输入URL后浏览器的过程
In this article, I want my readers to get a picture of a very basic concept of the web world. Previously, I've written articles on the fancy stuff of today’s market, i.e. Angular journey, basics of react, etc. But, today, I want my readers to get into the journey which they encounter at first when they hit any URL.
As the topic is self explanatory - when we hit any URL then what happens? - let’s start!
Before discussing what happens after hitting the URL, we must go through what a URL actually is, and what different parts of the URL mean - right? Without wasting any time, let’s understand more about URLs.
URL – Uniform Resource Locator
If you look into its full form, then it is self explanatory: it has the location of the resources which we want to access. It is an address of the place where we want to go to interact with or find information.
Let's look into your daily life. If you want to visit your friend’s house for some work or to get information, you need their address. The same thing goes here in this big web world: we have to give an address of the website which we want to access. The web site is like the house and the URL is the address.
Anatomy of a URL
Now, we know what a URL is but we still don’t know about the parts of a URL. Let’s go!
Let’s take an example:
Here, the first part is ‘https’. This basically tells the browser which protocol it should use. It can be http, https, ftp, etc. A protocol is a set of rules that browser use for communication over the network. 'https' is basically a secure version, i.e. information is exchanged in a secure way.
The second part www.example.com is a domain name. You can relate it to your friend’s house. It is an address of website. We use it to reach to the server (trained computer) that is responsible for serving the information for that website. Wait! You might think, a seconds before I mentioned URL is the address whereas I also mentioned domain name is also address. You may have been confused. Don’t be confused!
Difference between URL and Domain Name
The major difference between both is that the URL is a complete address. URL tells about the method through which information should exchange, the path after reaching that website. Whereas the domain name is part of a URL.
Let’s take our previous example to better understand. You can say that your friend’s house address is a domain name, whereas the URL not only tells the friend’s house address (domain name) but also how you are going to communicate like talking in a separate room (secure) or in front of everyone (info can get leak). It also tells the path, i.e. at which part of the house you will go after entering into the house. Hence, the domain name is part of the URL. A domain name with more information is a URL.
I hope now you are clear with the URL. Let’s get into the next part.
Domain Name
In the previous part, I explained about domain names, but not in depth. I want you to go into it more. As I told you, the Domain name is the address of the website. It gives a unique identity to your website in such a huge web world. No two domain names can be the same BUT - Yes! There is ‘but’. This is not the only definition of a domain name. There is another story behind it. Let’s get into that story.
As we know, when we hit any URL or you can say domain name, then that website gets opened with its content. A server (a trained computer) serves it. We also know that every computer has an IP address which is used for communication over the internet. It is an address as its self explaining ‘IP address’. When we hit any URL, then we are actually hitting the IP address of the computer which is responsible for serving the website content (hosting).
But, now, you might think what the hell...is everything an address? Why does this domain name exist if the IP address is there? Why can’t we use IP address to get content of the website?
Yes! You can use IP addresses to get content of the website but really!.. Would you be able to remember each website’s associated IP address? Obviously not! It’s hard to remember the IP address of every website. That’s why domain names came into the market.
You can relate it to your contact list. You can’t remember every person’s number, but you can remember their name. Same concept applies here as well. You can’t remember those scary IP addresses, but you can easily remember domain names.
This huge amount of data is maintained in a database where the domain name with its IP address is stored. A system that stores domain names with its corresponding IP address is known as DNS (Domain name system) (I believe you must have heard about it).
I think I have discussed enough basics. Now, get a deep dive into the process of when we hit any URL.
DNS lookup to find IP address
After hitting the URL, the first thing that needs to happen is to resolve IP address associated with the domain name. DNS helps in resolving this. DNS is like a phone book and helps us to provide the IP address that is associated with the domain name just like our phone book gives a mobile number which is associated with the person’s name.
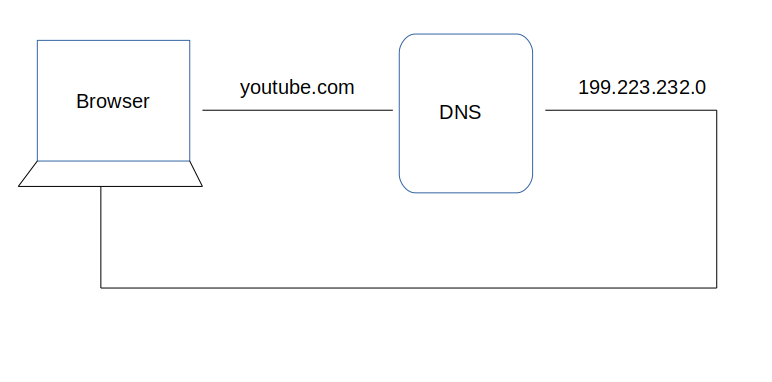
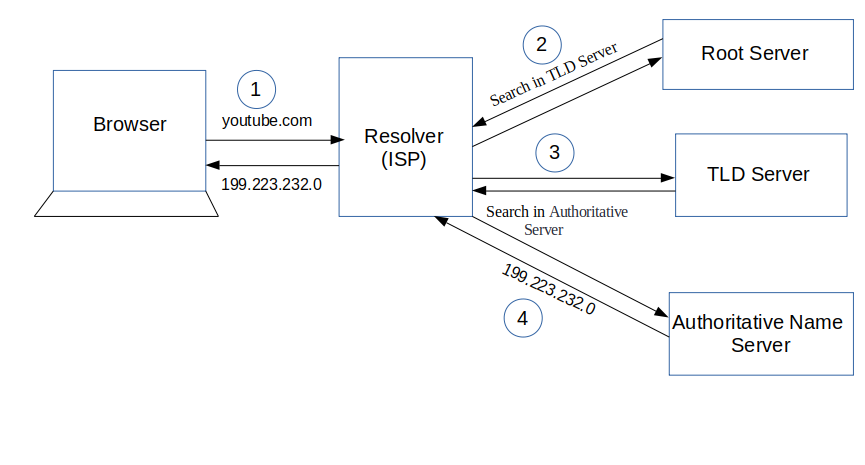
This is the overview, but there are four layers through which this domain name query goes through. Let’s understand the steps:
1. After hitting the URL, the browser cache is checked. As browser maintains its DNS records for some amount of time for the websites you have visited earlier. Hence, firstly, DNS query runs here to find the IP address associated with the domain name.
在最近的浏览的已缓存网址查询IP
2. The second place where DNS query runs in OS cache followed by router cache.
本机的host配置和DNS配置查找IP
3. If in the above steps, a DNS query does not get resolved, then it takes the help of resolver server. Resolver server is nothing but your ISP (Internet service provider). The query is sent to ISP where DNS query runs in ISP cache.
发送到网络服务提供商解析cache查找IP
4. If in 3rd steps as well, no results found, then request sends to top or root server of the DNS hierarchy. There it never happens that it says no results found, but actually it tells, from where this information you can get. If you are searching IP address of the top level domain (.com,.net,.Gov,. org). It tells the resolver server to search TLD server (Top level domain).
如果还是没有则到顶级或根服务器查找,没找到会给一些查找信息
5. Now, resolver asks TLD server to give IP address of our domain name. TLD stores address information of domain name. It tells the resolver to ask it to Authoritative Name server.
解析器请求TLD服务器并且向权威的名称服务器发请求
6. The authoritative name server is responsible for knowing everything about the domain name. Finally, resolver (ISP) gets the IP address associated with the domain name and sends it back to the browser.
After getting an IP address, resolver stores it in its cache so that next time, if the same query comes then it does not have to go to all these steps again. It can now provide IP address from their cache.
ISP得到IP并且发回给浏览器,同时缓存起来以备下次使用
This is all about the steps that is followed to resolve IP address that is associated with the domain name. Have a look below to better understand:
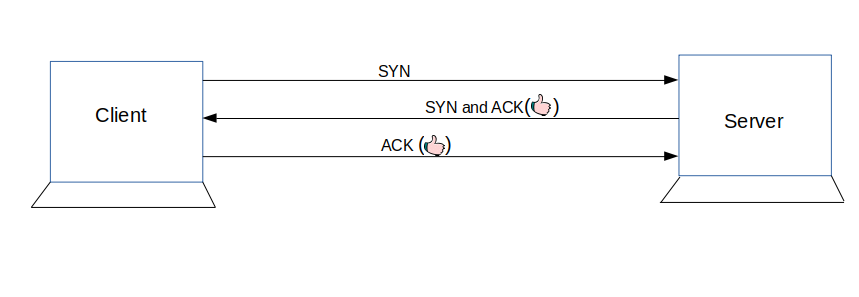
TCP connection initiates with the server by Browser
Once the IP address of the computer (where your website information is there) is found, it initiates connection with it. To communicate over the network, internet protocol is followed. TCP/IP is most common protocol. A connection is built between two using a process called ‘TCP 3-way handshake’. Let’s understand the process in brief:
1. A client computer sends a SYN message means, whether second computer is open for new connection or not.
2. Then another computer, if open for new connection, it sends acknowledge message with SYN message as well.
3. After this, first computer receives its message and acknowledge by sending an ACK message.
To better understand, look below diagram.
Communication Starts (Request Response Process)
Finally, the connection is built between client and server. Now, they both can communicate with each other and share information. After successful connection, browser (client) sends a request to a server that I want this content. The server knows everything of what response it should send for every request. Hence, the server responds back. This response contains every information that you requested like web page, status-code, cache-control, etc. Now, the browser renders the content that has been requested.
That’s it! All the above process happens when we hit any URL. Although this lengthy process takes less than seconds to complete. This is the answer to your question ‘what happens when we hit any URL in a browser?’
Thanks for reading!
If this article was helpful, tweet it.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
输入URL后浏览器的过程的更多相关文章
- 输入url后浏览器干了些什么(详解)
输入url后浏览器干了些什么(详解) DNS(Domain Name System, 域名系统) 解析 DNS解析的过程就是寻找哪台机器上有你真正需要的资源过程.但你在浏览器张红输入一个地址时,例如: ...
- 在浏览器输入url后并回车发生了哪些过程
1.解析URL ________________________________________________________________________ 关于URL: URL(Universa ...
- 在浏览器中输入URL后,执行的全部过程。会用到哪些协议?(一次完整的HTTP请求过程)
在浏览器中输入URL后,执行的全部过程.会用到哪些协议?(一次完整的HTTP请求过程) 整个流程如下: 域名解析 为了将消息从你的PC上传到服务器上,需要用到IP协议.ARP协议和OSPF协议. 发起 ...
- 从输入 URL 到浏览器接收的过程中发生了什么事情
从输入 URL 到浏览器接收的过程中发生了什么事情? 原文:http://www.codeceo.com/article/url-cpu-broswer.html 从触屏到 CPU 首先是「输入 U ...
- 在浏览器输入 URL 后会发生什么?超级详细介绍
一个古老的面试问题:当你在浏览器中输入whosmall.com并且按下回车之后发生了什么? 不过我们不再局限于平常的回答,而是想办法回答地尽可能具体,不遗漏任何细节. 这将是一个协作的过程,所以深入挖 ...
- 从输入 URL 到浏览器接收的过程中发生了什么事情?
从输入 URL 到浏览器接收的过程中发生了什么事情? What really happens when you navigate to a URL 上面两篇文章都解读的很好,值得阅读. 接下来在总结一 ...
- 在浏览器输入URL后发生了什么?
摘录部分一:https://www.cnblogs.com/kongxy/p/4615226.html 从输入URL到浏览器显示页面发生了什么 当在浏览器地址栏输入网址,如:www.baidu.com ...
- 【转】浏览器中输入url后发生了什么
原文地址:http://www.jianshu.com/p/c1dfc6caa520 在学习前端的过程中经常看到这样一个问题:当你在浏览器中输入url后发生了什么?下面是个人学习过程中的总结,供个人复 ...
- 输入URL到浏览器显示页面的过程,搜集各方面资料总结一下
面试中经常会被问到这个问题吧,唉,我最开始被问到的时候也就能大概说一些流程.被问得多了,自己就想去找找这个问题的全面回答,于是乎搜了很多资料和网上的文章,根据那些文章写一个总结. 写得不好,或者有意见 ...
随机推荐
- nacos配置本地多个实例(伪集群)
在本地配置多个nacos实例(伪集群),一般就是配置多个nacos端口,并启动多个startup.sh脚本.网上一些博客通过修改startup.sh脚本来指定不同nacos端口,比如:./startu ...
- c# checkedListBox设置多列横向显示 经验总结
1. 设置checkedListBox的MultiColumn 属性为true; 2. 调整checkedListBox的宽度,调整ColumnWidth的宽度
- odoo里面批量上传图片
import os import base64 def base_data_product_image(self): """ odoo里批量创建产品,并上传图片 图片为b ...
- Scrapy入门到放弃03:理解settings配置,监控Scrapy引擎
前言 代码未动,配置先行.本篇文章主要讲述一下Scrapy中的配置文件settings.py的参数含义,以及如何去获取一个爬虫程序的运行性能指标. 这篇文章无聊的一匹,没有代码,都是配置化的东西,但是 ...
- [WinError 10013]以一种访问权限不允许的方式做了一个访问套接字的尝试
Django报错截图如下: 原因分析:出现这种情况在Windows中很常见,就是端口被占用 解决步骤: 1:进入windows中的命令行窗口(win+R之后输入cmd就可以进去) 2:输入 net ...
- 🔥 LeetCode 热题 HOT 100(31-40)
75. 颜色分类 思路:将 2 往后放,0 往前放,剩余的1自然就放好了. 使用双指针:left.right 分别指向待插入的 0 和 2 的位置,初始 left 指向数组头,right 指向数组尾部 ...
- git合作开发流程
一.创建项目与管理 创建项目和管理项目都是管理账号需要做的事情,如果只是合作开发不进行管理,只需要浏览第二部分的内容即可. 1.创建项目 登录代码托管网站,点击添加项目,如下图所示: 填写相应的项目信 ...
- 解决ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'问题
Python学习遇到小问题:ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip' 今天想要装一下第三方库exifread的时候发现cmd窗口下无法执行pip命令,想了想 ...
- 【Flutter学习一】Android的App的三种开发方式
是时候学习新技术了: 转自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41346910/article/details/86692124 移动开发发展到现在,已经出现了三种开发方式.本文我将为 ...
- shell中cmd1 && cmd2 || cmd3的含义
在某些情况下,很多指令我想要一次输入去执行,而不想要分次去执行时,就要用到 && || 了.cmd 1 && cmd21,若cmd1执行完毕之后且正确执行($?=0), ...
