(4)ardunio 矩阵求解官方库改造,添加逆的求解
多此一举,原来官方库给了求逆的函数,在源码里
除此之外,还有转置矩阵,只不过样例没显示出来。
//Matrix Inversion Routine
// * This function inverts a matrix based on the Gauss Jordan method.
// * Specifically, it uses partial pivoting to improve numeric stability.
// * The algorithm is drawn from those presented in
// NUMERICAL RECIPES: The Art of Scientific Computing.
// * The function returns 1 on success, 0 on failure.
// * NOTE: The argument is ALSO the result matrix, meaning the input matrix is REPLACED
int MatrixMath::Invert(mtx_type* A, int n)
{
// A = input matrix AND result matrix
// n = number of rows = number of columns in A (n x n)
int pivrow = 0; // keeps track of current pivot row
int k, i, j; // k: overall index along diagonal; i: row index; j: col index
int pivrows[n]; // keeps track of rows swaps to undo at end
mtx_type tmp; // used for finding max value and making column swaps for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
// find pivot row, the row with biggest entry in current column
tmp = 0;
for (i = k; i < n; i++)
{
if (abs(A[i * n + k]) >= tmp) // 'Avoid using other functions inside abs()?'
{
tmp = abs(A[i * n + k]);
pivrow = i;
}
} // check for singular matrix
if (A[pivrow * n + k] == 0.0f)
{
Serial.println("Inversion failed due to singular matrix");
return 0;
} // Execute pivot (row swap) if needed
if (pivrow != k)
{
// swap row k with pivrow
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
tmp = A[k * n + j];
A[k * n + j] = A[pivrow * n + j];
A[pivrow * n + j] = tmp;
}
}
pivrows[k] = pivrow; // record row swap (even if no swap happened) tmp = 1.0f / A[k * n + k]; // invert pivot element
A[k * n + k] = 1.0f; // This element of input matrix becomes result matrix // Perform row reduction (divide every element by pivot)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
A[k * n + j] = A[k * n + j] * tmp;
} // Now eliminate all other entries in this column
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (i != k)
{
tmp = A[i * n + k];
A[i * n + k] = 0.0f; // The other place where in matrix becomes result mat
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
A[i * n + j] = A[i * n + j] - A[k * n + j] * tmp;
}
}
}
} // Done, now need to undo pivot row swaps by doing column swaps in reverse order
for (k = n - 1; k >= 0; k--)
{
if (pivrows[k] != k)
{
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
tmp = A[i * n + k];
A[i * n + k] = A[i * n + pivrows[k]];
A[i * n + pivrows[k]] = tmp;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
ESP8266 07模块
首先安装库
搜索

运行基本实例
这个例子没有矩阵求逆的函数,自己添加。
使用的ESP8266芯片 07板 可外置天线
源程序
#include <MatrixMath.h>
#include "math.h"
float a[4][4]={
{1,0,0,0},
{1,0.5,0,0},
{1,0,1,0},
{1,0,0,1},
};
float **b = new float *[4]; // 拷贝a
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
int i,j;
for (i=0; i< 4; i++)
{
b[i] = new float[4];
for (j=0; j< 4; j++)
b[i][j]=a[i][j]; // 拷贝a
}
Serial.print("\nMAT A IS:");
for (int i=0; i<=3; i++)
{ Serial.println();
for (int j=0; j<=3; j++)
{ Serial.print(a[i][j]);Serial.print(" , ");}
}
Matrix.NI(b,4);
Serial.print("\nMAT A- IS:");
for (int i=0; i<=3; i++)
{
Serial.println("");
for (int j=0; j<=3; j++)
{ Serial.print(b[i][j]);Serial.print(" , ");}
}
}
void loop()
{
// Matrix.Multiply((mtx_type*)A, (mtx_type*)B, N, N, N, (mtx_type*)C);
//
// Serial.println("\nAfter multiplying C = A*B:");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)A, N, N, "A");
//
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)B, N, N, "B");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)C, N, N, "C");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)v, N, 1, "v");
//
// Matrix.Add((mtx_type*) B, (mtx_type*) C, N, N, (mtx_type*) C);
// Serial.println("\nC = B+C (addition in-place)");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)C, N, N, "C");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)B, N, N, "B");
//
// Matrix.Copy((mtx_type*)A, N, N, (mtx_type*)B);
// Serial.println("\nCopied A to B:");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)B, N, N, "B");
//
// Matrix.Invert((mtx_type*)A, N);
// Serial.println("\nInverted A:");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)A, N, N, "A");
//
// Matrix.Multiply((mtx_type*)A, (mtx_type*)B, N, N, N, (mtx_type*)C);
// Serial.println("\nC = A*B");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)C, N, N, "C");
//
// // Because the library uses pointers and DIY indexing,
// // a 1D vector can be smoothly handled as either a row or col vector
// // depending on the dimensions we specify when calling a function
// Matrix.Multiply((mtx_type*)C, (mtx_type*)v, N, N, 1, (mtx_type*)w);
// Serial.println("\n C*v = w:");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)v, N, 1, "v");
// Matrix.Print((mtx_type*)w, N, 1, "w");
// while(1);
}
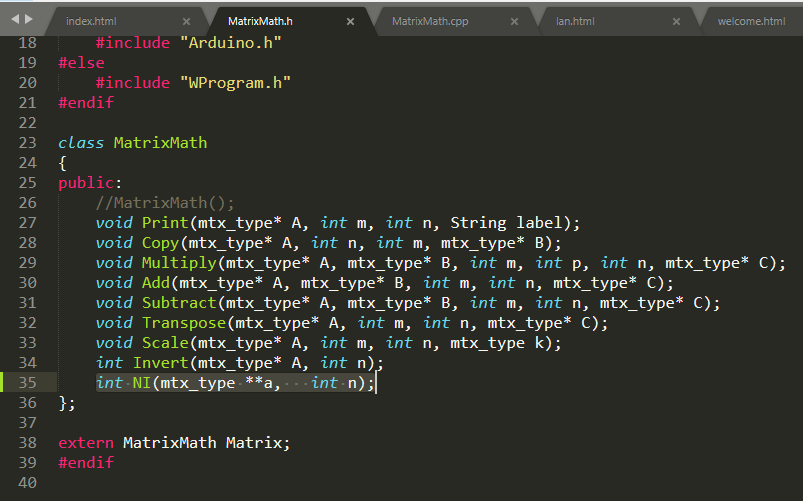
依赖库文家修改
头文件
添加一个函数
int NI(mtx_type **a, int n);
/*
* MatrixMath.h Library for Matrix Math
*
* Created by Charlie Matlack on 12/18/10.
* Modified from code by RobH45345 on Arduino Forums, algorithm from
* NUMERICAL RECIPES: The Art of Scientific Computing.
* Modified to work with Arduino 1.0/1.5 by randomvibe & robtillaart
* Made into a real library on GitHub by Vasilis Georgitzikis (tzikis)
* so that it's easy to use and install (March 2015)
*/ #ifndef MatrixMath_h
#define MatrixMath_h #define mtx_type float #if defined(ARDUINO) && ARDUINO >= 100
#include "Arduino.h"
#else
#include "WProgram.h"
#endif class MatrixMath
{
public:
//MatrixMath();
void Print(mtx_type* A, int m, int n, String label);
void Copy(mtx_type* A, int n, int m, mtx_type* B);
void Multiply(mtx_type* A, mtx_type* B, int m, int p, int n, mtx_type* C);
void Add(mtx_type* A, mtx_type* B, int m, int n, mtx_type* C);
void Subtract(mtx_type* A, mtx_type* B, int m, int n, mtx_type* C);
void Transpose(mtx_type* A, int m, int n, mtx_type* C);
void Scale(mtx_type* A, int m, int n, mtx_type k);
int Invert(mtx_type* A, int n);
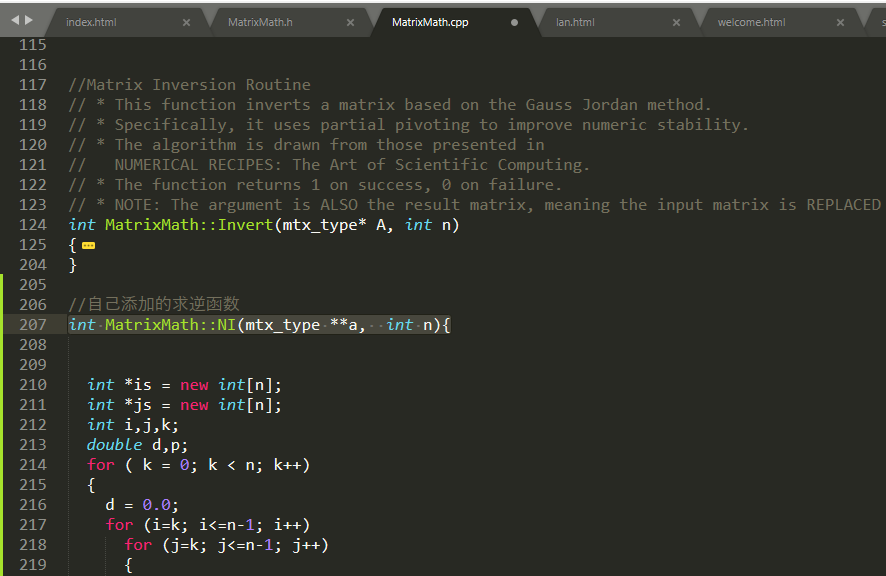
// 自己添加的求逆函数
int NI(mtx_type **a, int n);
}; extern MatrixMath Matrix;
#endif
库文件.cpp修改
修改后
/*
* MatrixMath.cpp Library for Matrix Math
*
* Created by Charlie Matlack on 12/18/10.
* Modified from code by RobH45345 on Arduino Forums, algorithm from
* NUMERICAL RECIPES: The Art of Scientific Computing.
*/ #include "MatrixMath.h" #define NR_END 1 MatrixMath Matrix; // Pre-instantiate // Matrix Printing Routine
// Uses tabs to separate numbers under assumption printed mtx_type width won't cause problems
void MatrixMath::Print(mtx_type* A, int m, int n, String label)
{
// A = input matrix (m x n)
int i, j;
Serial.println();
Serial.println(label);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
Serial.print(A[n * i + j]);
Serial.print("\t");
}
Serial.println();
}
} void MatrixMath::Copy(mtx_type* A, int n, int m, mtx_type* B)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
B[n * i + j] = A[n * i + j];
}
} //Matrix Multiplication Routine
// C = A*B
void MatrixMath::Multiply(mtx_type* A, mtx_type* B, int m, int p, int n, mtx_type* C)
{
// A = input matrix (m x p)
// B = input matrix (p x n)
// m = number of rows in A
// p = number of columns in A = number of rows in B
// n = number of columns in B
// C = output matrix = A*B (m x n)
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
C[n * i + j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < p; k++)
C[n * i + j] = C[n * i + j] + A[p * i + k] * B[n * k + j];
}
} //Matrix Addition Routine
void MatrixMath::Add(mtx_type* A, mtx_type* B, int m, int n, mtx_type* C)
{
// A = input matrix (m x n)
// B = input matrix (m x n)
// m = number of rows in A = number of rows in B
// n = number of columns in A = number of columns in B
// C = output matrix = A+B (m x n)
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
C[n * i + j] = A[n * i + j] + B[n * i + j];
} //Matrix Subtraction Routine
void MatrixMath::Subtract(mtx_type* A, mtx_type* B, int m, int n, mtx_type* C)
{
// A = input matrix (m x n)
// B = input matrix (m x n)
// m = number of rows in A = number of rows in B
// n = number of columns in A = number of columns in B
// C = output matrix = A-B (m x n)
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
C[n * i + j] = A[n * i + j] - B[n * i + j];
} //Matrix Transpose Routine
void MatrixMath::Transpose(mtx_type* A, int m, int n, mtx_type* C)
{
// A = input matrix (m x n)
// m = number of rows in A
// n = number of columns in A
// C = output matrix = the transpose of A (n x m)
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
C[m * j + i] = A[n * i + j];
} void MatrixMath::Scale(mtx_type* A, int m, int n, mtx_type k)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
A[n * i + j] = A[n * i + j] * k;
} //Matrix Inversion Routine
// * This function inverts a matrix based on the Gauss Jordan method.
// * Specifically, it uses partial pivoting to improve numeric stability.
// * The algorithm is drawn from those presented in
// NUMERICAL RECIPES: The Art of Scientific Computing.
// * The function returns 1 on success, 0 on failure.
// * NOTE: The argument is ALSO the result matrix, meaning the input matrix is REPLACED
int MatrixMath::Invert(mtx_type* A, int n)
{
// A = input matrix AND result matrix
// n = number of rows = number of columns in A (n x n)
int pivrow = 0; // keeps track of current pivot row
int k, i, j; // k: overall index along diagonal; i: row index; j: col index
int pivrows[n]; // keeps track of rows swaps to undo at end
mtx_type tmp; // used for finding max value and making column swaps for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
// find pivot row, the row with biggest entry in current column
tmp = 0;
for (i = k; i < n; i++)
{
if (abs(A[i * n + k]) >= tmp) // 'Avoid using other functions inside abs()?'
{
tmp = abs(A[i * n + k]);
pivrow = i;
}
} // check for singular matrix
if (A[pivrow * n + k] == 0.0f)
{
Serial.println("Inversion failed due to singular matrix");
return 0;
} // Execute pivot (row swap) if needed
if (pivrow != k)
{
// swap row k with pivrow
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
tmp = A[k * n + j];
A[k * n + j] = A[pivrow * n + j];
A[pivrow * n + j] = tmp;
}
}
pivrows[k] = pivrow; // record row swap (even if no swap happened) tmp = 1.0f / A[k * n + k]; // invert pivot element
A[k * n + k] = 1.0f; // This element of input matrix becomes result matrix // Perform row reduction (divide every element by pivot)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
A[k * n + j] = A[k * n + j] * tmp;
} // Now eliminate all other entries in this column
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (i != k)
{
tmp = A[i * n + k];
A[i * n + k] = 0.0f; // The other place where in matrix becomes result mat
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
A[i * n + j] = A[i * n + j] - A[k * n + j] * tmp;
}
}
}
} // Done, now need to undo pivot row swaps by doing column swaps in reverse order
for (k = n - 1; k >= 0; k--)
{
if (pivrows[k] != k)
{
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
tmp = A[i * n + k];
A[i * n + k] = A[i * n + pivrows[k]];
A[i * n + pivrows[k]] = tmp;
}
}
}
return 1;
} //自己添加的求逆函数
int MatrixMath::NI(mtx_type **a, int n){ int *is = new int[n];
int *js = new int[n];
int i,j,k;
double d,p;
for ( k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
d = 0.0;
for (i=k; i<=n-1; i++)
for (j=k; j<=n-1; j++)
{
p=fabs(a[i][j]);
if (p>d) { d=p; is[k]=i; js[k]=j;}
}
if ( 0.0 == d )
{
free(is); free(js); Serial.println("err**not inv\n");
return(0);
}
if (is[k]!=k)
for (j=0; j<=n-1; j++)
{
p=a[k][j];
a[k][j]=a[is[k]][j];
a[is[k]][j]=p;
}
if (js[k]!=k)
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
{
p=a[i][k];
a[i][k]=a[i][js[k]];
a[i][js[k]]=p;
}
a[k][k] = 1.0/a[k][k];
for (j=0; j<=n-1; j++)
if (j!=k)
{
a[k][j] *= a[k][k];
}
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
if (i!=k)
for (j=0; j<=n-1; j++)
if (j!=k)
{
a[i][j] -= a[i][k]*a[k][j];
}
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
if (i!=k)
{
a[i][k] = -a[i][k]*a[k][k];
}
}
for ( k = n-1; k >= 0; k--)
{
if (js[k]!=k)
for (j=0; j<=n-1; j++)
{
p = a[k][j];
a[k][j] = a[js[k]][j];
a[js[k]][j]=p;
}
if (is[k]!=k)
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
{
p = a[i][k];
a[i][k]=a[i][is[k]];
a[i][is[k]] = p;
}
}
free(is); free(js);
return(1); }
(4)ardunio 矩阵求解官方库改造,添加逆的求解的更多相关文章
- arm-none-eabi-gcc,makefile,stm官方库构建stm32f4xx工程
参考文章:http://www.stmcu.org/module/forum/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=603753&highlight=ubuntu ...
- 关于如何使用Altium Designer 10以上版本官方库
开卷有益:如果本帖不适合在此板块,请斑竹自行删除,发帖的目的纯属报答各位Amofans. Altium公司的Altium Designer 09版本及以下还能到Altium官网下载第三方Labr ...
- EXCEL类型库的添加
1. 创建新的C++工程 创建基于对话框的MFC程序 2. 添加库.添加Excel类库 在工程名上右键,选择“添加”—“类”(或者点击菜单栏的“项目”->“添加类”),选择“TypeLib中的M ...
- CMake 添加头文件目录,链接动态、静态库(添加子文件夹)
CMake支持大写.小写.混合大小写的命令. 当编译一个需要第三方库的项目时,需要知道: 去哪找头文件(.h),-I(GCC) INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES() 去哪找库文件(.so/.dl ...
- Qt下Eigen矩阵函数库的添加
第1步: 下载一个Eigen文件包,在官网下即可: http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/index.php?title=Main_Page 第2步: 用Qt随便建一个GUI工程,在. ...
- Eclispe使用Maven添加官方库的jar包
先到百度或google搜索maven仓库,在仓库中搜索需要的jar包,如poi.jar. 搜索到之后找到需要的jar包,找到这里
- 用Modelsim仿真QuartusII综合后网表时库的添加方法(转)
这两天做综合后仿真,发现FPGA器件库又不会加了,无奈上网找方法.说起来不好意思,很早就接触Modelsim这个仿真软件了,可是没有好好琢磨.把这两天找的方法贴出来,再加上自己的理解,以后忘了可以上博 ...
- Git学习笔记(一)创建版本库并添加文件
最近从廖雪峰老师的个人网站上学习git,做点笔记. ★★★★★ 先注册自己的username和email,否则会报如下错误: 注册:git config --global user.name &quo ...
- 初学git,初始化库|添加文件ignore|提交方法
1.初始化git仓库: 进入任意目录,右键选择:Git Bash Here,输入命令:git status 查看当前git库的状态. 如要排除文件,在库根目录下创建.gitignore文件(新建文件改 ...
随机推荐
- thinkphp 5.0.24 配置多模块注意的细节
/*index.php 文件 这一段用于生成模块用 build.php 只能生成诸如 admin hotel 开头为小写字母的模块 如果你设定的 大写开头 如 Hotel Admin 系统就会找不到 ...
- 【C语言】 strlen()入参空指针导致段错误
背景: 在工作中调试sqlite3相关代码的时候,调用printf()打印sqlite3_exec()的执行日志:因为sqlite3_exec()保存日志的参数传入时为NULL,且没有执行错误,所以再 ...
- 基于DigitalOcean+LAMP+WordPress搭建个人网站
1. 注册DigitalOcean并新建主机 为了搭建个人网站首先需要一个可以在公网范围访问的主机,可以选用国内如阿里云.国外如DigitalOcean的各种云主机提供商,这里选用DigitalOce ...
- Python 入门(3):运算符
Python语言支持以下类型的运算符: 算术运算符 比较(关系)运算符 赋值运算符 逻辑运算符 位运算符 成员运算符 身份运算符 运算符优先级 Python算术运算符: + 加 两个对象相加 a + ...
- 【LeetCode】 #7:反转整数 C语言
目录 题目 思路 初步想法 进一步想法 总结 最近打算练习写代码的能力,所以从简单题开始做. 大部分还是用C语言来解决. @(解法) 题目 给出一个 32 位的有符号整数,你需要将这个整数中每位上的数 ...
- ElasticSearch监控工具 - cerebro
官方地址:https://github.com/lmenezes/cerebro 需要有java环境 下载地址:https://github.com/lmenezes/cerebro/releases ...
- 女性对DeepNude脱衣技术的防护
写在前面的话 本文不提供下载方式,开源部分只是社区逆向后公开的部分源码 这篇文章有些人看了可能会比较极端,但不从技术角度分析又谈何防护?攻与防一直存在,不管是安全还是AI都是一样 你极端不极端,它就在 ...
- 【转载】C#使用ToList()将数组快速转换为List集合
在C#的编程中,数组和List集合是比较常用的两个集合类,有时候因为业务需要,需要将数组集合转换为List集合,此时就可以使用C#中的Linq的扩展方法ToList方法来实现,只需要简单的一条语句即可 ...
- 仿EXCEL插件,智表ZCELL产品V1.7 版本发布,增加自定义右键菜单功能
详细请移步 智表(ZCELL)官网www.zcell.net 更新说明 这次更新主要应用户要求,主要解决了自定义右键菜单事件的支持,并新增了公式中自定义函数传参.快捷键剪切等功能,欢迎大家体验使用. ...
- CI隐藏入口文件index.php
1.需要apache打开rewrite_module,然后修改httpd.conf的AllowOverride none 为AllowOverride All(里面,不同的环境目录不同) 2.在CI的 ...
