VINS(七)estimator_node 数据对齐 imu预积分 vision
首先通过vins_estimator mode监听几个Topic(频率2000Hz),将imu数据,feature数据,raw_image数据(用于回环检测)通过各自的回调函数封装起来
ros::Subscriber sub_imu = n.subscribe(IMU_TOPIC, , imu_callback, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
ros::Subscriber sub_image = n.subscribe("/feature_tracker/feature", , feature_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_raw_image = n.subscribe(IMAGE_TOPIC, , raw_image_callback);
imu_buf.push(imu_msg);
feature_buf.push(feature_msg);
image_buf.push(make_pair(img_ptr->image, img_msg->header.stamp.toSec()));
然后开启处理measurement的线程
std::thread measurement_process{process};
process()函数中,首先将获取的传感器数据imu_buf feature_buf对齐,注意这里只保证了相邻的feature数据之间有完整的imu数据,并不能保证imu和feature数据的精确对齐
// multiple IMU measurements and only one vision(features) measurements
std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>>
getMeasurements()
{
std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>> measurements; while (true)
{
if (imu_buf.empty() || feature_buf.empty())
return measurements; // synchronize, if strictly synchronize, should change to ">="
// end up with : imu_buf.front()->header.stamp < feature_buf.front()->header.stamp // 1. should have overlap
if (!(imu_buf.back()->header.stamp > feature_buf.front()->header.stamp))
{
ROS_WARN("wait for imu, only should happen at the beginning");
sum_of_wait++;
return measurements;
} // 2. should have complete imu measurements between two feature_buf msg
if (!(imu_buf.front()->header.stamp < feature_buf.front()->header.stamp))
{
ROS_WARN("throw img, only should happen at the beginning");
feature_buf.pop();
continue;
} sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr img_msg = feature_buf.front();
feature_buf.pop(); std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr> IMUs;
while (imu_buf.front()->header.stamp <= img_msg->header.stamp)
{
IMUs.emplace_back(imu_buf.front());
imu_buf.pop();
} measurements.emplace_back(IMUs, img_msg);
}
return measurements;
}
接下来进入对measurements数据的处理:
处理imu数据的接口函数是processIMU()
处理vision数据的借口函数是processImage()
(一)IMU
1. 核心API:
midPointIntegration(_dt, acc_0, gyr_0, _acc_1, _gyr_1, delta_p, delta_q, delta_v,
linearized_ba, linearized_bg,
result_delta_p, result_delta_q, result_delta_v,
result_linearized_ba, result_linearized_bg, );
其中,0代表上次测量值,1代表当前测量值,delta_p,delta_q,delta_v代表相对预积分初始参考系的位移,旋转四元数,以及速度(例如,从k帧预积分到k+1帧,则参考系是k帧的imu坐标系)
对应实现的是公式:
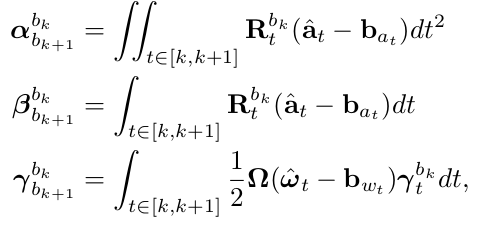
相应的离散实现使用Euler,Mid-point,或者龙格库塔(RK4)数值积分方法。
Euler方法如下:
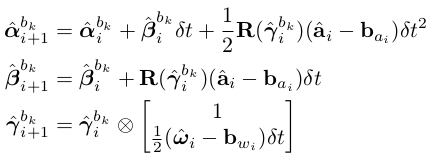
2. 求状态向量对bias的Jacobian,当bias变化较小时,使用Jacobian去更新状态;否则需要以当前imu为参考系,重新预积分,对应repropagation()。同时,需要计算error state model中误差传播方程的系数矩阵F和V:
// pre-integration
// time interval of two imu; last and current imu measurements; p,q,v relate to local frame; ba and bg; propagated p,q,v,ba,bg;
// whether to update Jacobian and calculate F,V
void midPointIntegration(double _dt,
const Eigen::Vector3d &_acc_0, const Eigen::Vector3d &_gyr_0,
const Eigen::Vector3d &_acc_1, const Eigen::Vector3d &_gyr_1,
const Eigen::Vector3d &delta_p, const Eigen::Quaterniond &delta_q, const Eigen::Vector3d &delta_v,
const Eigen::Vector3d &linearized_ba, const Eigen::Vector3d &linearized_bg,
Eigen::Vector3d &result_delta_p, Eigen::Quaterniond &result_delta_q, Eigen::Vector3d &result_delta_v,
Eigen::Vector3d &result_linearized_ba, Eigen::Vector3d &result_linearized_bg, bool update_jacobian)
{
//ROS_INFO("midpoint integration");
// mid-point integration with bias = 0
Vector3d un_acc_0 = delta_q * (_acc_0 - linearized_ba);
Vector3d un_gyr = 0.5 * (_gyr_0 + _gyr_1) - linearized_bg;
result_delta_q = delta_q * Quaterniond(, un_gyr() * _dt / , un_gyr() * _dt / , un_gyr() * _dt / );
Vector3d un_acc_1 = result_delta_q * (_acc_1 - linearized_ba);
Vector3d un_acc = 0.5 * (un_acc_0 + un_acc_1);
result_delta_p = delta_p + delta_v * _dt + 0.5 * un_acc * _dt * _dt;
result_delta_v = delta_v + un_acc * _dt;
// ba and bg donot change
result_linearized_ba = linearized_ba;
result_linearized_bg = linearized_bg; // jacobian to bias, used when the bias changes slightly and no need of repropagation
if(update_jacobian)
{
// same as un_gyr, gyrometer reference to the local frame bk
Vector3d w_x = 0.5 * (_gyr_0 + _gyr_1) - linearized_bg; // last acceleration measurement
Vector3d a_0_x = _acc_0 - linearized_ba;
// current acceleration measurement
Vector3d a_1_x = _acc_1 - linearized_ba; // used for cross-product
// pay attention to derivation of matrix product
Matrix3d R_w_x, R_a_0_x, R_a_1_x; R_w_x<<, -w_x(), w_x(),
w_x(), , -w_x(),
-w_x(), w_x(), ;
R_a_0_x<<, -a_0_x(), a_0_x(),
a_0_x(), , -a_0_x(),
-a_0_x(), a_0_x(), ;
R_a_1_x<<, -a_1_x(), a_1_x(),
a_1_x(), , -a_1_x(),
-a_1_x(), a_1_x(), ; // error state model
// should use discrete format and mid-point approximation
MatrixXd F = MatrixXd::Zero(, );
F.block<, >(, ) = Matrix3d::Identity();
F.block<, >(, ) = -0.25 * delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_0_x * _dt * _dt +
-0.25 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * (Matrix3d::Identity() - R_w_x * _dt) * _dt * _dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = MatrixXd::Identity(,) * _dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = -0.25 * (delta_q.toRotationMatrix() + result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix()) * _dt * _dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = -0.25 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * _dt * _dt * -_dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = Matrix3d::Identity() - R_w_x * _dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = -1.0 * MatrixXd::Identity(,) * _dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = -0.5 * delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_0_x * _dt +
-0.5 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * (Matrix3d::Identity() - R_w_x * _dt) * _dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = Matrix3d::Identity();
F.block<, >(, ) = -0.5 * (delta_q.toRotationMatrix() + result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix()) * _dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = -0.5 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * _dt * -_dt;
F.block<, >(, ) = Matrix3d::Identity();
F.block<, >(, ) = Matrix3d::Identity(); MatrixXd V = MatrixXd::Zero(,);
V.block<, >(, ) = 0.25 * delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * _dt * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = 0.25 * -result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * _dt * _dt * 0.5 * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = 0.25 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * _dt * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = V.block<, >(, );
V.block<, >(, ) = 0.5 * MatrixXd::Identity(,) * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = 0.5 * MatrixXd::Identity(,) * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = 0.5 * delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = 0.5 * -result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * R_a_1_x * _dt * 0.5 * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = 0.5 * result_delta_q.toRotationMatrix() * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = V.block<, >(, );
V.block<, >(, ) = MatrixXd::Identity(,) * _dt;
V.block<, >(, ) = MatrixXd::Identity(,) * _dt; //step_jacobian = F;
//step_V = V;
jacobian = F * jacobian;
covariance = F * covariance * F.transpose() + V * noise * V.transpose();
}
}
(二)Vision
首先判断该帧是否关键帧:
if (f_manager.addFeatureCheckParallax(frame_count, image))
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_OLD;
else
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_SECOND_NEW;
关键帧的判断依据是rotation-compensated过后的parallax足够大,并且tracking上的feature足够多;关键帧会保留在当前Sliding Window中,marginalize掉Sliding Window中最旧的状态,如果是非关键帧则优先marginalize掉。
1. 标定外参旋转矩阵
initial_ex_rotation.CalibrationExRotation(corres, pre_integrations[frame_count]->delta_q, calib_ric)
其中
pre_integrations[frame_count]->delta_q
是使用imu pre-integration获取的旋转矩阵,会和视觉跟踪求解fundamentalMatrix分解后获得的旋转矩阵构建约束方程,从而标定出外参旋转矩阵。
2. 线性初始化
if (solver_flag == INITIAL)
{
if (frame_count == WINDOW_SIZE)
{
bool result = false;
if( ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC != && (header.stamp.toSec() - initial_timestamp) > 0.1)
{
result = initialStructure();
initial_timestamp = header.stamp.toSec();
}
if(result)
{
solver_flag = NON_LINEAR;
solveOdometry();
slideWindow();
f_manager.removeFailures();
ROS_INFO("Initialization finish!");
last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_R0 = Rs[];
last_P0 = Ps[]; }
else
slideWindow();
}
else
frame_count++;
}
3. 非线性优化
else
{
TicToc t_solve;
solveOdometry();
ROS_DEBUG("solver costs: %fms", t_solve.toc()); if (failureDetection())
{
ROS_WARN("failure detection!");
failure_occur = ;
clearState();
setParameter();
ROS_WARN("system reboot!");
return;
} TicToc t_margin;
slideWindow();
f_manager.removeFailures();
ROS_DEBUG("marginalization costs: %fms", t_margin.toc());
// prepare output of VINS
key_poses.clear();
for (int i = ; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
key_poses.push_back(Ps[i]); last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_R0 = Rs[];
last_P0 = Ps[];
}
主要的初始化,非线性优化的api均在这里,因此放在后面去说明。
VINS(七)estimator_node 数据对齐 imu预积分 vision的更多相关文章
- 转载泡泡机器人——IMU预积分总结与公式推导1
IMU预积分技术最早由T Lupton于12年提出[1],C Forster于15年[2][3][4]将其进一步拓展到李代数上,形成了一套优雅的理论体系.Forster将IMU预积分在开源因子图优化库 ...
- 转载泡泡机器人——IMU预积分总结与公式推导2
本文为IMU预积分总结与公式推导系列技术报告的第二篇. 承接第一篇的内容,本篇将推导IMU预积分的测量值,并分析其测量误差的分布形式. 传统捷联惯性导航的递推算法,以初始状态为基础,利用IMU测量得到 ...
- IMU 预积分推导
给 StereoDSO 加 IMU,想直接用 OKVIS 的代码,但是有点看不懂.知乎上郑帆写的文章<四元数矩阵与 so(3) 左右雅可比>提到 OKVIS 的预积分是使用四元数,而预积分 ...
- VINS(三)IMU预积分
IMU的数据频率一般远高于视觉,在视觉两帧k,k+1之间通常会有>10组IMU数据.IMU的数据通过积分,可以获取当前位姿(p位置,q四元数表达的姿态).瞬时速度等参数. 在VIO中,如果参考世 ...
- IMU预积分
https://www.sohu.com/a/242760307_715754 http://www.sohu.com/a/243155537_715754 https://www.sohu.com/ ...
- SLAM+语音机器人DIY系列:(三)感知与大脑——2.带自校准九轴数据融合IMU惯性传感器
摘要 在我的想象中机器人首先应该能自由的走来走去,然后应该能流利的与主人对话.朝着这个理想,我准备设计一个能自由行走,并且可以与人语音对话的机器人.实现的关键是让机器人能通过传感器感知周围环境,并通过 ...
- 结构体的数据对齐 #pragma浅谈
之前若是有人拿个结构体或者联合体问我这个结构占用了多少字节的内存,我一定觉得这个人有点low, 直到某某公司的一个实习招聘模拟题的出现,让我不得不重新审视这个问题, 该问题大致如下: typedef ...
- 数据对齐 posix_memalign 函数详解
对齐 数 据的对齐(alignment)是指数据的地址和由硬件条件决定的内存块大小之间的关系.一个变量的地址是它大小的倍数的时候,这就叫做自然对齐 (naturally aligned).例如,对于一 ...
- 从零开始一起学习SLAM | 用四元数插值来对齐IMU和图像帧
视觉 Vs. IMU 小白:师兄,好久没见到你了啊,我最近在看IMU(Inertial Measurement Unit,惯性导航单元)相关的东西,正好有问题求助啊 师兄:又遇到啥问题啦? 小白:是这 ...
随机推荐
- 配置tomcat远程debug
Linux系统中在编辑catalina.sh文件,修改JAVA_OPTS的变量值为如下即可. JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS $JSSE_OPTS -Xdebug -Xrunjd ...
- hdu1113 Word Amalgamation(详解--map和string的运用)
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章.未经博主同意不得转载. vasttian https://blog.csdn.net/u012860063/article/details/35338617 转载请注明出 ...
- BZOJ2822:[AHOI2012]树屋阶梯(卡特兰数,高精度)
Description 暑假期间,小龙报名了一个模拟野外生存作战训练班来锻炼体魄,训练的第一个晚上,教官就给他们出了个难题.由于地上露营湿气重,必须选择在高处的树屋露营.小龙分配的树屋建立在一颗高度为 ...
- PHP-------ajax返回值 返回JSON 数据
ajax返回值 返回JSON 数据 ajax返回值 有text JSON ajax返回值 返回JSON 数据 <title>无标题文档</title> <sc ...
- Python 输出中文的笔记
import sysreload(sys)sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8') 导入csv乱码: 加入: import codecs csvfile.write(codecs. ...
- node里有没有清理require和dependencies的工具
写node的时候,常常以为自己需要某个package,于是require了一下,结果写着写着,又没有用到,安装了某个包save了一下,最后也没用到. 一个项目写完发现整个require和depende ...
- spring bean中构造函数,afterPropertiesSet和init-method的执行顺序
http://blog.csdn.net/super_ccc/article/details/50728529 1.xml文件 <bean id="aaa" class=&q ...
- linux内核自己添加模块(内核版本:3.0.101)
做内核驱动第一步都是学习如何添加模块,这是基础,有了这个基础,剩下就是写代码了. 由于2.4到2.6内核版本的更新,无论是系统调用还是模块添加机制都有了巨大的变化,本人也因此饱经挫折,最后在3.0.1 ...
- MVC学习八:MVC View提交数据
学习编程最主要的就是数据交互,MVC中数据交互是怎么样的呢? 1.Controller向View传输数据在http://www.cnblogs.com/WarBlog/p/7127574.html中有 ...
- 第20章 USART—串口通讯
本章参考资料:<STM32F76xxx参考手册>USART章节. 学习本章时,配合<STM32F76xxx参考手册>USART章节一起阅读,效果会更佳,特别是涉及到寄存器说明的 ...
