基于Quick_Thought Vectors的Sentence2Vec神经网络实现
一、前言
1、Skip-Thought-Vector论文 https://github.com/ryankiros/skip-thoughts
2、本文假设读者已了解Skip-Gram-Vector和RNN相关基础
3、quick_thought 论文:Lajanugen Logeswaran, Honglak Lee, An efficient framework for learning sentence representations. In ICLR, 2018.
二、实战
1、对数据进行分句(去掉过短的句子)、删除频率高的句子、分词
def fenju(data):
sentence=[]
for i in range(len(data)):
try:
m = re.findall('。',data[i][0])
# print(m)
if data[i][1] is not None and len(m)>0:
if len(m)>1:
content=data[i][0].split('。')
# print(content)
for c in range(len(content)):
if len(content[c])>10:
sentence.append(content[c]+'。')
elif len(data[i][0])>10:
sentence.append(data[i][0])
else:
continue
except:
continue
return sentence def _process_sentence_list(sentence_list, threshold=0.01):
sentence_count = Counter(sentence_list)
total_count = len(sentence_list)
# 计算句子频率
sentence_freqs = {w: c / total_count for w, c in sentence_count.items()}
# 剔除出现频率太高的句子
sentence=[]
for w in range(len(sentence_list)):
if sentence_freqs[sentence_list[w]] < threshold:
sentence.append(sentence_list[w])
else:
continue
return sentence def fenci(alltext, writefile, filename):
if not os.path.exists(writefile):
os.makedirs(writefile)
sentence = [' '.join(jieba.lcut(''.join(text.split()))) for text in alltext]
print(sentence)
with open(os.path.join(writefile, filename), "w") as fw:
fw.write("\n".join(sentence))
2、构建vocab、TFRecord文件(详细看github代码)
3、模型输入定义(3种模式train/eval/encode)
def build_inputs(self):
if self.mode == "encode":
encode_ids = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, (None, None), name="encode_ids")
encode_mask = tf.placeholder(tf.int8, (None, None), name="encode_mask")
else:
# Prefetch serialized tf.Example protos.
input_queue = input_ops.prefetch_input_data(
self.reader,
FLAGS.input_file_pattern,
shuffle=FLAGS.shuffle_input_data,
capacity=FLAGS.input_queue_capacity,
num_reader_threads=FLAGS.num_input_reader_threads)
print("input_queue",input_queue)
# Deserialize a batch.
serialized = input_queue.dequeue_many(FLAGS.batch_size)
encode = input_ops.parse_example_batch(serialized)
encode_ids = encode.ids
encode_mask = encode.mask
self.encode_ids = encode_ids
self.encode_mask = encode_mask
由于我们每个batch中句子都进行了padding,为了防止padding对训练的影响,这里需要传递掩码给到RNN网络--每个句子各自的原始长度(encode_mask)。
4、对输入句子进行embedding
def build_word_embeddings(self):
rand_init = self.uniform_initializer
self.word_embeddings = []
self.encode_emb = []
self.init = None
for v in self.config.vocab_configs:
if v.mode == 'fixed':
if self.mode == "train":
word_emb = tf.get_variable(
name=v.name,
shape=[v.size, v.dim],
trainable=False)
embedding_placeholder = tf.placeholder(
tf.float32, [v.size, v.dim])
embedding_init = word_emb.assign(embedding_placeholder) rand = np.random.rand(1, v.dim)
word_vecs = np.load(v.embs_file)
load_vocab_size = word_vecs.shape[0]
assert(load_vocab_size == v.size - 1)
word_init = np.concatenate((rand, word_vecs), axis=0)
self.init = (embedding_init, embedding_placeholder, word_init) else:
word_emb = tf.get_variable(
name=v.name,
shape=[v.size, v.dim]) encode_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(word_emb, self.encode_ids)
self.word_emb = word_emb
self.encode_emb.extend([encode_emb, encode_emb])##### if v.mode == 'trained':
for inout in ["", "_out"]:
word_emb = tf.get_variable(
name=v.name + inout,
shape=[v.size, v.dim],
initializer=rand_init)
if self.mode == 'train':
self.word_embeddings.append(word_emb) encode_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(word_emb, self.encode_ids)
self.encode_emb.append(encode_emb) if v.mode == 'expand':
for inout in ["", "_out"]:
encode_emb = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (
None, None, v.dim), v.name + inout)
self.encode_emb.append(encode_emb)
word_emb_dict = read_vocab_embs(v.vocab_file + inout + ".txt",
v.embs_file + inout + ".npy")
self.word_embeddings.append(word_emb_dict) if v.mode != 'expand' and self.mode == 'encode':
word_emb_dict = read_vocab(v.vocab_file)
self.word_embeddings.extend([word_emb_dict, word_emb_dict])
将句子中的每一个字都转化为vocab size长度的向量。v.mode的3种模式fixed(使用预训练的embedding)/train(训练)/expand(扩展)。 最终输出的形式[encode_emb,encode_emb],用来获取上下句联系。
5、构建encoder
encoder对句子进行encode,得到最终的hidden state,这里可用单层的LSTM网络\双向LSTM\双向GRU。
def _initialize_cell(self, num_units, cell_type="GRU"):
if cell_type == "GRU":
return tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell(num_units=num_units)
elif cell_type == "LSTM":
return tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(num_units=num_units)
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid cell type") def rnn(self, word_embs, mask, scope, encoder_dim, cell_type="GRU"):
length = tf.to_int32(tf.reduce_sum(mask, 1), name="length")
if self.config.bidir:
if encoder_dim % 2:
raise ValueError(
"encoder_dim must be even when using a bidirectional encoder.")
num_units = encoder_dim // 2
cell_fw = self._initialize_cell(num_units, cell_type=cell_type)
cell_bw = self._initialize_cell(num_units, cell_type=cell_type)
outputs, states = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(
cell_fw=cell_fw,
cell_bw=cell_bw,
inputs=word_embs,
sequence_length=length,
dtype=tf.float32,
scope=scope)
if cell_type == "LSTM":
states = [states[0][1], states[1][1]]
state = tf.concat(states, 1)
else:
cell = self._initialize_cell(encoder_dim, cell_type=cell_type)
outputs, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(
cell=cell,
inputs=word_embs,
sequence_length=length,
dtype=tf.float32,
scope=scope)
if cell_type == "LSTM":
state = state[1]
return state def build_encoder(self):
"""Builds the sentence encoder. Inputs:
self.encode_emb
self.encode_mask Outputs:
self.thought_vectors Raises:
ValueError: if config.bidirectional_encoder is True and config.encoder_dim
is odd.
"""
names = ["", "_out"]
self.thought_vectors = []
for i in range(2):
with tf.variable_scope("encoder" + names[i]) as scope:
if self.config.encoder == "gru":
sent_rep = self.rnn(self.encode_emb[i], self.encode_mask, scope, self.config.encoder_dim, cell_type="GRU")
elif self.config.encoder == "lstm":
sent_rep = self.rnn(self.encode_emb[i], self.encode_mask, scope, self.config.encoder_dim, cell_type="LSTM")
elif self.config.encoder == 'bow':
sent_rep = self.bow(self.encode_emb[i], self.encode_mask)
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid encoder") thought_vectors = tf.identity(sent_rep, name="thought_vectors")
self.thought_vectors.append(thought_vectors)
可见分别对[encode_emb,encode_emb]进行了encode,得到[thought_vectors,thought_vectors]
6、构建损失函数
def build_loss(self):
"""Builds the loss Tensor. Outputs:
self.total_loss
"""
all_sen_embs = self.thought_vectors if FLAGS.dropout:
mask_shp = [1, self.config.encoder_dim]
bin_mask = tf.random_uniform(mask_shp) > FLAGS.dropout_rate
bin_mask = tf.where(bin_mask, tf.ones(mask_shp), tf.zeros(mask_shp))
src = all_sen_embs[0] * bin_mask
dst = all_sen_embs[1] * bin_mask
scores = tf.matmul(src, dst, transpose_b=True)
else:
scores = tf.matmul(all_sen_embs[0], all_sen_embs[1], transpose_b=True)###study pre current post # Ignore source sentence
scores = tf.matrix_set_diag(scores, np.zeros(FLAGS.batch_size))
# Targets
targets_np = np.zeros((FLAGS.batch_size, FLAGS.batch_size))
ctxt_sent_pos = list(range(-FLAGS.context_size, FLAGS.context_size + 1))
ctxt_sent_pos.remove(0)
for ctxt_pos in ctxt_sent_pos:
targets_np += np.eye(FLAGS.batch_size, k=ctxt_pos)
targets_np_sum = np.sum(targets_np, axis=1, keepdims=True)
targets_np = targets_np/targets_np_sum
targets = tf.constant(targets_np, dtype=tf.float32) # Forward and backward scores
f_scores = scores[:-1]
b_scores = scores[1:] losses = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=targets, logits=scores) loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) tf.summary.scalar("losses/ent_loss", loss)
self.total_loss = loss if self.mode == "eval":
f_max = tf.to_int64(tf.argmax(f_scores, axis=1))
b_max = tf.to_int64(tf.argmax(b_scores, axis=1)) targets = range(FLAGS.batch_size - 1)
targets = tf.constant(list(targets), dtype=tf.int64)
fwd_targets = targets + 1 names_to_values, names_to_updates = tf.contrib.slim.metrics.aggregate_metric_map({
"Acc/Fwd Acc": tf.contrib.slim.metrics.streaming_accuracy(f_max, fwd_targets),
"Acc/Bwd Acc": tf.contrib.slim.metrics.streaming_accuracy(b_max, targets)
}) for name, value in names_to_values.items():
tf.summary.scalar(name, value) self.eval_op = names_to_updates.values()
损失函数图解如下:
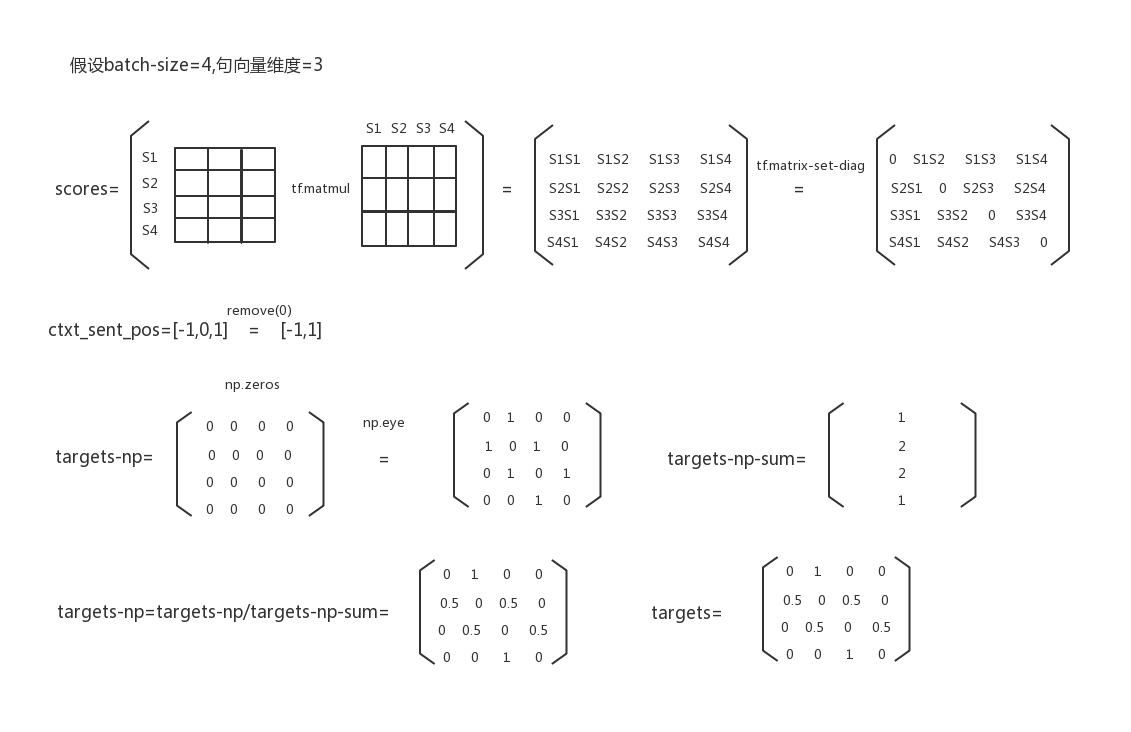
用 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=targets, logits=scores)进行交叉熵,从targets可以看出quick_thought思想是根据上下文来推出目标句的相似性,个人认为并没有学习到目标句的特征,我用quick_thought训练出来的句子向量进行多类别分类,效果不是很好(quick_thought 评估里的例子有电影情感分类)。
具体论文复现的代码https://github.com/lajanugen/S2V(英文)
修改https://github.com/jinjiajia/Quick_Thought(中文)
基于Quick_Thought Vectors的Sentence2Vec神经网络实现的更多相关文章
- 基于MTCNN多任务级联卷积神经网络进行的人脸识别 世纪晟人脸检测
神经网络和深度学习目前为处理图像识别的许多问题提供了最佳解决方案,而基于MTCNN(多任务级联卷积神经网络)的人脸检测算法也解决了传统算法对环境要求高.人脸要求高.检测耗时高的弊端. 基于MTCNN多 ...
- 基于MNIST数据的卷积神经网络CNN
基于tensorflow使用CNN识别MNIST 参数数量:第一个卷积层5x5x1x32=800个参数,第二个卷积层5x5x32x64=51200个参数,第三个全连接层7x7x64x1024=3211 ...
- 深度学习基础-基于Numpy的多层前馈神经网络(FFN)的构建和反向传播训练
本文是深度学习入门: 基于Python的实现.神经网络与深度学习(NNDL)以及花书的读书笔记.本文将以多分类任务为例,介绍多层的前馈神经网络(Feed Forward Networks,FFN)加上 ...
- 优化基于FPGA的深度卷积神经网络的加速器设计
英文论文链接:http://cadlab.cs.ucla.edu/~cong/slides/fpga2015_chen.pdf 翻译:卜居 转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/k ...
- 深度学习(五)基于tensorflow实现简单卷积神经网络Lenet5
原文作者:aircraft 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/DOMLX/p/8954892.html 参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/u01287127 ...
- 基于区域的全卷积神经网络(R-FCN)简介
在 Faster R-CNN 中,检测器使用了多个全连接层进行预测.如果有 2000 个 ROI,那么成本非常高. feature_maps = process(image)ROIs = region ...
- 人脸检测数据源制作与基于caffe构架的ALEXNET神经网络训练
本篇文章主要记录的是人脸检测数据源制作与ALEXNET网络训练实现检测到人脸(基于caffe). 1.数据获取 数据获取: ① benchmark是一个行业的基准(数据库.论文.源码.结果),例如WI ...
- 基于theano的深度卷积神经网络
使用了两个卷积层.一个全连接层和一个softmax分类器. 在测试数据集上正确率可以达到99.22%. 代码参考了neural-networks-and-deep-learning #coding:u ...
- GRNN/PNN:基于GRNN、PNN两神经网络实现并比较鸢尾花种类识别正确率、各个模型运行时间对比—Jason niu
load iris_data.mat P_train = []; T_train = []; P_test = []; T_test = []; for i = 1:3 temp_input = fe ...
随机推荐
- keepalived实现IP地址高可用
yum -y install keepalived vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf global_defs { router_id LVS_DEVEL_ngin ...
- LVM实践
[root@ftp:/root] > fdisk -l Disk /dev/sda: 53.7 GB, 53687091200 bytes, 104857600 sectors Units = ...
- YII实现dropDownList 联动事件
因功能需求,需要用到联动,特此记录分享 一.视图中 <div class="main-form"> <?php $form = ActiveForm::begin ...
- prim求最小生成树
一直以来只会Kruskal prim和dijkstra很像 只不过prim维护的是最短的边,而dijkstra维护的是最短的从起点到一个点的路径 同时prim要注意当前拓展的边是没有拓展过的 可以用堆 ...
- SimpleDateFormat 格式化 解析
package chengbaoDemo; import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text ...
- Windows平台编译openssl-0.9.8k库(32位、64位)
近期工作中使用到了openssl的win64位资料,所以进行前期调研,汇总结果例如以下: [注意]openssl代码所在文件夹中不要带中文,否则"nmake -f ms\ntdll.mak ...
- 【零基础入门学习Python笔记013】元祖:戴上了枷锁的列表
元组:戴上了枷锁的列表 因为和列表是近亲关系.所以元祖和列表在实际使用上是很相似的. 本节主要通过讨论元素和列表究竟有什么不同学习元祖. 元组是不可改变元素的.插入.删除或者排序都不能够.列表能够随意 ...
- node generator 模仿co
exports.run = function(fn ){ return function(onDone){ function thunk(tfn , ctx){ return function(sql ...
- emacs使用本地emacs server模式打开远程文件
使用emacs的用户都知道,一般要打开远程机器上的文件要使用TrampMode模式,调用方式例如以下: C-x C-f /remotehost:filename RET (or /method:use ...
- 【POJ 3273】 Monthly Expense (二分)
[POJ 3273] Monthly Expense (二分) 一个农民有块地 他列了个计划表 每天要花多少钱管理 但他想用m个月来管理 就想把这个计划表切割成m个月来完毕 想知道每一个月最少花费多少 ...
