Exercise: PCA in 2D
Step 0: Load data
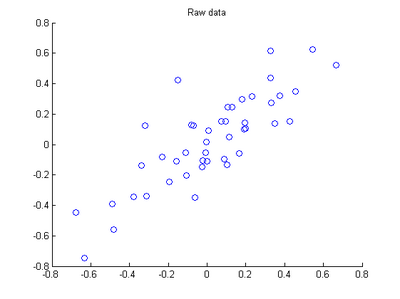
The starter code contains code to load 45 2D data points. When plotted using the scatter function, the results should look like the following:
Step 1: Implement PCA
In this step, you will implement PCA to obtain xrot, the matrix in which the data is "rotated" to the basis comprising
made up of the principal components
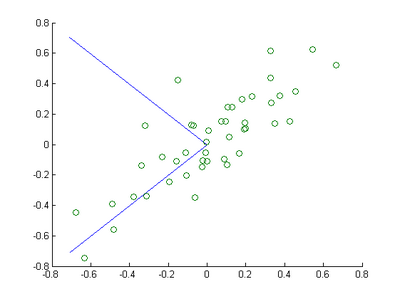
Step 1a: Finding the PCA basis
Find
and
, and draw two lines in your figure to show the resulting basis on top of the given data points.
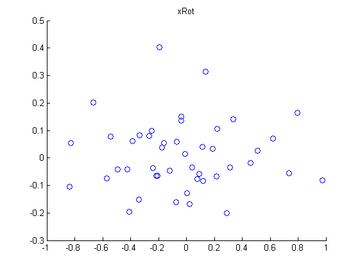
Step 1b: Check xRot
Compute xRot, and use the scatter function to check that xRot looks as it should, which should be something like the following:
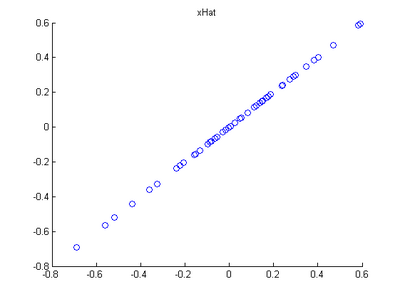
Step 2: Dimension reduce and replot
In the next step, set k, the number of components to retain, to be 1
Step 3: PCA Whitening
Step 4: ZCA Whitening
Code
close all %%================================================================
%% Step : Load data
% We have provided the code to load data from pcaData.txt into x.
% x is a * matrix, where the kth column x(:,k) corresponds to
% the kth data point.Here we provide the code to load natural image data into x.
% You do not need to change the code below. x = load('pcaData.txt','-ascii'); % 载入数据
figure();
scatter(x(, :), x(, :)); % 用圆圈绘制出数据分布
title('Raw data'); %%================================================================
%% Step 1a: Implement PCA to obtain U
% Implement PCA to obtain the rotation matrix U, which is the eigenbasis
% sigma. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
u = zeros(size(x, )); % You need to compute this
[n m]=size(x);
% x=x-repmat(mean(x,),,m); %预处理,均值为零 —— 2维,每一维减去该维上的均值
sigma=(1.0/m)*x*x'; % 协方差矩阵
[u s v]=svd(sigma); % --------------------------------------------------------
hold on
plot([ u(,)], [ u(,)]); % 画第一条线
plot([ u(,)], [ u(,)]); % 画第二条线
scatter(x(, :), x(, :));
hold off %%================================================================
%% Step 1b: Compute xRot, the projection on to the eigenbasis
% Now, compute xRot by projecting the data on to the basis defined
% by U. Visualize the points by performing a scatter plot. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xRot = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xRot=u'*x; % -------------------------------------------------------- % Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a line across the
% diagonal against a blue background.
figure();
scatter(xRot(, :), xRot(, :));
title('xRot'); %%================================================================
%% Step : Reduce the number of dimensions from to .
% Compute xRot again (this time projecting to dimension).
% Then, compute xHat by projecting the xRot back onto the original axes
% to see the effect of dimension reduction % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
k = ; % Use k = and project the data onto the first eigenbasis
xHat = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xHat = u*([u(:,),zeros(n,)]'*x); % 降维
% 使特征点落在特征向量所指的方向上而不是原坐标系上 % --------------------------------------------------------
figure();
scatter(xHat(, :), xHat(, :));
title('xHat'); %%================================================================
%% Step : PCA Whitening
% Complute xPCAWhite and plot the results. epsilon = 1e-;
% -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xPCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xPCAWhite = diag(./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x; % 每个特征除以对应的特征向量,以使每个特征有一致的方差
% --------------------------------------------------------
figure();
scatter(xPCAWhite(, :), xPCAWhite(, :));
title('xPCAWhite'); %%================================================================
%% Step : ZCA Whitening
% Complute xZCAWhite and plot the results. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xZCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xZCAWhite = u*diag(./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x; % --------------------------------------------------------
figure();
scatter(xZCAWhite(, :), xZCAWhite(, :));
title('xZCAWhite'); %% Congratulations! When you have reached this point, you are done!
% You can now move onto the next PCA exercise. :)
Exercise: PCA in 2D的更多相关文章
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:PCA in 2D
Exercise:PCA in 2D 习题的链接:Exercise:PCA in 2D pca_2d.m close all %%=================================== ...
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:PCA and Whitening
Exercise:PCA and Whitening 习题链接:Exercise:PCA and Whitening pca_gen.m %%============================= ...
- Deep Learning 4_深度学习UFLDL教程:PCA in 2D_Exercise(斯坦福大学深度学习教程)
前言 本节练习的主要内容:PCA,PCA Whitening以及ZCA Whitening在2D数据上的使用,2D的数据集是45个数据点,每个数据点是2维的.要注意区别比较二维数据与二维图像的不同,特 ...
- UFLDL教程笔记及练习答案二(预处理:主成分分析和白化)
首先将本节主要内容记录下来.然后给出课后习题的答案. 笔记: :首先我想推导用SVD求解PCA的合理性. PCA原理:如果样本数据X∈Rm×n.当中m是样本数量,n是样本的维数.PCA降维的目的就是为 ...
- Deep Learning 教程(斯坦福深度学习研究团队)
http://www.zhizihua.com/blog/post/602.html 说明:本教程将阐述无监督特征学习和深度学习的主要观点.通过学习,你也将实现多个功能学习/深度学习算法,能看到它们为 ...
- [Scikit-learn] 4.3 Preprocessing data
数据分析的重难点,就这么来了,欢迎欢迎,热烈欢迎. 4. Dataset transformations 4.3. Preprocessing data 4.3.1. Standardization, ...
- UFLDL教程之(三)PCA and Whitening exercise
Exercise:PCA and Whitening 第0步:数据准备 UFLDL下载的文件中,包含数据集IMAGES_RAW,它是一个512*512*10的矩阵,也就是10幅512*512的图像 ( ...
- PCA and kmeans MATLAB实现
MATLAB基础知识 l Imread: 读取图片信息: l axis:轴缩放:axis([xmin xmax ymin ymax zmin zmax cmin cmax]) 设置 x.y 和 ...
- Deep Learning 5_深度学习UFLDL教程:PCA and Whitening_Exercise(斯坦福大学深度学习教程)
前言 本文是基于Exercise:PCA and Whitening的练习. 理论知识见:UFLDL教程. 实验内容:从10张512*512自然图像中随机选取10000个12*12的图像块(patch ...
随机推荐
- 51Nod 天堂里的游戏
多年后,每当Noder看到吉普赛人,就会想起那个遥远的下午. Noder躺在草地上漫无目的的张望,二楼的咖啡馆在日光下闪着亮,像是要进化成一颗巨大的咖啡豆.天气稍有些冷,但草还算暖和.不远的地方坐着一 ...
- ora_tool
#!/bin/ksh # # Copyright (c) 1998, 2002, Oracle Corporation. All rights reserved. # version() { ...
- UI Framework-1: Aura Client API
Client API The Aura Client API is an API Aura uses to communicate with the client application using ...
- CSS命令
border-bottom-right-radius: 10px;/* 文本框的角的弯曲度*/ border-bottom-left-radius: 10px; border-top-left-rad ...
- 通过浏览器地址进行 post get 请求
首先安装curl 1.post chcp 65001 title 接口测试脚本 d: cd D:\curl\ curl -l -X POST -d "params" url ech ...
- iOS开发系列之四 - UITextView 使用方法小结
// 初始化输入框并设置位置和大小 UITextView *textView = [[UITextView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(10, 10, 300, 1 ...
- thinkphp5项目--企业单车网站(二)
thinkphp5项目--企业单车网站(二) 项目地址 fry404006308/BicycleEnterpriseWebsite: Bicycle Enterprise Websitehttps:/ ...
- RequestMapping、Responsebody、RequestBody
预备知识:@RequestMappingRequestMapping是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于类或方法上.用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径.@RequestM ...
- UVA - 12263 Rankings 模拟(拓扑排序)
题意:1~n这n个数,给你一个初始的顺序,再告诉你那两个数的大小关系发生了变化,求变化后的 顺序,不存在则输出IMPOSSIBLE 思路:这题很遗憾没在比赛的时候过掉,结束后加了一行就AC了.题目真的 ...
- jQuery - 设置内容和属性 设置内容 - text()、html() 以及 val() , 设置属性 - attr()
jQuery - 设置内容和属性 设置内容 - text().html() 以及 val() text() - 设置或返回所选元素的文本内容 html() - 设置或返回所选元素的内容(包括 HTM ...