Codeforces 916E(思维+dfs序+线段树+LCA)
题面
传送门
题目大意:给定初始根节点为1的树,有3种操作
1.把根节点更换为r
2.将包含u,v的节点的最小子树(即lca(u,v)的子树)所有节点的值+x
3.查询v及其子树的值之和
分析
看到批量修改子树,我们想到将树上操作转化为区间操作
通过DFS序我们可以实现这一点.
对于每个节点x,我们记录它在前序遍历中的位置l[x],再一次回到x时的序号r[x],则x及其子树的区间为前序遍历中的[l[x],r[x]]
具体可点击这篇博客
那么,3种操作如何进行:
操作1.用一个变量root记录当前根即可,时间复杂度O(1)" role="presentation" style="position: relative;">O(1)O(1)
以下求LCA,DFS序,子树,以及修改等操作都在初始的树上进行,再想办法将它转换为根不是1的情况
操作2.由于根节点变化,需要分类讨论
首先,定义三个点的LCA值lca(u,v,w)为lca(u,v),lca(u,w),lca(v,w)中深度最深的那一个
设修改的点为u,v,根节点为root
(1) 若lca(u,v)在root的子树中
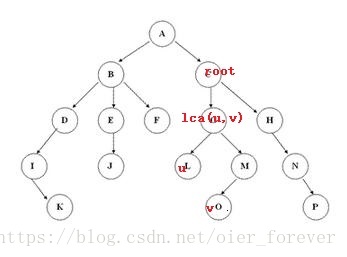
显然结果和根为1的情况一样,直接修改即可,时间复杂度O(log2n)" role="presentation" style="position: relative;">O(log2n)O(log2n)
(2)若lca(u,v,root)=root
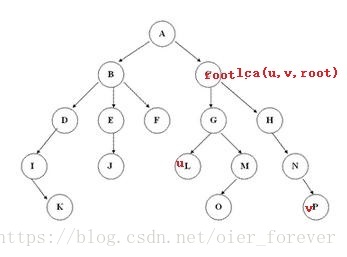
很明显包含u,v的最小子树就是整棵树,所以修改整棵树,时间复杂度O(log2n)" role="presentation" style="position: relative;">O(log2n)O(log2n)
(3)若root在lca(u,v,root)的子树中
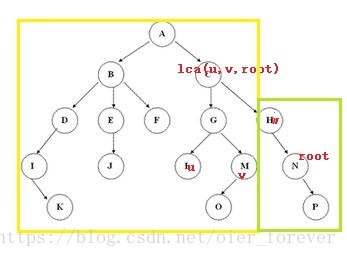
此时可采用类似容斥原理的方法
先将整棵树的值+x
再找到root的祖先中离lca(u,v,root)最近的整数w,将w及其子树(绿色部分)的值-x,剩下的就是包含u,v的最小子树了(黄色部分)
求w可用树上倍增,时间复杂度O(log2n)" role="presentation" style="position: relative;">O(log2n)O(log2n)
操作3.
类似操作2的分类讨论
设查询的点为u,根节点为root
(1)若u在root的子树中,则直接查询u的子树
(2)若u=root,查询整棵树
(3)若root在u的子树中
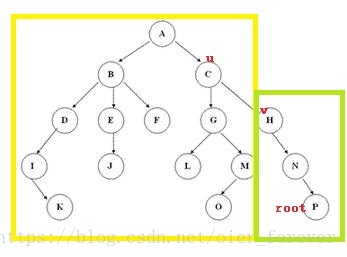
先查询整棵树的值之和,再找root的祖先中距离u最近的一个v
用整棵树的值之和-v及子树的值之和(绿色部分)=所求(黄色部分)
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#define maxn 100005
#define maxlog 32
using namespace std;
inline int qread(){
int x=0,sign=1;
char c=getchar();
while(c<'0'||c>'9'){
if(c=='-') sign=-1;
c=getchar();
}
while(c>='0'&&c<='9'){
x=x*10+c-'0';
c=getchar();
}
return x*sign;
}
int n,q;
int a[maxn];
int root=1;
struct edge{
int from;
int to;
int next;
}E[maxn<<1];
int head[maxn];
int size=0;
void add_edge(int u,int v){
size++;
E[size].from=u;
E[size].to=v;
E[size].next=head[u];
head[u]=size;
}
int cnt;
int log2n;
int l[maxn],r[maxn];
int deep[maxn],anc[maxn][maxlog];
void dfs(int x,int fa){
l[x]=++cnt;
anc[x][0]=fa;
for(int i=1;i<=log2n;i++){
anc[x][i]=anc[anc[x][i-1]][i-1];
}
for(int i=head[x];i;i=E[i].next){
int y=E[i].to;
if(y!=fa){
deep[y]=deep[x]+1;
dfs(y,x);
}
}
r[x]=cnt;
}
int lca(int x,int y){
if(deep[x]<deep[y]) swap(x,y);
for(int i=log2n;i>=0;i--){
if(deep[anc[x][i]]>=deep[y]){
x=anc[x][i];
}
}
if(x==y) return x;
for(int i=log2n;i>=0;i--){
if(anc[x][i]!=anc[y][i]){
x=anc[x][i];
y=anc[y][i];
}
}
return anc[x][0];
}
int tri_lca(int u,int v,int r){
int l1=lca(u,v);
int l2=lca(u,r);
int l3=lca(v,r);
int max_deep=max(deep[l1],max(deep[l2],deep[l3]));
if(deep[l1]==max_deep) return l1;
else if(deep[l2]==max_deep) return l2;
else return l3;
}
int get_close(int w,int r){
int x=r;
for(int i=log2n;i>=0;i--){
if(deep[anc[x][i]]>deep[w]){
x=anc[x][i];
}
}
return x;
}
struct node{
int l;
int r;
long long v;
long long mark;
int len(){
return r-l+1;
}
}tree[maxn<<2];
void push_up(int pos){
tree[pos].v=tree[pos<<1].v+tree[pos<<1|1].v;
}
void build(int l,int r,int pos){
tree[pos].l=l;
tree[pos].r=r;
tree[pos].v=0;
tree[pos].mark=0;
if(l==r) return;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(l,mid,pos<<1);
build(mid+1,r,pos<<1|1);
}
void push_down(int pos){
if(tree[pos].mark){
tree[pos<<1].mark+=tree[pos].mark;
tree[pos<<1|1].mark+=tree[pos].mark;
tree[pos<<1].v+=tree[pos].mark*tree[pos<<1].len();
tree[pos<<1|1].v+=tree[pos].mark*tree[pos<<1|1].len();
tree[pos].mark=0;
}
}
void update(int L,int R,long long v,int pos){
if(L<=tree[pos].l&&R>=tree[pos].r){
tree[pos].mark+=v;
tree[pos].v+=(v*tree[pos].len());
return;
}
push_down(pos);
int mid=(tree[pos].l+tree[pos].r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) update(L,R,v,pos<<1);
if(R>mid) update(L,R,v,pos<<1|1);
push_up(pos);
}
long long query(int L,int R,int pos){
if(L<=tree[pos].l&&R>=tree[pos].r){
return tree[pos].v;
}
push_down(pos);
int mid=(tree[pos].l+tree[pos].r)>>1;
long long ans=0;
if(L<=mid) ans+=query(L,R,pos<<1);
if(R>mid) ans+=query(L,R,pos<<1|1);
return ans;
}
void change(int u,int v,int x){
int xx=lca(u,v);
int lca_num=tri_lca(u,v,root);
if(l[root]<l[xx]||r[root]>r[xx]){
update(l[xx],r[xx],x,1);
return;
}else if(lca_num==root){
update(1,n,x,1);
return;
}else{
int w2=get_close(lca_num,root);
update(1,n,x,1);
update(l[w2],r[w2],-x,1);
return;
}
}
long long sum(int w){
if(l[root]<l[w]||r[root]>r[w]){
return query(l[w],r[w],1);
}else{
if(w==root){
return query(1,n,1);
}
int sonw=get_close(w,root);
// printf("%d\n",query(1,n,1));
// printf("%d\n",query(l[sonw],r[sonw],1));
return query(1,n,1)-query(l[sonw],r[sonw],1);
}
}
int main(){
int u,v,cmd,x;
n=qread();
q=qread();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) a[i]=qread();
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
u=qread();
v=qread();
add_edge(u,v);
add_edge(v,u);
}
deep[1]=1;
log2n=log2(n)+1;
dfs(1,0);
build(1,n,1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
update(l[i],l[i],a[i],1);
}
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){
cmd=qread();
if(cmd==1){
v=qread();
root=v;
}else if(cmd==2){
u=qread();
v=qread();
x=qread();
change(u,v,x);
}else{
v=qread();
printf("%I64d\n",sum(v));
}
// printf("debug: sum=%d\n",query(1,n,1));
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces 916E(思维+dfs序+线段树+LCA)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 1192B 全dfs序 + 线段树
题意:给你一颗树,每次会修改一条边的边权,问修改之后的树的直径是多少? 思路:来源于:https://www.cnblogs.com/TinyWong/p/11260601.html 得到树的全序df ...
- CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树
CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树 题意 就是树上有n个点,然后每个点都有一盏灯,给出初始的状态,1表示亮,0表示不亮,然后有两种操作,第一种是get x,表示你需要输出x的子树和x本身 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 6 E dfs序+线段树
题意:给出一颗有根树的构造和一开始每个点的颜色 有两种操作 1 : 给定点的子树群体涂色 2 : 求给定点的子树中有多少种颜色 比较容易想到dfs序+线段树去做 dfs序是很久以前看的bilibili ...
- Codeforces 343D Water Tree(DFS序 + 线段树)
题目大概说给一棵树,进行以下3个操作:把某结点为根的子树中各个结点值设为1.把某结点以及其各个祖先值设为0.询问某结点的值. 对于第一个操作就是经典的DFS序+线段树了.而对于第二个操作,考虑再维护一 ...
- Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2)A,B,C,D,E(STL,dp,贪心,bfs,dfs序+线段树)
A. Alex and broken contest time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input s ...
- CodeForces 877E Danil and a Part-time Job(dfs序+线段树)
Danil decided to earn some money, so he had found a part-time job. The interview have went well, so ...
- 【BZOJ-3252】攻略 DFS序 + 线段树 + 贪心
3252: 攻略 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 339 Solved: 130[Submit][Status][Discuss] D ...
- BZOJ2434 [Noi2011]阿狸的打字机(AC自动机 + fail树 + DFS序 + 线段树)
题目这么说的: 阿狸喜欢收藏各种稀奇古怪的东西,最近他淘到一台老式的打字机.打字机上只有28个按键,分别印有26个小写英文字母和'B'.'P'两个字母.经阿狸研究发现,这个打字机是这样工作的: 输入小 ...
- POJ 3321 DFS序+线段树
单点修改树中某个节点,查询子树的性质.DFS序 子树序列一定在父节点的DFS序列之内,所以可以用线段树维护. 1: /* 2: DFS序 +线段树 3: */ 4: 5: #include < ...
随机推荐
- noip2017简要题解。
重新写了一下去年的题来看看自己到底是有多傻逼. 小凯的疑惑 打表. 时间复杂度 搞了一大坨题面,但是真正有用的信息只有几个: 判断他给你的复杂度是多少. 判断当前循环进不进的去. 判断当前循环产生的贡 ...
- JVM---Java存储模型
1.概述 1.1.Java语言规范 规定了 JVM要维护 内部线程类似顺序化语意(只要程序的最终结果 等同于 它在严格的顺序化环境中执行的结果): 2.平台的存储模型 2.1.现代的处理器. ...
- NOIP模拟赛(by hzwer) T1 小奇挖矿
[题目背景] 小奇要开采一些矿物,它驾驶着一台带有钻头(初始能力值 w)的飞船,按既定 路线依次飞过喵星系的 n 个星球. [问题描述] 星球分为 2 类:资源型和维修型. 1. 资源型:含矿物质量 ...
- LeetCode--079--单词搜索(python)
给定一个二维网格和一个单词,找出该单词是否存在于网格中. 单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格.同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用. ...
- 微信小程序-wxml-空格
必须要在<text>标签中 先在标签中写decode="{{true}}"然后 就代表空格了 占一个中文字符
- SQL server 表copy 到别一张表
SQL server 表copy 到别一张表 ------------------ INSERT INTO 表名 (表字段) SELECT 表1字段 FROM 表名2: ---------- ...
- 20181019-JSP 教程/简介
JSP 教程 这是第一篇JSP JSP与PHP.ASP.ASP.NET等语言类似,运行在服务端的语言. JSP(全称Java Server Pages)是由Sun Microsystems公司倡导和许 ...
- C/C++头文件的编写
在C语言的学习过程中,我们一般把所有的代码写在一个文件中.随着自身水平的提高,我们发现代码越写越长,代码行数越来越多,把一个工程的所有代码写在一个文件中让人看起开非常吃力.于是我们开始想把代码中的函数 ...
- [CSP-S模拟测试]:d(贪心+树状数组)
题目传送门(内部题65) 输入格式 第一行,一个自然数$T$,代表数据组数.对于每组数据:第一行,一个正整数$n$,一个自然数$m$.接下来$n$行,每行两个正整数,$a_i,b_i$. 输出格式 对 ...
- Java 中如何使用clone()方法克隆对象?
java为什么要 对象克隆: 在程序开发时,有时可能会遇到以下情况:已经存在一个对象A,现在需要一个与A对象完全相同的B 对象,并对B 对象的属性值进行修改,但是A 对象原有的属性值不能改变.这时,如 ...
