python 平衡二叉树实现
平衡二叉树:
在上一节二叉树的基础上我们实现,如何将生成平衡的二叉树
所谓平衡二叉树:
我自己定义就是:任何一个节点的左高度和右高度的差的绝对值都小于2
如图所示,此时a的左高度等于3,有高度等于1,差值为2,属于不平衡中的左偏
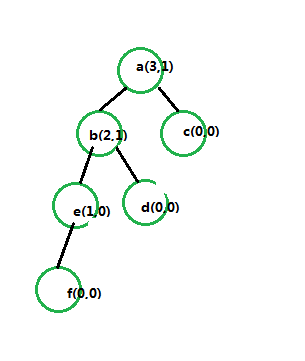
此时的处理办法就是:
将不平衡的元素的左枝的最右节点变为当前节点,
此时分两种情况:
一、左枝有最右节点
将最右节点的左枝赋予其父节点的右枝
二、左枝没有最右节点,
直接将左枝节点做父级节点,父级节点做其右枝
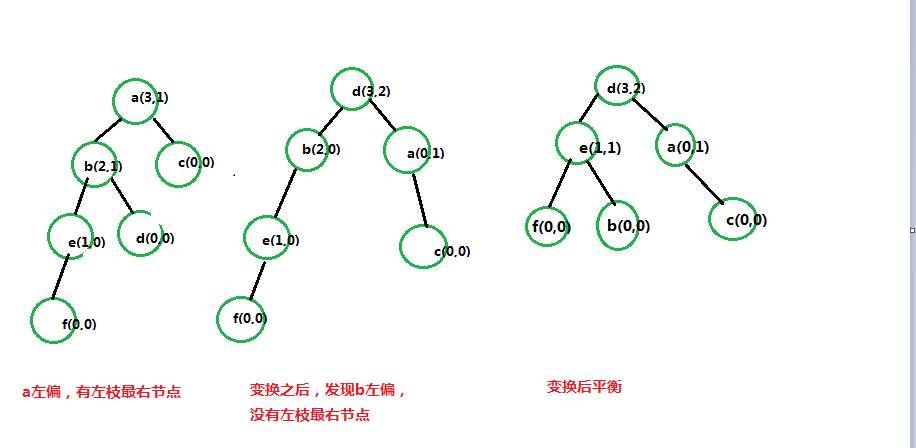
如图所示,图更清楚些。
可能会有疑问,为什么这样变换?
假定a左偏,就需要一个比a小的最少一个值d(因为d唯一 一个是比a小,而且比a的左枝所有数都大的值)做父集结点,a做d的右枝,这样在最上面的d节点就平衡了。
我们可以反证一下:
如果不是d是另一个数假设为h,此时h做父节点,a做父节点的右节点
因为a在h右边,所以 a > h
因为b,e,d,f都是h的左枝,所以 h>d>b>e>f
所以 a>h>d>b>e>f
所以在不加入新节点的情况下,就只能是d
左偏和右偏是一样的,可以完全镜像过来就ok了
处理了所有节点 的左偏和右偏使整个二叉树平衡,这就是平衡二叉树的基本思想
代码实现:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# 日期:2018/6/12 8:37
# Author:小鼠标 # 节点对象
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.left_children = None
self.left_height = 0
self.right_children = None
self.right_height = 0
self.value = None # 二叉树对象
class tree:
def __init__(self):
self.root = False
self.front_list = []
self.middle_list = []
self.after_list = []
# 生成二叉树
def create_tree(self,n=0,l=[]):
if l == []:
print("传入的列表为空")
return
if n > len(l)-1:
print("二叉树生成")
return
node = Node()
node.value = l[n]
if not self.root:
self.root = node
self.list = l
else:
self.add(self.root,node)
self.create_tree(n+1,l)
# 添加节点
def add(self,parent,new_node):
if new_node.value > parent.value:
# 插入值比父亲值大,所以在父节点右边
if parent.right_children == None:
parent.right_children = new_node
# 新插入节点的父亲节点的高度值为1,也就是子高度值0+1
parent.right_height = 1
# 插入值后 从下到上更新节点的height
else:
self.add(parent.right_children,new_node)
# 父亲节点的右高度等于右孩子,左右高度中较大的值 + 1
parent.right_height = max(parent.right_children.right_height, parent.right_children.left_height) + 1
# ======= 此处开始判断平衡二叉树=======
# 右边高度大于左边高度 属于右偏
if parent.right_height - parent.left_height >= 2:
self.right_avertence(parent)
else:
# 插入值比父亲值小,所以在父节点左边
if parent.left_children == None:
parent.left_children = new_node
parent.left_height = 1
else:
self.add(parent.left_children,new_node)
parent.left_height = max(parent.left_children.right_height, parent.left_children.left_height) + 1
# ======= 此处开始判断平衡二叉树=======
# 左边高度大于右边高度 属于左偏
if parent.left_height - parent.right_height >= 2:
self.left_avertence(parent)
# 更新当前节点下的所有节点的高度
def update_height(self,node):
# 初始化节点高度值为0
node.left_height = 0
node.right_height = 0
# 是否到最底层的一个
if node.left_children == None and node.right_children == None:
return
else:
if node.left_children:
self.update_height(node.left_children)
# 当前节点的高度等于左右子节点高度的较大值 + 1
node.left_height = max(node.left_children.left_height,node.left_children.right_height) + 1
if node.right_children:
self.update_height(node.right_children)
# 当前节点的高度等于左右子节点高度的较大值 + 1
node.right_height = max(node.right_children.left_height, node.right_children.right_height) + 1
# 检查是否仍有不平衡
if node.left_height - node.right_height >= 2:
self.left_avertence(node)
elif node.left_height - node.right_height <= -2:
self.right_avertence(node) def right_avertence(self,node):
# 右偏 就将当前节点的最左节点做父亲
new_code = Node()
new_code.value = node.value
new_code.left_children = node.left_children
best_left = self.best_left_right(node.right_children)
v = node.value
# 返回的对象本身,
if best_left == node.right_children and best_left.left_children == None:
# 说明当前节点没有有节点
node.value = best_left.value
node.right_children = best_left.right_children
else:
node.value = best_left.left_children.value
best_left.left_children = best_left.left_children.right_children
node.left_children = new_code
self.update_height(node) # 处理左偏情况
def left_avertence(self,node):
new_code = Node()
new_code.value = node.value
new_code.right_children = node.right_children
best_right = self.best_left_right(node.left_children,1)
v = node.value
# 返回的对象本身,
if best_right == node.left_children and best_right.right_children == None:
# 说明当前节点没有有节点
node.value = best_right.value
node.left_children = best_right.left_children
else:
node.value = best_right.right_children.value
best_right.right_children = best_right.right_children.left_children
node.right_children = new_code
self.update_height(node)
# 返回node节点最左(右)子孙的父级
def best_left_right(self,node,type=0):
# type=0 默认找最左子孙
if type == 0:
if node.left_children == None:
return node
elif node.left_children.left_children == None:
return node
else:
return self.best_left_right(node.left_children,type)
else:
if node.right_children == None:
return node
elif node.right_children.right_children == None:
return node
else:
return self.best_left_right(node.right_children,type)
# 前序(先中再左最后右)
def front(self,node=None):
if node == None:
self.front_list = []
node = self.root
# 输出当前节点
self.front_list.append(node.value)
# 先判断左枝
if not node.left_children == None:
self.front(node.left_children)
# 再判断右枝
if not node.right_children == None:
self.front(node.right_children)
# 返回最终结果
return self.front_list
# 中序(先左再中最后右)
def middle(self,node=None):
if node == None:
node = self.root
# 先判断左枝
if not node.left_children == None:
self.middle(node.left_children)
# 输出当前节点
self.middle_list.append(node.value)
# 再判断右枝
if not node.right_children == None:
self.middle(node.right_children)
return self.middle_list
# 后序(先左再右最后中)
def after(self,node=None):
if node == None:
node = self.root
# 先判断左枝
if not node.left_children == None:
self.after(node.left_children)
# 再判断右枝
if not node.right_children == None:
self.after(node.right_children)
self.after_list.append(node.value)
return self.after_list
# 节点删除
def del_node(self,v,node=None):
if node == None:
node = self.root
# 删除根节点
if node.value == v:
self.del_root(self.root)
return
# 删除当前节点的左节点
if node.left_children:
if node.left_children.value == v:
self.del_left(node)
return
# 删除当前节点的右节点
if node.right_children:
if node.right_children.value == v:
self.del_right(node)
return
if v > node.value:
if node.right_children:
self.del_node(v, node.right_children)
else:
print("删除的元素不存在")
else:
if node.left_children:
self.del_node(v, node.left_children)
else:
print("删除的元素不存在")
#删除当前节点的右节点
def del_right(self,node):
# 情况1 删除节点没有右枝
if node.right_children.right_children == None:
node.right_children = node.right_children.left_children
else:
best_left = self.best_left_right(node.right_children.right_children)
# 表示右枝最左孙就是右枝本身
if best_left == node.right_children.right_children and best_left.left_children == None:
node.right_children.value = best_left.value
node.right_children.right_children = best_left.right_children
else:
node.right_children.value = best_left.left_children.value
best_left.left_children = best_left.left_children.right_children
# 删除当前节点的左节点
def del_left(self,node):
# 情况1 删除节点没有右枝
if node.left_children.right_children == None:
node.left_children = node.left_children.left_children
else:
best_left = self.best_left_right(node.left_children.right_children)
# 表示右枝最左子孙就是右枝本身
if best_left == node.left_children.right_children and best_left.left_children == None:
node.left_children.value = best_left.value
node.left_children.right_children = best_left.right_children
else:
node.left_children.value = best_left.left_children.value
best_left.left_children = best_left.left_children.right_children
# 删除根节点
def del_root(self,node):
if node.right_children == None:
if node.left_children == None:
node.value = None
else:
self.root = node.left_children
else:
best_left = self.best_left_right(node.right_children)
# 表示右枝最左子孙就是右枝本身
if best_left == node.right_children and best_left.left_children == None:
node.value = best_left.value
node.right_children = best_left.right_children
else:
node.value = best_left.left_children.value
best_left.left_children = best_left.left_children.right_children # 搜索
def search(self,v,node=None):
if node == None:
node = self.root
if node.value == v:
return True
if v > node.value:
if not node.right_children == None:
return self.search(v, node.right_children)
else:
if not node.left_children == None:
return self.search(v, node.left_children)
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 需要建立二叉树的列表
list = [4, 6, 3, 1, 7, 9, 8, 5, 2]
t = tree()
t.create_tree(0,list)
res = t.front()
print('前序', res)
执行结果:
前序 [4, 2, 1, 3, 7, 6, 5, 9, 8]
通过前序可以画出二叉树
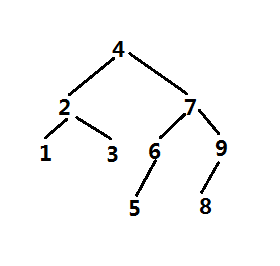
完美,哈哈。
这是我钻了两天才写出的代码,哈哈,努力还是有回报的,加油。
下一步就是代码优化了
python 平衡二叉树实现的更多相关文章
- 详细理解平衡二叉树AVL与Python实现
前言 上一篇文章讨论的二叉搜索树,其时间复杂度最好的情况下是O(log(n)),但是最坏的情况是O(n),什么时候是O(n)呢? 像这样: 如果先插入10,再插入20,再插入30,再插入40就会成上边 ...
- 平衡二叉树检查 牛客网 程序员面试金典 C++ Python
平衡二叉树检查 牛客网 程序员面试金典 C++ Python 题目描述 实现一个函数,检查二叉树是否平衡,平衡的定义如下,对于树中的任意一个结点,其两颗子树的高度差不超过1. 给定指向树根结点的指针T ...
- 【剑指Offer】平衡二叉树 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 解题方法 日期 题目地址:https://www.nowcoder.co ...
- 剑指offer——python【第39题】平衡二叉树
题目描述 输入一棵二叉树,判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树. 解题思路 平衡二叉树首先是二叉搜索树,且它每个节点的左子树和右子树高度差至多等于1:只要从根节点,依次递归判断每个节点是否满足如上条件即可 ...
- python判断平衡二叉树
题目:输入一棵二叉树,判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树.若左右子树深度差不超过1则为一颗平衡二叉树. 思路: 使用获取二叉树深度的方法来获取左右子树的深度 左右深度相减,若大于1返回False 通过递归对 ...
- Python 树表查找_千树万树梨花开,忽如一夜春风来(二叉排序树、平衡二叉树)
什么是树表查询? 借助具有特殊性质的树数据结构进行关键字查找. 本文所涉及到的特殊结构性质的树包括: 二叉排序树. 平衡二叉树. 使用上述树结构存储数据时,因其本身对结点之间的关系以及顺序有特殊要求, ...
- Python实现自平衡二叉树AVL
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from enum import Enum #参考http://blog.csdn.net/niteip/article/details/1184069 ...
- 常用查找数据结构及算法(Python实现)
目录 一.基本概念 二.无序表查找 三.有序表查找 3.1 二分查找(Binary Search) 3.2 插值查找 3.3 斐波那契查找 四.线性索引查找 4.1 稠密索引 4.2 分块索引 4.3 ...
- 基于python的七种经典排序算法
参考书目:<大话数据结构> 一.排序的基本概念和分类 所谓排序,就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或某些关键字的大小,递增或递减的排列起来的操作.排序算法,就是如何使得记录按照要求排列的方法. ...
随机推荐
- ewfwefwefe
qwdefwef fwefwef
- Flask开发遇到的问题:BuildError: Could not build url for endpoint 'main.followers' with values ['username']. Did you mean 'main.user' instead?
@(Flask Web Development 12th chapter) 描述 Flask开发中遇到BuildError: Could not build url for endpoint 'mai ...
- 关于jstl中碰到的Property 'username' not found on type java.lang.String异常
在jstl的forEach循环的时候总是有异常,刚开始以为是把类的属性名打错了,因为显示的是Property not found,但就算从类文件里面复制属性名过来依然显示的是Property not ...
- django1.4 简单事例 ,根目录下templates
django发展很快,但是有的是用的老版本,比如我现在看到一个项目,它用的是 Django1.4,而且app不是创建在了项目的根目录下,这样,它的Setting中设置就会不一样,若是设置错误,就会找不 ...
- Game Development Patterns and Best Practices (John P. Doran / Matt Casanova 著)
https://github.com/PacktPublishing/Game-Development-Patterns-and-Best-Practices https://github.com/m ...
- C#如何调用以管理员身份运行的cmd命令提示符
windows自从vista.win7.win8/8.1以及win10以来,命令行提示符分为两种模式,一种是普通用户模式,一种的管理员模式,很多情况下,我们的程序需要在命令提示符(管理员身份)的状况下 ...
- Vue.js 父子组件之间通信的方式
Vue 父子组件之间的同学有一下几种方式: 1. props 2. $emit -- 组件封装用的比较多 3. .sync -- 语法糖 4. $attrs 和 $listeners -- 组件封装用 ...
- 利用redis List队列简单实现秒杀 PHP代码实现
一 生产者producer部分 --------------------------------producer 部分注释--------------------------------------- ...
- CentOS下Redis的安装(转)
目录 CentOS下Redis的安装 前言 下载安装包 解压安装包并安装 启动和停止Redis 启动Redis 停止Redis 参考资料 CentOS下Redis的安装 前言 安装Redis需要知道自 ...
- volatile和不加volatile的区别
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25100840-id-3067899.html 对于一个地址,如果加上了volatile参数,这个地址也就不会经过编译器优化,也就是说这个 ...
