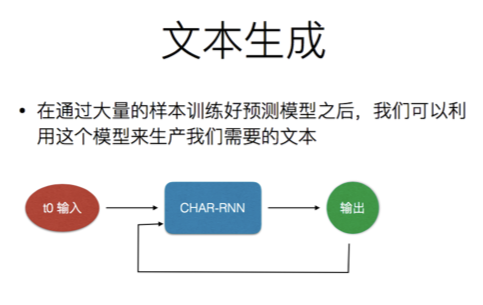
RNN 通过字符语言模型 理解BPTT
链接:https://github.com/karpathy/char-rnn
http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/
https://github.com/Teaonly/beginlearning/tree/master/july

"""
Minimal character-level Vanilla RNN model. Written by Andrej Karpathy (@karpathy)
BSD License
"""
import numpy as np
# data I/O
data = open('input.txt', 'r').read() # should be simple plain text file
chars = list(set(data))
data_size, vocab_size = len(data), len(chars)
print 'data has %d characters, %d unique.' % (data_size, vocab_size)
char_to_ix = { ch:i for i,ch in enumerate(chars) }
ix_to_char = { i:ch for i,ch in enumerate(chars) }
# hyperparameters
hidden_size = 100 # size of hidden layer of neurons
seq_length = 25 # number of steps to unroll the RNN for
learning_rate = 1e-1
# model parameters
Wxh = np.random.randn(hidden_size, vocab_size)*0.01 # input to hidden
Whh = np.random.randn(hidden_size, hidden_size)*0.01 # hidden to hidden
Why = np.random.randn(vocab_size, hidden_size)*0.01 # hidden to output
bh = np.zeros((hidden_size, 1)) # hidden bias
by = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1)) # output bias
def lossFun(inputs, targets, hprev):
"""
inputs,targets are both list of integers.
hprev is Hx1 array of initial hidden state
returns the loss, gradients on model parameters, and last hidden state
"""
xs, hs, ys, ps = {}, {}, {}, {}
hs[-1] = np.copy(hprev)
loss = 0
# forward pass
for t in xrange(len(inputs)):
xs[t] = np.zeros((vocab_size,1)) # encode in 1-of-k representation
xs[t][inputs[t]] = 1
hs[t] = np.tanh(np.dot(Wxh, xs[t]) + np.dot(Whh, hs[t-1]) + bh) # hidden state
ys[t] = np.dot(Why, hs[t]) + by # unnormalized log probabilities for next chars
ps[t] = np.exp(ys[t]) / np.sum(np.exp(ys[t])) # probabilities for next chars
loss += -np.log(ps[t][targets[t],0]) # softmax (cross-entropy loss)
# backward pass: compute gradients going backwards
dWxh, dWhh, dWhy = np.zeros_like(Wxh), np.zeros_like(Whh), np.zeros_like(Why)
dbh, dby = np.zeros_like(bh), np.zeros_like(by)
dhnext = np.zeros_like(hs[0])
for t in reversed(xrange(len(inputs))):
dy = np.copy(ps[t])
dy[targets[t]] -= 1 # backprop into y. see http://cs231n.github.io/neural-networks-case-study/#grad if confused here
dWhy += np.dot(dy, hs[t].T)
dby += dy
dh = np.dot(Why.T, dy) + dhnext # backprop into h
dhraw = (1 - hs[t] * hs[t]) * dh # backprop through tanh nonlinearity
dbh += dhraw
dWxh += np.dot(dhraw, xs[t].T)
dWhh += np.dot(dhraw, hs[t-1].T)
dhnext = np.dot(Whh.T, dhraw)
for dparam in [dWxh, dWhh, dWhy, dbh, dby]:
np.clip(dparam, -5, 5, out=dparam) # clip to mitigate exploding gradients
return loss, dWxh, dWhh, dWhy, dbh, dby, hs[len(inputs)-1]
def sample(h, seed_ix, n):
"""
sample a sequence of integers from the model
h is memory state, seed_ix is seed letter for first time step
"""
x = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1))
x[seed_ix] = 1
ixes = []
for t in xrange(n):
h = np.tanh(np.dot(Wxh, x) + np.dot(Whh, h) + bh)
y = np.dot(Why, h) + by
p = np.exp(y) / np.sum(np.exp(y))
ix = np.random.choice(range(vocab_size), p=p.ravel())
x = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1))
x[ix] = 1
ixes.append(ix)
return ixes
n, p = 0, 0
mWxh, mWhh, mWhy = np.zeros_like(Wxh), np.zeros_like(Whh), np.zeros_like(Why)
mbh, mby = np.zeros_like(bh), np.zeros_like(by) # memory variables for Adagrad
smooth_loss = -np.log(1.0/vocab_size)*seq_length # loss at iteration 0
while True:
# prepare inputs (we're sweeping from left to right in steps seq_length long)
if p+seq_length+1 >= len(data) or n == 0:
hprev = np.zeros((hidden_size,1)) # reset RNN memory
p = 0 # go from start of data
inputs = [char_to_ix[ch] for ch in data[p:p+seq_length]]
targets = [char_to_ix[ch] for ch in data[p+1:p+seq_length+1]]
# sample from the model now and then
if n % 100 == 0:
sample_ix = sample(hprev, inputs[0], 200)
txt = ''.join(ix_to_char[ix] for ix in sample_ix)
print '----\n %s \n----' % (txt, )
# forward seq_length characters through the net and fetch gradient
loss, dWxh, dWhh, dWhy, dbh, dby, hprev = lossFun(inputs, targets, hprev)
smooth_loss = smooth_loss * 0.999 + loss * 0.001
if n % 100 == 0: print 'iter %d, loss: %f' % (n, smooth_loss) # print progress
# perform parameter update with Adagrad
for param, dparam, mem in zip([Wxh, Whh, Why, bh, by],
[dWxh, dWhh, dWhy, dbh, dby],
[mWxh, mWhh, mWhy, mbh, mby]):
mem += dparam * dparam
param += -learning_rate * dparam / np.sqrt(mem + 1e-8) # adagrad update
p += seq_length # move data pointer
n += 1 # iteration counter
RNN 通过字符语言模型 理解BPTT的更多相关文章
- RNN实现字符级语言模型 - 恐龙岛(自己写RNN前向后向版本+keras版本)
问题描述:样本为所有恐龙名字,为了构建字符级语言模型来生成新的名称,你的模型将学习不同的名称模式,并随机生成新的名字. 在这里你将学习到: 如何存储文本数据以便使用rnn进行处理. 如何合成数据,通过 ...
- Python中文字符的理解:str()、repr()、print
Python中文字符的理解:str().repr().print 字数1384 阅读4 评论0 喜欢0 都说Python人不把文字编码这块从头到尾.从古至今全研究通透的话是完全玩不转的.我终于深刻的理 ...
- RNN(1) ------ “理解LSTM”(转载)
原文链接:http://www.jianshu.com/p/9dc9f41f0b29 Recurrent Neural Networks 人类并不是每时每刻都从一片空白的大脑开始他们的思考.在你阅读这 ...
- 用CNTK搞深度学习 (二) 训练基于RNN的自然语言模型 ( language model )
前一篇文章 用 CNTK 搞深度学习 (一) 入门 介绍了用CNTK构建简单前向神经网络的例子.现在假设读者已经懂得了使用CNTK的基本方法.现在我们做一个稍微复杂一点,也是自然语言挖掘中很火 ...
- python基础之Day7part2 史上最清晰字符编码理解
二.字符编码 基础知识: 文本编辑器存取文件原理与py执行原理异同: 存/写:进入文本编辑器 写内容 保存后 内存数据刷到硬盘 取/读:进入文本编辑器 找到内容 从硬盘读到内存 notepad把文件内 ...
- 对GBK的理解(内附全部字符编码列表):扩充的2万汉字低字节的高位不等于1,而且还剩许多编码空间没有利用
各种编码查询表:http://bm.kdd.cc/ 由于GB 2312-80只收录6763个汉字,有不少汉字,如部分在GB 2312-80推出以后才简化的汉字(如“啰”),部分人名用字(如中国前总理朱 ...
- 深入理解Python字符编码--转
http://blog.51cto.com/9478652/2057896 不论你是有着多年经验的 Python 老司机还是刚入门 Python 不久,你一定遇到过UnicodeEncodeError ...
- 深入理解Python字符编码
不论你是有着多年经验的 Python 老司机还是刚入门 Python 不久,你一定遇到过UnicodeEncodeError.UnicodeDecodeError 错误,每当遇到错误我们就拿着 enc ...
- RNN的介绍
一.状态和模型 在CNN网络中的训练样本的数据为IID数据(独立同分布数据),所解决的问题也是分类问题或者回归问题或者是特征表达问题.但更多的数据是不满足IID的,如语言翻译,自动文本生成.它们是一个 ...
随机推荐
- 前端框架之Vue.js
前言: 前端主流框架有Vue.react.angular,目前比较火因为Vue比较容易学习,运营起来比较快速: Vue是什么呢? 是一个基于MVVM架构的,前端框架: 如果你之前已经习惯了用jQuer ...
- (Nginx反向代理+NFS共享网页根目录)自动部署及可用性检测
1.nginx反向代理安装配置 #!/usr/bin/bash if [ -e /etc/nginx/nginx.conf ] then echo 'Already installed' exit e ...
- 常用java命令
javap 反编译 javap xxx.class 查看大概 javap -v -p xxx.class 查看详细 jps 查看有哪些java进程 jinfo 查看或设置java进程的 vm 参数,只 ...
- js 日期格式: UTC GMT 互相转换
//UTC 转指定格式日期 let date = '2018-03-07T16:00:00.000Z' console.log(moment(date).format('YYYY-MM-DD HH:m ...
- swftools安装教程
1 安装说明 本教程以环境为CentOS6.5+swftools-0.9.1.安装目录等可根据自己需要更改. 2 安装过程 1)下载软件 http://www.swftools.org/downloa ...
- mysql如何让自增id从某个位置开始设置方法
一般情况下两种方式: 1.本地数据不需要的情况下直接情况表(尽量不使用
- 自定义xadmin后台首页
登陆xadmin后台,首页默认是空白,可以自己添加小组件,xadmin一切都是那么美好,但是添加小组件遇到了个大坑,快整了2个礼拜,最终实现想要的界面.初始的页面如图: 本机后台显示这个页面正常,do ...
- day037 行记录的操作
1.库操作 2.表操作 3.行操作 1.库操作 1)创建数据库 语法: create database 数据库名 charset utf8; 数据库命名规则: 由数字,字母,下划线,@,#,$ 等组成 ...
- TTL集成门电路工作原理和电压传输特性
集成电路(Integrated Circuit 简称IC):即把电路中半导体器件,电阻,电容以及连线等制作在一块半导体基片上构成一个完整的电路,并封装到一个管壳内 集成电路的有点:体积小,重量轻,可靠 ...
- vue-router-9-HTML5 History 模式
vue-router 默认 hash 模式,页面不会重新加载 用路由的 history 模式,利用 history.pushState API 来完成 URL 跳转而无须重新加载页面. const r ...
