Chaikin Curves in Processing
转自:https://sighack.com/post/chaikin-curves
In this post, we’ll look at what Chaikin curves are, how to implement them in Processing as well as some ways you can use them in your artwork.
If you’re looking for a copy-pastable version of this algorithm in Processing, scroll to the end of the post!
All Processing code for this article, along with images and animated GIFs, can be found on Github
Chaikin Curves
In 1974, George Chaikin presented one of the first refinement-based corner cutting algorithms to generate a curve from a given set of control points. His approach involved generating a new curve by cutting the corners off the original (based on some fixed ratio), and repeating this a bunch of times.
Here is a visual demonstration of Chaikin’s corner-cutting algorithm with three iterations and a cut ratio of 25%:

Animation of Chaikin’s Corner-Cutting Algorithm for a Polyline
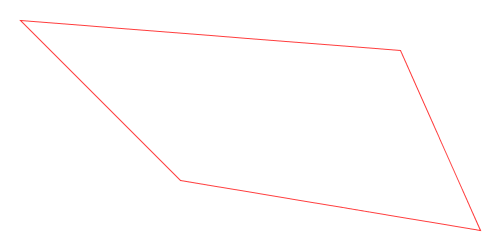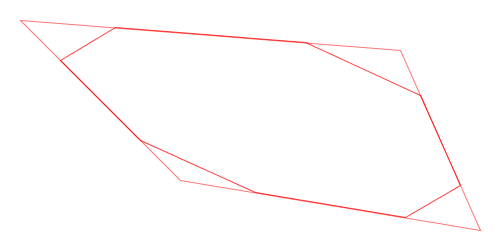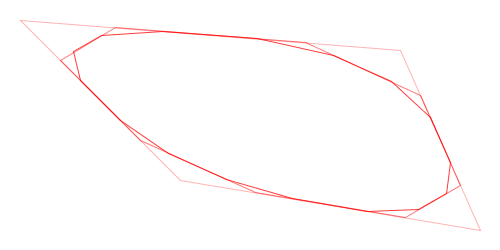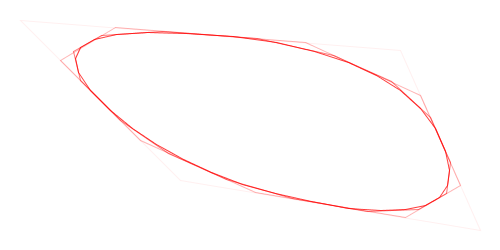
Animation of Chaikin’s Corner-Cutting Algorithm for a Closed Polygon
What Can I Do With Them?
Let’s now look at some ways you can incorporate Chaikin curves into your artwork.
Here is an example of using Chaikin’s corner-cutting algorithm to round out the polygons of a Voronoi diagram. As you can see, doing this gives a nice “cobbled” effect:
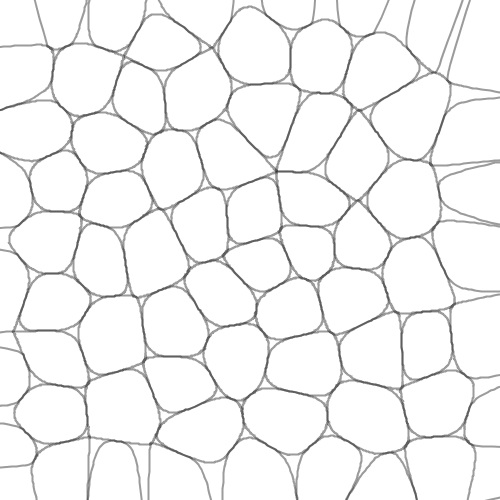
And here is the same image with the original Voronoi diagram overlaid on top in red, to show you how the rounding works:

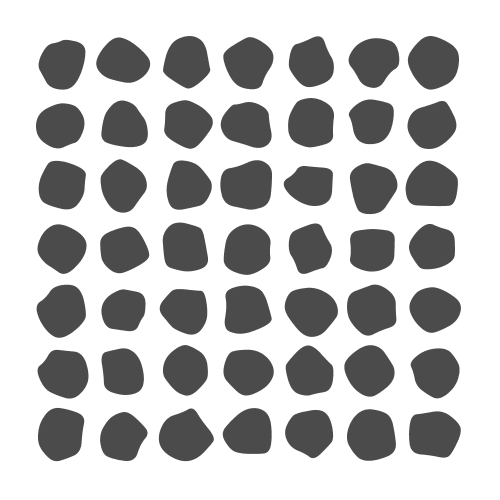
Here is another example where you can use deformed polygons (i.e. a regular polygon with some random perturbation in each vertex) as an input to the Chaikin corner-cutting algorithm to produce blob-like shapes:
Here is a similar idea to generating blobs as above, but instead overlaying them on top of one another at a low opacity to give a soft edge:

Below is a texture created from a single Chaikin curve. A random walk is used to create a sequence of line segments as we jump around the canvas, and it’s smoothed out at the end using the corner-cutting algorithm:
Here is a final example of creating a soft brush-like texture for your lines. Similar to the previous one, the image below uses a single set of points and applies a corner-cutting algorithm on it. However, I do this multiple times, with slight perturbations in the positions of the vertices each time.
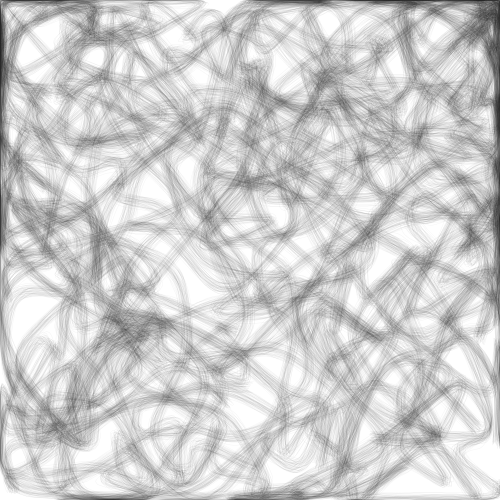

As you can see, the approach is fairly versatile and there are many ways you can incorporate Chaikin curves in your artwork! Let’s now look at how to implement this simple algorithm in Processing.
Implementation in Processing
Although the code I will show here is in Processing/Java, I want you to take away the following high-level algorithmic idea so you can implement it in any language of your choice.
High-Level Algorithm
The basic procedure for generating Chaikin curves is called the corner-cutting algorithm and looks something like this:
- Given an initial shape (open or closed) in the form of a sequence of vertices
- For each interior vertex forming a corner, replace it with two new vertices representing a cut.
Let’s try to implement this algorithm to better understand how it works.
Function Skeleton
Now let’s try to implement this in Processing! We first define an empty function as shown below:
/*
* The following function takes as input a curve (in the form of
* a PShape object), a cutting ratio, the number of iterations of
* the corner-cutting algorithm to use, and a boolean specifying
* whether the PShape provided is an open shape (e.g. line) or a
* closed polygon (e.g. hexagon).
*/
PShape chaikin(PShape shape, float ratio, int iterations, boolean close) {
PShape next = createShape(); // Take the shape specified in the 'shape' variable and
// generate a Chaikin version out of it inside 'next'. return next;
}
Above, we define an empty function the takes as input a PShape object. This is a handy way to store a shape comprising multiple vertices in Processing. We can use it to specify both open shapes (e.g. lines) as well as closed ones (i.e. polygons).
Since we’re going to be cutting the edges attached to each edge based on some fixed ratio, we take a ratio parameter that has a value between zero and one. For example, a ratio of 0.25 would mean cutting each edge one quarter and three quarters in.
Next, since we can run the cutting algorithm multiple times, we accept an iterations parameter specifying this number.
Finally, since our PShape might have been open or closed, and Processing provides no easy way to determine this, we take a boolean argument that lets us specify it manually.
Based on this, we can define two convenience functions to deal with open and closed shapes. The only difference in the functions below is the value of the last parameter passed to the chaikin() function call.
PShape chaikin_closed(PShape shape, float ratio, int iterations) {
return chaikin(shape, ratio, iterations, true);
}
PShape chaikin_open(PShape shape, float ratio, int iterations) {
return chaikin(shape, ratio, iterations, false);
}
A Recursive Algorithm
Now let’s get into the meat of it: how do we actually implement the corner-cutting algorithm?
Remember that Chaikin’s algorithm involves repeating the procedure a bunch of times (as specified by our iterations parameter). We can use recursion to achieve this; that is, we will call the chaikin() function from inside the chaikin() function itself:
PShape chaikin(PShape shape, float ratio, int iterations, boolean close) {
// If the number of iterations is zero, return shape as is
if (iterations == )
return shape;
PShape next = createShape();
...
// Perform one iteration of the corner-cutting algorithm here.
...
/*
* Call the chaikin() function with one less iteration and our
* newly-created shape so it's used as the new base shape. This
* returns a PShape which we give back to the user.
*
*/
return chaikin(next, ratio, iterations - , close);
}
The above code is an example of a recursive call. Let’s ignore the first if statement for now and look below that. When we first invoke the chaikin() function in our code, we first create a new shape and apply one iteration of the corner-cutting algorithm.
Now we use this new shape as the basis for the next iteration! We return the result of a chaikin() function call, but pass it the new shape as a base and give tell it to perform one less iteration (since we already performed one).
This way, the shape gets refined over and over! However, we need to stop at some point and return the shape as it currently stands. This is done when we see that the chaikin() function was invoked with an iterations value of zero. This brings us to the first if statement: we check if the number of iterations hit zero and return the shape immediately (without performing another iteration).
Cutting a Corner
Let’s now leave our skeleton function as is for now and write a function to cut a single corner of our shape:
ArrayList<PVector> chaikin_cut(PVector a, PVector b, float ratio) {
float x, y;
ArrayList<PVector> n = new ArrayList<PVector>();
/*
* If ratio is greater than 0.5 flip it so we avoid cutting across
* the midpoint of the line.
*/
if (ratio > 0.5) ratio = - ratio;
/* Find point at a given ratio going from A to B */
x = lerp(a.x, b.x, ratio);
y = lerp(a.y, b.y, ratio);
n.add(new PVector(x, y));
/* Find point at a given ratio going from B to A */
x = lerp(b.x, a.x, ratio);
y = lerp(b.y, a.y, ratio);
n.add(new PVector(x, y));
return n;
}
Above, the function takes two vertices (as PVector’s) that represent a single edge of our shape, and a cut ratio between zero and one as seen before. From this, we derive two new points: one at the specified ratio when going from point A to point B, and one when going in the reverse direction. For example, cutting an edge with a ratio of 0.25 would give us two points: the first at 25% from point A and the other at 75% from point A (or 25% from point B).
You’ll notice an if condition that checks the value of ratio and inverts it if the value is greater than 0.5. This is required to avoid cutting across the midpoint of the edge, which would otherwise lead to an incorrect ordering of vertices in the final shape. This little if statement fixes that before we do all our calculations.
To calculate this, we use Processing’s lerp() function to interpolate the X and Y coordinates as shown above.
Finally, we add the two new points into an ArrayList and return it.
Drawing Into a PShape Object
Let’s now get back to the function we left off earlier and finish it up. Let’s first look at how we can draw inside a PShape in Processing:
PShape chaikin(PShape shape, float ratio, int iterations, boolean close) {
...
PShape next = createShape();
next.beginShape();
// Draw the next iteration of the shape using corner cutting
if (close)
next.endShape(CLOSE);
else
next.endShape();
return chaikin(next, ratio, iterations - , close);
}
In Processing, in order to draw inside a PShape object, we must first call its beginShape() function. Once all drawing operations have completed, we must call endShape(). For closed polygons, we must additionally pass the CLOSE parameter to endShape().
Above, we beginShape() after calling createShape(), and depending on whether we specified this to be an open or closed shape, call the appropriate endShape() version (i.e. with or without the CLOSE parameter).
Cutting Corners
Now let’s look at the main logic for creating the next iteration of a given shape using the corner-cutting algorithm:
PShape chaikin(PShape shape, float ratio, int iterations, boolean close) {
...
next.beginShape();
/*
* Step 1: Figure out how many corners the shape has
* depending on whether it's open or closed.
*/
int num_corners = shape.getVertexCount();
if (!close)
num_corners = shape.getVertexCount() - ;
/*
* Step 2: Since we don't have access to edges directly
* with a PShape object, do a pairwise iteration
* over vertices instead. Same thing.
*/
for (int i = ; i < num_corners; i++) {
// Get the i'th and (i+1)'th vertex to work on that edge.
PVector a = shape.getVertex(i);
PVector b = shape.getVertex((i + ) % shape.getVertexCount());
// Step 3: Break it using our chaikin_cut() function
ArrayList<PVector> n = chaikin_cut(a, b, ratio);
/*
* Now we have to deal with one corner case. In the case
* of open shapes, the first and last endpoints shouldn't
* be moved. However, in the case of closed shapes, we
* cut all edges on both ends.
*/
if (!close && i == ) {
// For the first point of open shapes, ignore vertex A
next.vertex(a.x, a.y);
next.vertex(n.get().x, n.get().y);
} else if (!close && i == num_corners - ) {
// For the last point of open shapes, ignore vertex B
next.vertex(n.get().x, n.get().y);
next.vertex(b.x, b.y);
} else {
// For all other cases (i.e. interior edges of open
// shapes or edges of closed shapes), add both vertices
// returned by our chaikin_cut() method
next.vertex(n.get().x, n.get().y);
next.vertex(n.get().x, n.get().y);
}
}
if (close)
next.endShape(CLOSE);
else
next.endShape();
return chaikin(next, ratio, iterations - , close);
}
The logic above can be broken into three steps. We first figure out how many corners the shape has depending on whether it’s open or closed. In closed shapes (e.g., rectangles or triangles) each vertex represents a corner, making the number of vertices is the same as the number of corners in it. In the case of open shapes, the number of edges is one less that the number of vertices (since the last vertex is not connected back to the first one).
The second step is to iterate over each edge. Unfortunately, Processing doesn’t provide any function to do this directly, so we iterate over vertices in a pairwise fashion instead. Above, we get the i^th and (i+1)^th vertex in each loop iteration. We also make sure, that for closed shapes, when we reach the end, we wrap around to pick the first vertex (using the modulo operator).
Finally, for each edge, we break it using out chaikin_cut() function. This returns two vertices by cutting off both ends of our edge. At this point we deal with one last corner case: we make sure that for open shapes, we don’t change the first and last vertices and keep the originals.
And that’s it!
Here’s our final implementation in a nice copy-pasteable snippet:
ArrayList<PVector> chaikin_cut(PVector a, PVector b, float ratio) {
float x, y;
ArrayList<PVector> n = new ArrayList<PVector>();
/*
* If ratio is greater than 0.5 flip it so we avoid cutting across
* the midpoint of the line.
*/
if (ratio > 0.5) ratio = - ratio;
/* Find point at a given ratio going from A to B */
x = lerp(a.x, b.x, ratio);
y = lerp(a.y, b.y, ratio);
n.add(new PVector(x, y));
/* Find point at a given ratio going from B to A */
x = lerp(b.x, a.x, ratio);
y = lerp(b.y, a.y, ratio);
n.add(new PVector(x, y));
return n;
}
PShape chaikin(PShape shape, float ratio, int iterations, boolean close) {
// If the number of iterations is zero, return shape as is
if (iterations == )
return shape;
PShape next = createShape();
next.beginShape();
/*
* Step 1: Figure out how many corners the shape has
* depending on whether it's open or closed.
*/
int num_corners = shape.getVertexCount();
if (!close)
num_corners = shape.getVertexCount() - ;
/*
* Step 2: Since we don't have access to edges directly
* with a PShape object, do a pairwise iteration
* over vertices instead. Same thing.
*/
for (int i = ; i < num_corners; i++) {
// Get the i'th and (i+1)'th vertex to work on that edge.
PVector a = shape.getVertex(i);
PVector b = shape.getVertex((i + ) % shape.getVertexCount());
// Step 3: Break it using our chaikin_break() function
ArrayList<PVector> n = chaikin_cut(a, b, ratio);
/*
* Now we have to deal with one corner case. In the case
* of open shapes, the first and last endpoints shouldn't
* be moved. However, in the case of closed shapes, we
* cut all edges on both ends.
*/
if (!close && i == ) {
// For the first point of open shapes, ignore vertex A
next.vertex(a.x, a.y);
next.vertex(n.get().x, n.get().y);
} else if (!close && i == num_corners - ) {
// For the last point of open shapes, ignore vertex B
next.vertex(n.get().x, n.get().y);
next.vertex(b.x, b.y);
} else {
// For all other cases (i.e. interior edges of open
// shapes or edges of closed shapes), add both vertices
// returned by our chaikin_break() method
next.vertex(n.get().x, n.get().y);
next.vertex(n.get().x, n.get().y);
}
}
if (close)
next.endShape(CLOSE);
else
next.endShape();
return chaikin(next, ratio, iterations - , close);
}
PShape chaikin_close(PShape original, float ratio, int iterations) {
return chaikin(original, ratio, iterations, true);
}
PShape chaikin_open(PShape original, float ratio, int iterations) {
return chaikin(original, ratio, iterations, false);
}
Chaikin Curves in Processing的更多相关文章
- Video processing systems and methods
BACKGROUND The present invention relates to video processing systems. Advances in imaging technology ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_15_Image Registration:Image matching as a diffusion process: An analogy with Maxwell's demons——1998
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection:Edge and line oriented contour detection State of the art ——2011
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection:Learning to Detect Natural Image Boundaries Using Local Brightness, Color, and Texture Cues ——2004
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection:Statistical edge detection_ learning and evaluating edge cues——2003
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection: Optimal edge detection in two-dimensional images ——1996
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Computer Vision_Review:Local Invariant Feature Detectors: A Survey——2007.11
翻译 局部不变特征探测器:一项调查 摘要 -在本次调查中,我们概述了不变兴趣点探测器,它们如何随着时间的推移而发展,它们如何工作,以及它们各自的优点和缺点.我们首先定义理想局部特征检测器的属性.接下来 ...
- OLTP(on-line transaction processing)与OLAP(On-Line Analytical Processing)
OLTP与OLAP的介绍 数据处理大致可以分成两大类:联机事务处理OLTP(on-line transaction processing).联机分析处理OLAP(On-Line Analytical ...
- ECC-Elliptic Curves Cryptography,椭圆曲线密码编码学
ECC ECC-Elliptic Curves Cryptography,椭圆曲线密码编码学,是目前已知的公钥体制中,对每比特所提供加密强度最高的一种体制.在软件注册保护方面起到很大的作用,一般的序列 ...
随机推荐
- Navicat连接oracle,出现Only compatible with oci version 8.1
与本地oracle连接的时候,一般没问题,sqlplus和oci都是本地oracle自带的,(设置: 工具->选项->oci) 分别为: oci:D:\app\pcman\prod ...
- cube.js 通过presto-gateway 进行连接
cube.js 对于presto 的支持是通过presto-client 刚好简单修改了一个可以支持presto-gateway 连接的 以下是一个简单的集成,以及关于集成中原有的一些修改 环境准备 ...
- redis三种模式对比
模式类型 主从模式(redis2.8版本之前的模式).哨兵sentinel模式(redis2.8及之后的模式).redis cluster模式(redis3.0版本之后) 主从模式原理 同Mysql主 ...
- Navicat自动断开连接处理方式
问题描述 使用Navicat连接mysql后,如果一段时间不操作,那么会再次操作时会提示无响应,每次都这样确实折磨人,大大降低了工作效率! 问题解决 关闭连接→右键连接→连接属性 将上述心跳时间设置为 ...
- rancher2基础环境配置
一.主机配置 1.配置要求 参考节点要求 2.主机名配置 因为K8S的规定,主机名只支持包含 - 和 .(中横线和点)两种特殊符号,并且主机名不能出现重复. 3.Hosts 配置每台主机的hosts( ...
- Redis(一) 数据结构与底层存储 & 事务 & 持久化 & lua
参考文档:redis持久化:http://blog.csdn.net/freebird_lb/article/details/7778981 https://blog.csdn.net/jy69240 ...
- java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: host parameter is null
即 URL 应为 http://www.baidu.com 但是实际配置成了 www.baidu.com 所以出现此错误
- enable device: BAR 0 [mem 0x00000000-0x003fffff] not claimed
/******************************************************************************* * enable device: BA ...
- 【深入学习linux】CentOS 7 最小化安装后程序必须安装的组件
centos平台编译环境使用如下指令 安装make: yum -y install gcc automake autoconf libtool make 安装g++: yum install gcc ...
- Python80个练手项目列表
原文地址:https://www.shiyanlou.com/questions/102676/?utm_source=baidu&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaig ...
