决策树(Decision Trees)
- 简介
决策树是一个预测模型,通过坐标数据进行多次分割,找出分界线,绘制决策树。
在机器学习中,决策树学习算法就是根据数据,使用计算机算法自动找出决策边界。
每一次分割代表一次决策,多次决策而形成决策树,决策树可以通过核技巧把简单的线性决策面转换为非线性决策面。
- 基本思想
树是由节点和边两种元素组成的结构。有这几个关键词:根节点、父节点、子节点和叶子节点。
父节点和子节点是相对的,子节点由父节点根据某一规则分裂而来,然后子节点作为新的父亲节点继续分裂,直至不能分裂为止。而根节点是没有父节点的节点,即初始分裂节点,叶子节点是没有子节点的节点,如下图所示:

决策树利用如上图所示的树结构进行决策,每一个非叶子节点是一个判断条件,每一个叶子节点是结论。从跟节点开始,经过多次判断得出结论。
举个例子
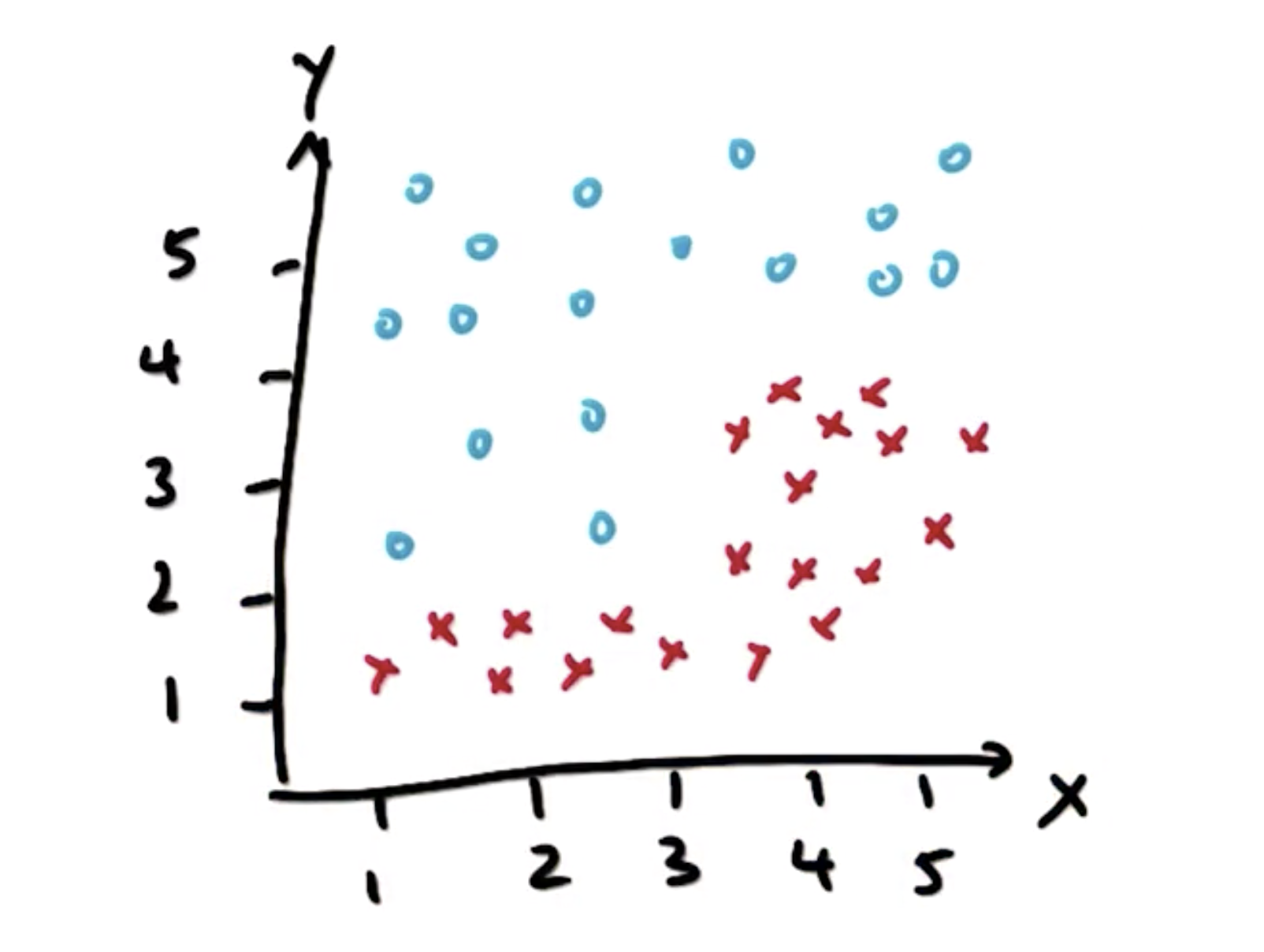
如图,利用决策树将两类样本点分类。
先从X轴观察,在X = 3时,样本点有一次明显的“突变”,我们以X = 3作为一次决策,进行一次划分:
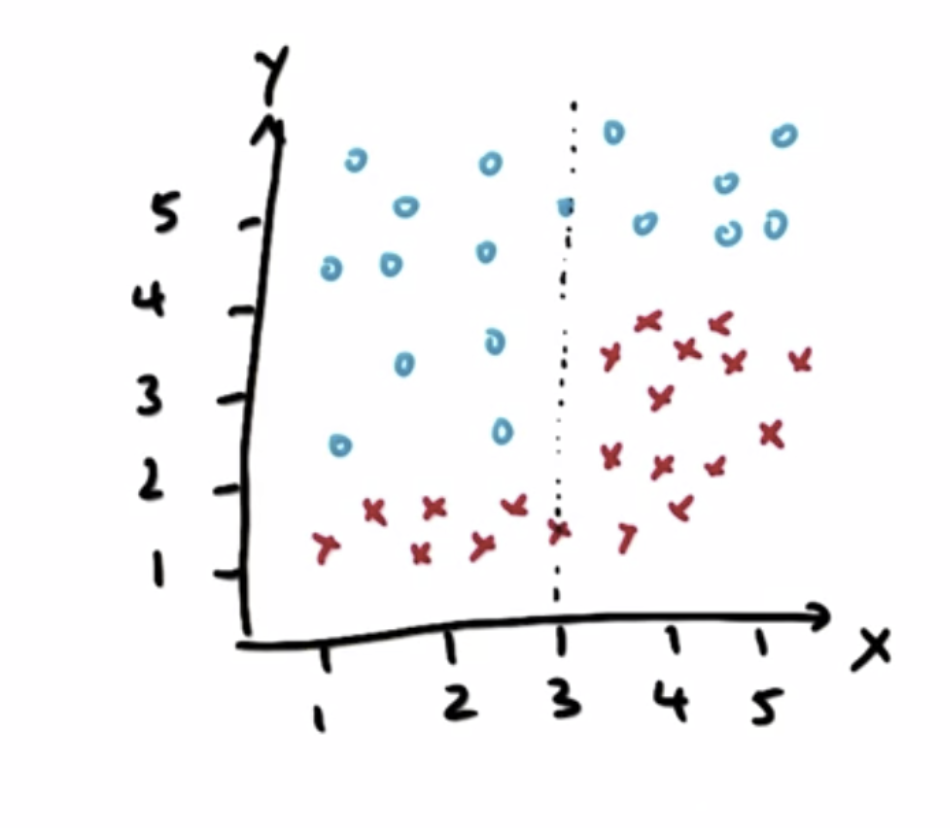
再从Y轴观察,两类样本点在Y = 4 和Y = 2处可以进行划分,进而进行两次划分:
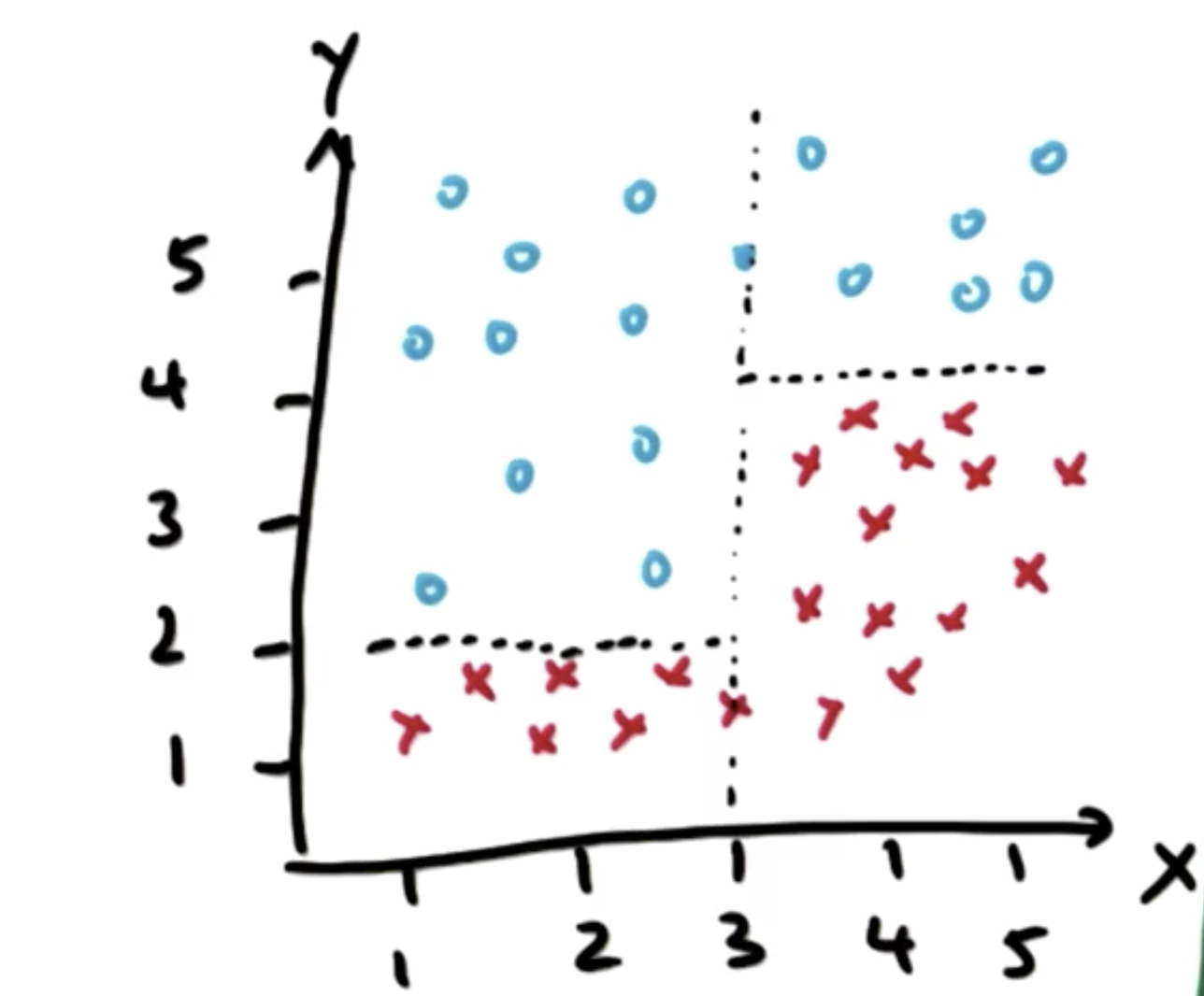
通过这几次划分,样本点被划分为四个部分,其中两类样本点各划为两部分,而且无法再继续分割,这种分割的过程就是决策树:
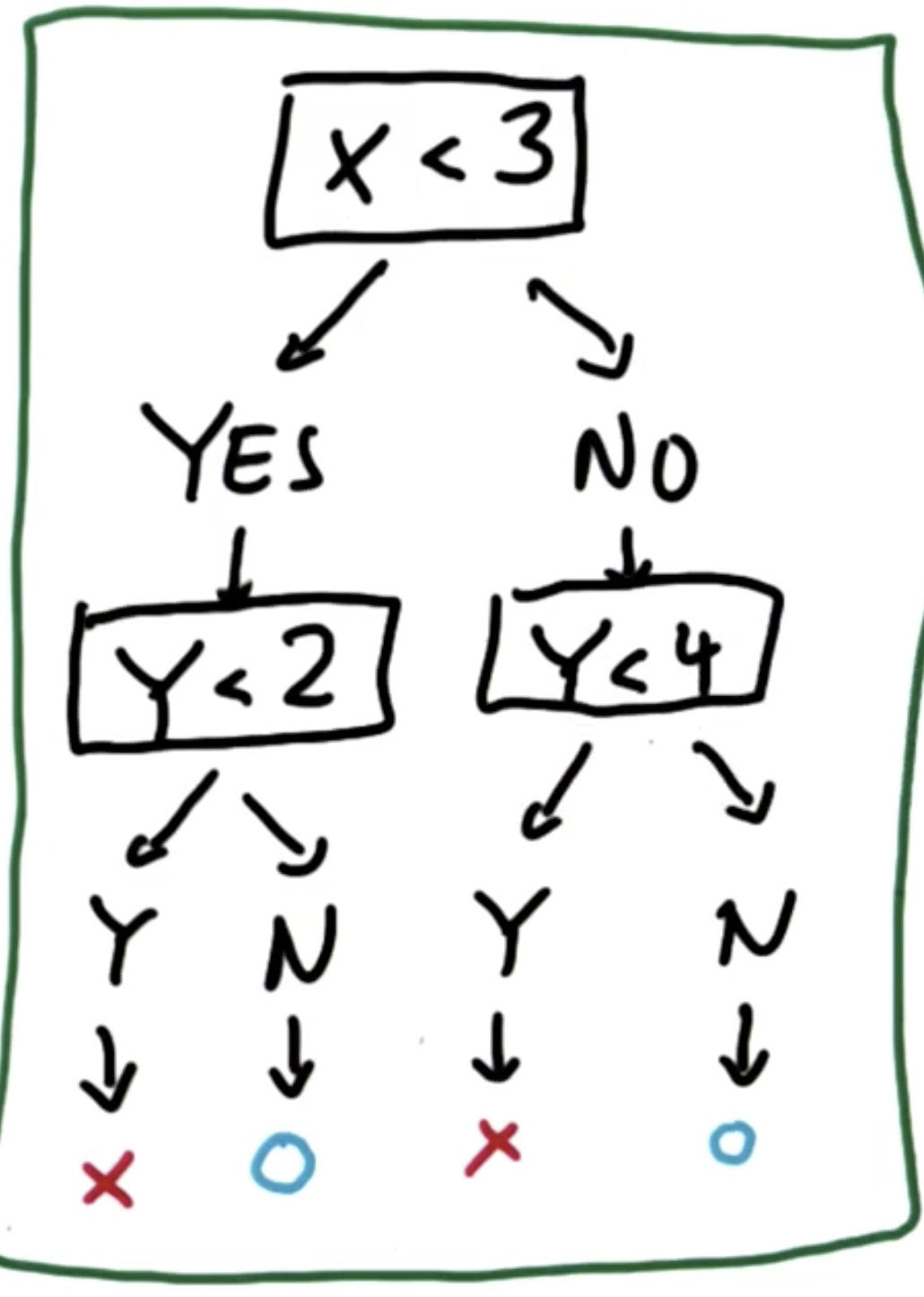
- 熵(entropy)
熵的作用:用于控制决策树在什么条件下做出决策,即在什么条件下分割数据
熵的定义:它是一系列样本中的不纯度的测量值(measure of impurity in a bunch of examples)
建立决策树的过程就是找到变量划分点从而产生尽可能的单一的子集,实际上决策树做决策的过程,就是对这个过程的递归重复。
熵描述了数据的混乱程度,熵越大,混乱程度越高,也就是纯度越低;反之,熵越小,混乱程度越低,纯度越高。 熵的计算公式如下所示:
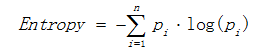
其中Pi表示类i的数量占比。以二分类问题为例,如果两类的数量相同,此时分类节点的纯度最低,熵等于1;如果节点的数据属于同一类时,此时节点的纯度最高,熵等于0。
熵的最大值为1,最小值为0
- 信息增益
用信息增益表示分裂前后跟的数据复杂度和分裂节点数据复杂度的变化值,计算公式表示为:
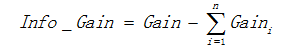
其中Gain表示节点的复杂度,Gain越高,说明复杂度越高。信息增益也可以说是分裂前的熵减去孩子节点的熵的和,信息增益越大,分裂后的熵减小得越多,分类的效果越明显。
- 偏差(bias)与方差(variance)
高偏差机器学习算法实际上会忽略训练数据,它几乎没有能力学习任何数据,这被称为偏差。
另一个极端情况就是高方差,它只能复现曾经出现过的东西,对于没有出现过的情况,他的反应非常差。
通过调整参数让偏差与方差平衡,使算法具有一定泛化能力,但仍然对训练数据开放,能根据数据调整模型,是机器学习的要点。
- 代码实现
环境:MacOS mojave 10.14.3
Python 3.7.0
使用库:scikit-learn 0.19.2
sklearn.tree官方库:https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/tree.html
>>> from sklearn import tree
>>> X = [[0, 0], [1, 1]] #两个样本点
>>> Y = [0, 1] #分别属于两个标签
>>> clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier() #进行分类
>>> clf = clf.fit(X, Y)
>>> clf.predict([[2., 2.]]) #预测新点
array([1]) #新点通过分类属于标签1
Main.py 主程序
import sys
from class_vis import prettyPicture, output_image
from prep_terrain_data import makeTerrainData import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from classifyDT import classify features_train, labels_train, features_test, labels_test = makeTerrainData() ### the classify() function in classifyDT is where the magic
### happens--fill in this function in the file 'classifyDT.py'!
clf = classify(features_train, labels_train) #### grader code, do not modify below this line prettyPicture(clf, features_test, labels_test)
accuracy = clf.score(features_test, labels_test) # output_image("test.png", "png", open("test.png", "rb").read())
print (accuracy)
acc = accuracy ### you fill this in!
classifyDT.py 决策树分类
def classify(features_train, labels_train):
### your code goes here--should return a trained decision tree classifer
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0)
clf.fit(features_train,labels_train)
return clf
perp_terrain_data.py 生成训练点
import random def makeTerrainData(n_points=1000):
###############################################################################
### make the toy dataset
random.seed(42)
grade = [random.random() for ii in range(0,n_points)]
bumpy = [random.random() for ii in range(0,n_points)]
error = [random.random() for ii in range(0,n_points)]
y = [round(grade[ii]*bumpy[ii]+0.3+0.1*error[ii]) for ii in range(0,n_points)]
for ii in range(0, len(y)):
if grade[ii]>0.8 or bumpy[ii]>0.8:
y[ii] = 1.0 ### split into train/test sets
X = [[gg, ss] for gg, ss in zip(grade, bumpy)]
split = int(0.75*n_points)
X_train = X[0:split]
X_test = X[split:]
y_train = y[0:split]
y_test = y[split:] grade_sig = [X_train[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_train)) if y_train[ii]==0]
bumpy_sig = [X_train[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_train)) if y_train[ii]==0]
grade_bkg = [X_train[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_train)) if y_train[ii]==1]
bumpy_bkg = [X_train[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_train)) if y_train[ii]==1] # training_data = {"fast":{"grade":grade_sig, "bumpiness":bumpy_sig}
# , "slow":{"grade":grade_bkg, "bumpiness":bumpy_bkg}} grade_sig = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
bumpy_sig = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
grade_bkg = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1]
bumpy_bkg = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1] test_data = {"fast":{"grade":grade_sig, "bumpiness":bumpy_sig}
, "slow":{"grade":grade_bkg, "bumpiness":bumpy_bkg}} return X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test
# return training_data, test_data
class_vis.py 绘图与保存图像
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg') import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylab as pl
import numpy as np #import numpy as np
#import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#plt.ioff() def prettyPicture(clf, X_test, y_test):
x_min = 0.0; x_max = 1.0
y_min = 0.0; y_max = 1.0 # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
h = .01 # step size in the mesh
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) # Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max()) plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=pl.cm.seismic) # Plot also the test points
grade_sig = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
bumpy_sig = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
grade_bkg = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1]
bumpy_bkg = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1] plt.scatter(grade_sig, bumpy_sig, color = "b", label="fast")
plt.scatter(grade_bkg, bumpy_bkg, color = "r", label="slow")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("bumpiness")
plt.ylabel("grade") plt.savefig("test.png")
得到结果,正确率90.8%
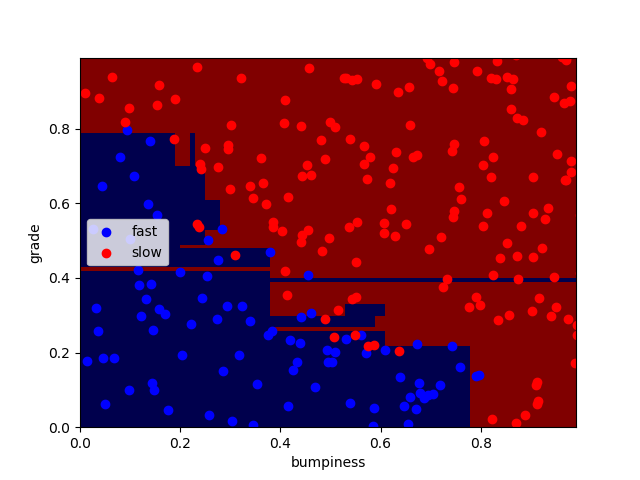
其中,狭长区域为过拟合
- 决策树的参数
min_samples_split可分割的样本数量下限,默认值为2
对于决策树最下层的每一个节点,是否还要继续分割,min_samples_split决定了能够继续进行分割的最少分割样本
acc_min_samples.py acc_min_samples对比
import sys
from class_vis import prettyPicture
from prep_terrain_data import makeTerrainData import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl features_train, labels_train, features_test, labels_test = makeTerrainData() ########################## DECISION TREE ################################# ### your code goes here--now create 2 decision tree classifiers,
### one with min_samples_split=2 and one with min_samples_split=50
### compute the accuracies on the testing data and store
### the accuracy numbers to acc_min_samples_split_2 and
### acc_min_samples_split_50, respectively from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
clf1 = DecisionTreeClassifier(min_samples_split=2)
clf2 = DecisionTreeClassifier(min_samples_split=50) clf1.fit(features_train,labels_train)
clf2.fit(features_train,labels_train) acc_min_samples_split_2 = clf1.score(features_test, labels_test)
acc_min_samples_split_50 = clf2.score(features_test, labels_test) print (acc_min_samples_split_2)
print (acc_min_samples_split_50) #choose one of two
prettyPicture(clf1, features_test, labels_test)
# prettyPicture(clf2, features_test, labels_test)
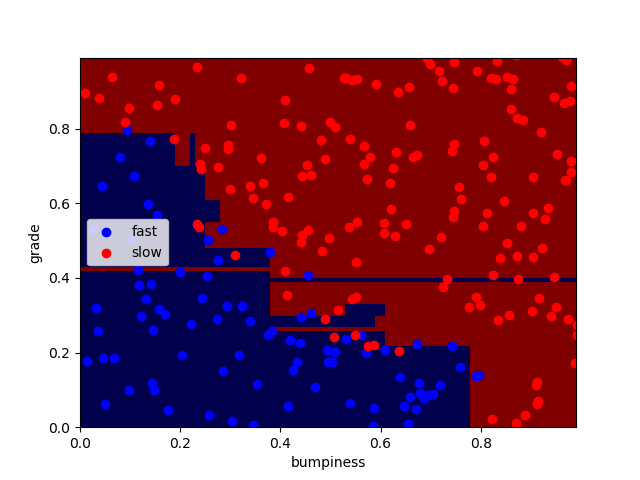

上图,min_samples_split分别为2 和50
得到正确率分别为90.8%和91.2%
- 决策树的优点与缺点
易于使用,易于理解
容易过拟合,尤其对于具有包含大量特征的数据时,复杂的决策树可能会过拟合数据,通过仔细调整参数,避免过拟合(对于节点上只有单个数据点的决策树,几乎肯定是过拟合)
决策树(Decision Trees)的更多相关文章
- 海量数据挖掘MMDS week6: 决策树Decision Trees
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/49445465 海量数据挖掘Mining Massive Datasets(MMDs) -Jure Le ...
- Decision Trees 决策树
Decision Trees (DT)是用于分类和回归的非参数监督学习方法. 目标是创建一个模型,通过学习从数据特征推断出的简单决策规则来预测目标变量的值. 例如,在下面的例子中,决策树从数据中学习用 ...
- Facebook Gradient boosting 梯度提升 separate the positive and negative labeled points using a single line 梯度提升决策树 Gradient Boosted Decision Trees (GBDT)
https://www.quora.com/Why-do-people-use-gradient-boosted-decision-trees-to-do-feature-transform Why ...
- CatBoost使用GPU实现决策树的快速梯度提升CatBoost Enables Fast Gradient Boosting on Decision Trees Using GPUs
python机器学习-乳腺癌细胞挖掘(博主亲自录制视频)https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&ut ...
- Logistic Regression vs Decision Trees vs SVM: Part II
This is the 2nd part of the series. Read the first part here: Logistic Regression Vs Decision Trees ...
- Logistic Regression Vs Decision Trees Vs SVM: Part I
Classification is one of the major problems that we solve while working on standard business problem ...
- 机器学习算法 --- Pruning (decision trees) & Random Forest Algorithm
一.Table for Content 在之前的文章中我们介绍了Decision Trees Agorithms,然而这个学习算法有一个很大的弊端,就是很容易出现Overfitting,为了解决此问题 ...
- 机器学习算法 --- Decision Trees Algorithms
一.Decision Trees Agorithms的简介 决策树算法(Decision Trees Agorithms),是如今最流行的机器学习算法之一,它即能做分类又做回归(不像之前介绍的其他学习 ...
- 机器学习算法实践:决策树 (Decision Tree)(转载)
前言 最近打算系统学习下机器学习的基础算法,避免眼高手低,决定把常用的机器学习基础算法都实现一遍以便加深印象.本文为这系列博客的第一篇,关于决策树(Decision Tree)的算法实现,文中我将对决 ...
随机推荐
- mysql 每个月创建新表
1.CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`%` PROCEDURE `aa`()BEGIN SET @sqlstr = CONCAT('create table cdrpbx10_',DATE ...
- 02.OOP面向对象-2.例子
class clothes: #初始化属性 def __init__(self,name,color): self.name = name self.color = color #转字符串 def _ ...
- mplayer configure选项中文注释
mplayer configure选项中文注释(MPlayer-1.0rc2) http://blogold.chinaunix.net/u3/104581/showart_2322466.html ...
- java的数据的类型
1分类: 基本数据类型长度: Java中简单类型,占用字节数, 以及包装类 浮点数的默认类型是Double(8个字节) 如果想直接想一个变量赋值一个float(4个字节)要在数值后面添加f/F 如同向 ...
- Python爬虫之正則表達式
1.经常使用符号 . :匹配随意字符,换行符 \n 除外 * :匹配前一个字符0次或无限次 ? :匹配前一个字符0次或1次 .* :贪心算法.尽可能的匹配多的字符 .*? :非贪心算法 () ...
- Routh-Hurwitz Criterion 劳斯稳定判据
Routh-Hurwitz Criterion 为什么仅仅要有一个极点在右半平面,那么系统就不会稳定? 比如H(s) =( 1/(s+1) ) * ( 1/(s+3) ) * ( 1/(s-2) ) ...
- poj 2683 Ohgas' Fortune 利率计算
水题. 代码: //poj 2683 //sep9 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int cases; sca ...
- FOJ题目Problem 2082 过路费 (link cut tree边权更新)
Problem 2082 过路费 Accept: 382 Submit: 1279 Time Limit: 1000 mSec Memory Limit : 32768 KB Proble ...
- 又一次发现Oracle太美之glogin.sql
又一次发现Oracle太美之glogin.sql 刚開始接触Oracle的时候,有时候一登陆一个生产环境.常常会出现以下的情况: [oracle@rh64 app]$ sqlplus / as sys ...
- 移动端H5页面编辑器开发实战--原理结构篇
很久前的写的文章了,转载下发到这里 原文地址: https://blog.csdn.net/tech_meizu/article/details/52288797
