广度优先搜索(BreadthFirstSearch)& 迪克斯特拉算法 (Dijkstra's algorithm)
BFS可回答两类问题:
1.从节点A出发,有前往节点B的路径吗?
2.从节点A出发,前往节点B的哪条路径经过的节点最少?
BFS中会用到“队列”的概念。队列是一种先进先出(FIFO, first in first out)的数据结构,与栈不同,栈是后进先出(LIFO, last in first out)的数据结构。
还会用到“字典”的概念。字典在现在很多语言中都存在且广泛使用,字典中的元素是一组<键(key),值(value)>对,key的值是不可以重复的。关于字典的详细内容,网上有很多资料可以查阅。
问题描述:想从你的朋友中找出一个芒果销售商,如果你的朋友中没有,那么就从朋友的朋友中查找。(这里假设名字最后一个字母为“m”的即为芒果销售商)。这样就是从“you”这个节点出发,是否有到“Xm”这个节点的路径的问题。
思路:先从你的朋友开始查找,如果朋友A是芒果销售商,则程序结束,如果不是,则将A的朋友排到队列中。然后检查朋友B是否为芒果销售商,循环,直到找到芒果销售商或者队列中的朋友们都被检查了一遍。因为会有某个人C既是A的朋友又是B的朋友,而C只需要检查一次,因此要分配一个列表用于记录已经检查过哪些朋友了。
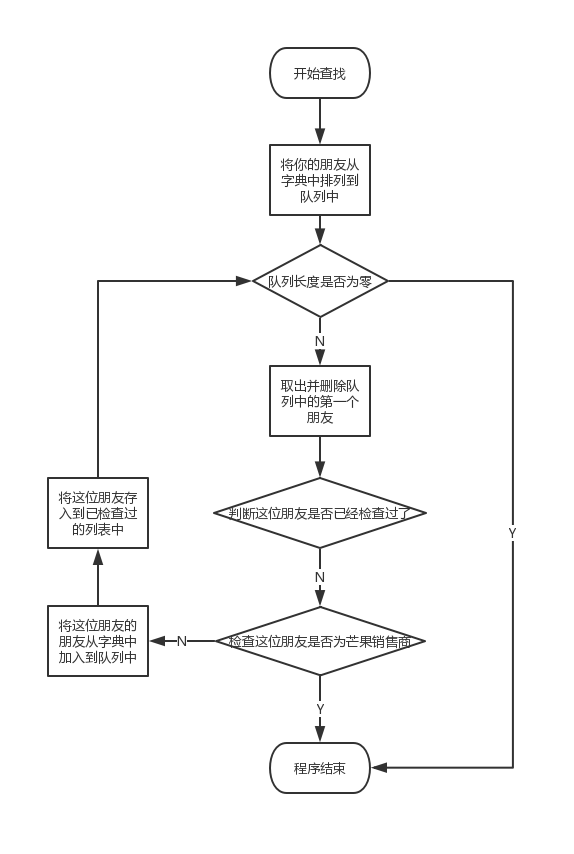
Python代码:
>>> from collections import deque
>>> graph = {}
>>> graph["you"]=["alice","bob","claire"]
>>> graph["bob"] = ["anuj","peggy"]
>>> graph["alice"] = ["peggy"]
>>> graph["claire"]=["thom","jonny"]
>>> graph["anuj"]=[]
>>> graph["peggy"]=[]
>>> graph["thom"]=[]
>>> graph["jonny"]=[]
>>> def search(name):
search_queue = deque()
search_queue += graph[name]
searched = []
while search_queue:
person = search_queue.popleft()
if person not in searched:
if person_is_seller(person):
print (person + " is a mango seller!")
return True
else:
search_queue += graph[person]
searched.append(person)
return False
>>> def person_is_seller(name):
return name[-1] == 'm'
>>> search("you")
thom is a mango seller!
True
C#代码:
namespace Algorithms
{
public static class BFS
{
public static bool BreadthFirstSearch(string name, Dictionary<string,List<string>>graph)
{
Queue<string> search_queue = new Queue<string>();
foreach (var item in graph[name])
search_queue.Enqueue(item);
List<string> searched = new List<string>();
while (search_queue.Count != 0)
{
string person = search_queue.Dequeue();
if (!searched.Contains(person))
{
if (JudgeSeller(person))
{
Console.WriteLine(person + " is a mango seller!");
return true;
}
else
{
foreach (var item in graph[person])
search_queue.Enqueue(item);
searched.Add(person);
}
}
}
return false;
}
private static bool JudgeSeller(string name)
{
if (name[name.Length - 1] == 'm')
return true;
return false;
}
}
}
测试:
namespace Algorithms
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dictionary<string, List<string>> graph = new Dictionary<string, List<string>>();
graph["you"] = new List<string>() { "alice", "bob", "claire" };
graph["alice"] = new List<string>() { "peggy" };
graph["bob"] = new List<string>() { "anuj", "peggy" };
graph["claire"] = new List<string>() { "thom", "jonny" };
graph["anuj"] = new List<string>();
graph["peggy"] = new List<string>();
graph["thom"] = new List<string>();
graph["jonny"] = new List<string>(); if (!BFS.BreadthFirstSearch("you", graph))
{
Console.WriteLine("no mango seller!");
}
Console.Read();
}
}
}
Dijkstra's algorithm 用于计算出最短路径,但是这个算法在使用上有很多限制条件。
问题描述:从A地到B地的各种可能的路径中,哪条路径所用的时间最短。(图中的数字表示从某地到另外某地所用的时间)
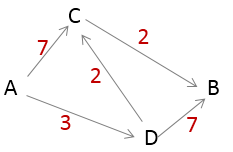
图1
思路:记录从A点到其他各个节点的所需的时间,如表1所示(现在还不知道从A到B的时间,则先设置为无穷大)
| D | 3 |
| C | 7 |
| B | ∞ |
表1
从所需时间最短的D点再出发,计算从A经过D到其他个各节点的时间,如表2所示
| C | 5 |
| B | 10 |
表2
直接前往C点需要的时间为7,而经过D点前往C点所需的时间为5,时间缩短了,则更新从A到各个点所需的时间的列表,如表3所示
| D | 3 |
| C | 5 |
| B | 10 |
表3
现在除了节点D之外,从A到C的时间是最短的了,则计算从A经过C再到其他节点的时间,如表4所示。
| B | 7 |
表4
现在从A经过D再经过C然后到B的时间为7,小于表3记录的到B的时间,则更新这个时间。
就这样得到了花费时间最短的路径。总结一下就是,不断的获得从起点到某点的最短时间,然后更新这个时间列表。在 Dijkstra's algorithm中,这些数字被称为“权重(weight)”,而带权重的图则被称为加权图(weighted graph),那么不带权重的则被称为非加权图(unweighted graph)。对于计算非加权图中的最短路径,可使用BFS,计算加权图中的最短路径,可使用 Dijkstra's algorithm。然而, Dijkstra's algorithm不适用于带环的图,即图1中的箭头如果是双向的话那么就是不适用的。此外,它还不适用于带有负权重的情况。
Dijkstra算法的实现需要使用三个散列表。第一个散列表记录的是每个点的邻居及权重。第二个散列表记录的是从起点开始到每个节点的权重,第三个散列表记录的是各个节点父节点。
Python代码:
#第一个散列表,记录每个点的邻居及权重
graph={}
graph["A"]={}
graph["A"]["C"]=7
graph["A"]["D"]=3
graph["C"]={}
graph["C"]["B"]=2
graph["D"]={}
graph["D"]["C"]=2
graph["D"]["B"]=7
graph["B"]={} #第二个散列表,记录从起点A到其他各个节点的权重
#由于节点B不是A的邻居,则A到B的权重暂设置为无穷大
costs={}
infinity = float("inf")
costs["C"]=7
costs["D"]=3
costs["B"]=infinity #第三个散列表,用于存储节点的父节点
parents={}
parents["C"]="A"
parents["D"]="A"
parents["B"]=None #用于记录已经处理过的节点的数组
processed=[] #先在未处理的节点数组中找到权重最小的节点
def find_lowest_cost_node(costs):
lowest_cost = float("inf")
lowest_cost_node = None
for node in costs:
cost = costs[node]
if cost < lowest_cost and node not in processed:
lowest_cost = cost
lowest_cost_node = node
return lowest_cost_node node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs)
while node is not None:
cost = costs[node]
neighbors=graph[node]
for n in neighbors.keys():
new_cost=cost + neighbors[n]
if costs[n] > new_cost:
costs[n] = new_cost
parents[n]=node
processed.append(node)
node=find_lowest_cost_node(costs) for node in costs:
print("Node:" + node+ " Cost:" + str(costs[node]) + "\r\n") for node in parents:
print("ChildNode:" + node + " ParentNode:" + parents[node] + "\r\n")
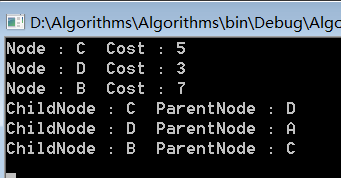
运行结果:
Node:C Cost:5 Node:D Cost:3 Node:B Cost:7 ChildNode:C ParentNode:D ChildNode:D ParentNode:A ChildNode:B ParentNode:C >>>
C#代码:
public class DijkstraAlgorithm
{
public Dictionary<string, double> Costs { get; set; }
public Dictionary<string, string> Parents { get; set; }
public Dictionary<string, Dictionary<string,double>> Graph { get; set; }
private List<string> processed = new List<string>();
public DijkstraAlgorithm()
{
Costs = new Dictionary<string, double>();
Parents = new Dictionary<string, string>();
Graph = new Dictionary<string, Dictionary<string, double>>();
} public void Dijkstra_Algorithm()
{
string node = FindLowestCostNode();
while(node != null)
{
double cost = Costs[node];
Dictionary<string, double> neighbors = Graph[node];
foreach(KeyValuePair<string,double> item in neighbors)
{
double new_cost = cost + item.Value;
if (Costs[item.Key] > new_cost)
{
Costs[item.Key] = new_cost;
Parents[item.Key] = node;
}
}
processed.Add(node);
node = FindLowestCostNode();
}
}
private string FindLowestCostNode()
{
string lowestcostnode = null;
double lowestcost = double.PositiveInfinity;
foreach(KeyValuePair<string,double> item in Costs)
{
if(item.Value < lowestcost && !processed.Contains(item.Key))
{
lowestcost = item.Value;
lowestcostnode = item.Key;
}
}
return lowestcostnode;
} }
字典的初始化以及运行结果:
DijkstraAlgorithm Dalgorithm = new DijkstraAlgorithm();
Dalgorithm.Graph["A"] = new Dictionary<string, double>(); Dalgorithm.Graph["A"]["C"] = 7;
Dalgorithm.Graph["A"]["D"] = 3; Dalgorithm.Graph["C"] = new Dictionary<string, double>();
Dalgorithm.Graph["C"]["B"] = 2;
Dalgorithm.Graph["D"] = new Dictionary<string, double>();
Dalgorithm.Graph["D"]["C"] = 2;
Dalgorithm.Graph["D"]["B"] = 7; Dalgorithm.Graph["B"] = new Dictionary<string, double>(); Dalgorithm.Costs["C"] = 7;
Dalgorithm.Costs["D"] = 3;
Dalgorithm.Costs["B"] = double.PositiveInfinity; Dalgorithm.Parents["C"] = "A";
Dalgorithm.Parents["D"] = "A";
Dalgorithm.Parents["B"] = null; Dalgorithm.Dijkstra_Algorithm(); foreach(KeyValuePair<string,double> item in Dalgorithm.Costs)
{
Console.WriteLine("Key : " + item.Key + " Value : " + item.Value);
} foreach(KeyValuePair<string,string> item in Dalgorithm.Parents)
Console.WriteLine("Key : " + item.Key + " Value : " + item.Value); Console.Read();
广度优先搜索(BreadthFirstSearch)& 迪克斯特拉算法 (Dijkstra's algorithm)的更多相关文章
- 用js简单实现一下迪克斯特拉算法
今天看书看到了迪克斯特拉算法,大概用js实现一下呢,计算最短路径. 首先,迪克斯特拉算法只适用于有向无环图,且没有负权重,本例关系图如下哦,数字为权重,emmmm,画得稍微有点丑~ //大概用js实现 ...
- 迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra) (基础dij+堆优化) BY:优少
首先来一段百度百科压压惊... 迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)是由荷兰计算机科学家狄克斯特拉于1959 年提出的,因此又叫狄克斯特拉算法.是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有权图中最 ...
- C# 迪杰斯特拉算法 Dijkstra
什么也不想说,现在直接上封装的方法: using System; using System.Collections.Concurrent; using System.Collections.Gener ...
- 图->最短路径->单源最短路径(迪杰斯特拉算法Dijkstra)
文字描述 引言:如下图一个交通系统,从A城到B城,有些旅客可能关心途中中转次数最少的路线,有些旅客更关心的是节省交通费用,而对于司机,里程和速度则是更感兴趣的信息.上面这些问题,都可以转化为求图中,两 ...
- 迪杰斯特拉算法dijkstra(可打印最短路径)
#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <string> using namespace std; #def ...
- [算法导论]迪克斯特拉算法 @ Python
class Graph: def __init__(self): self.V = [] self.w = {} class Vertex: def __init__(self, x): self.k ...
- Dijkstra Algorithm 迪克特斯拉算法--Python
迪克斯拉特算法: 1.找出代价最小的节点,即可在最短时间内到达的节点: 2.更新节点的邻居的开销: 3.重复这个过程,直到图中的每个节点都这样做了: 4.计算最终路径. ''' 迪克斯特拉算法: 1. ...
- CF1272E. Nearest Opposite Parity 题解 广度优先搜索
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/1272/problem/E 题目大意: 有一个长度为n的数组 \(a\) ,数组坐标从 \(1\) 到 \(n\) . 假设你现 ...
- Dijkstra【迪杰斯特拉算法】
有关最短路径的最后一个算法——Dijkstra 迪杰斯特拉算法是由荷兰计算机科学家迪杰斯特拉于1959 年提出的,因此又叫迪杰斯特拉算法.是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有权图中最短路 ...
随机推荐
- golang中的标准库flag
Go语言内置的flag包实现了命令行参数的解析,flag包使得开发命令行工具更为简单. os.Args 如果你只是简单的想要获取命令行参数,可以像下面的代码示例一样使用os.Args来获取命令行参数. ...
- golang中字符串-字节切片,字符串-字符切片的互转
package main import ( "fmt" "reflect" ) func B2S(bs []uint8) string { // 将字节切片转换 ...
- spring内嵌cglib包,这里藏着一个大坑
问题发现 2022-01-21 早上 9 点,订单系统出现大面积的"系统未知错误"报错,导致部分用户无法正常下单.查询后台日志,可以看到大量的 duplicate class at ...
- python matplotlib通过 plt.scatter在图上画圆
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt lena = mpimg.imread(r'C:\Users\Administrator.WIN-QV9HPTF0DHS\Desktop ...
- 软件版本GA、Beta、RC含义
Alpha:是内部测试版,一般不向外部发布,会有很多Bug.一般只有测试人员使用.Beta:也是测试版,这个阶段的版本会一直加入新的功能.在Alpha版之后推出.RC:(Release Candida ...
- android 如何动态设置View的margin和padding
感谢大佬:https://blog.csdn.net/a107494639/article/details/7341077 1.动态设置padding,拿ImageView为例: ImageView ...
- new方法实现原理
new方法实现原理 完整的创建一个可用的对象:Person *p=[Person new]; new方法的内部会分别调用两个方法来完成3件事情: (1)使用alloc方法来分配存储空间(返回分配的对象 ...
- Linux-一次执行多个命令 ; && ||
一次执行多个命令,多个命令之间用:号隔开 cmd1;cmd2:cmd3 这样前后执行的时候没有依赖性,如果有下列要求呢 1. cmd1执行失败那就不要执行后面的命令 2. cmd1失败了才去指令后面的 ...
- term&match得区别 text&keyword区别
Text 概念 Text 数据类型被用来索引长文本,比如说电子邮件的主体部分或者一款产品的介绍.这些文本会被分析,在建立索引前会将这些文本进行分词,转化为词的组合,建立索引.允许 ES来检索这些词语. ...
- pytorch学习
1 torch.hub torch.hub是一个包含计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域的诸多经典模型调用中心API 我没有运行成功代码 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38410428/a ...
