vc++上的MFC的对象序列化和反序列化
注意点:
1. 必须类型序列化声明
DECLARE_SERIAL( Person )
2. 必须写出实现宏
IMPLEMENT_SERIAL(Person, CObject, VERSIONABLE_SCHEMA | 2)
3. 重写CObject中的Serialize函数
void Person::Serialize( CArchive& ar )
{
CObject::Serialize(ar);
//关键代码
if(ar.IsStoring()) {
//序列化
ar << this->age << this->sex << this->name;
} else {
//反序列化
ar >> this->age >> this->sex >> this->name;
}
}
序列化后的数据
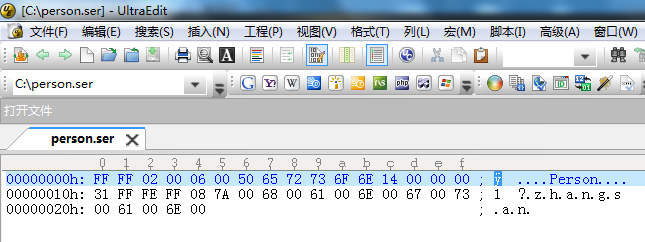
- //Person.h
- #pragma once
- #include <afx.h>
- #include <string>
- #include <atlstr.h>
- using namespace std;
- class Person: public CObject
- {
- private:
- //注意MFC 不支持 标准std:string对象序列化, boost库支持std:string
- CString name;
- int age;
- char sex;
- public:
- DECLARE_SERIAL( Person )
- Person(void);
- Person(CString name, int age, char sex);
- virtual ~Person(void);
- virtual void Serialize(CArchive& ar);
- void setName(CString pName);
- CString getName();
- void setAge(int age);
- int getAge();
- void setSex(char sex);
- char getSex();
- };
- //Person.cpp
- #include "StdAfx.h"
- #include "Person.h"
- #include <afx.h>
- #include <string>
- //必须写出实现宏
- IMPLEMENT_SERIAL(Person, CObject, VERSIONABLE_SCHEMA | 2)
- Person::Person(void)
- {
- }
- Person::Person( CString name, int age, char sex )
- {
- this->name = name;
- this->age = age;
- this->sex = sex;
- }
- Person::~Person(void)
- {
- }
- void Person::setName( CString name)
- {
- this->name = name;
- }
- CString Person::getName()
- {
- return this->name;
- }
- void Person::setAge( int age )
- {
- this->age = age;
- }
- int Person::getAge()
- {
- return this->age;
- }
- void Person::setSex( char sex )
- {
- this->sex = sex;
- }
- char Person::getSex()
- {
- return this->sex;
- }
- void Person::Serialize( CArchive& ar )
- {
- CObject::Serialize(ar);
- //关键代码
- if(ar.IsStoring()) {
- //序列化
- ar << this->age << this->sex << this->name;
- } else {
- //反序列化
- ar >> this->age >> this->sex >> this->name;
- }
- }
- // main.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include <tchar.h>
- #include <afx.h>
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
- {
- Person person;
- person.setAge(20);
- person.setName("zhangsan");
- person.setSex('1');
- CFile myFile(_T("c:/person.ser"), CFile::modeCreate | CFile::modeReadWrite);
- // Create a storing archive.
- CArchive arStore(&myFile, CArchive::store);
- // Write the object to the archive
- arStore.WriteObject(&person);
- arStore.Flush();
- // Close the storing archive
- arStore.Close();
- // Create a loading archive.
- myFile.SeekToBegin();
- CArchive arLoad(&myFile, CArchive::load);
- // Verify the object is in the archive.
- Person* p = (Person*) arLoad.ReadObject(person.GetRuntimeClass());
- arLoad.Close();
- //wcout << "姓名:" << name.GetBuffer(name.GetLength()) << endl;
- CString name = p->getName();
- wchar_t* pch = name.GetBuffer(0);
- wcout << "姓名:" << pch << endl;
- name.ReleaseBuffer(); //注意内在释放
- cout << "性别:" << p->getSex() << endl;
- cout << "年龄:" << p->getAge() << endl;
- delete p;
- return 0;
- }
vc++上的MFC的对象序列化和反序列化的更多相关文章
- java 对象序列化与反序列化
Java序列化与反序列化是什么? 为什么需要序列化与反序列化? 如何实现Java序列化与反序列化? 本文围绕这些问题进行了探讨. 1.Java序列化与反序列化 Java序列化是指把Java对象转换为 ...
- C#对象序列化与反序列化zz
C#对象序列化与反序列化(转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/LiZhiW/p/3622365.html) 1. 对象序列化的介绍........................ ...
- C#对象序列化与反序列化
C#对象序列化与反序列化(转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/LiZhiW/p/3622365.html) 1. 对象序列化的介绍.......................... ...
- Java学习笔记——IO操作之对象序列化及反序列化
对象序列化的概念 对象序列化使得一个程序可以把一个完整的对象写到一个字节流里面:其逆过程则是从一个字节流里面读出一个事先存储在里面的完整的对象,称为对象的反序列化. 将一个对象保存到永久存储设备上称为 ...
- Java之对象序列化和反序列化
一.对象序列化和反序列化存在的意义: 当你创建对象,只要你需要,他就一直存在,但当程序结束,对象就会消失,但是存在某种情况,如何让程序在不允许的状态,仍然保持该对象的信息.并在下次程序运行的时候使用该 ...
- Java 序列化 对象序列化和反序列化
Java 序列化 对象序列化和反序列化 @author ixenos 对象序列化是什么 1.对象序列化就是把一个对象的状态转化成一个字节流. 我们可以把这样的字节流存储为一个文件,作为对这个对象的复制 ...
- Java对象序列化与反序列化
对象序列化的目标是将对象保存在磁盘中或者在网络中进行传输.实现的机制是允许将对象转为与平台无关的二进制流. java中对象的序列化机制是将允许对象转为字节序列.这些字节序列可以使Java对象脱离程序存 ...
- FastJson实现复杂对象序列化与反序列化
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/xqhadoop/article/details/62217954 一.认识FastJson 1.优势 fastjson是目前java语言中最快的jso ...
- Java Io 对象序列化和反序列化
Java 支持将任何对象进行序列化操作,序列化后的对象文件便可通过流进行网络传输. 1. 对象序列化就是将对象转换成字节序列,反之叫对象的反序列化 2. 序列化流ObjectOut ...
随机推荐
- OC - 21.CALayer核心要点及实例解析
CALayer基础 CALayer是每一个UI控件的核心,一个UI控件之所以能显示可以说是CALayer的功劳 每一个UI控件默认都为自己创建一个CALayer对象,通过drawRect方法将内容绘制 ...
- 认识html文件基本结构
html文件的结构:一个HTML文件是有自己固定的结构的. <html> <head>...</head> <body>...</body> ...
- .net中XML的创建01(传统方法)
XML传统的创建: 传统的创建主要是依据XmlDocument的对象展开的,通过XmlDocument对象可以创建元素(XmlElement).属性(XmlAttribute)以及文本节点(Creat ...
- 【USACO 1.1.4】破碎的项链
[题目描述] 你有一条由N个红色的,白色的,或蓝色的珠子组成的项链(3<=N<=350),珠子是随意安排的.这里是 n=29 的二个例子: 1 2 ...
- VirtualBox开发环境的搭建详解(转)
VirtualBox开发环境的搭建详解 有关VirtualBox的介绍请参考:VirtualBox_百度百科 由于VirtualBox官网提供的搭建方法不够详细,而且本人在它指导下,从下载所需的开 ...
- Android学习----ADB
adb是什么?:adb的全称为Android Debug Bridge,就是起到调试桥的作用.通过adb我们可以在Eclipse中方面通过DDMS来调试Android程序,说白了就是debug工具.a ...
- jQuery中的综合动画
所谓综合动画,就是在链式表达式依次执行相关animate函数,其中的参数是以键值对的方式存在的. 如下示例,就展示了一个基本的综合动画. <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC " ...
- php的session实现
对于两次http请求,如果第一次http请求的重要数据要被第二次请求获取,办法是将第一次http请求数据保存下来,保存的办法很多,大体上有使用数据库,缓存,文件等等,那么php中的session实现实 ...
- d038: 星罗密布
内容: 输出图形 *****$***$$$*$$$$$ 规律是...自己发现吧. 要求输入3,输出上面三行的图形 输入说明: 行数小于40 输出说明: 输入样例: 3 输出样例 : ***** ...
- 未能写入输出文件 c:/WINDOWS/Microsoft.NET/Framework/v2.0.50727/Temporary
ERROR: 未能写入输出文件“c:/WINDOWS/Microsoft.NET/Framework/v2.0.50727/Temporary ASP.NET Files/root/.... 一般遇到 ...
