SpringBoot Controller 中使用多个@RequestBody的正确姿势
最近遇到Controller中需要多个@RequestBody的情况,但是发现并不支持这种写法,
这样导致
1、单个字符串等包装类型都要写一个对象才可以用@RequestBody接收;
2、多个对象需要封装到一个对象里才可以用@RequestBody接收。
查阅StackOverFlow,受到一个解决方案的启发,本人改进为以下版本,并给出了详尽的注释,希望对大家有帮助。
改进后的方案支持:
1、支持通过注解的value指定JSON的key来解析对象。
2、支持通过注解无value,直接根据参数名来解析对象
3、支持GET方式和其他请求方式
4、支持基本类型属性注入
5、支持通过注解无value且参数名不匹配JSON串key时,根据属性解析对象。
6、支持多余属性(不解析、不报错)、支持参数“共用”(不指定value时,参数名不为JSON串的key)
7、支持当value和属性名找不到匹配的key时,对象是否匹配所有属性。
重要更新记录:
2019年02月25日 新增xml方式参考配置
2019年02月07日 fix 当list参数为空时,parameterType.newInstance会导致异常。
2018年12月28日 新增测试用例,完善解析部分代码
2018年10月23日 完善项目格式
2018年08月28日 创建第一版
项目仅供参考,如因使用不当造成任何问题,请自行负责,有问题欢迎探讨改进。
项目地址(建议去拉最新代码):
https://github.com/chujianyun/Spring-MultiRequestBody
另外代码应该会尽量持续更新完善,欢迎大家贡献代码。
步骤如下:
0、除spring的Jar包外涉及的主要Maven依赖
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>commons-lang</groupId>
-
<artifactId>commons-lang</artifactId>
-
<version>2.4</version>
-
</dependency>
-
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
-
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
-
<version>1.2.35</version>
-
</dependency>
-
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
-
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
-
<version>2.6</version>
-
</dependency>
其中fastjson用来解析json对象,commons-lang用来字符串判空(也可以自己手写),commons-io用来读取请求封装为字符串类型(也可以自己封装)。
1、重写方法参数解析器
-
package com.chujianyun.web.bean;
-
-
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
-
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
-
import io.github.chujianyun.annotation.MultiRequestBody;
-
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
-
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
-
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.WebDataBinderFactory;
-
import org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest;
-
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
-
import org.springframework.web.method.support.ModelAndViewContainer;
-
-
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
-
import java.io.IOException;
-
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
-
import java.util.HashSet;
-
import java.util.Set;
-
-
/**
-
* 多RequestBody解析器
-
*
-
* @author 明明如月
-
* @date 2018/08/27
-
*/
-
public class MultiRequestBodyArgumentResolver implements HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
-
-
private static final String JSONBODY_ATTRIBUTE = "JSON_REQUEST_BODY";
-
-
/**
-
* 设置支持的方法参数类型
-
*
-
* @param parameter 方法参数
-
* @return 支持的类型
-
*/
-
@Override
-
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
-
// 支持带@MultiRequestBody注解的参数
-
return parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(MultiRequestBody.class);
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 参数解析,利用fastjson
-
* 注意:非基本类型返回null会报空指针异常,要通过反射或者JSON工具类创建一个空对象
-
*/
-
@Override
-
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
-
-
String jsonBody = getRequestBody(webRequest);
-
-
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(jsonBody);
-
// 根据@MultiRequestBody注解value作为json解析的key
-
MultiRequestBody parameterAnnotation = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(MultiRequestBody.class);
-
//注解的value是JSON的key
-
String key = parameterAnnotation.value();
-
Object value;
-
// 如果@MultiRequestBody注解没有设置value,则取参数名FrameworkServlet作为json解析的key
-
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(key)) {
-
value = jsonObject.get(key);
-
// 如果设置了value但是解析不到,报错
-
if (value == null && parameterAnnotation.required()) {
-
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("required param %s is not present", key));
-
}
-
} else {
-
// 注解为设置value则用参数名当做json的key
-
key = parameter.getParameterName();
-
value = jsonObject.get(key);
-
}
-
-
// 获取的注解后的类型 Long
-
Class<?> parameterType = parameter.getParameterType();
-
// 通过注解的value或者参数名解析,能拿到value进行解析
-
if (value != null) {
-
//基本类型
-
if (parameterType.isPrimitive()) {
-
return parsePrimitive(parameterType.getName(), value);
-
}
-
// 基本类型包装类
-
if (isBasicDataTypes(parameterType)) {
-
return parseBasicTypeWrapper(parameterType, value);
-
// 字符串类型
-
} else if (parameterType == String.class) {
-
return value.toString();
-
}
-
// 其他复杂对象
-
return JSON.parseObject(value.toString(), parameterType);
-
}
-
-
// 解析不到则将整个json串解析为当前参数类型
-
if (isBasicDataTypes(parameterType)) {
-
if (parameterAnnotation.required()) {
-
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("required param %s is not present", key));
-
} else {
-
return null;
-
}
-
}
-
-
// 非基本类型,不允许解析所有字段,必备参数则报错,非必备参数则返回null
-
if (!parameterAnnotation.parseAllFields()) {
-
// 如果是必传参数抛异常
-
if (parameterAnnotation.required()) {
-
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("required param %s is not present", key));
-
}
-
// 否则返回null
-
return null;
-
}
-
// 非基本类型,允许解析,将外层属性解析
-
Object result;
-
try {
-
result = JSON.parseObject(jsonObject.toString(), parameterType);
-
} catch (JSONException jsonException) {
-
// TODO:: 异常处理返回null是否合理?
-
result = null;
-
}
-
-
// 如果非必要参数直接返回,否则如果没有一个属性有值则报错
-
if (!parameterAnnotation.required()) {
-
return result;
-
} else {
-
boolean haveValue = false;
-
Field[] declaredFields = parameterType.getDeclaredFields();
-
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
-
field.setAccessible(true);
-
if (field.get(result) != null) {
-
haveValue = true;
-
break;
-
}
-
}
-
if (!haveValue) {
-
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("required param %s is not present", key));
-
}
-
return result;
-
}
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 基本类型解析
-
*/
-
private Object parsePrimitive(String parameterTypeName, Object value) {
-
final String booleanTypeName = "boolean";
-
if (booleanTypeName.equals(parameterTypeName)) {
-
return Boolean.valueOf(value.toString());
-
}
-
final String intTypeName = "int";
-
if (intTypeName.equals(parameterTypeName)) {
-
return Integer.valueOf(value.toString());
-
}
-
final String charTypeName = "char";
-
if (charTypeName.equals(parameterTypeName)) {
-
return value.toString().charAt(0);
-
}
-
final String shortTypeName = "short";
-
if (shortTypeName.equals(parameterTypeName)) {
-
return Short.valueOf(value.toString());
-
}
-
final String longTypeName = "long";
-
if (longTypeName.equals(parameterTypeName)) {
-
return Long.valueOf(value.toString());
-
}
-
final String floatTypeName = "float";
-
if (floatTypeName.equals(parameterTypeName)) {
-
return Float.valueOf(value.toString());
-
}
-
final String doubleTypeName = "double";
-
if (doubleTypeName.equals(parameterTypeName)) {
-
return Double.valueOf(value.toString());
-
}
-
final String byteTypeName = "byte";
-
if (byteTypeName.equals(parameterTypeName)) {
-
return Byte.valueOf(value.toString());
-
}
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 基本类型包装类解析
-
*/
-
private Object parseBasicTypeWrapper(Class<?> parameterType, Object value) {
-
if (Number.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterType)) {
-
Number number = (Number) value;
-
if (parameterType == Integer.class) {
-
return number.intValue();
-
} else if (parameterType == Short.class) {
-
return number.shortValue();
-
} else if (parameterType == Long.class) {
-
return number.longValue();
-
} else if (parameterType == Float.class) {
-
return number.floatValue();
-
} else if (parameterType == Double.class) {
-
return number.doubleValue();
-
} else if (parameterType == Byte.class) {
-
return number.byteValue();
-
}
-
} else if (parameterType == Boolean.class) {
-
return value.toString();
-
} else if (parameterType == Character.class) {
-
return value.toString().charAt(0);
-
}
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 判断是否为基本数据类型包装类
-
*/
-
private boolean isBasicDataTypes(Class clazz) {
-
Set<Class> classSet = new HashSet<>();
-
classSet.add(Integer.class);
-
classSet.add(Long.class);
-
classSet.add(Short.class);
-
classSet.add(Float.class);
-
classSet.add(Double.class);
-
classSet.add(Boolean.class);
-
classSet.add(Byte.class);
-
classSet.add(Character.class);
-
return classSet.contains(clazz);
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 获取请求体JSON字符串
-
*/
-
private String getRequestBody(NativeWebRequest webRequest) {
-
HttpServletRequest servletRequest = webRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
-
-
// 有就直接获取
-
String jsonBody = (String) webRequest.getAttribute(JSONBODY_ATTRIBUTE, NativeWebRequest.SCOPE_REQUEST);
-
// 没有就从请求中读取
-
if (jsonBody == null) {
-
try {
-
jsonBody = IOUtils.toString(servletRequest.getReader());
-
webRequest.setAttribute(JSONBODY_ATTRIBUTE, jsonBody, NativeWebRequest.SCOPE_REQUEST);
-
} catch (IOException e) {
-
throw new RuntimeException(e);
-
}
-
}
-
return jsonBody;
-
}
-
}
2、编写解析的方法注解:
-
package com.chujianyun.web.annotation;
-
-
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
-
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
-
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
-
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
-
-
/**
-
* Controller中方法接收多个JSON对象
-
*
-
* @author 明明如月
-
* @date 2018/08/27
-
*/
-
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
-
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
-
public @interface MultiRequestBody {
-
/**
-
* 是否必须出现的参数
-
*/
-
boolean required() default true;
-
-
/**
-
* 当value的值或者参数名不匹配时,是否允许解析最外层属性到该对象
-
*/
-
boolean parseAllFields() default true;
-
-
/**
-
* 解析时用到的JSON的key
-
*/
-
String value() default "";
-
}
3、在配置Bean中注入
特别注意: 如果加入本配置导致页面访问404 可以去掉 @EnableWebMvc注解
-
package com.chujianyun.web.config;
-
-
import com.chujianyun.web.bean.MultiRequestBodyArgumentResolver;
-
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
-
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
-
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
-
import org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter;
-
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
-
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
-
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
-
-
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
-
import java.util.List;
-
-
/**
-
* 添加多RequestBody解析器
-
* @author 明明如月
-
* @date 2018/08/27
-
*/
-
@Configuration
-
@EnableWebMvc
-
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
-
@Override
-
public void addArgumentResolvers(List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> argumentResolvers) {
-
argumentResolvers.add(new MultiRequestBodyArgumentResolver());
-
}
-
-
@Bean
-
public HttpMessageConverter<String> responseBodyConverter() {
-
return new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
-
super.configureMessageConverters(converters);
-
converters.add(responseBodyConverter());
-
}
-
}
xml配置方式(感谢网友 "熔 岩"提供了的xml参考配置方式)
-
<mvc:annotation-driven>
-
<mvc:message-converters>
-
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
-
<constructor-arg value="UTF-8"/>
-
</bean>
-
<bean class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter">
-
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
-
<list>
-
<value>application/json</value>
-
<value>text/html</value>
-
<value>text/plain</value>
-
</list>
-
</property>
-
<property name="fastJsonConfig" ref="fastJsonConfig"/>
-
</bean>
-
</mvc:message-converters>
-
-
<mvc:argument-resolvers>
-
<bean class="io.github.chujianyun.bean.MultiRequestBodyArgumentResolver"/>
-
</mvc:argument-resolvers>
-
</mvc:annotation-driven>
使用方法:
-
package com.chujianyun.web.controller;
-
-
import com.chujianyun.web.annotation.MultiRequestBody;
-
import com.chujianyun.web.domain.Dog;
-
import com.chujianyun.web.domain.User;
-
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
-
-
/**
-
* 演示控制器
-
* @author 明明如月
-
* @date 2018/08/27
-
*/
-
@Controller
-
@RequestMapping("/xhr/test")
-
public class DemoController {
-
-
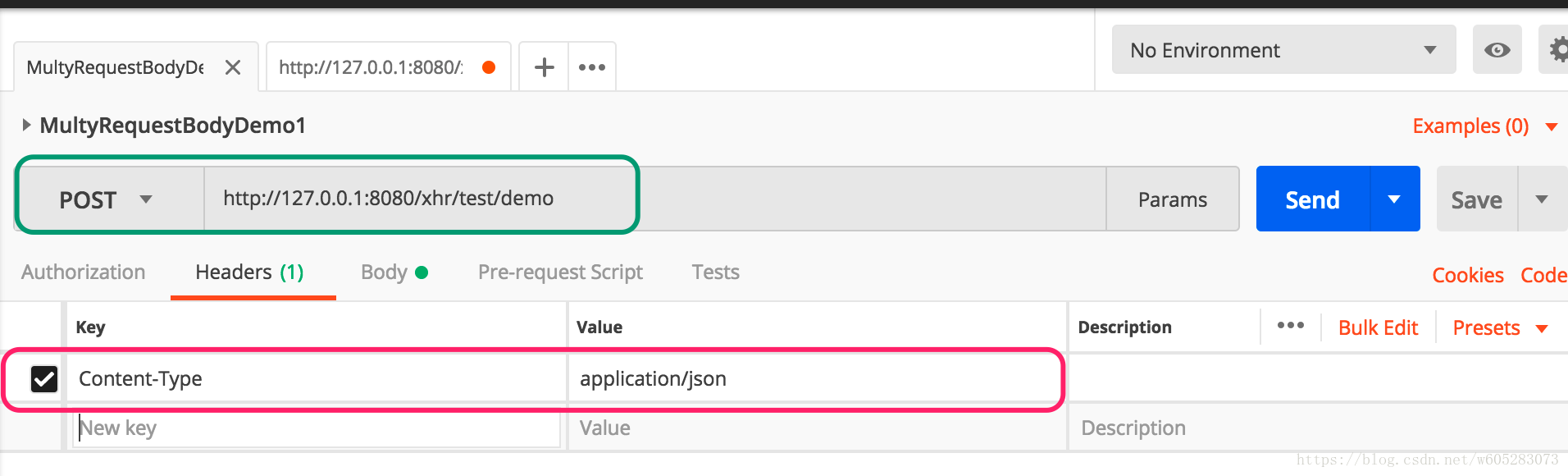
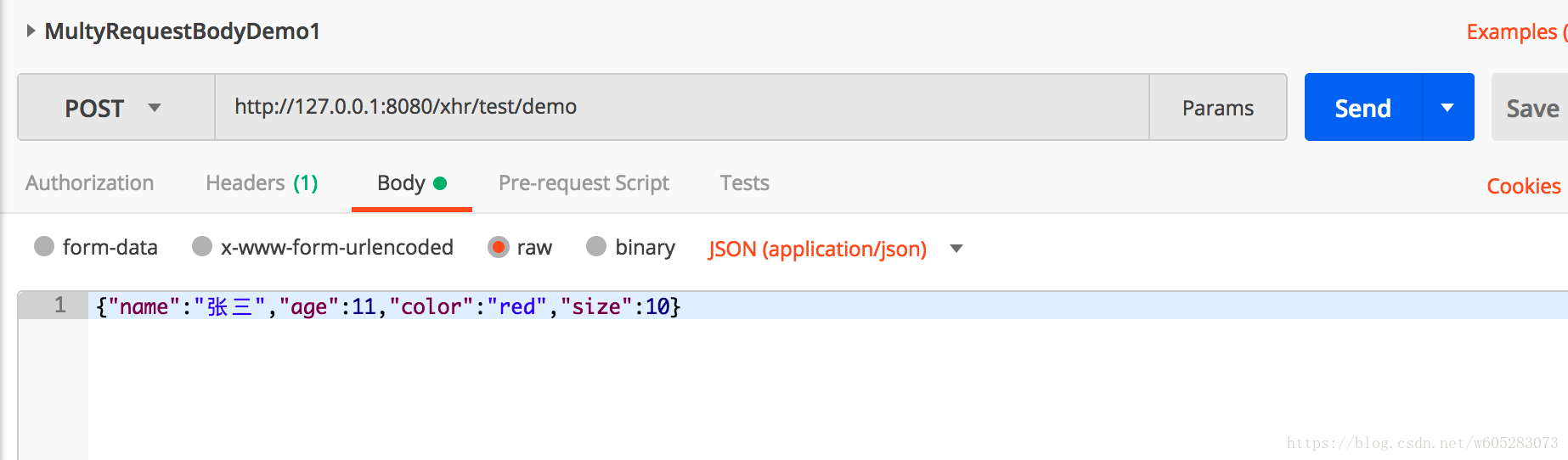
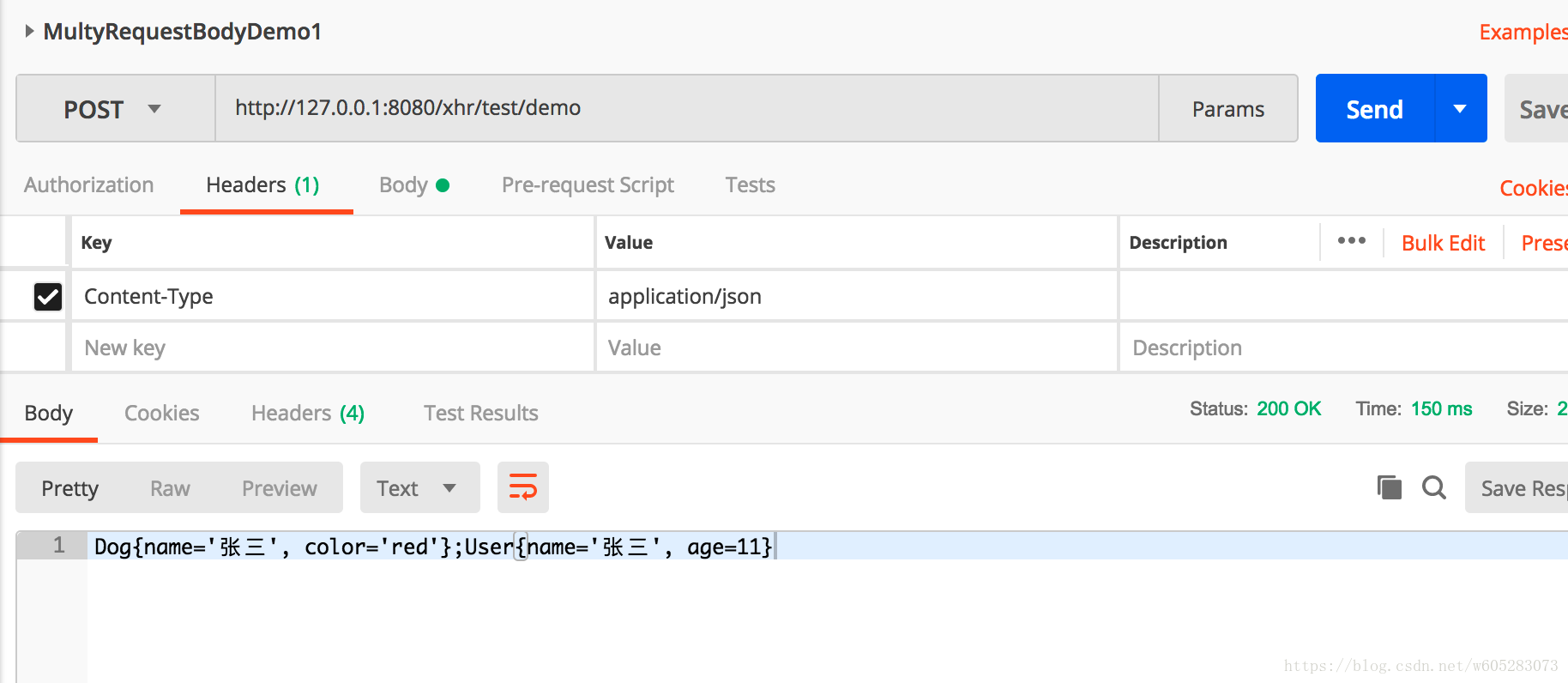
@RequestMapping("/demo")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo1(@MultiRequestBody Dog dog, @MultiRequestBody User user) {
-
System.out.println(dog.toString()+user.toString());
-
return dog.toString()+";"+user.toString();
-
}
-
-
-
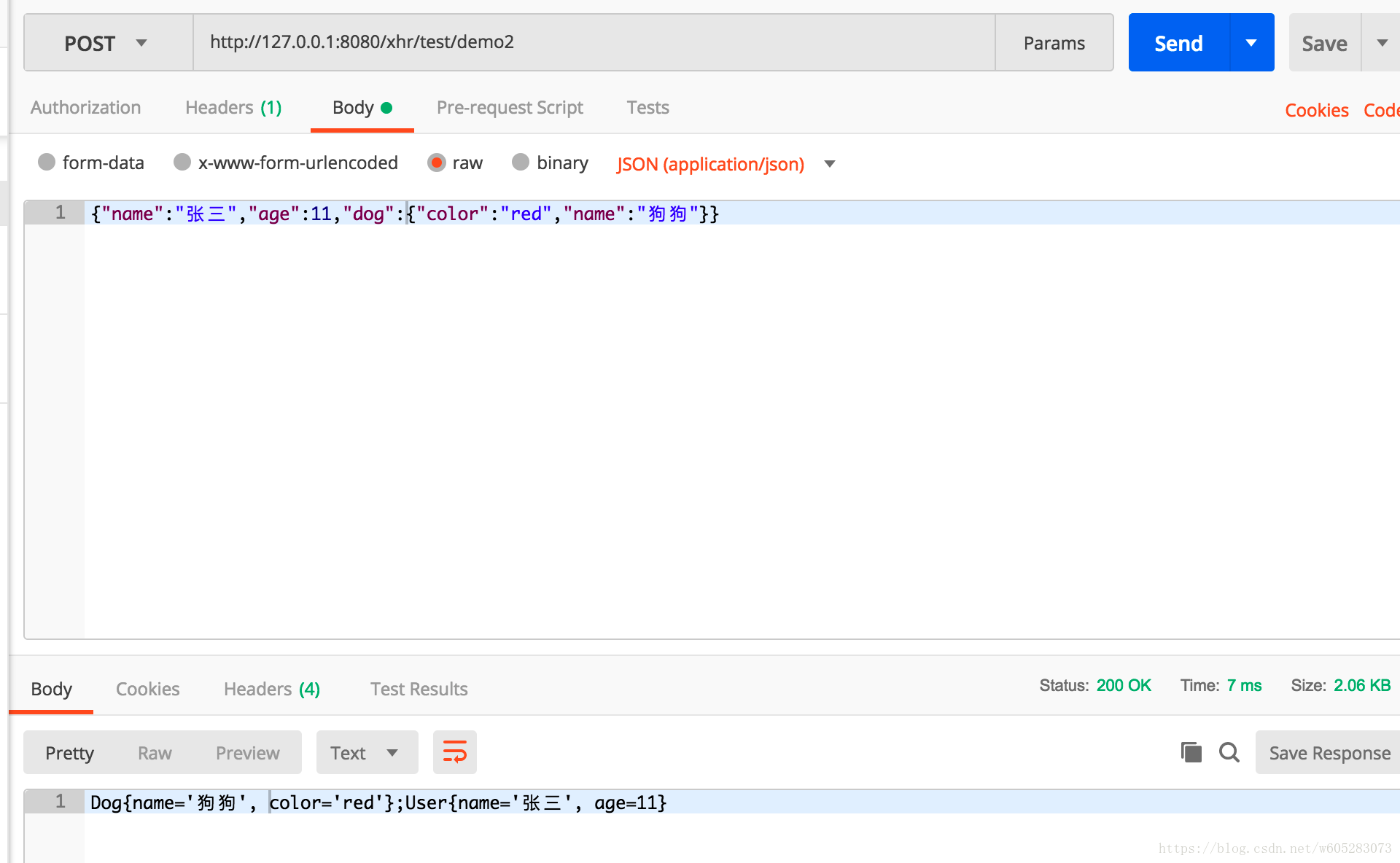
@RequestMapping("/demo2")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo2(@MultiRequestBody("dog") Dog dog, @MultiRequestBody User user) {
-
System.out.println(dog.toString()+user.toString());
-
return dog.toString()+";"+user.toString();
-
}
-
-
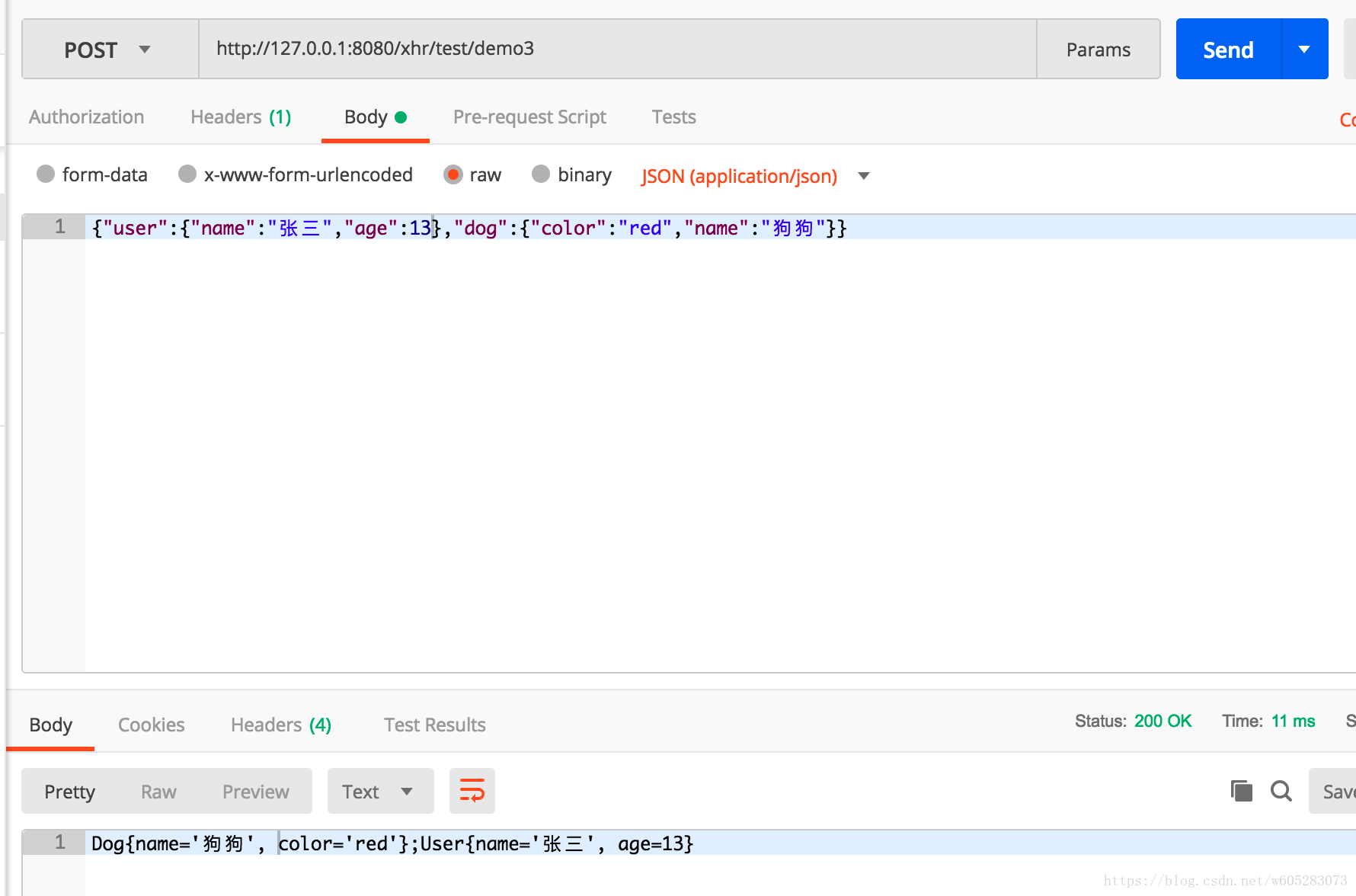
@RequestMapping("/demo3")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo3(@MultiRequestBody("dog") Dog dog, @MultiRequestBody("user") User user) {
-
System.out.println(dog.toString()+user.toString());
-
return dog.toString()+";"+user.toString();
-
}
-
-
-
-
@RequestMapping("/demo4")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo4(@MultiRequestBody("dog") Dog dog, @MultiRequestBody Integer age) {
-
System.out.println(dog.toString() + age.toString());
-
return dog.toString() + ";age属性为:"+age.toString();
-
}
-
-
-
@RequestMapping("/demo5")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo5(@MultiRequestBody("color") String color, @MultiRequestBody("age") Integer age) {
-
return "color="+color + "; age=" + age;
-
}
-
-
@RequestMapping("/demo6")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo6(@MultiRequestBody("dog") Dog dog, @MultiRequestBody Integer age) {
-
System.out.println(dog.toString() + age.toString());
-
return dog.toString() + ";age属性为:"+age.toString();
-
}
-
-
-
@RequestMapping("/demo7")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo7(@MultiRequestBody Dog color2, @MultiRequestBody("age") Integer age) {
-
return "color="+color2 + "; age=" + age;
-
}
-
-
-
@RequestMapping("/demo9")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo9( @MultiRequestBody Dog dog) {
-
return dog.toString();
-
}
-
@RequestMapping("/demo10")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo10( @MultiRequestBody(parseAllFields = false,required = false) Dog dog) {
-
return dog.toString();
-
}
-
-
@RequestMapping("/testList")
-
@ResponseBody
-
public String multiRequestBodyDemo1(@MultiRequestBody List test, @MultiRequestBody String str) {
-
-
return test.toString() + str;
-
}
-
-
}
两个实体:
-
package com.chujianyun.web.domain;
-
-
/**
-
* @author 明明如月
-
* @date 2018/08/27
-
*/
-
public class Dog {
-
-
private String name;
-
-
private String color;
-
-
-
public String getName() {
-
return name;
-
}
-
-
public void setName(String name) {
-
this.name = name;
-
}
-
-
public String getColor() {
-
return color;
-
}
-
-
public void setColor(String color) {
-
this.color = color;
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public String toString() {
-
return "Dog{" +
-
"name='" + name + '\'' +
-
", color='" + color + '\'' +
-
'}';
-
}
-
}
-
package com.chujianyun.web.domain;
-
-
/**
-
* @author 明明如月
-
* @date 2018/08/27
-
*/
-
public class User {
-
-
private String name;
-
-
private Integer age;
-
-
public String getName() {
-
return name;
-
}
-
-
public void setName(String name) {
-
this.name = name;
-
}
-
-
public Integer getAge() {
-
return age;
-
}
-
-
public void setAge(Integer age) {
-
this.age = age;
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public String toString() {
-
return "User{" +
-
"name='" + name + '\'' +
-
", age=" + age +
-
'}';
-
}
-
}
效果:
demo
demo2
demo3
如果觉得本文对你有帮助,欢迎点赞评论,欢迎关注我,我将努力创作更多更好的文章。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/w605283073/article/details/82119284 </div>SpringBoot Controller 中使用多个@RequestBody的正确姿势的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot Controller 中 HttpServletRequest ServletInputStream 读取不到数据该怎么处理
在Springboot程序启动后,会默认添加OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter和HiddenHttpMethodFilter过滤器.在HiddenHttpMethodFilt ...
- springboot使用百度富文本UEditor遇到的问题一览(springboot controller中request.getInputStream无法读取)
先吐槽一下UEditor作为一个前端的js类库,非要把4种后端的代码给出来,而实际生产中用的框架不同,其代码并不具有适应性.(通常类似其它项目仅仅是给出数据交互的规范.格式,后端实现就可以自由定制) ...
- 在日志中记录Java异常信息的正确姿势
遇到的问题 今天遇到一个线上的BUG,在执行表单提交时失败,但是从程序日志中看不到任何异常信息. 在Review源代码时发现,当catch到异常时只是输出了e.getMessage(),如下所示: l ...
- angular4.0中form表单双向数据绑定正确姿势
issue:用[(ngModel)]="property"指令双向数据绑定,报错. reason1:使用ngModel绑定数据需要注入FormsModule模块,在app.modu ...
- SpringBoot 中 @RequestBody的正确使用方法
SpringBoot 中 @RequestBody的正确使用方法 最近在接收一个要离职同事的工作,接手的项目是用SpringBoot搭建的,其中看到了这样的写法: @RequestMapping(&q ...
- SpringBoot12 QueryDSL01之QueryDSL介绍、springBoot项目中集成QueryDSL
1 QueryDSL介绍 1.1 背景 QueryDSL的诞生解决了HQL查询类型安全方面的缺陷:HQL查询的扩展需要用字符串拼接的方式进行,这往往会导致代码的阅读困难:通过字符串对域类型和属性的不安 ...
- springboot项目中使用maven resources
maven resource 组件可以把pom的变量替换到相关的resouces目录中的资源文件变量 示例项目:内容中心 (文章管理) 生成jar包,生成docker ,生成k8s文件 1.项目结构 ...
- SpringBoot Controller接收参数的几种方式盘点
本文不再更新,可能存在内容过时的情况,实时更新请移步我的新博客:SpringBoot Controller接收参数的几种方式盘点: SpringBoot Controller接收参数的几种常用方式盘点 ...
- SpringBoot:SpringBoot项目中 HttpServletRequest ServletInputStream 读取不到文件数据流
在Springboot程序启动后,会默认添加OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter和HiddenHttpMethodFilter过滤器.在HiddenHttpMethodFilt ...
随机推荐
- Eureka 系列(06)消息广播(下):TaskDispacher 之 Acceptor - Worker 模式
Eureka 系列(06)消息广播(下):TaskDispacher 之 Acceptor - Worker 模式 [TOC] Spring Cloud 系列目录 - Eureka 篇 Eureka ...
- Linux文件数据类型
文件的元数据信息及其含义 查看方式 stat file 例如: 修改文件的时间戳 touch 命令格式: touch [ OPTION ] ... FILE ... 例如: touch aaa.tx ...
- CentOS 7 安装 nginx1.15
1,安装依赖 yum -y install gcc zlib zlib-devel pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel SSL功能需要openssl库 gzip模块需要z ...
- linux终端命令行缩短显示路径
1,修改.bashrc文件(用户根目录下) vim 打开.bashrc文件,找到如下这行: else PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ ...
- Javafx弹窗
在javafx中可能用到一些弹窗,比如点击某个按钮后弹出弹窗提示信息等等 Alert alert = new Alert(AlertType.INFORMATION); alert.setTitle( ...
- css3两个汤圆亲吻动效
效果图: 模板来源:https://www.17sucai.com/pins/demo-show?id=35132 自己仿写出来的效果图: 笔记: 1.transform:translate(-50% ...
- HTML事件处理程序---内联onclick事件
HTML事件处理程序绑定方法: <input type="button" value="click me" onclick="show(this ...
- Java中如何实现序列化,有什么意义?
序列化就是一种用来处理对象流的机制,所谓对象流也就是将对象的内容进行流化.可以对流化后的对象进行读写操作,也可将流化后的对象传输于网络之间.序列化是为了解决对象流读写操作时可能引发的问题(如果不进行序 ...
- vue-bus全局事件中心简单Demo
1.vue-cli搭建好项目之后,使用npm安装vue-bus npm install vue-bus 2.在入口文件main.js中全局注册 import Vue from 'vue'; impor ...
- 泛型(Java 5 开始)
前言 Java 5 开始之前,从集合读取的数据都必须进行类型转换,如果插入错误的数据就会报错. 有了泛型,编译器会自动为你的插入进行转换,并在插入时告知是否插入了类型错误的对象. 将类型由原来的具体的 ...