openmesh - src - trimesh delete and add elements
openmesh - src - trimesh delete and add elements
openmesh 版本 8.1
About
本文主要介绍openmesh的如下接口
- add_vertex
- add_face
- delete_vertex
- delete_edge
- delete_face
- delete_isolated_vertices
add_vertex
入口代码位于:\src\OpenMesh\Core\Mesh\PolyMeshT.hh。涉及到的源代码如下:
template <class Kernel>class PolyMeshT : public Kernel{/// Alias for new_vertex(const Point&).inline SmartVertexHandle add_vertex(const Point& _p){ return new_vertex(_p); }/*** \brief Adds a new vertex initialized to a custom position.** \sa new_vertex(), new_vertex_dirty()*/inline SmartVertexHandle new_vertex(const Point& _p){VertexHandle vh(Kernel::new_vertex());this->set_point(vh, _p);return make_smart(vh, this);}//..............}// kernel::new_vertexclass OPENMESHDLLEXPORT ArrayKernel : public BaseKernel, public ArrayItems{inline VertexHandle new_vertex(){vertices_.push_back(Vertex());vprops_resize(n_vertices());//TODO:should it be push_back()?return handle(vertices_.back());}// --- handle -> item ---VertexHandle handle(const Vertex& _v) const{return VertexHandle( int( &_v - &vertices_.front()));}}// AttribKernelT// 顶点的位置,作为顶点的属性进行管理template <class MeshItems, class Connectivity>class AttribKernelT : public Connectivity{void set_point(VertexHandle _vh, const Point& _p){ this->property(points_, _vh) = _p; }}
从上面中的代码知,add_vertex的过程,就是创建了Vertex,然后创建关联的VertexHandle,并将顶点的位置记录到顶点property中。
add_face
入口代码位于:src\OpenMesh\Core\Mesh\TriConnectivity.cc
SmartFaceHandleTriConnectivity::add_face(const VertexHandle* _vertex_handles, size_t _vhs_size){// need at least 3 verticesif (_vhs_size < 3) return make_smart(InvalidFaceHandle, this);/// face is triangle -> okif (_vhs_size == 3)return PolyConnectivity::add_face(_vertex_handles, _vhs_size);/// face is not a triangle -> triangulateelse{//omlog() << "triangulating " << _vhs_size << "_gon\n";VertexHandle vhandles[3];vhandles[0] = _vertex_handles[0];FaceHandle fh;unsigned int i(1);--_vhs_size;while (i < _vhs_size){vhandles[1] = _vertex_handles[i];vhandles[2] = _vertex_handles[++i];fh = PolyConnectivity::add_face(vhandles, 3);}return make_smart(fh, this);}}
从上面的代码可知,对于TriMesh,如果超过三个顶点,那么会进行三角化的过程,这个三角化的过程是,将第一个顶点作为所有三角形的公共点,接下来数组中的相邻两个点作为每个三角形的另外两个顶点。图示如下:
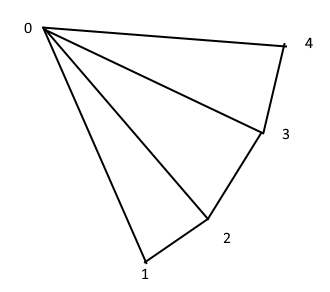
进一步查看PolyConnectivity::add_face(_vertex_handles, _vhs_size);,完整的代码如下(TODO详细剖析下面的代码):
SmartFaceHandlePolyConnectivity::add_face(const VertexHandle* _vertex_handles, size_t _vhs_size){VertexHandle vh;size_t i, ii, n(_vhs_size);HalfedgeHandle inner_next, inner_prev,outer_next, outer_prev,boundary_next, boundary_prev,patch_start, patch_end;// Check sufficient working storage availableif (edgeData_.size() < n){edgeData_.resize(n); // 数据类型为:std::vector<AddFaceEdgeInfo>;// struct AddFaceEdgeInfo { HalfedgeHandle halfedge_handle; bool is_new; bool needs_adjust; }next_cache_.resize(6*n); //数据类型为:std::vector<std::pair<HalfedgeHandle, HalfedgeHandle> >// for set_next_halfedge and vertex' set_halfedge}size_t next_cache_count = 0;// don't allow degenerated facesassert (n > 2);// test for topological errorsfor (i=0, ii=1; i<n; ++i, ++ii, ii%=n){// 需要添加三角形的顶点必须是位于当前拓扑结构的边界if ( !is_boundary(_vertex_handles[i]) ){omerr() << "PolyMeshT::add_face: complex vertex\n";return make_smart(InvalidFaceHandle, this);}// Initialise edge attributes// 查找是否存在点i和点ii构成的半边edgeData_[i].halfedge_handle = find_halfedge(_vertex_handles[i],_vertex_handles[ii]);edgeData_[i].is_new = !edgeData_[i].halfedge_handle.is_valid();edgeData_[i].needs_adjust = false;// 如果存在这个半边,并且该半边不是边界,那么添加的为重复半边,直接returnif (!edgeData_[i].is_new && !is_boundary(edgeData_[i].halfedge_handle)){omerr() << "PolyMeshT::add_face: complex edge\n";return make_smart(InvalidFaceHandle, this);}}// re-link patches if necessaryfor (i=0, ii=1; i<n; ++i, ++ii, ii%=n){// 如果存在点i点ii构成的半边i-to-ii,和点ii和点ii+1构建的半边,ii-to-ii+1if (!edgeData_[i].is_new && !edgeData_[ii].is_new){inner_prev = edgeData_[i].halfedge_handle;inner_next = edgeData_[ii].halfedge_handle;// 如果i-to-ii的下一个半边不是ii-to-ii+1,那么需要修正拓扑结构关系// TODO:需要了解下出现此种情况的具体场景是什么if (next_halfedge_handle(inner_prev) != inner_next){// here comes the ugly part... we have to relink a whole patch// search a free gap// free gap will be between boundary_prev and boundary_nextouter_prev = opposite_halfedge_handle(inner_next);outer_next = opposite_halfedge_handle(inner_prev);boundary_prev = outer_prev;doboundary_prev =opposite_halfedge_handle(next_halfedge_handle(boundary_prev));while (!is_boundary(boundary_prev));boundary_next = next_halfedge_handle(boundary_prev);// ok ?if (boundary_prev == inner_prev){omerr() << "PolyMeshT::add_face: patch re-linking failed\n";return make_smart(InvalidFaceHandle, this);}assert(is_boundary(boundary_prev));assert(is_boundary(boundary_next));// other halfedges' handlespatch_start = next_halfedge_handle(inner_prev);patch_end = prev_halfedge_handle(inner_next);assert(boundary_prev.is_valid());assert(patch_start.is_valid());assert(patch_end.is_valid());assert(boundary_next.is_valid());assert(inner_prev.is_valid());assert(inner_next.is_valid());// relinknext_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(boundary_prev, patch_start);next_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(patch_end, boundary_next);next_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(inner_prev, inner_next);}}}// create missing edgesfor (i=0, ii=1; i<n; ++i, ++ii, ii%=n)if (edgeData_[i].is_new)edgeData_[i].halfedge_handle = new_edge(_vertex_handles[i], _vertex_handles[ii]);// create the faceFaceHandle fh(new_face());set_halfedge_handle(fh, edgeData_[n-1].halfedge_handle);// setup halfedgesfor (i=0, ii=1; i<n; ++i, ++ii, ii%=n){vh = _vertex_handles[ii];inner_prev = edgeData_[i].halfedge_handle;inner_next = edgeData_[ii].halfedge_handle;assert(inner_prev.is_valid());assert(inner_next.is_valid());size_t id = 0;if (edgeData_[i].is_new) id |= 1;if (edgeData_[ii].is_new) id |= 2;if (id){outer_prev = opposite_halfedge_handle(inner_next);outer_next = opposite_halfedge_handle(inner_prev);assert(outer_prev.is_valid());assert(outer_next.is_valid());// set outer linksswitch (id){case 1: // prev is new, next is oldboundary_prev = prev_halfedge_handle(inner_next);assert(boundary_prev.is_valid());next_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(boundary_prev, outer_next);set_halfedge_handle(vh, outer_next);break;case 2: // next is new, prev is oldboundary_next = next_halfedge_handle(inner_prev);assert(boundary_next.is_valid());next_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(outer_prev, boundary_next);set_halfedge_handle(vh, boundary_next);break;case 3: // both are newif (!halfedge_handle(vh).is_valid()){set_halfedge_handle(vh, outer_next);next_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(outer_prev, outer_next);}else{boundary_next = halfedge_handle(vh);boundary_prev = prev_halfedge_handle(boundary_next);assert(boundary_prev.is_valid());assert(boundary_next.is_valid());next_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(boundary_prev, outer_next);next_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(outer_prev, boundary_next);}break;}// set inner linknext_cache_[next_cache_count++] = std::make_pair(inner_prev, inner_next);}else edgeData_[ii].needs_adjust = (halfedge_handle(vh) == inner_next);// set face handleset_face_handle(edgeData_[i].halfedge_handle, fh);}// process next halfedge cachefor (i = 0; i < next_cache_count; ++i)set_next_halfedge_handle(next_cache_[i].first, next_cache_[i].second);// adjust vertices' halfedge handlefor (i=0; i<n; ++i)if (edgeData_[i].needs_adjust)adjust_outgoing_halfedge(_vertex_handles[i]);return make_smart(fh, this);}
delete_vertex
入口代码位置见:src\OpenMesh\Core\Mesh\PolyConnectivity.cc
void PolyConnectivity::delete_vertex(VertexHandle _vh, bool _delete_isolated_vertices){// store incident faces// 先找到顶点周围的所有面std::vector<FaceHandle> face_handles;face_handles.reserve(8);for (VFIter vf_it(vf_iter(_vh)); vf_it.is_valid(); ++vf_it)face_handles.push_back(*vf_it);// delete collected faces// 删除所有关联的面std::vector<FaceHandle>::iterator fh_it(face_handles.begin()),fh_end(face_handles.end());for (; fh_it!=fh_end; ++fh_it)delete_face(*fh_it, _delete_isolated_vertices);// 然后将该顶点标记为已删除status(_vh).set_deleted(true);}
上述代码实现中的重点部分是delete_face,那么接下来先来看一下delete_face的代码实现。
delete_face
入口代码位置见:src\OpenMesh\Core\Mesh\PolyConnectivity.cc
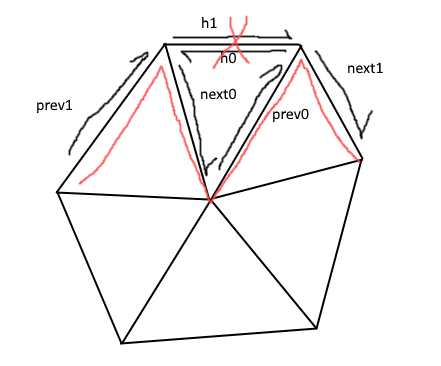
void PolyConnectivity::delete_face(FaceHandle _fh, bool _delete_isolated_vertices){assert(_fh.is_valid() && !status(_fh).deleted());// mark face deleted,将该facehandle标记为已经删除status(_fh).set_deleted(true);// this vector will hold all boundary edges of face _fh// these edges will be deleted// 用来存储面的所有边界边,这些边将会被删除std::vector<EdgeHandle> deleted_edges;deleted_edges.reserve(3);// this vector will hold all vertices of face _fh// for updating their outgoing halfedge// 用来存储面的所有顶点,用来更新这些顶点的outgoing 半边;std::vector<VertexHandle> vhandles;vhandles.reserve(3);// for all halfedges of face _fh do:// 1) invalidate face handle.// 2) collect all boundary halfedges, set them deleted// 3) store vertex handlesHalfedgeHandle hh;for (FaceHalfedgeIter fh_it(fh_iter(_fh)); fh_it.is_valid(); ++fh_it){hh = *fh_it;set_boundary(hh);//set_face_handle(hh, InvalidFaceHandle);// 如果边界半边opposite半边也是边界,那么这个边需要被删除if (is_boundary(opposite_halfedge_handle(hh)))deleted_edges.push_back(edge_handle(hh));vhandles.push_back(to_vertex_handle(hh));}// delete all collected (half)edges// these edges were all boundary// delete isolated vertices (if _delete_isolated_vertices is true)// 此处的逻辑可以见代码后的图示。if (!deleted_edges.empty()){std::vector<EdgeHandle>::iterator del_it(deleted_edges.begin()),del_end(deleted_edges.end());HalfedgeHandle h0, h1, next0, next1, prev0, prev1;VertexHandle v0, v1;for (; del_it!=del_end; ++del_it){h0 = halfedge_handle(*del_it, 0);v0 = to_vertex_handle(h0);next0 = next_halfedge_handle(h0);prev0 = prev_halfedge_handle(h0);h1 = halfedge_handle(*del_it, 1);v1 = to_vertex_handle(h1);next1 = next_halfedge_handle(h1);prev1 = prev_halfedge_handle(h1);// adjust next and prev handlesset_next_halfedge_handle(prev0, next1);set_next_halfedge_handle(prev1, next0);// mark edge deleted if the mesh has a edge statusif ( has_edge_status() )status(*del_it).set_deleted(true);// mark corresponding halfedges as deleted// As the deleted edge is boundary,// all corresponding halfedges will also be deleted.if ( has_halfedge_status() ) {status(h0).set_deleted(true);status(h1).set_deleted(true);}// update v0if (halfedge_handle(v0) == h1){// isolated ?if (next0 == h1){if (_delete_isolated_vertices)status(v0).set_deleted(true);set_isolated(v0);}else set_halfedge_handle(v0, next0);}// update v1if (halfedge_handle(v1) == h0){// isolated ?if (next1 == h0){if (_delete_isolated_vertices)status(v1).set_deleted(true);set_isolated(v1);}else set_halfedge_handle(v1, next1);}}}// update outgoing halfedge handles of remaining vertices// 边界的顶点对应的半边必须是边界的。std::vector<VertexHandle>::iterator v_it(vhandles.begin()),v_end(vhandles.end());for (; v_it!=v_end; ++v_it)adjust_outgoing_halfedge(*v_it);}
deleted_edges相关的逻辑示意图如下:
delete_edge
void PolyConnectivity::delete_edge(EdgeHandle _eh, bool _delete_isolated_vertices){FaceHandle fh0(face_handle(halfedge_handle(_eh, 0)));FaceHandle fh1(face_handle(halfedge_handle(_eh, 1)));if (fh0.is_valid()) delete_face(fh0, _delete_isolated_vertices);if (fh1.is_valid()) delete_face(fh1, _delete_isolated_vertices);// If there is no face, we delete the edge// hereif ( ! fh0.is_valid() && !fh1.is_valid()) {// mark edge deleted if the mesh has a edge statusif ( has_edge_status() )status(_eh).set_deleted(true);// mark corresponding halfedges as deleted// As the deleted edge is boundary,// all corresponding halfedges will also be deleted.if ( has_halfedge_status() ) {status(halfedge_handle(_eh, 0)).set_deleted(true);status(halfedge_handle(_eh, 1)).set_deleted(true);}}}
delete_edge的实现是将边关联的face删除,然后将edge和关联的half_edge的状态设置为删除。
delete_isolated_vertices
unsigned int ArrayKernel::delete_isolated_vertices(){assert(has_vertex_status());//this function requires vertex status propertyunsigned int n_isolated = 0;for (KernelVertexIter v_it = vertices_begin(); v_it != vertices_end(); ++v_it){if (is_isolated(handle(*v_it))){status(handle(*v_it)).set_deleted(true);n_isolated++;}}return n_isolated;}
直接判断出是否为孤立点,然后标记为删除。
openmesh - src - trimesh delete and add elements的更多相关文章
- How do I add elements to a Scala List?
Scala List FAQ: How do I add elements to a Scala List? This is actually a trick question, because yo ...
- How to add elements to a List in Scala
Scala List FAQ: How do I add elements to a Scala List? This is actually a trick question, because yo ...
- select 下拉菜单Option对象使用add(elements,index)方法动态添加
原生js 的add函数为下拉菜单增加选项 1.object.add(oElement [, iIndex]) index 可选参数:指定元素放置所在的索引号,整形值.如果没有指定值,将添加到集合的最后 ...
- openmesh - impl - Remove Duplicated Vertices
openmesh - impl - Remove Duplicated Vertices 关于openmesh元素删除实现的介绍参见:openmesh - src - trimesh delete a ...
- 【OpenMesh】创建一个正方体
原文出处: http://openmesh.org/Documentation/OpenMesh-Doc-Latest/tutorial.html 这个例程演示了: 如何声明MyMesh 如何添加顶点 ...
- 调用 webapi的put和delete 报"Method Not Allowed" 405 错误。
修改引用到webapi的Dll文件对应的项目的web.config 选择生成读写方法webapi会生成四个读写的方法(CRUD),两个获取数据的.一个更新.一个删除,默认情况下更新和删除是不对外开外的 ...
- Mongodb 语法,update,insert,delete,find
---恢复内容开始--- db.Users.update({OrganizationCode:"Global"},{$set:{OrganizationCode:"Fre ...
- C++ 重载new和delete操作符
原因: C++标准库提供的new和delete操作符,是一个通用实现,未针对具体对象做具体分析 存在分配器速度慢.小型对象空间浪费严重等问题,不适用于对效率和内存有限制的应用场景 好处: 灵活的内 ...
- Import the Add Email and Post Configuration to the SiteMap managed solution -Dynamices CRM
We have prepared a managed solution named Add Email and Post Configuration to SiteMap that you can i ...
随机推荐
- 【编程思想】【设计模式】【创建模式creational】建造者模式builder
Python版 https://github.com/faif/python-patterns/blob/master/creational/builder.py #!/usr/bin/python ...
- Appium获取toast消息(二)
刚接触appium进行移动端设备的UI自动化,在遇到toast消息的时候很是苦恼了一阵,最后通过强大的搜索引擎找到了个相对解决方法,废话不多说,直接贴代码↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓ ...
- Nginx+ uWSGI +django进行部署
一:uWSGI的安装 sudo pip install uwsgi 如果安装报错: conda install -c conda-forge uwsgi conda install -c conda- ...
- 【Jenkins系列】-备份机制
Jenkins是主从模式,从节点可以做集群.负载,从而实现从节点的高可用,但是主节点是单节点,一旦主节点宕机,会导致Jenkins服务不可用.Jenkins主节点本身是不支持集群的,需要通过其他变通方 ...
- windows下更换MySql数据库数据文件夹位置
详细解决地址 ,感谢博主 :https://blog.csdn.net/u010953266/article/details/56499361 概述 由于更换硬盘,系统重新安装了一遍,原来的mysq ...
- 解析Redis操作五大数据类型常用命令
摘要:分享经常用到一些命令和使用场景总结,以及对Redis中五大数据类型如何使用cmd命令行的形式进行操作的方法. 本文分享自华为云社区<Redis操作五大数据类型常用命令解析>,作者:灰 ...
- odoo views中html的奇怪问题
在我创建了字段类型为 fields.Html 以后,确出现了两种不同的情况 下图中,content是此类型的,可以正常显示不需要加widget(小部件)="html" <fo ...
- CF139A Petr and Book 题解
Content 小 P 有一本 \(n\) 页的书,现给出他一周七天每天的阅读页数,求它在星期几读完这本书. 数据范围:\(1\leqslant n\leqslant 1000\). Solution ...
- MimeTypes数值表
我们常常需要再前端附件进行上传的时候,就设定只能选择固定的后缀的上传文件,这时就需要用到我们MimeTypes表 MimeTypes表 mimes = [("ez", " ...
- PC chrome开启自带的dark mode
地址 复制下面的地址到chrome地址栏打开,再设置为 Enable 就可以开启了. chrome://flags/#enable-force-dark
