Python 基础 一
Python 基础 一
一、关于Python的介绍
python的创始人为吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum),这一两年在国内很流行,应用很广泛。
二、Python的基础知识(1)
1.编译和解释的区别
编译器是把源程序的每一条语句都编译成机器语言,并保存成二进制文件,这样运行时计算机可以直接以机器语言来运行此程序,速度很快;
解释器则是只在执行程序时,才一条一条的解释成机器语言给计算机来执行,所以运行速度是不如编译后的程序运行的快的.(Python就是解释型的语言)
这是因为计算机不能直接认识并执行我们写的语句,它只能认识机器语言(是二进制的形式)
2.Python的安装
1、下载安装包
https://www.python.org/downloads/
2、安装
默认安装路径:C:\python27
3、配置环境变量
【右键计算机】--》【属性】--》【高级系统设置】--》【高级】--》【环境变量】--》【在第二个内容框中找到 变量名为Path 的一行,双击】 --> 【Python安装目录追加到变值值中,用 ; 分割】
如:原来的值;C:\python27,切记前面有分号
三、变量
3.1、变量声明:
1. Python将所有数据存为内存对象
2. Python中,变量事实上是指向内存对象的引用
3. 动态类型:在任何时刻,只要需要,某个对象引用都可以重新引用一个不同的对象(可以是不同的数据类型)内建函数type()用于返回给定数据项的数据类型
4. "="用于将变量名与内存中的某个对象绑定:如果对象实现存在,就直接进行绑定;否则,则由"="创建引用的对象,变量名也是对象存在内存,比如:name='jerry',name这个指针指向jerry,name='tom'的时候,name是指针指向tom,但是jerry仍在内存中存放着,只是没有被变量名指向,到一定时候会被垃圾收集器回收,和java有点像。其中当test='jerry'时,test和name这两个变量名指向内存的地址是一样的。id(test),id(name),变量名是内存引用的标识或符号。
3.2、变量定义的规则:
1. 变量名只能是 字母、数字或下划线的任意组合
2. 变量名的第一个字符不能是数字
3. 以下关键字不能声明为变量名
['and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'exec', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'print', 'raise','return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
3.3、变量的官方建议命名实例
- 使用下划线'_'作为连接,如 name_variables
四、字符编码
ASCII 其最多只能用 8 位来表示(一个字节),即:2**8 = 256-1,所以,ASCII码最多只能表示 255 个符号,python2.x解释器默认是ASCII编码。
Unicode规定所有的字符和符号最少由 16 位来表示(2个字节),即:2 **16 = 65536,注:此处说的的是最少2个字节,可能更多,比如汉字就需要3个字节,python3.x解释器默认是Unicode编码。
UTF-8,是对Unicode编码的压缩和优化,他不再使用最少使用2个字节,而是将所有的字符和符号进行分类:ASCII码中的内容用1个字节保存、欧洲的字符用2个字节保存,东亚的字符用3个字节保存
五、输入、输出、注释
1、Python3.x提供了一个input(),可以让用户输入字符串。比如输入用户的名字:
python3中格式化输出默认接收的都视为字符串,如果你获取的是要数字类型则需要另外强制转换为int()转换为数字类型才能获得数字
输入密码时,如果想要不可见,需要利用 getpass 模块中的 getpass 方法
input()在输入字符串的时候报错,变量未定义,数值型则没有报错,如果是字符串则需要引号'' or "",或者事先定义变量赋值
注释:
#号可以从一行的任何地方开始
'''''',"""""",三引号用于多行注释
\,表示续行符
注意:如果''''''三引号是在一个def 函数或者class 定义类的下方则是对这个函数或者类的说明,可以通过__doc__动态获得文档子串
六、流程控制
1.If语句与流程控制
python的比较操作:
所有的Python对象都支持比较操作:
- 可用于测试值相等、相对大小等
- 如果是复合对象,python会检查其所有部分,包括自动遍历各级嵌套对象,知道可以得出最终结果
测试操作符:
- "==" 操作符测试值的相等性
- "is" 表达式测试对象的一致性
- "in" 成员关系测试
如何实现比较操作:
python中不同类型的比较方法:
- (1)数字:通过相对大小进行比较
- (2)字符串:按照字典次序逐次进行比较
- (3)列表和元组:自左至右比较各部分内容
- (4)字典:对排序之后的(键、值)列表进行比较
python中真和假的含义:
- (1)非0数字为真,否则为假
- (2)非空对象为真,否则为假
- (3)None则始终为假
比较和相等测试会递归地应用于数据结构中
返回值为True或False
组合条件测试:
- X and Y: 与运算
- X or Y: 或运算
- not X : 非运算
if测试的语法结构:
if boolean_expression1:
suite1
elif boolean_expression2:
suite2
else:
else_suite
注意:
elif语句是可选的
仅用与占位,而后在填充相关语句时,可以使用pass
if/else三元表达式:
通常在为某变量设定默认值时通常用到如下表达式
A = X if Y else Z
或:
if Y:
A = X
else
A = Z
其通用条件表达式语法格式为:
expression1 if boolean_express else expression2
如果boolean_express的值为True,则条件表达式的结果为express1,否则为express2
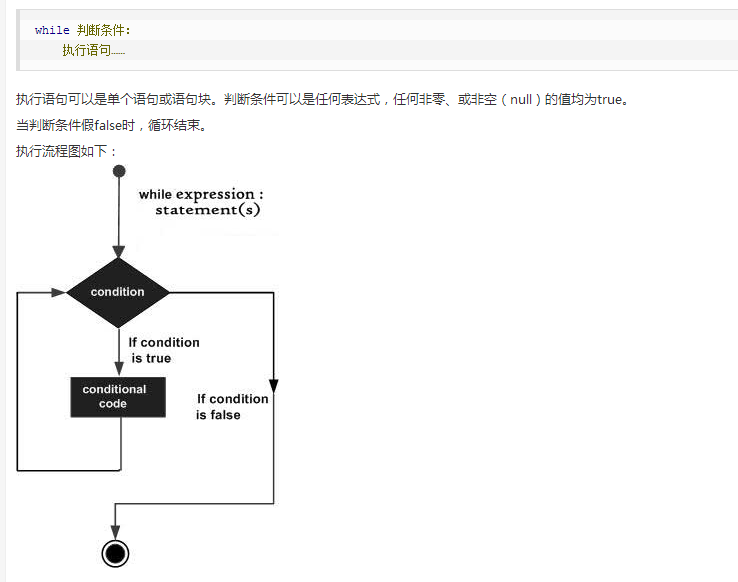
七、循环for,while
循环机制及应用场景
while循环:
- (1)用于编写通用迭代结构
- (2)顶端测试为真即会执行循环体,并会重复多次测试直到为假后执行循环后的其他语句
for循环:
- (1)一个通用的序列迭代器,用于遍历任何有序的序列对象内的元素
- (2)可用于字符串、元组、列表和其他的内置可迭代对象,以及通过类所创建的新对象
python也提供了一些能够进行隐性迭代的工具:
- (1)in成员关系测试
- (2)列表解析
- (3)map、reduce和filter函数
break: 跳出最内层的循环
continue: 跳出所处的最近层循环的开始处
pass: 占位语句
外层变量,可以被内层代码使用
内层变量,不应被外层代码使用
while循环:
while True: 死循环
语法格式:
while boolean_express:
while_suite
else:
else_suite
注意:
- else分支为可选部分
- 只要boolean_express的结果为True,循环就会执行
- boolean_express的结果为False时终止循环,此时如果有else分支,则会执行
for循环:
语法格式:
for expression1 in iterable:
for_suite
else:
else_suite
通常,expression或是一个单独的变量,或是一个变量序列,一般以元组的形式给出
如果以元组或列表用于expression,则其中的每个数据项都会拆分到表达式的项
T =
[(1,2),(3,4),(5,6),(7,8)]
for (a,b) in T:
print(a,b)
编写循环的技巧:
(1)for循环比while循环执行速度快
(2)python提供了两个内置函数,用于在for循环中定制特殊的循环python3.x 只有range,python2.x有(range,xrange)
- range: 一次性地返回连续的整数列表
- xrange: 一次产生一个数据元素,相较于range更节约空间
- zip:返回并行的元素元组的列表,常用于在for循环中遍历数个序列

八、数据类型
核心数据类型:
- 数字:int, long(python3.5已经没有), float, complex, bool
- 字符:str, unicode
- 列表:list
- 字典:dict
- 元组:tuple
- 集合:set(可变集合),frozenset(不可变集合)
- 文件:file
数字类型:
python的数字字面量:整数,布尔型,浮点数,复数,所有数字类型均为不可变
int(整型)
数字类型:
python的数字字面量:整数,布尔型,浮点数,复数,所有数字类型均为不可变
int(整型)
在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
bool(布尔型)
float(浮点型)
数字操作:+ , -, *, /, //, **, %, -x, +x
附上源码:
class int(object):
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
"""
def bit_length(self):
""" 返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数 """
"""
int.bit_length() -> int Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
>>> bin(37)
'0b100101'
>>> (37).bit_length()
"""
return 0 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 返回该复数的共轭复数 """
""" Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """
pass def __abs__(self):
""" 返回绝对值 """
""" x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """
pass def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass def __and__(self, y):
""" x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """
pass def __cmp__(self, y):
""" 比较两个数大小 """
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass def __coerce__(self, y):
""" 强制生成一个元组 """
""" x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """
pass def __divmod__(self, y):
""" 相除,得到商和余数组成的元组 """
""" x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """
pass def __div__(self, y):
""" x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """
pass def __float__(self):
""" 转换为浮点类型 """
""" x.__float__() <==> float(x) """
pass def __floordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """
pass def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 内部调用 __new__方法或创建对象时传入参数使用 """
pass def __hash__(self):
"""如果对象object为哈希表类型,返回对象object的哈希值。哈希值为整数。在字典查找中,哈希值用于快速比较字典的键。两个数值如果相等,则哈希值也相等。"""
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass def __hex__(self):
""" 返回当前数的 十六进制 表示 """
""" x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """
pass def __index__(self):
""" 用于切片,数字无意义 """
""" x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """
pass def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__
""" 构造方法,执行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 时,自动调用,暂时忽略 """
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass def __int__(self):
""" 转换为整数 """
""" x.__int__() <==> int(x) """
pass def __invert__(self):
""" x.__invert__() <==> ~x """
pass def __long__(self):
""" 转换为长整数 """
""" x.__long__() <==> long(x) """
pass def __lshift__(self, y):
""" x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """
pass def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass def __mul__(self, y):
""" x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """
pass def __neg__(self):
""" x.__neg__() <==> -x """
pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass def __nonzero__(self):
""" x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """
pass def __oct__(self):
""" 返回改值的 八进制 表示 """
""" x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """
pass def __or__(self, y):
""" x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """
pass def __pos__(self):
""" x.__pos__() <==> +x """
pass def __pow__(self, y, z=None):
""" 幂,次方 """
""" x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass def __radd__(self, y):
""" x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """
pass def __rand__(self, y):
""" x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """
pass def __rdivmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """
pass def __rdiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass def __repr__(self):
"""转化为解释器可读取的形式 """
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass def __str__(self):
"""转换为人阅读的形式,如果没有适于人阅读的解释形式的话,则返回解释器课阅读的形式"""
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass def __rfloordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """
pass def __rlshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """
pass def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass def __rmul__(self, y):
""" x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """
pass def __ror__(self, y):
""" x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """
pass def __rpow__(self, x, z=None):
""" y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass def __rrshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """
pass def __rshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """
pass def __rsub__(self, y):
""" x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
pass def __rtruediv__(self, y):
""" x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass def __rxor__(self, y):
""" x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """
pass def __sub__(self, y):
""" x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
pass def __truediv__(self, y):
""" x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """
pass def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs):
""" 返回数值被截取为整形的值,在整形中无意义 """
pass def __xor__(self, y):
""" x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """
pass denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分母 = 1 """
"""the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 虚数,无意义 """
"""the imaginary part of a complex number""" numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分子 = 数字大小 """
"""the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 实属,无意义 """
"""the real part of a complex number""" int
字符类型:不可变对象
字符串字面量:把文本放入单引号、双引号或三引号中,python2.x默认不是国际字符集unicode,需要unicode定义时加上u,python3无需加
>>> str1 = u'hello world'
>>> type(str1)
unicode
文档字串:模块、类或函数的第一条语句是一个字符的话,该字符串就成为文档字符串,可以使用__doc__属性引用
>>> def printName():
'test function'
print('hello world') >>> printName.__doc__
适用于字符串常用方法:
str.capitalize() 将字符串的首字母变大写
str.upper() 将字符串变成大写
str.lower() 将字符串变成小写
str.index() 找出索引对应的字符串
str.find() 同上
str.format() 也是格式化的一种
str.join() 以str为分隔符连接字符串
str.strip() 将字符串两边中的空格去掉
str.replace() 查找替换
str.count() 找出字符串中元素出现的次数
str.center() 以什么字符从字符串两边填充
str.split() 以什么为分隔符分隔字符串
str.title() 把每个单词的首字母变大写
str.isupper() 判断是否为大写
str.islower() 判断是否为小写
str.isalnum() 判断是否是字母数字
str.isalpha() 判断是否是字母下划线
str.isdigit() 判断是否是数字
str.isspace() 判断是否为空
str.startswith() 找出以什么为开头的字符元素
str.endswith() 找出以什么为结尾的字符元素
附上源码:
class str(basestring):
"""
str(object='') -> string Return a nice string representation of the object.
If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object.
"""
def capitalize(self):
""" 首字母变大写 """
"""
S.capitalize() -> string Return a copy of the string S with only its first character
capitalized.
"""
return "" def center(self, width, fillchar=None):
""" 内容居中,width:总长度;fillchar:空白处填充内容,默认无 """
"""
S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> string Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
"""
return "" def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 子序列个数 """
"""
S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in
string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted
as in slice notation.
"""
return 0 def decode(self, encoding=None, errors=None):
""" 解码 """
"""
S.decode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object Decodes S using the codec registered for encoding. encoding defaults
to the default encoding. errors may be given to set a different error
handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
a UnicodeDecodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore' and 'replace'
as well as any other name registered with codecs.register_error that is
able to handle UnicodeDecodeErrors.
"""
return object() def encode(self, encoding=None, errors=None):
""" 编码,针对unicode """
"""
S.encode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object Encodes S using the codec registered for encoding. encoding defaults
to the default encoding. errors may be given to set a different error
handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and
'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with
codecs.register_error that is able to handle UnicodeEncodeErrors.
"""
return object() def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None):
""" 是否以 xxx 结束 """
"""
S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
"""
return False def expandtabs(self, tabsize=None):
""" 将tab转换成空格,默认一个tab转换成8个空格 """
"""
S.expandtabs([tabsize]) -> string Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed.
"""
return "" def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 寻找子序列位置,如果没找到,返回 -1 """
"""
S.find(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. Return -1 on failure.
"""
return 0 def format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format
""" 字符串格式化,动态参数,将函数式编程时细说 """
"""
S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> string Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs.
The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
"""
pass def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 子序列位置,如果没找到,报错 """
S.index(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int Like S.find() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
"""
return 0 def isalnum(self):
""" 是否是字母和数字 """
"""
S.isalnum() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False def isalpha(self):
""" 是否是字母 """
"""
S.isalpha() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False def isdigit(self):
""" 是否是数字 """
"""
S.isdigit() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are digits
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False def islower(self):
""" 是否小写 """
"""
S.islower() -> bool Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is
at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False def isspace(self):
"""
S.isspace() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are whitespace
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False def istitle(self):
"""
S.istitle() -> bool Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one
character in S, i.e. uppercase characters may only follow uncased
characters and lowercase characters only cased ones. Return False
otherwise.
"""
return False def isupper(self):
"""
S.isupper() -> bool Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is
at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False def join(self, iterable):
""" 连接 """
"""
S.join(iterable) -> string Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the
iterable. The separator between elements is S.
"""
return "" def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None):
""" 内容左对齐,右侧填充 """
"""
S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> string Return S left-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
"""
return "" def lower(self):
""" 变小写 """
"""
S.lower() -> string Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase.
"""
return "" def lstrip(self, chars=None):
""" 移除左侧空白 """
"""
S.lstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
"""
return "" def partition(self, sep):
""" 分割,前,中,后三部分 """
"""
S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it,
the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not
found, return S and two empty strings.
"""
pass def replace(self, old, new, count=None):
""" 替换 """
"""
S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> string Return a copy of string S with all occurrences of substring
old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
"""
return "" def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
"""
S.rfind(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. Return -1 on failure.
"""
return 0 def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
"""
S.rindex(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int Like S.rfind() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
"""
return 0 def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None):
"""
S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> string Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
"""
return "" def rpartition(self, sep):
"""
S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return
the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the
separator is not found, return two empty strings and S.
"""
pass def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None):
"""
S.rsplit([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the
delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and working
to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit splits are
done. If sep is not specified or is None, any whitespace string
is a separator.
"""
return [] def rstrip(self, chars=None):
"""
S.rstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
"""
return "" def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None):
""" 分割, maxsplit最多分割几次 """
"""
S.split([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the
delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any
whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are removed
from the result.
"""
return [] def splitlines(self, keepends=False):
""" 根据换行分割 """
"""
S.splitlines(keepends=False) -> list of strings Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries.
Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends
is given and true.
"""
return [] def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None):
""" 是否起始 """
"""
S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
"""
return False def strip(self, chars=None):
""" 移除两段空白 """
"""
S.strip([chars]) -> string or unicode Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing
whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
"""
return "" def swapcase(self):
""" 大写变小写,小写变大写 """
"""
S.swapcase() -> string Return a copy of the string S with uppercase characters
converted to lowercase and vice versa.
"""
return "" def title(self):
"""
S.title() -> string Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with uppercase
characters, all remaining cased characters have lowercase.
"""
return "" def translate(self, table, deletechars=None):
"""
转换,需要先做一个对应表,最后一个表示删除字符集合
intab = "aeiou"
outtab = ""
trantab = maketrans(intab, outtab)
str = "this is string example....wow!!!"
print str.translate(trantab, 'xm')
""" """
S.translate(table [,deletechars]) -> string Return a copy of the string S, where all characters occurring
in the optional argument deletechars are removed, and the
remaining characters have been mapped through the given
translation table, which must be a string of length 256 or None.
If the table argument is None, no translation is applied and
the operation simply removes the characters in deletechars.
"""
return "" def upper(self):
"""
S.upper() -> string Return a copy of the string S converted to uppercase.
"""
return "" def zfill(self, width):
"""方法返回指定长度的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。"""
"""
S.zfill(width) -> string Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field
of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
"""
return "" def _formatter_field_name_split(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass def _formatter_parser(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass def __contains__(self, y):
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
pass def __eq__(self, y):
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass def __format__(self, format_spec):
"""
S.__format__(format_spec) -> string Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec.
"""
return "" def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass def __getitem__(self, y):
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass def __getslice__(self, i, j):
"""
x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass def __ge__(self, y):
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass def __gt__(self, y):
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass def __hash__(self):
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass def __init__(self, string=''): # known special case of str.__init__
"""
str(object='') -> string Return a nice string representation of the object.
If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass def __len__(self):
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass def __le__(self, y):
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass def __lt__(self, y):
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass def __mul__(self, n):
""" x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass def __ne__(self, y):
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass def __repr__(self):
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass def __rmul__(self, n):
""" x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
pass def __sizeof__(self):
""" S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """
pass def __str__(self):
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass
列表类型:可变对象
表达式符号:[]
创建列表:
name_list = ['alex', 'seven', 'eric']
或
name_list = list(['alex', 'seven', 'eric'])
容器类型
任意对象的有序集合,通过索引访问其中的元素,可变对象
异构混合类型,可以任意嵌套其它类型
支持在原处修改:
修改指定的索引元素,修改指定的分片,删除语句,类的内置方法
适用于列表常用方法:
list.append() 在列表尾部插入
list.copy() 浅复制,只会复制第一层,如果有嵌套序列则不会复制,如果需要复制则要导入copy模块
list.count() 统计列表中元素的次数
list.extend() 把另外一个列表合并,并不是追加
list.index() 列表中元素出现的索引位置
list.insert() 在列表中指定索引位置前插入元素
list.pop() 没有指定索引,则弹出最后一个元素,返回的结果是弹出的索引对应的元素
list.remove() 删除指定的元素
list.reverse() 进行逆序
list.sort() 进行排序,python3无法把数字和字符串一起排序
l1 + l2 : 合并两个列表,返回一个新的列表,不会修改原列表
l1 * N : 把l1重复N次,返回一个新列表
附上源码:
class list(object):
"""
list() -> new empty list
list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
"""
def append(self, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.append(object) -- append object to end """
pass def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """
return 0 def extend(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.extend(iterable) -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable """
pass def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
"""
return 0 def insert(self, index, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index """
pass def pop(self, index=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last).
Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
"""
pass def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.remove(value) -- remove first occurrence of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
"""
pass def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* """
pass def sort(self, cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) -- stable sort *IN PLACE*;
cmp(x, y) -> -1, 0, 1
"""
pass def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
pass def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """
pass def __delslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__delslice__(i, j) <==> del x[i:j] Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass def __iadd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iadd__(y) <==> x+=y """
pass def __imul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__imul__(y) <==> x*=y """
pass def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of list.__init__
"""
list() -> new empty list
list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass def __reversed__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the list """
pass def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
pass def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """
pass def __setslice__(self, i, j, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__setslice__(i, j, y) <==> x[i:j]=y Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.__sizeof__() -- size of L in memory, in bytes """
pass __hash__ = None
字典类型:dict 可变对象
表达式符号:{}
创建字典:
person = {"name": "tomcat", 'age': 18}
或
person = dict({"name": "tomcat", 'age': 18})
字典在其他编程语言中又称作关联数组或散列表
通过键(key)实现元素存取,无序的,可变类型容器,长度可变,异构,嵌套
{}: 空字典
{'x':32,'y':[1,2,3,4]}
两种遍历字典方法:
第一种:
for k,v in
dict.items():
print(k,v)
第二种:高效(推荐使用)
for key in dict:
print(key,dict[key])
字典中常用的方法:
适用于字典常用方法:
dict.clear() 清除字典中所有元素
dict.copy() 字典复制,d2 = d1.copy(),是浅复制,如果深复制需要copy模块
dict.fromkeys(S) 生成一个新字典
dict.get(key) 取得某个key的value
dict.has_key(key) 判断字典是否有这个key
dict.items() 将字典的键值拆成元组,全部元组组成一个列表
dict.keys() 返回所有的key为一个列表
dict.values() 返回所有的value为一个列表
dict.pop(key) 弹出某个key-value
dict.popitem() 随机弹出key-value
dict.update(key) 将一个字典合并到当前字典中
dict.iteritems() 生成key-value迭代器,可以用next()取下个key-value
dict.iterkeys() 生成key迭代器
dict.itervalues() 生成values迭代器
元组类型:不可变对象
表达式符号:()
创建元组:
ages = (11, 22, 33, 44, 55)
或
ages = tuple((11, 22, 33, 44, 55))
容器类型
任意对象的有序集合,通过索引访问其中的元素,不可变对象
异构混合类型,可以任意嵌套其它类型
虽然元组本身不可变,但如果元组内嵌套了可变类型的元素,那么此类元素的修改不会返回新元组
(): 空元组
(1,): 单个元组需要尾部加上逗号,如果元素是数字没有加逗号则不是元组
(1,2): 多元素元组
1,2,3,4: 在定义变量时没有加上小括号,默认是元组,最好不建议使用
适用于元组常用方法:
tuple.count() 统计元组中元素的个数
tuple.index() 找出元组中元素的索引位置
Python 基础 一的更多相关文章
- python之最强王者(2)——python基础语法
背景介绍:由于本人一直做java开发,也是从txt开始写hello,world,使用javac命令编译,一直到使用myeclipse,其中的道理和辛酸都懂(请容许我擦干眼角的泪水),所以对于pytho ...
- Python开发【第二篇】:Python基础知识
Python基础知识 一.初识基本数据类型 类型: int(整型) 在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31-2**31-1,即-2147483648-2147483647 在64位 ...
- Python小白的发展之路之Python基础(一)
Python基础部分1: 1.Python简介 2.Python 2 or 3,两者的主要区别 3.Python解释器 4.安装Python 5.第一个Python程序 Hello World 6.P ...
- Python之路3【第一篇】Python基础
本节内容 Python简介 Python安装 第一个Python程序 编程语言的分类 Python简介 1.Python的由来 python的创始人为吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum) ...
- 进击的Python【第三章】:Python基础(三)
Python基础(三) 本章内容 集合的概念与操作 文件的操作 函数的特点与用法 参数与局部变量 return返回值的概念 递归的基本含义 函数式编程介绍 高阶函数的概念 一.集合的概念与操作 集合( ...
- 进击的Python【第二章】:Python基础(二)
Python基础(二) 本章内容 数据类型 数据运算 列表与元组的基本操作 字典的基本操作 字符编码与转码 模块初探 练习:购物车程序 一.数据类型 Python有五个标准的数据类型: Numbers ...
- Python之路【第一篇】python基础
一.python开发 1.开发: 1)高级语言:python .Java .PHP. C# Go ruby c++ ===>字节码 2)低级语言:c .汇编 2.语言之间的对比: 1)py ...
- python基础之day1
Python 简介 Python是著名的“龟叔”Guido van Rossum在1989年圣诞节期间,为了打发无聊的圣诞节而编写的一个编程语言. Python为我们提供了非常完善的基础代码库,覆盖了 ...
- python基础之文件读写
python基础之文件读写 本节内容 os模块中文件以及目录的一些方法 文件的操作 目录的操作 1.os模块中文件以及目录的一些方法 python操作文件以及目录可以使用os模块的一些方法如下: 得到 ...
- python基础之编码问题
python基础之编码问题 本节内容 字符串编码问题由来 字符串编码解决方案 1.字符串编码问题由来 由于字符串编码是从ascii--->unicode--->utf-8(utf-16和u ...
随机推荐
- MyEclipse下安装MyBatis Generator代码反向生成工具
一.离线方式: 在http://mybatis.googlecode.com/svn/sub-projects/generator/trunk/eclipse/UpdateSite/下载 featur ...
- Bug跟踪的流程
本文以翼发云协同项目管理系统为例子来讲解Bug跟踪的流程,它以工作流为中心的集成式Bug跟踪软件,它广泛地应用于研发行业的产品缺陷管理 与跟踪.事务跟踪.问题跟踪.任务跟踪.查询跟踪.需求管理.变更跟 ...
- 构建微服务(Building Microservices)-PDF 文档
闲时翻译了几篇基于Spring Cloud.Netflix OSS 构建微服务的英文文章,为方便分享交流,整理为PDF文档. PDF 文档目录: 目录 一.微服务操作模型... 3 1. 前提 ...
- CSS.01 -- 选择器及相关的属性文本、文字、字体、颜色、
与html相比,Css支持更丰富的文档外观,Css可以为任何元素的文本和背景设置颜色:允许在任何元素外围设置边框:允许改变文本的大小,装饰(如下划线),间隔,甚至可以确定是否显示文本. 什么是CSS? ...
- [python爬虫]爬取学校教务处成绩
学校教务处网站 登陆窗口 表单数据 观察登陆窗口和提交的表单数据可知只要将账号.密码.验证码正确赋值提交即可模拟登陆. 账号和密码都有,问题的关键就在验证码上. 右键验证码图片审查观察源码如下图: 刚 ...
- Nginx + ngx_lua安装测试【CentOs下】
最近打算搞搞nginx,扒着各位先驱的文章自己进行测试下,中间过程也是错误不断,记录一下,以备使用. nginx的安装挺简单的,主要还是研究下一些第三方的模块,首先想试下初始化 ...
- Unity利用Sapi进行windows语音开发
软件中的语音技术主要包含两种:语音识别speech recognition和语音合成speech synthesis.一般地,开发者会因为技术实力和资金实力等各方面的问题无力完成专业的语音引擎,因此通 ...
- Visual Studio 2015 Professional 破解
Visual Studio 2015 Professional 版本 破解序列号:HMGNV-WCYXV-X7G9W-YCX63-B98R2
- 【转】Eclipse 如何添加Android SDK
问题描述: 如何为Eclipse编程软件添加Android SDK功能,使其能进行Android开发. 解决方法: 软件版本:Eclipse 3.7,installer_r18-windows.e ...
- Ubuntu14.04配置Apache支持多个站点
怎样在一个Ubuntu的机器上(虚拟机)配置Apache支持多个网站呢? 比如你有一台独立的Ubuntu虚拟机,配有一个外网的IP(45.46.47.48),并且注册了两个域名AAA.com和BBB. ...
