使用linux的GDB打印STL(vector,map,set..................)
在linux用gdb或者cgdb计较不爽的地方是无法打印STL的东西,所有啊去网上找了找解决方案https://www.douban.com/note/182826844/?qq-pf-to=pcqq.c2c
本帖把怎么配置这个东西写出了,万一以后忘了,可以回头找找。
首先是下载gdb文件 https://sourceware.org/gdb/wiki/STLSupport ------》找到网页里面的
 然后点击进去下载stl_views_1.0.3.gdb
然后点击进去下载stl_views_1.0.3.gdb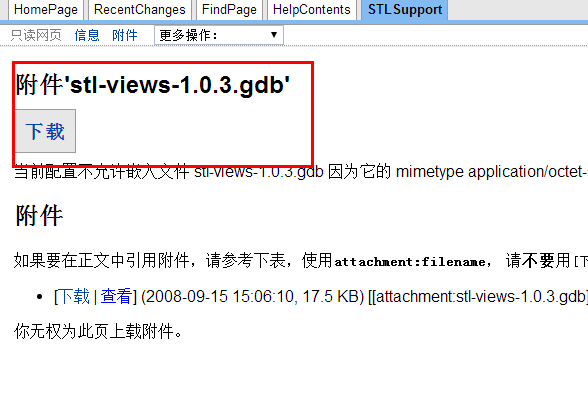
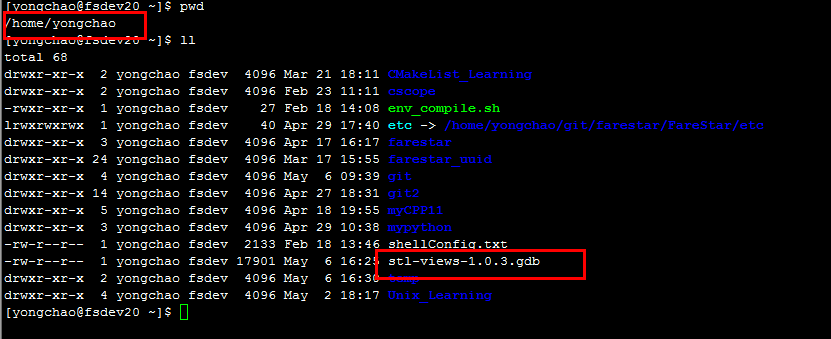
接下来把这个东西当到linux下,位置随便放,我放到了我的用户目录下
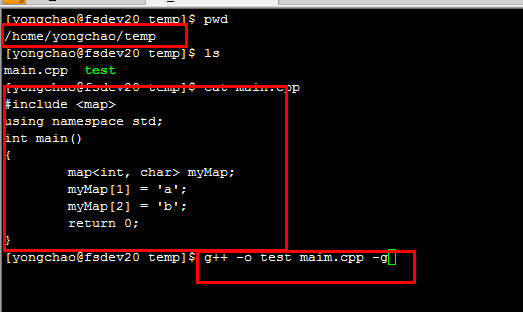
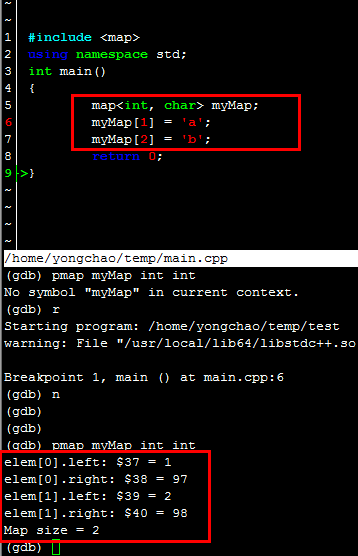
然后写一个小程序测试一下,
接着cgdb test 进入调试模式,然后加载刚才的stl_views_1.0.3.gdb
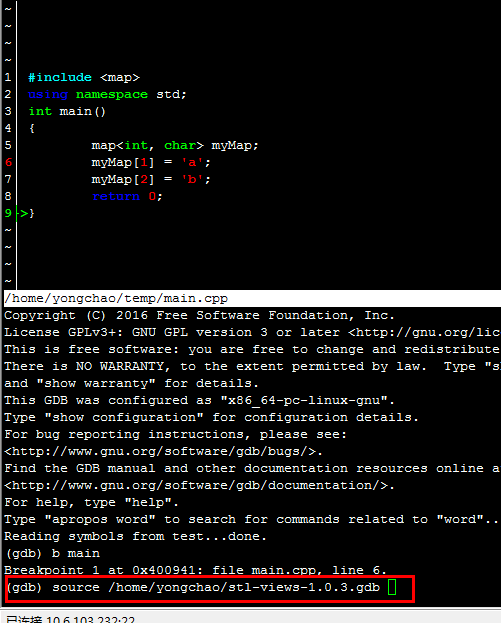
接着就可以看看pmap的命令了
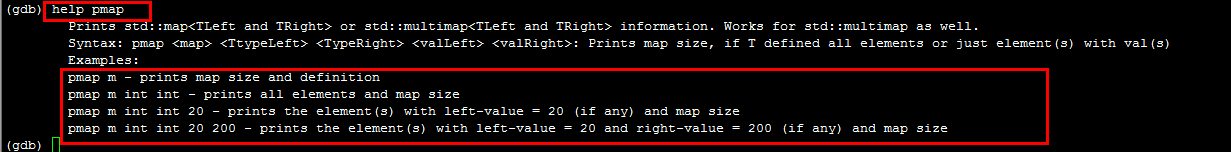
pmap variable------------>打印variable这个map的定义和map里面的个数
pmap variable int int(就是单纯的两个int) ------------>打印pmap的元素和map的个数
pmap variable int int 20------------>打印索引是20的map的值 和map的个数
pmap variable int int 20 200------->打印索引是20 值是200的map值和map的个数
东西很好用,就怕以后链接失效找不到这个文件了,下面会把这个文件东西拷贝在下面。以后用到了,自己建立一个stl_views_1.0.3.gdb,然后把下面的东西拷贝进去使用。
#
# STL GDB evaluators/views/utilities - 1.03
#
# The new GDB commands:
# are entirely non instrumental
# do not depend on any "inline"(s) - e.g. size(), [], etc
# are extremely tolerant to debugger settings
#
# This file should be "included" in .gdbinit as following:
# source stl-views.gdb or just paste it into your .gdbinit file
#
# The following STL containers are currently supported:
#
# std::vector<T> -- via pvector command
# std::list<T> -- via plist or plist_member command
# std::map<T,T> -- via pmap or pmap_member command
# std::multimap<T,T> -- via pmap or pmap_member command
# std::set<T> -- via pset command
# std::multiset<T> -- via pset command
# std::deque<T> -- via pdequeue command
# std::stack<T> -- via pstack command
# std::queue<T> -- via pqueue command
# std::priority_queue<T> -- via ppqueue command
# std::bitset<n> -- via pbitset command
# std::string -- via pstring command
# std::widestring -- via pwstring command
#
# The end of this file contains (optional) C++ beautifiers
# Make sure your debugger supports $argc
#
# Simple GDB Macros writen by Dan Marinescu (H-PhD) - License GPL
# Inspired by intial work of Tom Malnar,
# Tony Novac (PhD) / Cornell / Stanford,
# Gilad Mishne (PhD) and Many Many Others.
# Contact: dan_c_marinescu@yahoo.com (Subject: STL)
#
# Modified to work with g++ 4.3 by Anders Elton
# Also added _member functions, that instead of printing the entire class in map, prints a member. #
# std::vector<>
# define pvector
if $argc ==
help pvector
else
set $size = $arg0._M_impl._M_finish - $arg0._M_impl._M_start
set $capacity = $arg0._M_impl._M_end_of_storage - $arg0._M_impl._M_start
set $size_max = $size -
end
if $argc ==
set $i =
while $i < $size
printf "elem[%u]: ", $i
p *($arg0._M_impl._M_start + $i)
set $i++
end
end
if $argc ==
set $idx = $arg1
if $idx < || $idx > $size_max
printf "idx1, idx2 are not in acceptable range: [0..%u].\n", $size_max
else
printf "elem[%u]: ", $idx
p *($arg0._M_impl._M_start + $idx)
end
end
if $argc ==
set $start_idx = $arg1
set $stop_idx = $arg2
if $start_idx > $stop_idx
set $tmp_idx = $start_idx
set $start_idx = $stop_idx
set $stop_idx = $tmp_idx
end
if $start_idx < || $stop_idx < || $start_idx > $size_max || $stop_idx > $size_max
printf "idx1, idx2 are not in acceptable range: [0..%u].\n", $size_max
else
set $i = $start_idx
while $i <= $stop_idx
printf "elem[%u]: ", $i
p *($arg0._M_impl._M_start + $i)
set $i++
end
end
end
if $argc >
printf "Vector size = %u\n", $size
printf "Vector capacity = %u\n", $capacity
printf "Element "
whatis $arg0._M_impl._M_start
end
end document pvector
Prints std::vector<T> information.
Syntax: pvector <vector> <idx1> <idx2>
Note: idx, idx1 and idx2 must be in acceptable range [..<vector>.size()-].
Examples:
pvector v - Prints vector content, size, capacity and T typedef
pvector v - Prints element[idx] from vector
pvector v - Prints elements in range [idx1..idx2] from vector
end #
# std::list<>
# define plist
if $argc ==
help plist
else
set $head = &$arg0._M_impl._M_node
set $current = $arg0._M_impl._M_node._M_next
set $size =
while $current != $head
if $argc ==
printf "elem[%u]: ", $size
p *($arg1*)($current + )
end
if $argc ==
if $size == $arg2
printf "elem[%u]: ", $size
p *($arg1*)($current + )
end
end
set $current = $current._M_next
set $size++
end
printf "List size = %u \n", $size
if $argc ==
printf "List "
whatis $arg0
printf "Use plist <variable_name> <element_type> to see the elements in the list.\n"
end
end
end document plist
Prints std::list<T> information.
Syntax: plist <list> <T> <idx>: Prints list size, if T defined all elements or just element at idx
Examples:
plist l - prints list size and definition
plist l int - prints all elements and list size
plist l int - prints the third element in the list (if exists) and list size
end define plist_member
if $argc ==
help plist_member
else
set $head = &$arg0._M_impl._M_node
set $current = $arg0._M_impl._M_node._M_next
set $size =
while $current != $head
if $argc ==
printf "elem[%u]: ", $size
p (*($arg1*)($current + )).$arg2
end
if $argc ==
if $size == $arg3
printf "elem[%u]: ", $size
p (*($arg1*)($current + )).$arg2
end
end
set $current = $current._M_next
set $size++
end
printf "List size = %u \n", $size
if $argc ==
printf "List "
whatis $arg0
printf "Use plist_member <variable_name> <element_type> <member> to see the elements in the list.\n"
end
end
end document plist_member
Prints std::list<T> information.
Syntax: plist <list> <T> <idx>: Prints list size, if T defined all elements or just element at idx
Examples:
plist_member l int member - prints all elements and list size
plist_member l int member - prints the third element in the list (if exists) and list size
end #
# std::map and std::multimap
# define pmap
if $argc ==
help pmap
else
set $tree = $arg0
set $i =
set $node = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header._M_left
set $end = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header
set $tree_size = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_node_count
if $argc ==
printf "Map "
whatis $tree
printf "Use pmap <variable_name> <left_element_type> <right_element_type> to see the elements in the map.\n"
end
if $argc ==
while $i < $tree_size
set $value = (void *)($node + )
printf "elem[%u].left: ", $i
p *($arg1*)$value
set $value = $value + sizeof($arg1)
printf "elem[%u].right: ", $i
p *($arg2*)$value
if $node._M_right !=
set $node = $node._M_right
while $node._M_left !=
set $node = $node._M_left
end
else
set $tmp_node = $node._M_parent
while $node == $tmp_node._M_right
set $node = $tmp_node
set $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parent
end
if $node._M_right != $tmp_node
set $node = $tmp_node
end
end
set $i++
end
end
if $argc ==
set $idx = $arg3
set $ElementsFound =
while $i < $tree_size
set $value = (void *)($node + )
if *($arg1*)$value == $idx
printf "elem[%u].left: ", $i
p *($arg1*)$value
set $value = $value + sizeof($arg1)
printf "elem[%u].right: ", $i
p *($arg2*)$value
set $ElementsFound++
end
if $node._M_right !=
set $node = $node._M_right
while $node._M_left !=
set $node = $node._M_left
end
else
set $tmp_node = $node._M_parent
while $node == $tmp_node._M_right
set $node = $tmp_node
set $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parent
end
if $node._M_right != $tmp_node
set $node = $tmp_node
end
end
set $i++
end
printf "Number of elements found = %u\n", $ElementsFound
end
if $argc ==
set $idx1 = $arg3
set $idx2 = $arg4
set $ElementsFound =
while $i < $tree_size
set $value = (void *)($node + )
set $valueLeft = *($arg1*)$value
set $valueRight = *($arg2*)($value + sizeof($arg1))
if $valueLeft == $idx1 && $valueRight == $idx2
printf "elem[%u].left: ", $i
p $valueLeft
printf "elem[%u].right: ", $i
p $valueRight
set $ElementsFound++
end
if $node._M_right !=
set $node = $node._M_right
while $node._M_left !=
set $node = $node._M_left
end
else
set $tmp_node = $node._M_parent
while $node == $tmp_node._M_right
set $node = $tmp_node
set $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parent
end
if $node._M_right != $tmp_node
set $node = $tmp_node
end
end
set $i++
end
printf "Number of elements found = %u\n", $ElementsFound
end
printf "Map size = %u\n", $tree_size
end
end document pmap
Prints std::map<TLeft and TRight> or std::multimap<TLeft and TRight> information. Works for std::multimap as well.
Syntax: pmap <map> <TtypeLeft> <TypeRight> <valLeft> <valRight>: Prints map size, if T defined all elements or just element(s) with val(s)
Examples:
pmap m - prints map size and definition
pmap m int int - prints all elements and map size
pmap m int int - prints the element(s) with left-value = (if any) and map size
pmap m int int - prints the element(s) with left-value = and right-value = (if any) and map size
end define pmap_member
if $argc ==
help pmap_member
else
set $tree = $arg0
set $i =
set $node = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header._M_left
set $end = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header
set $tree_size = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_node_count
if $argc ==
printf "Map "
whatis $tree
printf "Use pmap <variable_name> <left_element_type> <right_element_type> to see the elements in the map.\n"
end
if $argc ==
while $i < $tree_size
set $value = (void *)($node + )
printf "elem[%u].left: ", $i
p (*($arg1*)$value).$arg2
set $value = $value + sizeof($arg1)
printf "elem[%u].right: ", $i
p (*($arg3*)$value).$arg4
if $node._M_right !=
set $node = $node._M_right
while $node._M_left !=
set $node = $node._M_left
end
else
set $tmp_node = $node._M_parent
while $node == $tmp_node._M_right
set $node = $tmp_node
set $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parent
end
if $node._M_right != $tmp_node
set $node = $tmp_node
end
end
set $i++
end
end
if $argc ==
set $idx = $arg5
set $ElementsFound =
while $i < $tree_size
set $value = (void *)($node + )
if *($arg1*)$value == $idx
printf "elem[%u].left: ", $i
p (*($arg1*)$value).$arg2
set $value = $value + sizeof($arg1)
printf "elem[%u].right: ", $i
p (*($arg3*)$value).$arg4
set $ElementsFound++
end
if $node._M_right !=
set $node = $node._M_right
while $node._M_left !=
set $node = $node._M_left
end
else
set $tmp_node = $node._M_parent
while $node == $tmp_node._M_right
set $node = $tmp_node
set $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parent
end
if $node._M_right != $tmp_node
set $node = $tmp_node
end
end
set $i++
end
printf "Number of elements found = %u\n", $ElementsFound
end
printf "Map size = %u\n", $tree_size
end
end document pmap_member
Prints std::map<TLeft and TRight> or std::multimap<TLeft and TRight> information. Works for std::multimap as well.
Syntax: pmap <map> <TtypeLeft> <TypeRight> <valLeft> <valRight>: Prints map size, if T defined all elements or just element(s) with val(s)
Examples:
pmap_member m class1 member1 class2 member2 - prints class1.member1 : class2.member2
pmap_member m class1 member1 class2 member2 lvalue - prints class1.member1 : class2.member2 where class1 == lvalue
end #
# std::set and std::multiset
# define pset
if $argc ==
help pset
else
set $tree = $arg0
set $i =
set $node = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header._M_left
set $end = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_header
set $tree_size = $tree._M_t._M_impl._M_node_count
if $argc ==
printf "Set "
whatis $tree
printf "Use pset <variable_name> <element_type> to see the elements in the set.\n"
end
if $argc ==
while $i < $tree_size
set $value = (void *)($node + )
printf "elem[%u]: ", $i
p *($arg1*)$value
if $node._M_right !=
set $node = $node._M_right
while $node._M_left !=
set $node = $node._M_left
end
else
set $tmp_node = $node._M_parent
while $node == $tmp_node._M_right
set $node = $tmp_node
set $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parent
end
if $node._M_right != $tmp_node
set $node = $tmp_node
end
end
set $i++
end
end
if $argc ==
set $idx = $arg2
set $ElementsFound =
while $i < $tree_size
set $value = (void *)($node + )
if *($arg1*)$value == $idx
printf "elem[%u]: ", $i
p *($arg1*)$value
set $ElementsFound++
end
if $node._M_right !=
set $node = $node._M_right
while $node._M_left !=
set $node = $node._M_left
end
else
set $tmp_node = $node._M_parent
while $node == $tmp_node._M_right
set $node = $tmp_node
set $tmp_node = $tmp_node._M_parent
end
if $node._M_right != $tmp_node
set $node = $tmp_node
end
end
set $i++
end
printf "Number of elements found = %u\n", $ElementsFound
end
printf "Set size = %u\n", $tree_size
end
end document pset
Prints std::set<T> or std::multiset<T> information. Works for std::multiset as well.
Syntax: pset <set> <T> <val>: Prints set size, if T defined all elements or just element(s) having val
Examples:
pset s - prints set size and definition
pset s int - prints all elements and the size of s
pset s int - prints the element(s) with value = (if any) and the size of s
end #
# std::dequeue
# define pdequeue
if $argc ==
help pdequeue
else
set $size =
set $start_cur = $arg0._M_impl._M_start._M_cur
set $start_last = $arg0._M_impl._M_start._M_last
set $start_stop = $start_last
while $start_cur != $start_stop
p *$start_cur
set $start_cur++
set $size++
end
set $finish_first = $arg0._M_impl._M_finish._M_first
set $finish_cur = $arg0._M_impl._M_finish._M_cur
set $finish_last = $arg0._M_impl._M_finish._M_last
if $finish_cur < $finish_last
set $finish_stop = $finish_cur
else
set $finish_stop = $finish_last
end
while $finish_first != $finish_stop
p *$finish_first
set $finish_first++
set $size++
end
printf "Dequeue size = %u\n", $size
end
end document pdequeue
Prints std::dequeue<T> information.
Syntax: pdequeue <dequeue>: Prints dequeue size, if T defined all elements
Deque elements are listed "left to right" (left-most stands for front and right-most stands for back)
Example:
pdequeue d - prints all elements and size of d
end #
# std::stack
# define pstack
if $argc ==
help pstack
else
set $start_cur = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_start._M_cur
set $finish_cur = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_finish._M_cur
set $size = $finish_cur - $start_cur
set $i = $size -
while $i >=
p *($start_cur + $i)
set $i--
end
printf "Stack size = %u\n", $size
end
end document pstack
Prints std::stack<T> information.
Syntax: pstack <stack>: Prints all elements and size of the stack
Stack elements are listed "top to buttom" (top-most element is the first to come on pop)
Example:
pstack s - prints all elements and the size of s
end #
# std::queue
# define pqueue
if $argc ==
help pqueue
else
set $start_cur = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_start._M_cur
set $finish_cur = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_finish._M_cur
set $size = $finish_cur - $start_cur
set $i =
while $i < $size
p *($start_cur + $i)
set $i++
end
printf "Queue size = %u\n", $size
end
end document pqueue
Prints std::queue<T> information.
Syntax: pqueue <queue>: Prints all elements and the size of the queue
Queue elements are listed "top to bottom" (top-most element is the first to come on pop)
Example:
pqueue q - prints all elements and the size of q
end #
# std::priority_queue
# define ppqueue
if $argc ==
help ppqueue
else
set $size = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_finish - $arg0.c._M_impl._M_start
set $capacity = $arg0.c._M_impl._M_end_of_storage - $arg0.c._M_impl._M_start
set $i = $size -
while $i >=
p *($arg0.c._M_impl._M_start + $i)
set $i--
end
printf "Priority queue size = %u\n", $size
printf "Priority queue capacity = %u\n", $capacity
end
end document ppqueue
Prints std::priority_queue<T> information.
Syntax: ppqueue <priority_queue>: Prints all elements, size and capacity of the priority_queue
Priority_queue elements are listed "top to buttom" (top-most element is the first to come on pop)
Example:
ppqueue pq - prints all elements, size and capacity of pq
end #
# std::bitset
# define pbitset
if $argc ==
help pbitset
else
p /t $arg0._M_w
end
end document pbitset
Prints std::bitset<n> information.
Syntax: pbitset <bitset>: Prints all bits in bitset
Example:
pbitset b - prints all bits in b
end #
# std::string
# define pstring
if $argc ==
help pstring
else
printf "String \t\t\t= \"%s\"\n", $arg0._M_data()
printf "String size/length \t= %u\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_length
printf "String capacity \t= %u\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_capacity
printf "String ref-count \t= %d\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_refcount
end
end document pstring
Prints std::string information.
Syntax: pstring <string>
Example:
pstring s - Prints content, size/length, capacity and ref-count of string s
end #
# std::wstring
# define pwstring
if $argc ==
help pwstring
else
call printf("WString \t\t= \"%ls\"\n", $arg0._M_data())
printf "WString size/length \t= %u\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_length
printf "WString capacity \t= %u\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_capacity
printf "WString ref-count \t= %d\n", $arg0._M_rep()._M_refcount
end
end document pwstring
Prints std::wstring information.
Syntax: pwstring <wstring>
Example:
pwstring s - Prints content, size/length, capacity and ref-count of wstring s
end #
# C++ related beautifiers (optional)
# set print pretty on
set print object on
set print static-members on
set print vtbl on
set print demangle on
set demangle-style gnu-v3
set print sevenbit-strings off
使用linux的GDB打印STL(vector,map,set..................)的更多相关文章
- GDB打印STL容器内容
GDB调试不能打印stl容器内容,下载此文件,将之保存为~/.gdbinit就可以使用打印命令了. 打印list用plist命令,打印vector用pvector,依此类推. (gdb) pvecto ...
- 2015-2016 ACM-ICPC, NEERC, Southern Subregional Contest A Email Aliases(模拟STL vector+map)
Email AliasesCrawling in process... Crawling failed Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:524288KB ...
- Codeforces 731 C.Socks-并查集+STL(vector+map)
C. Socks time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- gdb打印STL和boost容器
http://note.youdao.com/noteshare?id=b581e0db0084b6ba3011d9d27d372c91
- gdb打印vector
1.gdb版本大于7.0 (gdb) p yourVector 2.打印整个vector (gdb) p *(yourVector._M_impl._M_start)@yourVector.size( ...
- GDB —— 优化STL容器变量的显示
步骤 wget http://www.yolinux.com/TUTORIALS/src/dbinit_stl_views-1.03.txt cp dbinit_stl_views-1.03.txt ...
- 使用GDB调试STL容器
GDB中print方法并不能直接打印STL容器中保存的变量,想知道STL容器保存的变量,使用如下办法: 1. 创建文件~/.gdbinit: # # STL GDB evaluators/views/ ...
- [STL] Implement "map", "set"
练习热身 Ref: STL中map的数据结构 C++ STL中标准关联容器set, multiset, map, multimap内部采用的就是一种非常高效的平衡检索二叉树:红黑树,也成为RB树(Re ...
- C++ STL vector容器学习
STL(Standard Template Library)标准模板库是C++最重要的组成部分,它提供了一组表示容器.迭代器.函数对象和算法的模板.其中容器是存储类型相同的数据的结构(如vector, ...
随机推荐
- apache启动目录(禁止目录)与设置默认入口文件的方法
设置默认入口文件的方法: 打开apache的conf目录,找到httpd.conf文件,打开这个文件,搜索dir_module,找到以下截图修改位置进行修改,注意重启apache服务器,修改位置才会生 ...
- ByteBuffer使用之道
缓冲区分配和包装 在能够读和写之前,必须有一个缓冲区,用静态方法 allocate() 来分配缓冲区: ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); ...
- 服装销售系统数据库课程设计(MVC)
<数据库课程设计> 名称:Jia服装销售网站 姓名:陈文哲 学号:…… 班级:11软件工程 指导老师:索剑 目录 目录 1 需求分析 3 一:销售部门机构情况 3 二:销售部门的业务活动情 ...
- resin 4.0数据源的配置
在resin 的conf 文件下有resin.xml 我们在这里能够配置数据源以及配置项目 一.配置多个数据源,多个项目共享这些数据源.也就是这些数据源配置在<host> </ ...
- EditText操作收集
1.android EditText插入字符串到光标所在位置 EditText mTextInput=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.input);//EditText对象 i ...
- LabVIEW系列——自定义错误
1.自定义错误代码文本文件在labview中三处: a).E:\Program Files\National Instruments\LabVIEW 8.6\project\errors ...
- cookie 和 HttpSession
保存会话数据的两种技术 Cookie Cookie 是客户端技术,程序把每个用户的数据以cookie的形式写给用户的浏览器.当用户使用浏览器再去访问服务器中的web资源时,就会带着各自的数据去.web ...
- hdu2034java
人见人爱A-B Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submis ...
- 科讯CMS V9标签清单
全新整理V9标签清单 ====================网站通用标签============== {$GetSiteTitle} 显示网站标题 {$GetSiteName} 显示网站名称 {$G ...
- 使用linq语句获取指定条数的记录
//获得指定个数的子文件夹,用于分页 var pageAlbums = (from SPFolder pf in lstSubAlbums select pf) ...
