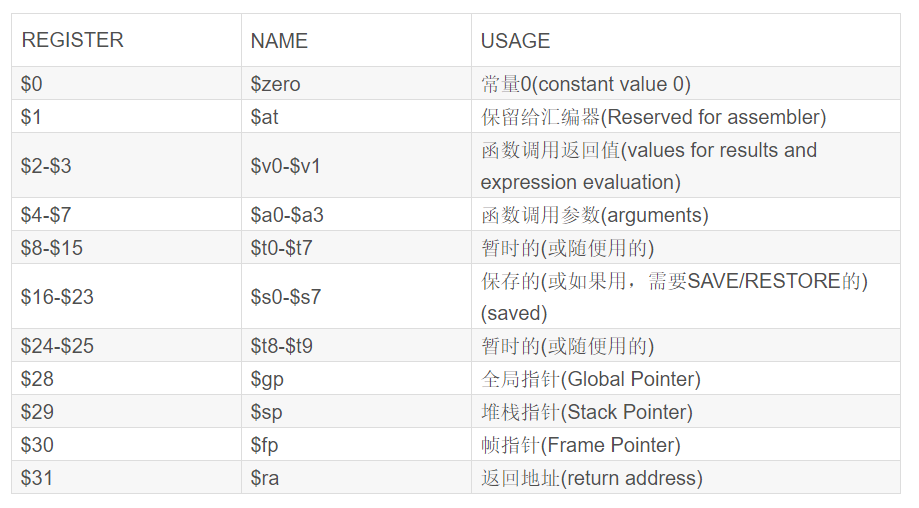
mips汇编中重要的寄存器:
1.堆栈指针$sp,也就是$29指向堆栈的栈顶,类似于x86中的ebp和rbp指针;
2.$0寄存器的值始终为常数0;
3.PC寄存器保留程序执行的下一条指令,相当于x86架构中的eip寄存器;
4.参数传递的时候,$a0-$a3寄存器保存函数的前四个参数,其他的参数保存在栈中;
5.$ra寄存器,保存着函数的返回地址,这一点也不同于x86汇编中将返回地址保存在栈中。在函数A执行到调用函数B的指令时,函数调用指令复制当前的$PC寄存器的值到$RA寄存器,然后跳转到B函数去执行,即当前$RA寄存器的值就是函数执行结束时的返回地址。
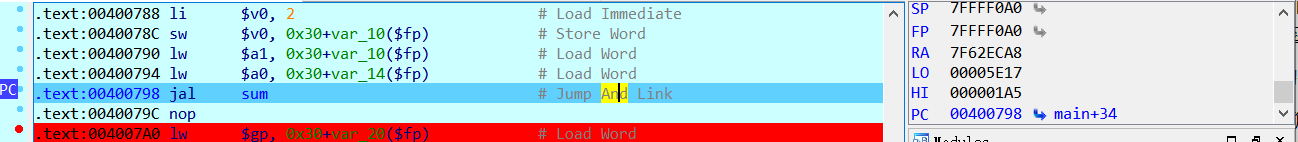 如上图所示,调用sum函数之前,$ra寄存器的值是0x7f62eca8。
如上图所示,调用sum函数之前,$ra寄存器的值是0x7f62eca8。
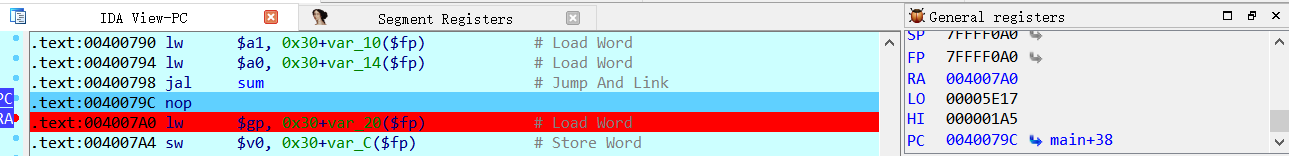
进入分支延迟槽之后,$ra寄存器的值被赋值为$pc寄存器的下一条指令地址。在结束sun函数调用之后,通过:jr $ra指令跳转回main函数继续执行。
5.mips架构下,对静态数据段的访问,通过$gp寄存器配合基址寻址来实现;
7.$30寄存器表示帧指针,指向正在被调用的栈桢,mips和x86由于堆栈结构的区别,调用栈时会出现一些不同。mips硬件并不直接支持堆栈,x86有单独的push和pop指令,但是mips没有栈操作指令,所有对栈的操作都是统一的内存访问方式。
x86中,栈桢入口点开辟栈桢的操作:
push ebp
mov ebp,esp
sub esp,0x30
x86中,栈桢出口点退栈的操作:
leave # push ebp
# mov ebp,esp
ret # pop eip
由以上函数入口点和出口点的操作我们可以清晰地看出,x86架构中,同一个函数中,esp始终指向函数调用栈的栈顶,ebp始终指向函数调用栈的栈基。
但是在mips架构下,没有指向栈基的寄存器,这时候如何确定函数调用的栈桢呢?
$fp(帧指针)和 $sp(栈指针) 来确定函数的调用栈。$sp寄存器作为堆栈寄存器,始终指向栈顶。进入一个函数是,需要将当前栈指针向下移动n字节,这个大小为n字节的存储空间就是此函数的Stack Frame的存储区域,此后栈指针便不再移动,只通过函数返回是将栈指针加上偏移量恢复栈现场。由于不能随便移动栈指针,所以寄存器压栈和出栈时都要指定偏移量。
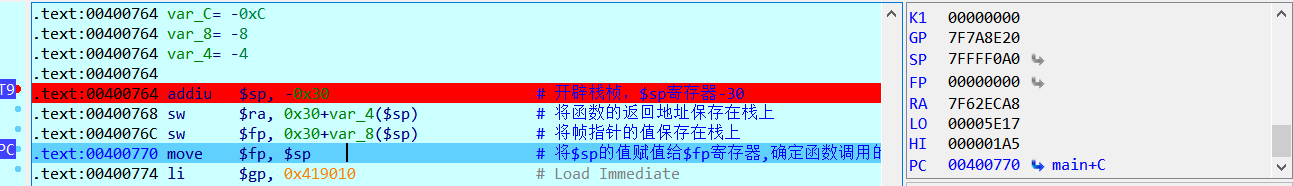
可以看到,mips架构中,在函数入口处以addiu $sp,-0x30来开辟栈桢,当程序运行到0x400770地址处时,$fp寄存器的值被保留到了栈上,$fp寄存器的值为0。
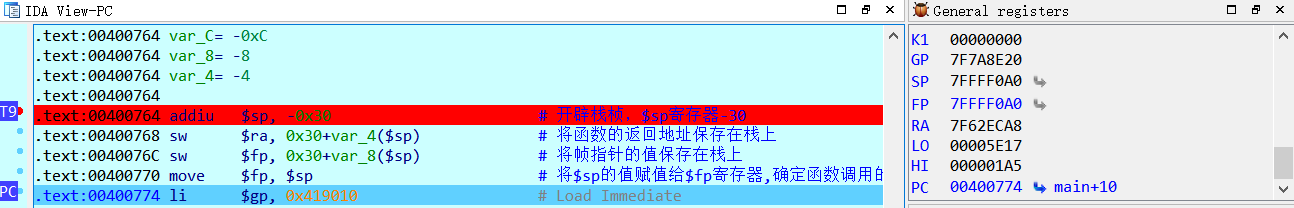
继续单步执行,看到将$sp寄存器的值赋值给了$fp寄存器,这时候堆栈寄存器和帧指针同时指向当前调用栈的栈顶。

继续单步执行,0x40079c地址处,我们在sum函数的入口处下一个断点,由于mips架构的分支延迟机制,nop指令就是一个分支延迟槽。执行完nop指令之后,接下来我们会步进到sum函数中,进入sum函数之后,我们再来观察$sp寄存器和$fp寄存器的变化情况。

可以看到,addiu指令再次开辟了8字节大小的栈桢。

单步执行到0x40073c地址处,$fp寄存器的值在赋值前被保留在栈上,$fp寄存器被再次赋值,指向当前调用栈的栈顶。

结束函数调用之后,$fp和$sp还原为指向main函数调用栈的栈顶。可以看到,$fp寄存器主要用来进行基址寻址。所有针对栈区变量的取址,都通过基址寻址来对内存进行访问。
mips汇编函数调用过程中与x86架构的区别:
- mips架构和x86架构中,栈的增长方向相同,都是从高地址向低地址增长,但是没有栈底指针,所以调用一个函数是,需要将当前栈向低地址处移动n比特这个大小为n比特的空间就是此函数的栈桢存储区域;
- mips架构中有叶子函数和非叶子函数的区别,叶子函数就是此函数自身不再调用别的函数,非叶子函数就是此函数自身调用别的函数。如果函数A调用函数B,调用者函数会在自己的栈顶预留一部分空间来保存被调用者(函数B)的参数,称之为参数调用空间;
- 函数调用过程中,父函数调用子函数,复制当前$PC的值到$RA寄存器,然后跳转到子函数执行。到子函数是,子函数如果为非叶子函数,则子函数的返回地址会先存入堆栈
- 参数传递方式,前四个参数通过$a0-$a3来传递,多于的参数会放入调用参数空间(参数会被保存在栈上),可以类比x86_64参数传递规则来进行记忆。
mips架构的四种取址方式:
1.基址寻址;(load-store)
根据我们上面的例子可以看到,基址寻址是对mips架构下堆栈数据进行存储和加载的主要方式。
2.立即数寻址;(load-store)
3.寄存器寻址;(R型指令)
4.伪立即数寻址;(J型指令)
叶子函数和非叶子函数:
一个函数如果不再调用其他的函数,那么这个函数是叶子函数,一个函数如果调用其他的函数,那么这个函数是非叶子函数。一般来说,函数都是非叶子函数。
叶子函数和非叶子函数在存放返回地址的时候,存在差异。叶子函数只把返回地址保存在$ra寄存其中,结束函数调用的时候,通过jr $ra指令返回即可。非叶子函数把在函数调用初始把$ra寄存器中的返回地址保存在栈中,然后结束函数调用的时候将栈中保存的返回地址加载到$ra寄存器中,再通过jr $ra指令返回。
举例如下:
叶子函数函数入口:

非叶子函数函数入口:
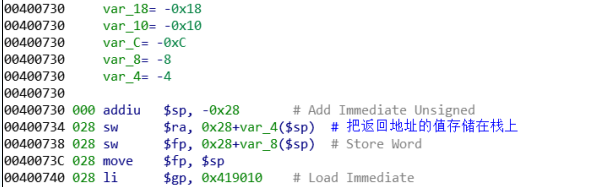
叶子函数函数出口:

非叶子函数函数出口:
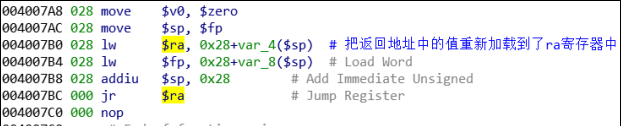
叶子函数和非叶子函数的差别,造成栈溢出漏洞利用的差别。对于非叶子函数而言,如果我们的溢出可以覆盖栈上保存的$ra寄存器的值,这时候在栈上的值返回给$ra寄存器的时候,我们就可以劫持程序的数据流。
通过《揭秘家用路由器0day漏洞挖掘技术》这本书中的一个例子来展示MIPS32架构下函数的参数传递及堆栈布局的变化:
#include<stdio.h> int more_reg(int a,int b,int c,int d,int e)
{
char dst[100]={0};
sprintf(dst,"%d%d%d%d%d\n",a,b,c,d,e);
} int main()
{
int a1=1,a2=2,a3=3,a4=4,a5=5;
more_reg(a1,a2,a3,a4,a5);
return 0;
}
静态链接,编译选项:
mips-linux-gnu-gcc -o demo1 demo1.c -static

由上图看到,函数传递了5个参数,前四个参数首先保存在栈上,然后在调用more_reg函数的时候,把栈区的变量传递到$a0-$a3这四个寄存器中。其中第五个参数保留在0x40+var_30($sp)这个地址处。可以看到,虽然函数more_reg的前四个参数是由$a0-$a3这四个寄存器传递的,但是栈区仍然保留了16个字节的参数空间,就是0x40+var_20($fp)到0x40+var_30($fp)这段空间。
断点0x400660处,就是将变量值从临时变量$v0中取出,存储到0x40+var_30($fp)处,然后0x40+var_30($fp)作为第五个参数传递到more_reg函数中去。
MIPS系统调用
mips架构中,syscall用于从内核请求服务。对于MIPS,必须在$v0中传递服务编号/代号,然后将参数赋值给$a0,$a1,$a2三个,然后使用syscall指令触发中断,来调用相应函数。
如果linux中搭建了mips的交叉编译环境的话,mips的系统调用号可以在/usr/mips-linux-gnu/include/asm/unistd.h中看到,调用号是从4000开始的。
#define __NR_Linux 4000
#define __NR_syscall (__NR_Linux + 0)
#define __NR_exit (__NR_Linux + 1)
#define __NR_fork (__NR_Linux + 2)
#define __NR_read (__NR_Linux + 3)
#define __NR_write (__NR_Linux + 4)
#define __NR_open (__NR_Linux + 5)
#define __NR_close (__NR_Linux + 6)
#define __NR_waitpid (__NR_Linux + 7)
#define __NR_creat (__NR_Linux + 8)
#define __NR_link (__NR_Linux + 9)
#define __NR_unlink (__NR_Linux + 10)
#define __NR_execve (__NR_Linux + 11)
#define __NR_chdir (__NR_Linux + 12)
#define __NR_time (__NR_Linux + 13)
#define __NR_mknod (__NR_Linux + 14)
#define __NR_chmod (__NR_Linux + 15)
#define __NR_lchown (__NR_Linux + 16)
#define __NR_break (__NR_Linux + 17)
#define __NR_unused18 (__NR_Linux + 18)
#define __NR_lseek (__NR_Linux + 19)
#define __NR_getpid (__NR_Linux + 20)
#define __NR_mount (__NR_Linux + 21)
#define __NR_umount (__NR_Linux + 22)
#define __NR_setuid (__NR_Linux + 23)
#define __NR_getuid (__NR_Linux + 24)
#define __NR_stime (__NR_Linux + 25)
#define __NR_ptrace (__NR_Linux + 26)
#define __NR_alarm (__NR_Linux + 27)
#define __NR_unused28 (__NR_Linux + 28)
#define __NR_pause (__NR_Linux + 29)
#define __NR_utime (__NR_Linux + 30)
#define __NR_stty (__NR_Linux + 31)
#define __NR_gtty (__NR_Linux + 32)
#define __NR_access (__NR_Linux + 33)
#define __NR_nice (__NR_Linux + 34)
#define __NR_ftime (__NR_Linux + 35)
#define __NR_sync (__NR_Linux + 36)
#define __NR_kill (__NR_Linux + 37)
#define __NR_rename (__NR_Linux + 38)
#define __NR_mkdir (__NR_Linux + 39)
#define __NR_rmdir (__NR_Linux + 40)
#define __NR_dup (__NR_Linux + 41)
#define __NR_pipe (__NR_Linux + 42)
#define __NR_times (__NR_Linux + 43)
#define __NR_prof (__NR_Linux + 44)
#define __NR_brk (__NR_Linux + 45)
#define __NR_setgid (__NR_Linux + 46)
#define __NR_getgid (__NR_Linux + 47)
#define __NR_signal (__NR_Linux + 48)
#define __NR_geteuid (__NR_Linux + 49)
#define __NR_getegid (__NR_Linux + 50)
#define __NR_acct (__NR_Linux + 51)
#define __NR_umount2 (__NR_Linux + 52)
#define __NR_lock (__NR_Linux + 53)
#define __NR_ioctl (__NR_Linux + 54)
#define __NR_fcntl (__NR_Linux + 55)
#define __NR_mpx (__NR_Linux + 56)
#define __NR_setpgid (__NR_Linux + 57)
#define __NR_ulimit (__NR_Linux + 58)
#define __NR_unused59 (__NR_Linux + 59)
#define __NR_umask (__NR_Linux + 60)
#define __NR_chroot (__NR_Linux + 61)
#define __NR_ustat (__NR_Linux + 62)
#define __NR_dup2 (__NR_Linux + 63)
#define __NR_getppid (__NR_Linux + 64)
#define __NR_getpgrp (__NR_Linux + 65)
#define __NR_setsid (__NR_Linux + 66)
#define __NR_sigaction (__NR_Linux + 67)
#define __NR_sgetmask (__NR_Linux + 68)
#define __NR_ssetmask (__NR_Linux + 69)
#define __NR_setreuid (__NR_Linux + 70)
#define __NR_setregid (__NR_Linux + 71)
#define __NR_sigsuspend (__NR_Linux + 72)
#define __NR_sigpending (__NR_Linux + 73)
#define __NR_sethostname (__NR_Linux + 74)
#define __NR_setrlimit (__NR_Linux + 75)
#define __NR_getrlimit (__NR_Linux + 76)
#define __NR_getrusage (__NR_Linux + 77)
#define __NR_gettimeofday (__NR_Linux + 78)
#define __NR_settimeofday (__NR_Linux + 79)
#define __NR_getgroups (__NR_Linux + 80)
#define __NR_setgroups (__NR_Linux + 81)
#define __NR_reserved82 (__NR_Linux + 82)
#define __NR_symlink (__NR_Linux + 83)
#define __NR_unused84 (__NR_Linux + 84)
#define __NR_readlink (__NR_Linux + 85)
#define __NR_uselib (__NR_Linux + 86)
#define __NR_swapon (__NR_Linux + 87)
#define __NR_reboot (__NR_Linux + 88)
#define __NR_readdir (__NR_Linux + 89)
#define __NR_mmap (__NR_Linux + 90)
#define __NR_munmap (__NR_Linux + 91)
#define __NR_truncate (__NR_Linux + 92)
#define __NR_ftruncate (__NR_Linux + 93)
#define __NR_fchmod (__NR_Linux + 94)
#define __NR_fchown (__NR_Linux + 95)
#define __NR_getpriority (__NR_Linux + 96)
#define __NR_setpriority (__NR_Linux + 97)
#define __NR_profil (__NR_Linux + 98)
#define __NR_statfs (__NR_Linux + 99)
#define __NR_fstatfs (__NR_Linux + 100)
#define __NR_ioperm (__NR_Linux + 101)
#define __NR_socketcall (__NR_Linux + 102)
#define __NR_syslog (__NR_Linux + 103)
#define __NR_setitimer (__NR_Linux + 104)
#define __NR_getitimer (__NR_Linux + 105)
#define __NR_stat (__NR_Linux + 106)
#define __NR_lstat (__NR_Linux + 107)
#define __NR_fstat (__NR_Linux + 108)
#define __NR_unused109 (__NR_Linux + 109)
#define __NR_iopl (__NR_Linux + 110)
#define __NR_vhangup (__NR_Linux + 111)
#define __NR_idle (__NR_Linux + 112)
#define __NR_vm86 (__NR_Linux + 113)
#define __NR_wait4 (__NR_Linux + 114)
#define __NR_swapoff (__NR_Linux + 115)
#define __NR_sysinfo (__NR_Linux + 116)
#define __NR_ipc (__NR_Linux + 117)
#define __NR_fsync (__NR_Linux + 118)
#define __NR_sigreturn (__NR_Linux + 119)
#define __NR_clone (__NR_Linux + 120)
#define __NR_setdomainname (__NR_Linux + 121)
#define __NR_uname (__NR_Linux + 122)
#define __NR_modify_ldt (__NR_Linux + 123)
#define __NR_adjtimex (__NR_Linux + 124)
#define __NR_mprotect (__NR_Linux + 125)
#define __NR_sigprocmask (__NR_Linux + 126)
#define __NR_create_module (__NR_Linux + 127)
#define __NR_init_module (__NR_Linux + 128)
#define __NR_delete_module (__NR_Linux + 129)
#define __NR_get_kernel_syms (__NR_Linux + 130)
#define __NR_quotactl (__NR_Linux + 131)
#define __NR_getpgid (__NR_Linux + 132)
#define __NR_fchdir (__NR_Linux + 133)
#define __NR_bdflush (__NR_Linux + 134)
#define __NR_sysfs (__NR_Linux + 135)
#define __NR_personality (__NR_Linux + 136)
#define __NR_afs_syscall (__NR_Linux + 137) /* Syscall for Andrew File System */
可以写一个write.c的,然后生成汇编代码,看一下write函数的系统调用。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h> int main()
{
char *dst="Hello world!\n";
write(1,dst,13);
return 0;
}
以下命令编译:
mips-linux-gnu-gcc write_syscall.c -S -o write_syscall.s
生成汇编代码如下所示:
.file 1 "write_syscall.c"
.section .mdebug.abi32
.previous
.nan legacy
.module fp=xx
.module nooddspreg
.abicalls
.text
.rdata
.align 2
$LC0:
.ascii "Hello world!\012\000"
.text
.align 2
.globl main
.set nomips16
.set nomicromips
.ent main
.type main, @function
main:
.frame $fp,40,$31 # vars= 8, regs= 2/0, args= 16, gp= 8
.mask 0xc0000000,-4
.fmask 0x00000000,0
.set noreorder
.set nomacro
addiu $sp,$sp,-40
sw $31,36($sp)
sw $fp,32($sp)
move $fp,$sp
lui $28,%hi(__gnu_local_gp)
addiu $28,$28,%lo(__gnu_local_gp)
.cprestore 16
lui $2,%hi($LC0)
addiu $2,$2,%lo($LC0)
sw $2,28($fp)
li $6,13 # 0xd $a2寄存器
lw $5,28($fp) # $a1 寄存器
li $4,1 # 0x1 $a0寄存器
lw $2,%call16(write)($28) # $v0寄存器
move $25,$2
.reloc 1f,R_MIPS_JALR,write
1: jalr $25
nop lw $28,16($fp)
move $2,$0
move $sp,$fp
lw $31,36($sp)
lw $fp,32($sp)
addiu $sp,$sp,40
jr $31
nop .set macro
.set reorder
.end main
.size main, .-main
.ident "GCC: (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0"
简化之后,write.s的系统调用可以写为如下形式:
.section .text
.globl __start
.set noreorder
__start:
addiu $sp,$sp,-32
lui $t6,0x4142
ori $t6,$t6,0x430a
sw $t6,0($sp)
li $a0,1
addiu $a1,$sp,0
li $a2,5
li $v0,4004
syscall
shell脚本编译为二进制可执行文件:
#!/bin/sh
# $ sh name.sh <source file><excute file> src=$1
dst=$2
mips-linux-gnu-as $src -o s.o
mips-linux-gnu-ld s.o -o $dst
rm s.o
readelf -S write定位text段入口地址:
pwndbg> disass /r 0x4000d0
Dump of assembler code for function _ftext:
0x004000d0 <+0>: 27 bd ff e0 addiu sp,sp,-32
0x004000d4 <+4>: 3c 0e 41 42 lui t6,0x4142
0x004000d8 <+8>: 35 ce 43 0a ori t6,t6,0x430a
0x004000dc <+12>: af ae 00 00 sw t6,0(sp)
0x004000e0 <+16>: 24 04 00 01 li a0,1
0x004000e4 <+20>: 27 a5 00 00 addiu a1,sp,0
0x004000e8 <+24>: 24 06 00 05 li a2,5
0x004000ec <+28>: 24 02 0f a4 li v0,4004
0x004000f0 <+32>: 00 00 00 0c syscall
0x004000f4 <+36>: 00 00 00 00 nop
0x004000f8 <+40>: 00 00 00 00 nop
0x004000fc <+44>: 00 00 00 00 nop
End of assembler dump.
可以提取16进制数来写shellcode。
qemu: uncaught target signal 4 (Illegal instruction) - core dumped Illegal instruction (core dumped)
在我们前面的write程序执行的时候,会出现这样两行报错。出现的原因是调用write系统调用之后,没有调用exit系统调用退出,继续执行了非法代码,下面写入exit系统调用来使程序正常退出:
.section .text
.globl __start
.set noreorder
__start:
addiu $sp,$sp,-32
lui $t6,0x4142
ori $t6,$t6,0x430a
sw $t6,0($sp)
li $a0,1
addiu $a1,$sp,0
li $a2,5
li $v0,4004
syscall
li $a0,1
li $v0,4001
li $a1,0
li $a2,0
syscall
MIPS汇编学习的更多相关文章
- 汇编学习笔记(11)int指令和端口
格式 int指令也是一种内中断指令,int指令的格式为int n,n是中断类型码.也就是说,使用int指令可以调用任意的中断例程,例如我们可以显示的调用0号中断例程,还记得在汇编学习笔记(10)中我们 ...
- MIPS指令学习二
1.MIPS寻址方式 MIPS架构的寻址模式有寄存器寻址.立即数寻址.寄存器相对寻址和PC相对寻址4种,其中寄存器相对寻址.PC相对寻址介绍如下: 1.1.寄存器相对寻址 这种寻址模式主要被加载/存储 ...
- Win32汇编学习(4):绘制文本
这次,我们将学习如何在窗口的客户区"绘制"字符串.我们还将学习关于"设备环境"的概念. 理论: "绘制"字符串 Windows 中的文本是一 ...
- android ARM 汇编学习 —— hello world
android ARM 汇编学习—— 在 android 设备上编译c/cpp代码并用objdump/readelf等工具分析 adb putty 连上手机,用busybox vi 写一个 hello ...
- MIPS 汇编指令学习
MIPS 寄存器 MIPS comes with 32 general purpose registers named $0. . . $31Registers also have symbolic ...
- MIPS汇编及模拟器下载
1. 简述汇编语言发展 在计算机发展初期,人们用0-1序列来表示每一条语言,亦即二进制的机器指令 由于机器指令过于繁琐,程序员们开发出了一种新的语言,这种用符号表示的计算机语言被称为汇编语言 计算机继 ...
- 计算机系统6-> 计组与体系结构3 | MIPS指令集(中)| MIPS汇编指令与机器表示
上一篇计算机系统5-> 计组与体系结构2 | MIPS指令集(上)| 指令系统从顶层讲解了一个指令集 / 指令系统应当具备哪些特征和工作原理.这一篇就聚焦MIPS指令集(MIPS32),看看其汇 ...
- 汇编学习笔记(3)[bx]和loop
本文是<汇编语言>一书的学习笔记,对应书中的4-6章. 汇编程序的执行 要想将源代码变为可执行的程序需经过编译.连接两个步骤,WIN7操作系统下需要MASM程序来进行编译连接工作.将MAS ...
- 【Delphi内联汇编学习1】Delphi与汇编
我一直认为Delphi功能与C++相比毫不逊色,提供了丰富的控件和类.全部API以及嵌入的汇编.最近小弟在把C版的Huffman压缩改用Delphi写时,顺便“研究”了一下Delphi的位操作和嵌入式 ...
随机推荐
- kubelet分析-csi driver注册分析-Node Driver Registrar源码分析
kubernetes ceph-csi分析目录导航 Node Driver Registrar分析 node-driver-registrar是一个sidecar容器,通过Kubelet的插件注册机制 ...
- mysql字符集utf8和utf8mb4区别
1.起因 公司游戏项目上线第一天,出现单个区服异常宕机的问题,根据日志排查下来,连接数据的时候报错,后面排查是因为有玩家插入Emoji 等表情导致无法存储如数据库,数据库字符集编码为utf8,后续改成 ...
- 关于开箱即用的文档静态网站生成器VuePress
关于VuePress 一个由Vue驱动的静态文档网站生成框架,具有开箱即用的优点. 给项目添加.gitignore .gitignore是git用来排除目录的清单,我们把以下目录加入其中,以便每次操作 ...
- MySQL原理 - InnoDB引擎 - 行记录存储 - Off-page 列
本文基于 MySQL 8 在前面的两篇文章,我们分析了 MySQL InnoDB 引擎的两种行记录存储格式: Compact 格式 Redundant 格式 在这里简单总结下: Compact 格式结 ...
- idea debug无法启动 Error running 'Tomcat8': Unable to open debugger port (127.0.0.1:50168): java.net.SocketException "socket closed
在日志里显示在 event log 里的 Error running 'server_web': Address localhost:1099 is already in use 显示1099单口已被 ...
- nginx限流模块(防范DDOS攻击)
Nginx限流模式(防范DDOS攻击) nginx中俩个限流模块: 1.ngx_http_limit_req_module(按请求速率限流) 2.ngx_http_limit_conn_module( ...
- Whitzard OJ Introduce to packing
1.概述 这个就是个smc,为什么会归于加壳,我个人理解是和UPX的运行方式有点像把,不对应该是说和压缩壳的运行方式 很相似,都是先运行一段解密代码,之前的符号表也替换了下 2.解题 有两种方式一种是 ...
- 160crackme002
一.查壳 结果:vb写的,并且无壳 二.运行程序 发现了这个程度调用了vb调用窗口的api.这时有两种方式: 1.再重新调试,运行到有窗口的时候,F12暂停,按ctrl+K,查看dll调用,再数据窗口 ...
- 嵌入式Redis服务器在Spring Boot测试中的使用
1.概述 Spring Data Redis提供了一种与Redis实例集成的简单方法. 但是,在某些情况下,使用嵌入式服务器比使用真实服务器创建开发和测试环境更方便. 因此,我们将学习如何设置和使用嵌 ...
- 成功解决1406, “Data too long for column ‘txt‘ at row 1“
这是因为数据库里该字段的数据类型所给的数据空间太小.MySQL将截断超过指定列宽度的任何插入值.为了让这个不报错,可以尝试切换MySQL模式不使用严格模式. SET @@global.sql_mode ...
