实验 3:Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率
一、实验目的
在实验 2 的基础上进一步熟悉 Mininet 自定义拓扑脚本,以及与损耗率相关的设定;初步了解 Mininet 安装时自带的 POX 控制器脚本编写,测试路径损耗率。
二、实验任务
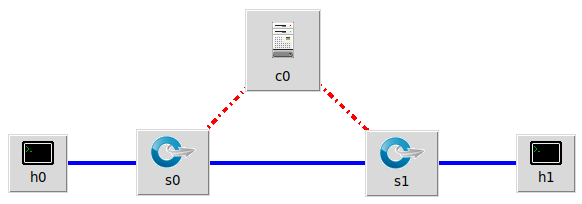
h0 向 h1 发送数据包,由于在 Mininet 脚本中设置了连接损耗率,在传输过程中会丢失一些包,本次实验的目的是展示如何通过控制器计算路径损耗速率(h0-s0-s1-h1)。这里假设控制器预先知道网络拓扑。控制器将向 s0 和 s1 发送flow_stats_request,当控制器接收到来自 s0 的 response 时,将特定流的数据包数保存在 input_pkts 中,当控制器接收到来自 s1 的 response 时,将接收到特定流的数据包数保存在 output_pkts 中,差值就是丢失的数据包数量。
基于上述拓扑,编写 Mininet 脚本,设置特定的交换机间的路径损耗速率,然后编写 POX 控制器脚本,实现对路径的损耗率的测量。
三、实验步骤
- 实验环境
安装了 Ubuntu 18.04.5 Desktop amd64 的虚拟机 - 实验过程
- 新建并编辑 pox 脚本 flow_stats.py:
# standard includes
from pox.core import core
from pox.lib.util import dpidToStr
import pox.openflow.libopenflow_01 as of
from pox.lib.addresses import IPAddr, EthAddr
# include as part of the betta branch
from pox.openflow.of_json import *
from pox.lib.recoco import Timer
import time
log = core.getLogger()
src_dpid = 0
dst_dpid = 0
input_pkts = 0
output_pkts = 0
def getTheTime(): #fuction to create a timestamp
flock = time.localtime()
then = "[%s-%s-%s" %(str(flock.tm_year),str(flock.tm_mon),str(flock.tm_mday))
if int(flock.tm_hour)<10:
hrs = "0%s" % (str(flock.tm_hour))
else:
hrs = str(flock.tm_hour)
if int(flock.tm_min)<10:
mins = "0%s" % (str(flock.tm_min))
else:
mins = str(flock.tm_min)
if int(flock.tm_sec)<10:
secs = "0%s" % (str(flock.tm_sec))
else:
secs = str(flock.tm_sec)
then +="]%s.%s.%s" % (hrs,mins,secs)
return then
# handler for timer function that sends the requests to all the
# switches connected to the controller.
def _timer_func ():
for connection in core.openflow._connections.values():
connection.send(of.ofp_stats_request(body=of.ofp_flow_stats_request()))
connection.send(of.ofp_stats_request(body=of.ofp_port_stats_request()))
log.debug("Sent %i flow/port stats request(s)", len(core.openflow._connections))
# handler to display flow statistics received in JSON format
# structure of event.stats is defined by ofp_flow_stats()
def _handle_flowstats_received (event):
#stats = flow_stats_to_list(event.stats)
#log.debug("FlowStatsReceived from %s: %s", dpidToStr(event.connection.dpid), stats)
global src_dpid, dst_dpid, input_pkts, output_pkts
#print "src_dpid=", dpidToStr(src_dpid), "dst_dpid=", dpidToStr(dst_dpid)
for f in event.stats:
if f.match.dl_type==0x0800 and f.match.nw_dst==IPAddr("192.168.123.2") and f.match.nw_tos==0x64 and event.connection.dpid==src_dpid:
#print "input: ", f.byte_count, f.packet_count
input_pkts = f.packet_count
if f.match.dl_type==0x0800 and f.match.nw_dst==IPAddr("192.168.123.2") and f.match.nw_tos==0x64 and event.connection.dpid==dst_dpid:
#print "output: ", f.byte_count, f.packet_count
output_pkts = f.packet_count
if input_pkts !=0:
print getTheTime(), "Path Loss Rate =", (input_pkts-output_pkts)*1.0/input_pkts*100, "%"
# handler to display port statistics received in JSON format
def _handle_portstats_received (event):
#print "\n<<<STATS-REPLY: Return PORT stats for Switch", event.connection.dpid,"at ",getTheTime()
#for f in event.stats:
#if int(f.port_no)<65534:
#print " PortNo:", f.port_no, " Fwd's Pkts:", f.tx_packets, " Fwd's Bytes:", f.tx_bytes, " Rc'd Pkts:", f.rx_packets, " Rc's Bytes:", f.rx_bytes
#print " PortNo:", f.port_no, " TxDrop:", f.tx_dropped, " RxDrop:", f.rx_dropped, " TxErr:", f.tx_errors, " RxErr:", f.rx_errors, " CRC:", f.rx_crc_err, " Coll:", f.collisions
stats = flow_stats_to_list(event.stats)
log.debug("PortStatsReceived from %s: %s", dpidToStr(event.connection.dpid), stats)
def _handle_ConnectionUp (event):
global src_dpid, dst_dpid
print "ConnectionUp: ", dpidToStr(event.connection.dpid)
for m in event.connection.features.ports:
if m.name == "s0-eth0":
src_dpid = event.connection.dpid
elif m.name == "s1-eth0":
dst_dpid = event.connection.dpid
msg = of.ofp_flow_mod()
msg.priority =1
msg.idle_timeout = 0
msg.match.in_port =1
msg.actions.append(of.ofp_action_output(port = of.OFPP_ALL))
event.connection.send(msg)
msg = of.ofp_flow_mod()
msg.priority =1
msg.idle_timeout = 0
msg.match.in_port =2
msg.actions.append(of.ofp_action_output(port = of.OFPP_ALL))
event.connection.send(msg)
msg = of.ofp_flow_mod()
msg.priority =10
msg.idle_timeout = 0
msg.hard_timeout = 0
msg.match.dl_type = 0x0800
msg.match.nw_tos = 0x64
msg.match.in_port=1
msg.match.nw_dst = "192.168.123.2"
msg.actions.append(of.ofp_action_output(port = 2))
event.connection.send(msg)
msg = of.ofp_flow_mod()
msg.priority =10
msg.idle_timeout = 0
msg.hard_timeout = 0
msg.match.dl_type = 0x0800
msg.match.nw_tos = 0x64
msg.match.nw_dst = "192.168.123.1"
msg.actions.append(of.ofp_action_output(port = 1))
event.connection.send(msg)
# main functiont to launch the module
def launch ():
# attach handsers to listners
core.openflow.addListenerByName("FlowStatsReceived",
_handle_flowstats_received)
core.openflow.addListenerByName("PortStatsReceived",
_handle_portstats_received)
core.openflow.addListenerByName("ConnectionUp", _handle_ConnectionUp)
# timer set to execute every five seconds
Timer(1, _timer_func, recurring=True)
- 在 pox 安装目录下(Mininet 完整安装包含了 pox)执行以下命令运行 pox 脚本
$ ./pox.py flow_stats
- 编辑 Mininet 脚本 mymininet.py
#!/usr/bin/python
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.node import Node
from mininet.link import TCLink
from mininet.log import setLogLevel, info
from threading import Timer
from mininet.util import quietRun
from time import sleep
def myNet(cname='controller', cargs='-v ptcp:'):
"Create network from scratch using Open vSwitch."
info( "*** Creating nodes\n" )
controller = Node( 'c0', inNamespace=False )
switch = Node( 's0', inNamespace=False )
switch1 = Node( 's1', inNamespace=False )
h0 = Node( 'h0' )
h1 = Node( 'h1' )
info( "*** Creating links\n" )
linkopts0=dict(bw=100, delay='1ms', loss=0)
linkopts1=dict(bw=100, delay='1ms', loss=0)
link0=TCLink( h0, switch, **linkopts0)
link1 = TCLink( switch, switch1, **linkopts1)
link2 = TCLink( h1, switch1, **linkopts0)
#print link0.intf1, link0.intf2
link0.intf2.setMAC("0:0:0:0:0:1")
link1.intf1.setMAC("0:0:0:0:0:2")
link1.intf2.setMAC("0:1:0:0:0:1")
link2.intf2.setMAC("0:1:0:0:0:2")
info( "*** Configuring hosts\n" )
h0.setIP( '192.168.123.1/24' )
h1.setIP( '192.168.123.2/24' )
info( "*** Starting network using Open vSwitch\n" )
switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl del-br dp0' )
switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl add-br dp0' )
switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl del-br dp1' )
switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl add-br dp1' )
controller.cmd( cname + ' ' + cargs + '&' )
for intf in switch.intfs.values():
print intf
print switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl add-port dp0 %s' % intf )
for intf in switch1.intfs.values():
print intf
print switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl add-port dp1 %s' % intf )
# Note: controller and switch are in root namespace, and we
# can connect via loopback interface
switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl set-controller dp0 tcp:127.0.0.1:6633' )
switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl set-controller dp1 tcp:127.0.0.1:6633' )
info( '*** Waiting for switch to connect to controller' )
while 'is_connected' not in quietRun( 'ovs-vsctl show' ):
sleep( 1 )
info( '.' )
info( '\n' )
#info( "*** Running test\n" )
h0.cmdPrint( 'ping -Q 0x64 -c 20 ' + h1.IP() )
sleep( 1 )
info( "*** Stopping network\n" )
controller.cmd( 'kill %' + cname )
switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl del-br dp0' )
switch.deleteIntfs()
switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl del-br dp1' )
switch1.deleteIntfs()
info( '\n' )
if __name__ == '__main__':
setLogLevel( 'info' )
info( '*** Scratch network demo (kernel datapath)\n' )
Mininet.init()
myNet()!
- 执行命令运行 Mininet 脚本 mymininet.py
$ sudo python mymininet.py
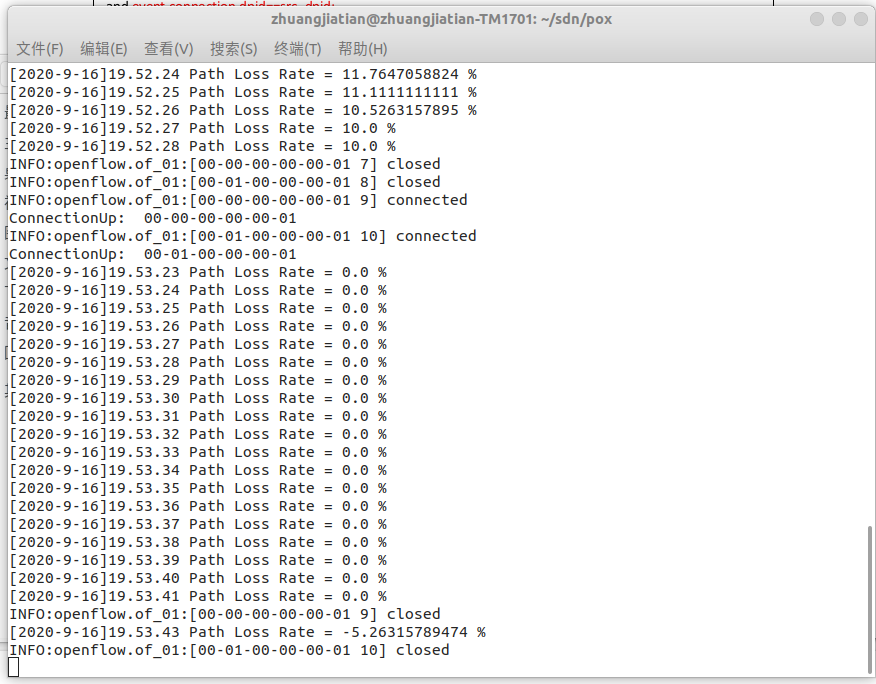
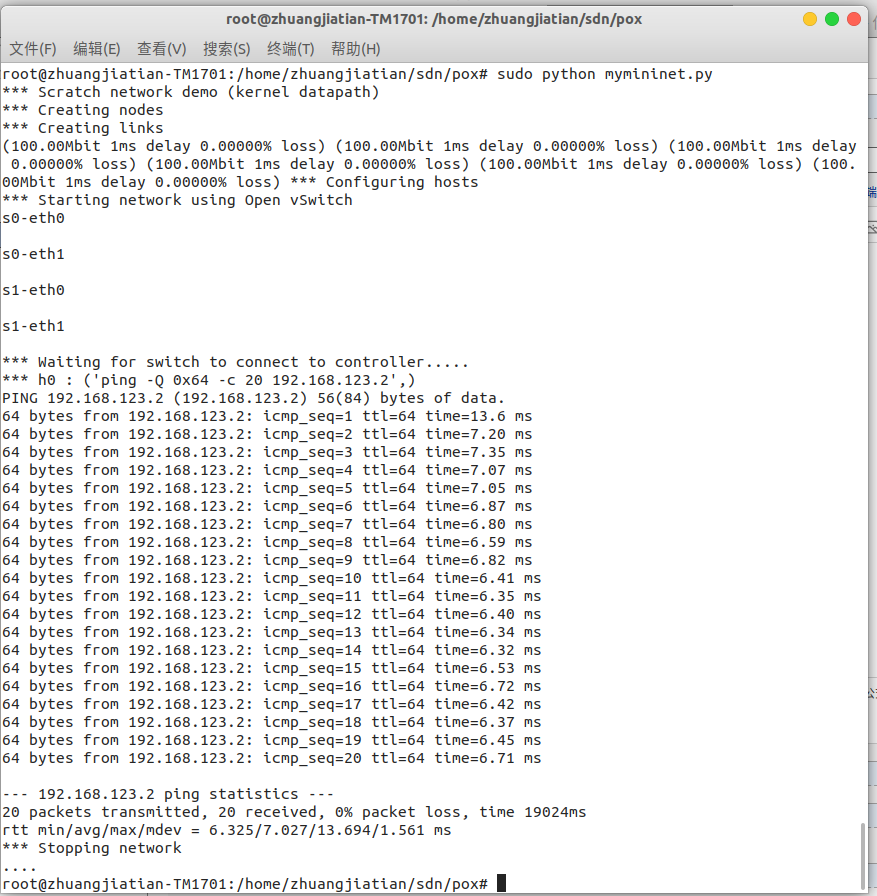
Ping 默认是每 1 秒钟测一次, ping 的结果会显示一个丢包率,这里的丢包率是根据 ping 不通的次数占总次数的百分比计算得到的。上图中由于一共 ping 了 20次,每次都能通,所以丢包率是 0。观察 pox 侧的实时状态更新平均丢包率为 0,结果符合 Mininet 脚本中设置的损耗率,也有可能出现负值,可以认为没有丢包。
如果修改代码中 s0 和 s1 之间链路的丢包率为 10。
info( "*** Creating links\n" )
linkopts0=dict(bw=100, delay='1ms', loss=0)
linkopts1=dict(bw=100, delay='1ms', loss=10)
link0=TCLink( h0, switch, **linkopts0)
link1 = TCLink( switch, switch1, **linkopts1)
link2 = TCLink( h1, switch1, **linkopts0)
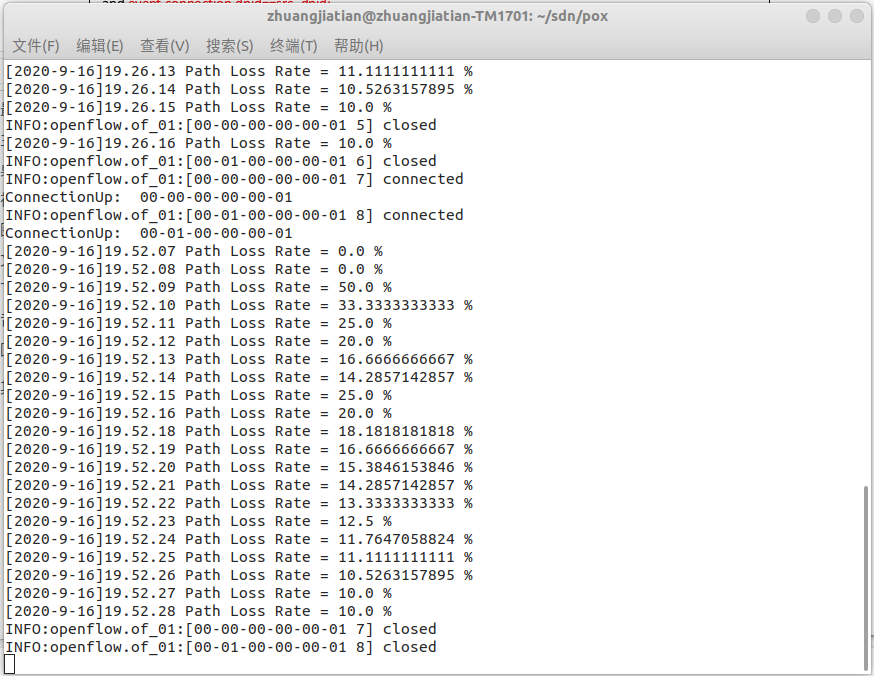
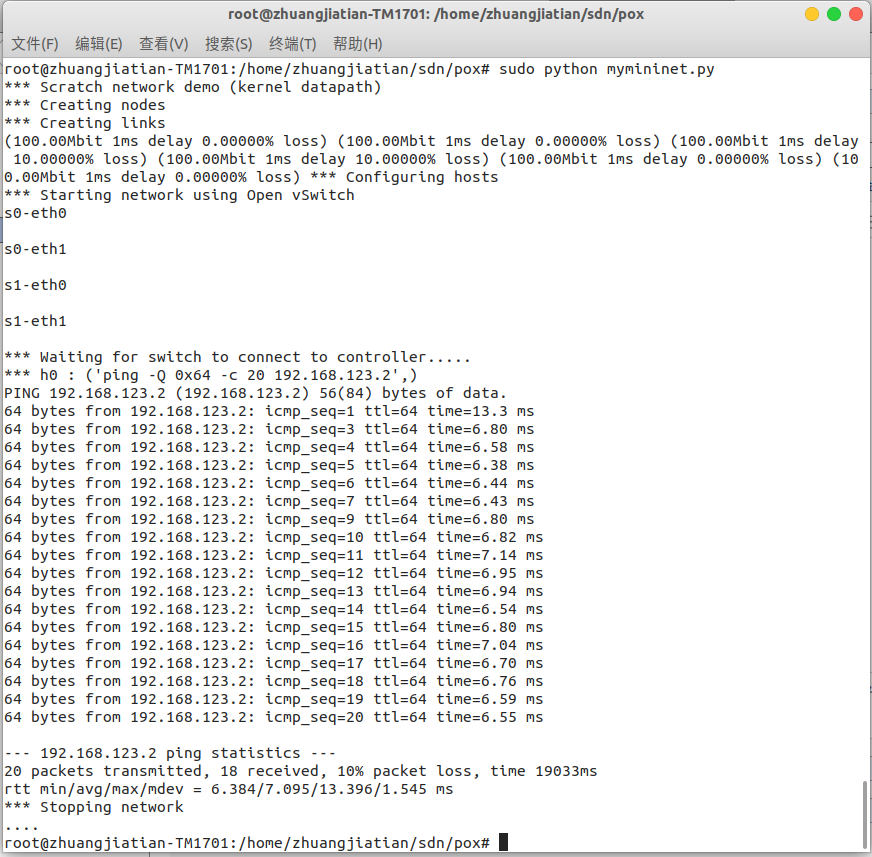
重新运行 Mininet 脚本 mymininet3.py,20 秒时间的 ping 过程中有 icmp_seq 为
2/8 共 2 次 ping 不通,所以丢包率计算为 10%。
四、实验心得
通过本次实验,在实验2的基础上进一步熟悉Mininet自定义拓扑脚本,了解了Mininet安装时自带的POX控制器脚本编写,以及路径损耗率的测试方式。
实验 3:Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率的更多相关文章
- Mininet实验 基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率
实验原理 在SDN环境中,控制器可以通过对交换机下发流表操作来控制交换机的转发行为,此外,还可以利用控制器测量路径的损耗率.在本实验中,基于Mininet脚本,设置特定的交换机间的路径损耗速率,然后编 ...
- Mininet系列实验(四):基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率
1 实验目的 熟悉Mininet自定义拓扑脚本的编写与损耗率的设定: 熟悉编写POX脚本,测量路径损耗速率 2 实验原理 在SDN环境中,控制器可以通过对交换机下发流表操作来控制交换机的转发行为,此外 ...
- 实验 3:Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率
实验目的 在实验 2 的基础上进一步熟悉 Mininet 自定义拓扑脚本,以及与损耗率相关的设 定:初步了解 Mininet 安装时自带的 POX 控制器脚本编写,测试路径损耗率. 实验任务 h0 向 ...
- SDN实验 3: Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率
验 3:Mininet 实验--测量路径的损耗率 一.实验目的 在实验 2 的基础上进一步熟悉 Mininet 自定义拓扑脚本,以及与损耗率相关的设定:初步了解 Mininet 安装时自带的 POX ...
- 基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率
基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率 控制器采用POX,基于OVS仿真 Mininet脚本 创建Node mininet.node Node 创建链路连接 mininet.link TCLink 设置i ...
- 软件定义网络实验记录③--Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率
一.实验目的 在实验 2 的基础上进一步熟悉 Mininet 自定义拓扑脚本,以及与损耗率相关的设定: 初步了解 Mininet 安装时自带的 POX 控制器脚本编写,测试路径损耗率. 二.实验任务 ...
- Mininet实验 基于Mininet实现BGP路径挟持攻击实验
参考:基于Mininet实现BGP路径挟持攻击实验 实验目的: 掌握如何mininet内模拟AS. 掌握BGP路径挟持的原理和分析过程. 实验原理: 互联网是由相互连接的自治系统AS组成的,通过一个通 ...
- 软件定义网络实验记录②--Mininet 实验——拓扑的命令脚本生成
一.实验目的 掌握 Mininet 的自定义拓扑生成方法:命令行创建.Python 脚本编写 二.实验任务 通过使用命令行创建.Python 脚本编写生成拓扑,熟悉 Mininet 的基本功能. 三. ...
- 实验 2:Mininet 实验——拓扑的命令脚本生成
一.实验目的 掌握 Mininet 的自定义拓扑生成方法:命令行创建.Python 脚本编写 二.实验任务 通过使用命令行创建.Python 脚本编写生成拓扑,熟悉 Mininet 的基本功能. 三. ...
随机推荐
- 《MySQL数据库》MySQL备份恢复
前言 MySQL数据库最重要的部分就是数据,所以保证数据不被损坏尤为重要,大家都知道911事件,当时非常多的数据丢失,导致经济混乱.接下来我们就来讲讲MySQL是如何保障数据完整,应对特殊情况,如何恢 ...
- android开发中防止刚进入activity时edittext获取焦点,防止自动自动弹出软键盘
刚进入activity的时候,如果布局组件有edittext的话,往往edittext会获取焦点,自动弹出软键盘,影响整个界面的视觉效果.解决方法如下: 可以在edittext的父布局结构中(例如Li ...
- Unity坐标系详解
1. World Space(世界坐标系): 我们在场景中添加的物体(如:Cube),他们都是以世界坐标显示在场景中.transform.position 获取的便是这个 坐标数值. 2. Scene ...
- 深入了解Netty【一】BIO、NIO、AIO简单介绍
引言 在Java中提供了三种IO模型:BIO.NIO.AIO,模型的选择决定了程序通信的性能. 1.1.使用场景 BIO BIO适用于连接数比较小的应用,这种IO模型对服务器资源要求比较高. NIO ...
- 平衡二叉搜索树/AVL二叉树 C实现
//AVTree.h #ifndef MY_AVLTREE_H #define MY_AVLTREE_H typedef int ElementType; struct TreeNode { Elem ...
- Zabbix value cache working in low memory mode
Zabbix监控自身时告警"Zabbix value cache working in low memory mode",出现这个问题是因为Zabbix Server的参数Valu ...
- H5选择器
1.标签选择器 注意点:1. 标签选择器选中当前所有的标签,而不能单独选择某个标签 2.标签选择器不无多深都能被选中 3.只要是HTML中的标签就可以作为表亲啊选择器(h/a/img/ul/o ...
- Hint usenl usage /*+ leading(emp,dept) usenl(emp) */
SQL> select /*+ leading(emp,dept) usenl(emp) */ emp.*,dept.* from tb_emp03 emp,tb_dept03 dept whe ...
- Java中枚举的用法
public enum Week { DAY1("周一", 0.9), DAY2("周二", 0.9), DAY3("周三", 0.8), ...
- [业界方案]用Jaeger来学习分布式追踪系统Opentracing
[业界方案]用Jaeger来学习分布式追踪系统Opentracing 目录 [业界方案]用Jaeger来学习分布式追踪系统Opentracing 0x00 摘要 0x01 缘由 & 问题 1. ...
