Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(5):Create Entity Data Model
Create Entity Data Model:
Here, we are going to create an Entity Data Model (EDM) for SchoolDB database and understand the basic building blocks.
Entity Data Model is a model that describes entities and the relationships between them. Let's create first simple EDM for SchoolDB database using Visual Studio 2012 and Entity Framework 6.
1. Open Visual Studio 2012 and create a console project.
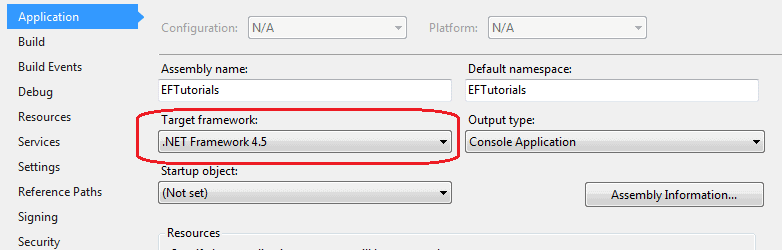
Go to PROJECT menu of visual studio -> {project name} properties - and make sure that the project's target framework is .NET Framework 4.5, as shown below.
2. Now, add Entity Data Model by right clicking on the project in the solution explorer -> Add -> click New Item and select ADO.NET Entity Data Model from popup, Give the new item the name 'School' and click Add button.
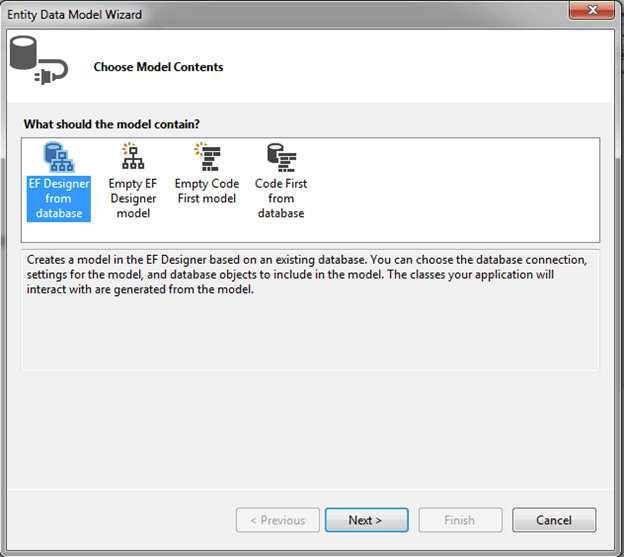
3. Entity Data Model Wizard in VS2012 opens with four options to select from: EF Designer from database for database first approach, Empty EF Designer model for model first approach, Empty Code First model and Code First from database for Code-First approach. We will focus on the database-first approach in the basic tutorials so select EF Designer from database option and clickNext.
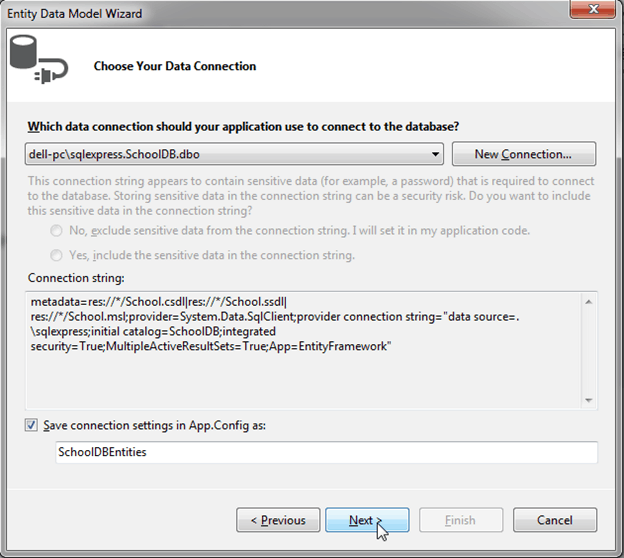
4. You can choose from your existing DB Connections or create a new connection by clicking on the 'New Connection' button. We will use the existing DB connection to the SchoolDB Database. This will also add a connection string to your app.config file with the default suffix with DB name. You can change this if you want. Click 'Next' after you set up your DB connection.
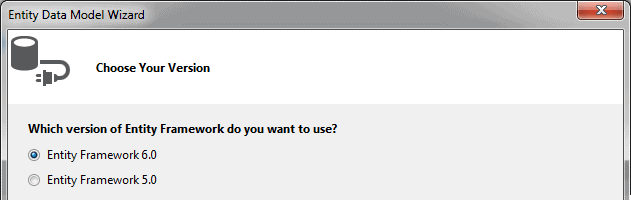
5. In this step, you need to choose the version of Entity Framework. We will use Entity Framework 6.0 in the basic tutorials so select Entity Framework 6.0 and click Next.
Note: If you have already installed the latest version of Entity Framework using NuGet manager as shown in the Setup Environment section then this step of the wizard will no longer appear since you have already installed Entity Framework.
6. This step will display all the Tables, Views and Stored Procedures (SP) in the database. Select the Tables, Views and SPs you want, keep the default checkboxes selected and click Finish. You can change Model Namespace if you want.
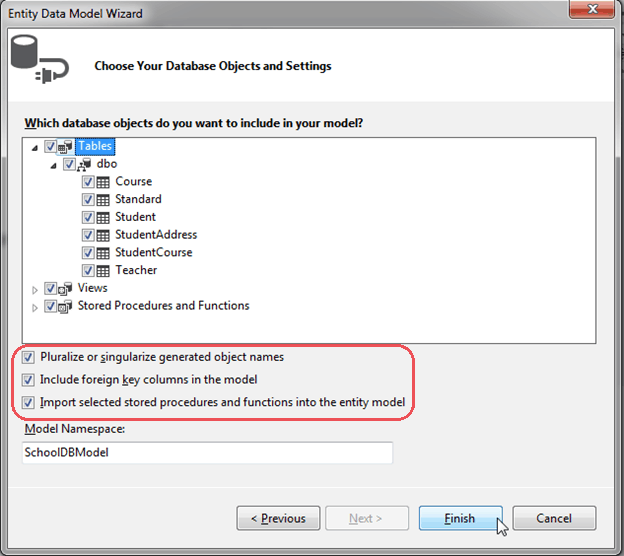
Pluralize or singularize generated object names checkbox singularizes an entityset name, if the table name in the database is plural. For example, if SchoolDB has Students table name then entityset would be singular Student. Similarly, relationships between the models will be pluralized if the table has one-to-many or many-to-many relationship with other tables. For example, Student has many-to-many relationship with Course table so Student entity set will have plural property name 'Courses' for the collection of courses.
The second checkbox, Include foreign key columns in the model, includes foreign key property explicitly to represent the foreign key. For example, Student table has one-to-many relationship with Standard table. So every student is associated with only one standard. To represent this in the model, Student entityset includes StandardId property with Standard navigation property. If this checkbox is unchecked then it will only include the Standard property, but not the StandardId in the Student entityset.
The third checkbox, Import selected stored procedures and functions into entity model, automatically creates Function Imports for the stored procedures and functions. You don't need to manually import this, as was necessary prior to Entity Framework 5.0.
7. After clicking on 'Finish', a School.edmx file will be added into your project.
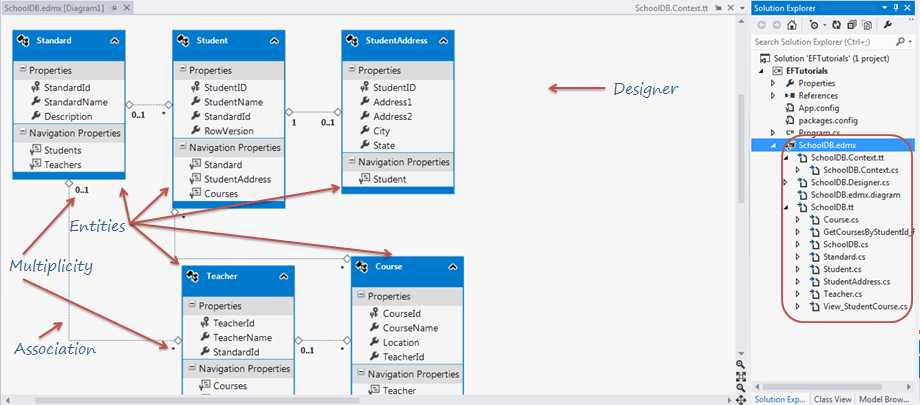
Open EDM designer by double clicking on School.edmx. This displays all the entities for selected tables and the relationships between them as shown below:
EDM also adds a connection string in the config file as shown below.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<configSections>
<!-- For more information on Entity Framework configuration, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=237468 -->
<section name="entityFramework" type="System.Data.Entity.Internal.ConfigFile.EntityFrameworkSection, EntityFramework, Version=6.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" requirePermission="false"/>
</configSections>
<startup>
<supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.5"/>
</startup>
<entityFramework>
<defaultConnectionFactory type="System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.SqlConnectionFactory, EntityFramework"/>
<providers>
<provider invariantName="System.Data.SqlClient" type="System.Data.Entity.SqlServer.SqlProviderServices, EntityFramework.SqlServer"/>
</providers>
</entityFramework>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="SchoolDBEntities" connectionString="metadata=res://*/SchoolDB.csdl|res://*/SchoolDB.ssdl|res://*/SchoolDB.msl;provider=System.Data.SqlClient;provider connection string="data source=.\sqlexpress;initial catalog=SchoolDB;integrated security=True;multipleactiveresultsets=True;application name=EntityFramework"" providerName="System.Data.EntityClient"/>
</connectionStrings>
</configuration>
In this way, you can create a simple EDM from your existing database.
Now, let's examine all the building blocks of generated EDM (School.edmx) as shown in the above figure.
Entity-Table Mapping:
Each entity in EDM is mapped with the database table. You can check the entity-table mapping by right clicking on any entity in the EDM designer -> select Table Mapping. Also, if you change any property name of the entity from designer then the table mapping would reflect that change automatically.
Context & Entity Classes:
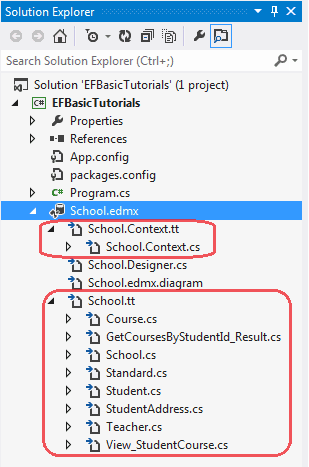
Every Entity Data Model generates one context class and entity class for each DB table included in the EDM. Expand School.edmx and see two important files, {EDM Name}.Context.tt and {EDM Name}.tt:
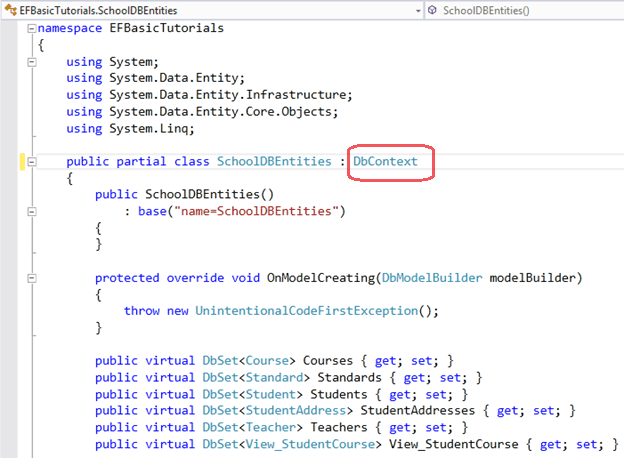
School.Context.tt: This T4 template file generates a context class whenever you change Entity Data Model (.edmx file). You can see the context class file by expanding School.Context.tt. The context class resides in {EDM Name}.context.cs file. The default context class name is {DB Name} + Entities. For example, the context class name for SchoolDB is SchoolDBEntities, then the context class is derived from DBContext class in Entity Framework. (Prior to EF 5.0 it had been derived from ObjectContext.)
School.tt: School.tt is a T4 template file that generates entity classes for each DB table. Entity classes are POCO (Plain Old CLR Object) classes. The following code snippet shows the Student entity.
public partial class Student
{
public Student()
{
this.Courses = new HashSet<Course>();
} public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardId { get; set; }
public byte[] RowVersion { get; set; } public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
public virtual StudentAddress StudentAddress { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Course> Courses { get; set; }
}
EDM Designer: EDM designer represents your conceptual model. It consists of Entities, and associations & multiplicity between the entities. Initially, it will look exactly like your database table structure but you can add, merge or remove columns, which are not required by your application from this designer. You can even add a new object in this model, which can have columns from different database tables from context menu, as shown in the figure above. Remember, whatever changes done here should be mapped with the storage model. So you have to be careful, while making any changes in the designer.
You can open this EDM designer in XML view where you can see all the three parts of the EDM - Conceptual schema (CSDL), Storage schema (SSDL) and mapping schema (MSL), together in XML view.
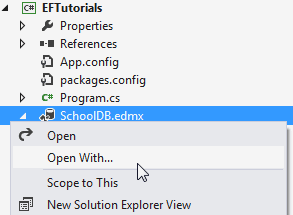
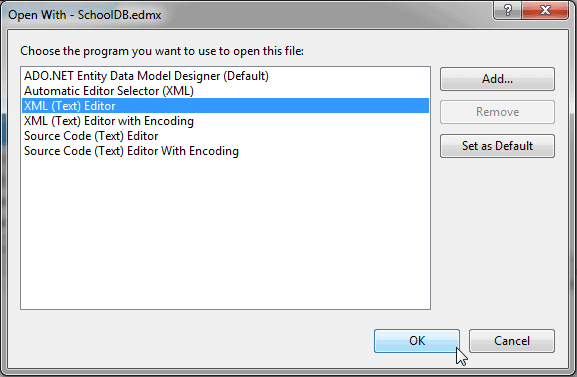
Right click on School.edmx -> click 'Open with..', this will open a popup window.
Select 'XML (text) Editor' in the popup window.
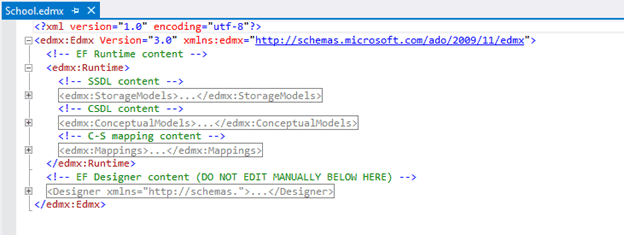
Visual Studio cannot display the model in Design view and in XML format at the same time, so you will see a message asking whether it’s OK to close the Design view of the model. Click Yes. This will open the XML format view. You can see the following XML view by toggling all outlining as shown below.
You can see SSDL content, CSDL content and C-S mapping content here. If you expand SSDL and CSDL, each one has some common XML node under each schema node. You don't need to edit the xml data because this can be accomplished easier in the Model Browser.
Learn about Model Browser in the next section.
Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(5):Create Entity Data Model的更多相关文章
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(4):Setup Entity Framework Environment
Setup Entity Framework Environment: Entity Framework 5.0 API was distributed in two places, in NuGet ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(42):Colored Entity
Colored Entity in Entity Framework 5.0 You can change the color of an entity in the designer so that ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(27):Update Entity Graph
Update Entity Graph using DbContext: Updating an entity graph in disconnected scenario is a complex ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(40):Validate Entity
Validate Entity You can write custom server side validation for any entity. To accomplish this, over ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(26):Add Entity Graph
Add Entity Graph using DbContext: Adding entity graph with all new entities is a simple task. We can ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(13):Database First
Database First development with Entity Framework: We have seen this approach in Create Entity Data M ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(1):Introduction
以下系列文章为Entity Framework Turial Basics系列 http://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/EntityFramework5/enti ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(32):Enum Support
Enum in Entity Framework: You can now have an Enum in Entity Framework 5.0 onwards. EF 5 should targ ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(31):Migration from EF 4.X
Migration from Entity Framework 4.1/4.3 to Entity Framework 5.0/6.0 To migrate your existing Entity ...
随机推荐
- linux内嵌汇编语言
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-21254310-id-1828921.html http://www.cnblogs.com/lxgeek/archive/2011/01 ...
- Technocup 2019 C. Compress String
一个字符串 $s$,你要把它分成若干段,有两种合法的段 1.段长为 $1$,代价为 $a$ 2.这个段是前面所有段拼起来组成的字符串的字串,代价为 $b$ 问最小代价 $|s| \leq 5000$ ...
- 一文搞定 Git 相关概念和常用指令
我几乎每天都使用 Git,但仍然无法记住很多命令. 通常,只需要记住下图中的 6 个命令就足以供日常使用.但是,为了确保使用地很顺滑,其实你应该记住 60 到 100 个命令. Git 相关术语 Gi ...
- python 编码拓展,小数据池,
编码拓展: 1.在所有类型的编码中,编码的二进制互不识别, 2.在传输的过程中不能是万国码的二进制解码传输, 因此将unicode变为utf - 8或者变成gbk编码尤为重要; 利用encode编码为 ...
- virtualvm一次插件安装想到的
在麒麟操作系统visualvm安装插件失败,因为使用的内网,所以在官网下载了插件到本地:因为本地安装的jdk1.6,为了享受jdk1.8,在visualvm文件中增加了对于jdk1.8的引用: exp ...
- Road to OI
我学OI已经三年有余了.回首向来萧瑟处,在镜花水月一般的OI生涯面前,我不敢,也没资格称“也无风雨也无晴”.这三年我过得浑浑噩噩,玩了很多游戏,看了很多番,追过一个女孩,OI却搞得一塌糊涂.留给我的时 ...
- loj 6485 LJJ学二项式定理 —— 单位根反演
题目:https://loj.ac/problem/6485 先把 \( a_{i mod 4} \) 处理掉,其实就是 \( \sum\limits_{i=0}^{3} a_{i} \sum\lim ...
- Ubuntu下部署GitLab-——基于14.04系统
搭建GitLab的目的: 方便公司开发管理代码 GitLab实现的功能: 1.关闭了gitlab的注册功能 2.修改了默认端口 3.汉化 0.前期准备 # 环境 Ubuntu 14.04 root@i ...
- 在Mac系统下使用自己安装的PHP
今天在安装单元测试框架PHPUnit,需要PHP的最低版本是5.6,由于我的MacBook自带的PHP版本是5.5.36,不能满足安装条件. 看了一下这个网址:https://php-osx.liip ...
- UVA548(二叉树遍历)
You are to determine the value of the leaf node in a given binary tree that is the terminal node of ...