Netty原理和使用
性能主题
Netty原理和使用
Netty是一个高性能 事件驱动的异步的非堵塞的IO(NIO)框架,用于建立TCP等底层的连接,基于Netty可以建立高性能的Http服务器。支持HTTP、 WebSocket 、Protobuf、
Binary
TCP |和UDP,Netty已经被很多高性能项目作为其Socket底层基础,如HornetQ Infinispan Vert.x
Play Framework
Finangle和
Cassandra。其竞争对手是:Apache MINA和
Grizzly。
传统堵塞的IO读取如下:
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("input.bin");
int byte = is.read(); // 当前线程等待结果到达直至错误
而使用NIO如下:
while (true) {
selector.select(); // 从多个通道请求事件
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectorKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
handleKey(key);
it.remove();
}
}
堵塞与非堵塞原理
传统硬件的堵塞如下,从内存中读取数据,然后写到磁盘,而CPU一直等到磁盘写完成,磁盘的写操作是慢的,这段时间CPU被堵塞不能发挥效率。
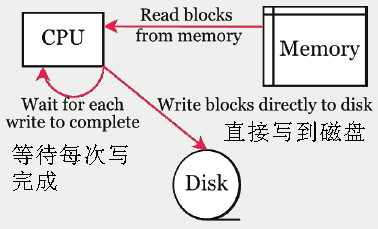
使用非堵塞的DMA如下图:CPU只是发出写操作这样的指令,做一些初始化工作,DMA具体执行,从内存中读取数据,然后写到磁盘,当完成写后发出一个中断事件给CPU。这段时间CPU是空闲的,可以做别的事情。这个原理称为Zero.copy零拷贝。

Netty底层基于上述Java NIO的零拷贝原理实现:

比较
- Tomcat是一个Web服务器,它是采取一个请求一个线程,当有1000客户端时,会耗费很多内存。通常一个线程将花费
256kb到1mb的stack空间。 - Node.js是一个线程服务于所有请求,在错误处理上有限制
- Netty是一个线程服务于很多请求,如下图,当从Java NIO获得一个Selector事件,将激活通道Channel。

演示
Netty的使用代码如下:
Channel channel = ...
ChannelFuture cf = channel.write(data);
cf.addListener(
new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if(!future.isSuccess() {
future.cause().printStacktrace();
...
}
...
}
});
...
cf.sync();
通过引入观察者监听,当有数据时,将自动激活监听者中的代码运行。
我们使用Netty建立一个服务器代码:
public class EchoServer {
private final int port;
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
// Configure the server.
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
// new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO),
new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
// Start the server.
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
// Wait until the server socket is closed.
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// Shut down all event loops to terminate all threads.
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
这段代码调用:在9999端口启动
new EchoServer(9999).run();
我们需要完成的代码是EchoServerHandler:
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(EchoServerHandler.class.getName());
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ctx.write(msg);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// Close the connection when an exception is raised.
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Unexpected exception from downstream.", cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
原理
一个Netty服务器的原理如下:
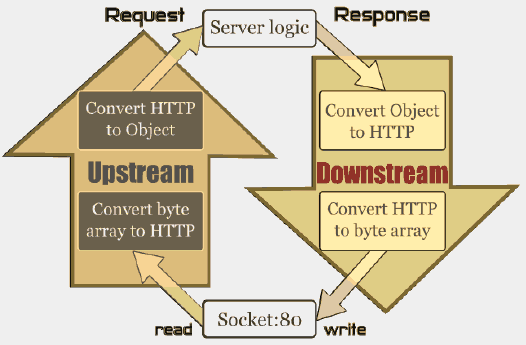
图中每次请求的读取是通过UpStream来实现,然后激活我们的服务逻辑如EchoServerHandler,而服务器向外写数据,也就是响应是通过DownStream实现的。每个通道Channel包含一对UpStream和DownStream,以及我们的handlers(EchoServerHandler),如下图,这些都是通过channel pipeline封装起来的,数据流在管道里流动,每个Socket对应一个ChannelPipeline。
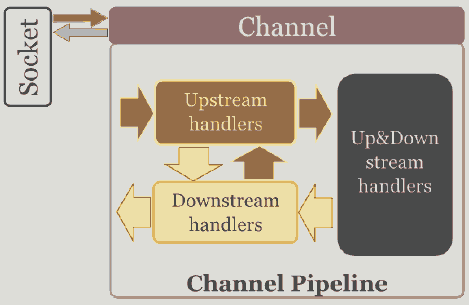
CHANNELPIPELINE是关键,它类似Unix的管道,有以下作用:
- 为每个Channel 保留 ChannelHandlers ,如EchoServerHandler
- 所有的事件都要通过它
- 不断地修改:类似unix的SH管道: echo "Netty is shit...." | sed -e 's/is /is the /'
- 一个Channel对应一个
ChannelPipeline - 包含协议编码解码 安全验证SSL/TLS和应用逻辑
客户端代码
前面我们演示了服务器端代码,下面是客户端代码:
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
private final int firstMessageSize;
public EchoClient(String host, int port, int firstMessageSize) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
this.firstMessageSize = firstMessageSize;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
// Configure the client.
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true).handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
// new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO),
new EchoClientHandler(firstMessageSize));
}
});
// Start the client.
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
// Wait until the connection is closed.
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// Shut down the event loop to terminate all threads.
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
客户端的应用逻辑EchoClientHandler:
public class EchoClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(EchoClientHandler.class.getName());
private final ByteBuf firstMessage;
/**
* Creates a client-side handler.
*/
public EchoClientHandler(int firstMessageSize) {
if (firstMessageSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("firstMessageSize: " + firstMessageSize);
}
firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(firstMessageSize);
for (int i = 0; i < firstMessage.capacity(); i++) {
firstMessage.writeByte((byte) i);
}
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);
System.out.print("active");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ctx.write(msg);
System.out.print("read");
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
System.out.print("readok");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// Close the connection when an exception is raised.
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Unexpected exception from downstream.", cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
原文地址:https://www.jdon.com/concurrent/netty.html
Netty原理和使用的更多相关文章
- 《深入探索Netty原理及源码分析》文集小结
<深入探索Netty原理及源码分析>文集小结 https://www.jianshu.com/p/239a196152de
- Netty原理架构解析
Netty原理架构解析 转载自:http://www.sohu.com/a/272879207_463994本文转载关于Netty的原理架构解析,方便之后巩固复习 Netty是一个异步事件驱动的网络应 ...
- 【Netty】最透彻的Netty原理架构解析
这可能是目前最透彻的Netty原理架构解析 本文基于 Netty 4.1 展开介绍相关理论模型,使用场景,基本组件.整体架构,知其然且知其所以然,希望给大家在实际开发实践.学习开源项目方面提供参考. ...
- 这可能是目前最透彻的Netty原理架构解析
https://juejin.im/post/5be00763e51d453d4a5cf289 本文基于 Netty 4.1 展开介绍相关理论模型,使用场景,基本组件.整体架构,知其然且知其所以然,希 ...
- 每日扫盲(四):java之Netty原理和使用
转自:https://www.jdon.com/concurrent/netty.html Netty是一个高性能 事件驱动的异步的非堵塞的IO(NIO)框架,用于建立TCP等底层的连接,基于Nett ...
- netty原理解析
netty主要采用的是reactor模式(事件)驱动模型,以下主要对reactor进行总结: C/S架构可以抽象为如下模型: C就是Client(客户端),上面的B是Browser(浏览器) S就是S ...
- Netty原理分析
Netty是一个高性能.异步事件驱动的NIO框架,它提供了对TCP.UDP和文件传输的支持,作为一个异步NIO框架,Netty的所有IO操作都是异步非阻塞的,通过Future-Listener机制,用 ...
- Netty原理剖析
1. Netty简介 Netty是一个高性能.异步事件驱动的NIO框架,基于JAVA NIO提供的API实现.它提供了对TCP.UDP和文件传输的支持,作为一个异步NIO框架,Netty的所有IO操作 ...
- netty 原理
netty 实现 1. 各组件之间的关系 每个ServerBootstrap与一个事件循环对象(一个线程)都会与一个Channel绑定,如NioServerSocketChannel 2. 如何绑定 ...
随机推荐
- POJ 1988 带偏移量的并查集
题意: 思路: 数据范围很大 貌似只能用并查集了-- //By SiriusRen #include <cstdio> using namespace std; int p,f[33333 ...
- C# 返回分页查询的总页数
/// <summary> /// 返回分页查询操作的的总页数 /// </summary> /// <param name="count">总 ...
- shell项目-告警系统
告警系统 1. 告警系统需求分析 需求:使用shell定制各种个性化告警工具,但需要统一化管理.规范化管理. 思路:指定一个脚本包,包含主程序.子程序.配置文件.邮件引擎.输出日志等. 主程序:作为整 ...
- 洛谷 P3111 [USACO14DEC]牛慢跑Cow Jog_Sliver
P3111 [USACO14DEC]牛慢跑Cow Jog_Sliver 题目描述 The cows are out exercising their hooves again! There are N ...
- (九)unity4.6学习Ugui中文文档-------參考-UGUI Rect Transform
大家好.我是孙广东. 转载请注明出处:http://write.blog.csdn.net/postedit/38922399 更全的内容请看我的游戏蛮牛地址:http://www.unit ...
- 教你win7解除阻止程序运行怎么操作
教你win7解除阻止程序运行怎么操作 来源:http://www.windows7en.com/jiaocheng/27594.html 有时候我下载的软件,被win7系统禁止了运行了时软件不能使用, ...
- Objective-C基础笔记(8)Foundation常用类NSString
一.创建字符串的方法 void stringCreate(){ //方法1 NSString *str1 = @"A String!"; //方法2 NSString *str2 ...
- C# 异步延时执行
https://blog.csdn.net/xiawu1990/article/details/78350253?utm_source=blogxgwz7 var t = Task.Run(async ...
- [NPM] Publish npm packages using npm publish
In this lesson we will publish our package. We will first add a prepublish script that runs our buil ...
- kibana中信息分类查询显示的方法
1.什么是kibana? kibana是ELK(elasticsearch+logstash+kibana)中的K,它是一个可灵活的分析和可视化平台,主要是显示数据以及根据这些数据绘出一些可视化图表, ...
