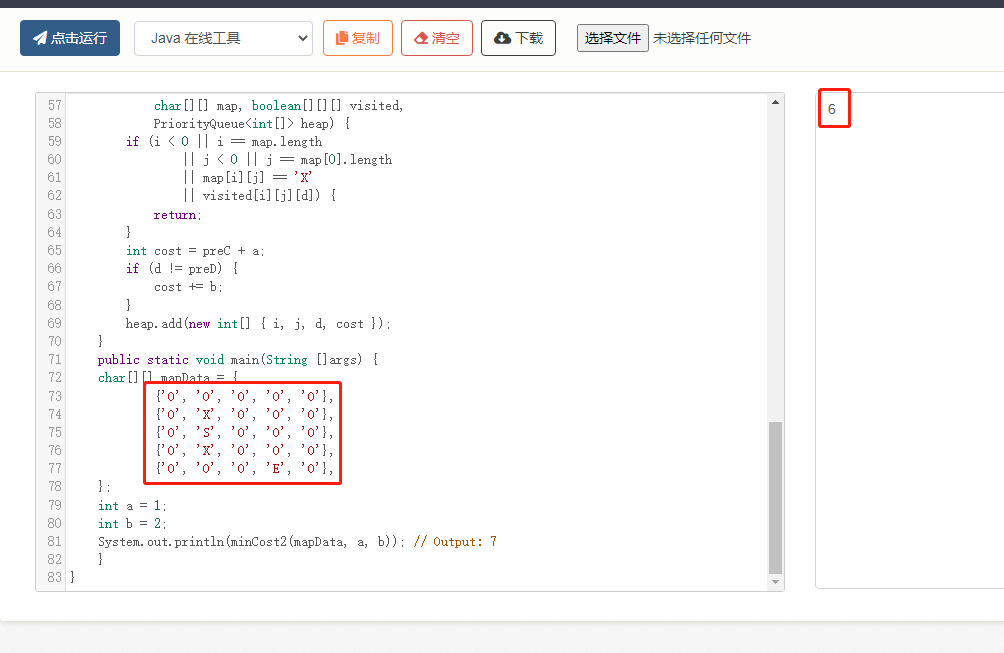
2023-03-11:给定一个N*M的二维矩阵,只由字符‘O‘、‘X‘、‘S‘、‘E‘组成, ‘O‘表示这个地方是可通行的平地, ‘X‘表示这个地方是不可通行的障碍, ‘S‘表示这个地方有一个士兵,全
2023-03-11:给定一个N*M的二维矩阵,只由字符’O’、‘X’、‘S’、'E’组成,
'O’表示这个地方是可通行的平地,
'X’表示这个地方是不可通行的障碍,
'S’表示这个地方有一个士兵,全图保证只有一个士兵,
'E’表示这个地方有一个敌人,全图保证只有一个敌人,
士兵可以在上、下、左、右四个方向上移动,
走到相邻的可通行的平地上,走一步耗费a个时间单位,
士兵从初始地点行动时,不管去哪个方向,都不用耗费转向的代价,
但是士兵在行动途中,如果需要转向,需要额外再付出b个时间单位。
返回士兵找到敌人的最少时间。
如果因为障碍怎么都找不到敌人,返回-1,
1 <= N,M <= 1000,
1 <= a,b <= 100000,
只会有一个士兵、一个敌人。
来自华为。
答案2023-03-11:
Dijkstra算法+优先级队列。
代码根据山寨版chatgpt稍做修改写的。这不得不承认chatgpt很强大,这还是山寨版的,感觉比我自己写得还要好。
以下代码是生成的rust代码,稍微做了修改。如下:
use rand::Rng;
use std::cmp::Reverse;
use std::collections::BinaryHeap;
fn random_map(n: usize, m: usize) -> Vec<Vec<char>> {
let mut map = vec![vec!['O'; m]; n];
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..m {
if rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, 2) == 0 {
map[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
let si = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, n);
let sj = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, m);
map[si][sj] = 'S';
let (mut ei, mut ej) = (si, sj);
while ei == si && ej == sj {
ei = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, n);
ej = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, m);
}
map[ei][ej] = 'E';
map
}
fn main() {
let n = 3;
let m = 4;
let v = 10;
println!("功能测试开始");
for _ in 0..2000 {
let map = random_map(n, m);
let a = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, v + 1);
let b = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, v + 1);
let ans1 = min_cost1(&map, a, b);
let ans2 = min_cost2(&map, a, b);
if ans1 != ans2 {
println!("出错了");
println!("{}", ans1);
println!("{}", ans2);
return;
}
}
println!("功能测试结束");
println!("性能测试开始");
let n = 1000;
let m = 1000;
let v = 100000;
let a = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, v + 1);
let b = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, v + 1);
let map = random_map(n, m);
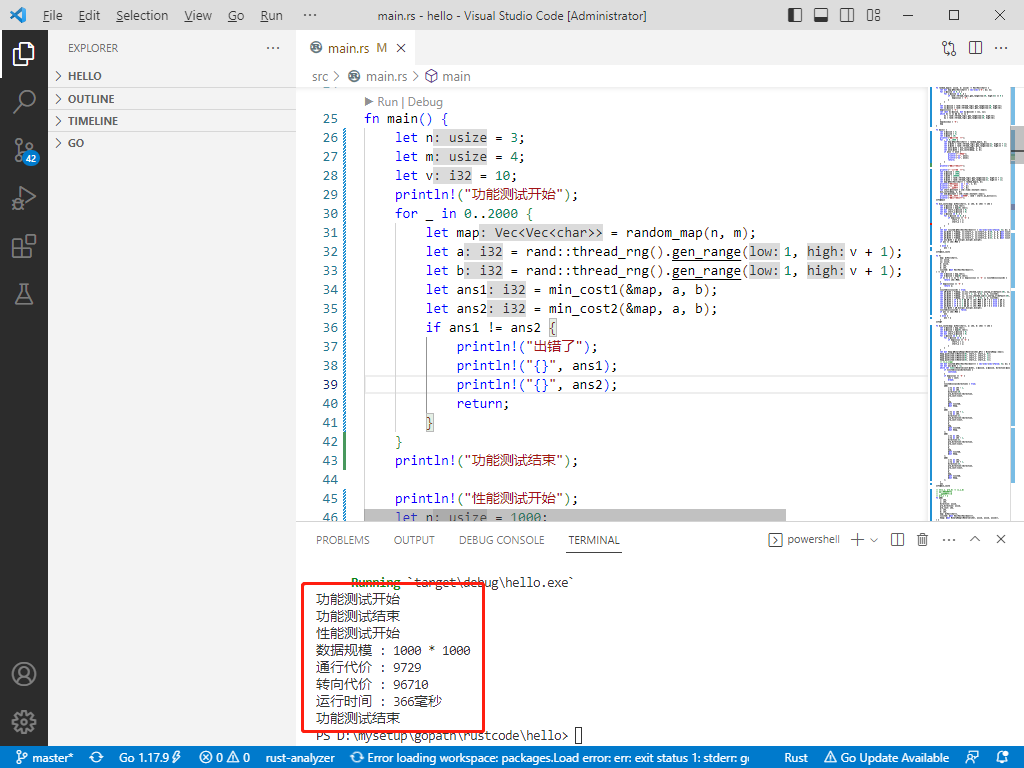
println!("数据规模 : {} * {}", n, m);
println!("通行代价 : {}", a);
println!("转向代价 : {}", b);
let start = std::time::Instant::now();
min_cost2(&map, a, b);
let end = std::time::Instant::now();
println!("运行时间 : {}毫秒", (end - start).as_millis());
println!("功能测试结束");
}
fn min_cost1(map: &[Vec<char>], a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
let n = map.len();
let m = map[0].len();
let mut start_x = 0;
let mut start_y = 0;
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..m {
if map[i][j] == 'S' {
start_x = i;
start_y = j;
}
}
}
let mut visited = vec![vec![vec![false; 4]; m]; n];
let p1 = f(&map, start_x, start_y, 0, a, b, &mut visited);
let p2 = f(&map, start_x, start_y, 1, a, b, &mut visited);
let p3 = f(&map, start_x, start_y, 2, a, b, &mut visited);
let p4 = f(&map, start_x, start_y, 3, a, b, &mut visited);
let ans = p1.min(p2).min(p3).min(p4);
if ans == i32::MAX {
-1
} else {
ans - a
}
}
fn f(
map: &[Vec<char>],
si: usize,
sj: usize,
d: usize,
a: i32,
b: i32,
visited: &mut Vec<Vec<Vec<bool>>>,
) -> i32 {
let n = map.len();
let m = map[0].len();
if si >= n || sj >= m || map[si][sj] == 'X' || visited[si][sj][d] {
return i32::MAX;
}
if map[si][sj] == 'E' {
return a;
}
visited[si][sj][d] = true;
let p0 = f(&map, si.checked_sub(1).unwrap_or(0), sj, 0, a, b, visited);
let p1 = f(&map, si + 1, sj, 1, a, b, visited);
let p2 = f(&map, si, sj.checked_sub(1).unwrap_or(0), 2, a, b, visited);
let p3 = f(&map, si, sj + 1, 3, a, b, visited);
let p0 = if d != 0 && p0 != i32::MAX { p0 + b } else { p0 };
let p1 = if d != 1 && p1 != i32::MAX { p1 + b } else { p1 };
let p2 = if d != 2 && p2 != i32::MAX { p2 + b } else { p2 };
let p3 = if d != 3 && p3 != i32::MAX { p3 + b } else { p3 };
let ans = p0.min(p1).min(p2).min(p3);
visited[si][sj][d] = false;
if ans == i32::MAX {
ans
} else {
ans + a
}
}
fn min_cost2(map: &[Vec<char>], a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
let n = map.len();
let m = map[0].len();
let mut start_x = 0;
let mut start_y = 0;
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..m {
if map[i][j] == 'S' {
start_x = i;
start_y = j;
}
}
}
let mut heap = BinaryHeap::new();
heap.push((Reverse(0), start_x, start_y, 0));
heap.push((Reverse(0), start_x, start_y, 1));
heap.push((Reverse(0), start_x, start_y, 2));
heap.push((Reverse(0), start_x, start_y, 3));
// (i,j,朝向)
let mut visited = vec![vec![vec![false; 4]; m]; n];
let mut ans = -1;
while let Some((Reverse(cost), x, y, direction)) = heap.pop() {
if visited[x][y][direction] {
continue;
}
if map[x][y] == 'E' {
ans = cost;
break;
}
visited[x][y][direction] = true;
add(
x as i32 - 1,
y as i32,
0,
direction,
cost,
a,
b,
map,
&mut visited,
&mut heap,
);
add(
x as i32 + 1,
y as i32,
1,
direction,
cost,
a,
b,
map,
&mut visited,
&mut heap,
);
add(
x as i32,
y as i32 - 1,
2,
direction,
cost,
a,
b,
map,
&mut visited,
&mut heap,
);
add(
x as i32,
y as i32 + 1,
3,
direction,
cost,
a,
b,
map,
&mut visited,
&mut heap,
);
}
ans
}
// 从(x,y, pre_d) -> (i,j,d)
// 走格子的代价a
// 转向的代价是b
// pre_c + a
fn add(
i: i32,
j: i32,
direction: usize,
pre_direction: usize,
pre_cost: i32,
a: i32,
b: i32,
map: &[Vec<char>],
visited: &mut Vec<Vec<Vec<bool>>>,
heap: &mut BinaryHeap<(Reverse<i32>, usize, usize, usize)>,
) {
let n = map.len() as i32;
let m = map[0].len() as i32;
if i < 0
|| i >= n
|| j < 0
|| j >= m
|| map[i as usize][j as usize] == 'X'
|| visited[i as usize][j as usize][direction]
{
return;
}
let mut cost = pre_cost + a;
if direction != pre_direction {
cost += b;
}
heap.push((Reverse(cost), i as usize, j as usize, direction));
}
以下代码是生成的golang代码,稍微做了修改。如下:
package main
import (
"container/heap"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
func minCost1(mapData [][]byte, a int, b int) int {
// 获取地图大小和起点位置
n, m := len(mapData), len(mapData[0])
startX, startY := 0, 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if mapData[i][j] == 'S' {
startX, startY = i, j
break
}
}
}
// 初始化 visited 数组
visited := make([][][]bool, n)
for i := range visited {
visited[i] = make([][]bool, m)
for j := range visited[i] {
visited[i][j] = make([]bool, 4)
}
}
// 计算从四个方向到达终点的最短距离
p1 := f(mapData, startX, startY, 0, a, b, visited)
p2 := f(mapData, startX, startY, 1, a, b, visited)
p3 := f(mapData, startX, startY, 2, a, b, visited)
p4 := f(mapData, startX, startY, 3, a, b, visited)
// 返回四个方向中最小的距离
ans := min(p1, min(p2, min(p3, p4)))
if ans == 1<<31-1 {
return -1
} else {
return ans - a
}
}
func f(mapData [][]byte, si int, sj int, d int, a int, b int, visited [][][]bool) int {
// 如果出现越界、墙壁或者已经访问过的情况,返回一个大整数表示无法到达该位置
if si < 0 || si == len(mapData) || sj < 0 || sj == len(mapData[0]) || mapData[si][sj] == 'X' || visited[si][sj][d] {
return 1<<31 - 1
}
// 如果到达终点,返回 a 表示到达终点所需的代价
if mapData[si][sj] == 'E' {
return a
}
// 标记该位置已经被访问过
visited[si][sj][d] = true
// 计算从四个方向到达下一个位置所需的代价(如果可以到达的话)
var p [4]int
p[0] = f(mapData, si-1, sj, 0, a, b, visited)
p[1] = f(mapData, si+1, sj, 1, a, b, visited)
p[2] = f(mapData, si, sj-1, 2, a, b, visited)
p[3] = f(mapData, si, sj+1, 3, a, b, visited)
if d != 0 && p[0] != 1<<31-1 {
p[0] += b
}
if d != 1 && p[1] != 1<<31-1 {
p[1] += b
}
if d != 2 && p[2] != 1<<31-1 {
p[2] += b
}
if d != 3 && p[3] != 1<<31-1 {
p[3] += b
}
// 返回四个方向中最小的代价,并且取消对该位置的访问标记
ans := min(p[0], min(p[1], min(p[2], p[3])))
visited[si][sj][d] = false
if ans == 1<<31-1 {
return ans
} else {
return ans + a
}
}
func min(a int, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
} else {
return b
}
}
func minCost2(mapData [][]byte, a int, b int) int {
// 获取地图大小和起点位置
n, m := len(mapData), len(mapData[0])
startX, startY := 0, 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if mapData[i][j] == 'S' {
startX, startY = i, j
break
}
}
}
// 初始化优先队列和 visited 数组
h := &minHeap{}
heap.Init(h)
heap.Push(h, node{startX, startY, 0, 0})
heap.Push(h, node{startX, startY, 1, 0})
heap.Push(h, node{startX, startY, 2, 0})
heap.Push(h, node{startX, startY, 3, 0})
visited := make([][][]bool, n)
for i := range visited {
visited[i] = make([][]bool, m)
for j := range visited[i] {
visited[i][j] = make([]bool, 4)
}
}
// 运行 Dijkstra 算法并返回答案
ans := -1
for h.Len() > 0 {
cur := heap.Pop(h).(node)
if visited[cur.x][cur.y][cur.dir] {
continue
}
if mapData[cur.x][cur.y] == 'E' {
ans = cur.cost
break
}
visited[cur.x][cur.y][cur.dir] = true
add(cur.x-1, cur.y, 0, cur.dir, cur.cost, a, b, mapData, visited, h)
add(cur.x+1, cur.y, 1, cur.dir, cur.cost, a, b, mapData, visited, h)
add(cur.x, cur.y-1, 2, cur.dir, cur.cost, a, b, mapData, visited, h)
add(cur.x, cur.y+1, 3, cur.dir, cur.cost, a, b, mapData, visited, h)
}
return ans
}
type node struct {
x, y, dir, cost int
}
type minHeap []node
func (h minHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h minHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].cost < h[j].cost }
func (h minHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *minHeap) Push(x interface{}) { *h = append(*h, x.(node)) }
func (h *minHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[:n-1]
return x
}
func add(i, j, d, preD, preC, a, b int, mapData [][]byte, visited [][][]bool, h *minHeap) {
if i < 0 || i == len(mapData) || j < 0 || j == len(mapData[0]) || mapData[i][j] == 'X' || visited[i][j][d] {
return
}
cost := preC + a
if d != preD {
cost += b
}
heap.Push(h, node{i, j, d, cost})
}
func randomMap(n, m int) [][]byte {
mapData := make([][]byte, n)
for i := range mapData {
mapData[i] = make([]byte, m)
for j := range mapData[i] {
if rand.Float32() < 0.5 {
mapData[i][j] = 'O'
} else {
mapData[i][j] = 'X'
}
}
}
si := rand.Intn(n)
sj := rand.Intn(m)
mapData[si][sj] = 'S'
var ei, ej int
for {
ei = rand.Intn(n)
ej = rand.Intn(m)
if ei != si || ej != sj {
break
}
}
mapData[ei][ej] = 'E'
return mapData
}
func main() {
n, m := 3, 4
v := 10
fmt.Println("功能测试开始")
for i := 0; i < 2000; i++ {
mapData := randomMap(n, m)
a := rand.Intn(v) + 1
b := rand.Intn(v) + 1
ans1 := minCost1(mapData, a, b)
ans2 := minCost2(mapData, a, b)
if ans1 != ans2 {
fmt.Println("出错了")
fmt.Println(ans1)
fmt.Println(ans2)
}
}
fmt.Println("功能测试结束")
fmt.Println("性能测试开始")
n = 1000
m = 1000
v = 100000
a := rand.Intn(v) + 1
b := rand.Intn(v) + 1
mapData := randomMap(n, m)
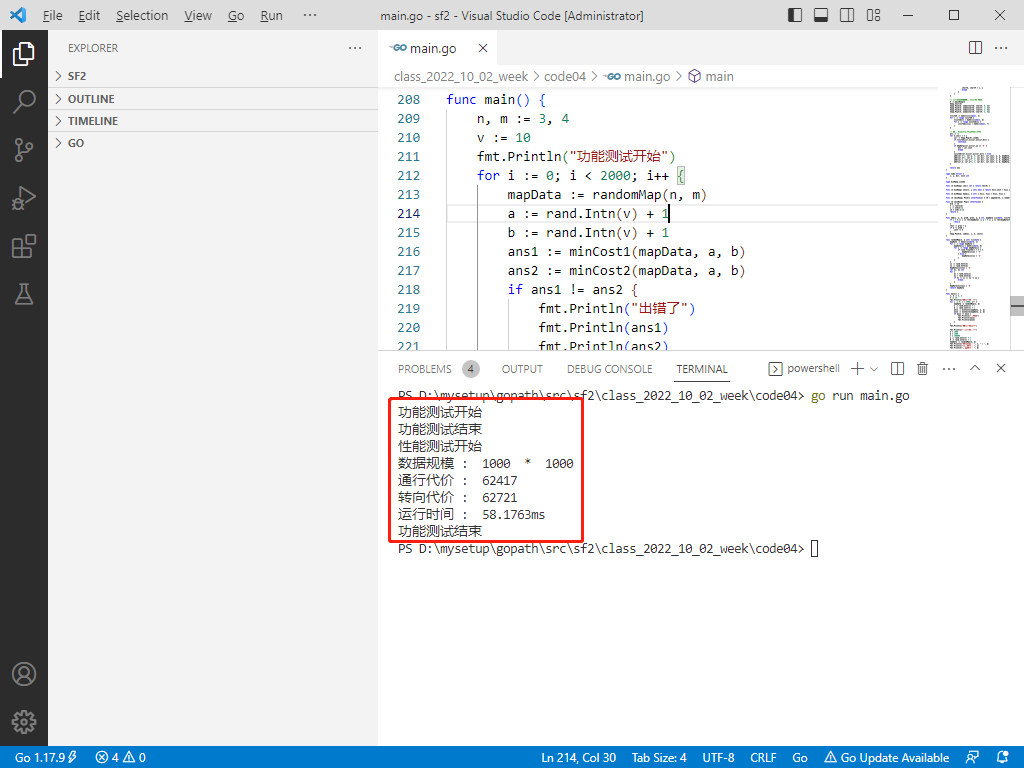
fmt.Println("数据规模 : ", n, " * ", m)
fmt.Println("通行代价 : ", a)
fmt.Println("转向代价 : ", b)
start := time.Now()
minCost2(mapData, a, b)
end := time.Now()
fmt.Println("运行时间 : ", end.Sub(start))
fmt.Println("功能测试结束")
}
2023-03-11:给定一个N*M的二维矩阵,只由字符‘O‘、‘X‘、‘S‘、‘E‘组成, ‘O‘表示这个地方是可通行的平地, ‘X‘表示这个地方是不可通行的障碍, ‘S‘表示这个地方有一个士兵,全的更多相关文章
- [CareerCup] 11.6 Search a 2D Matrix 搜索一个二维矩阵
11.6 Given an M x N matrix in which each row and each column is sorted in ascending order, write a m ...
- 旋转图像 给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵表示一个图像。
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵表示一个图像. 将图像顺时针旋转 90 度. 说明: 你必须在原地旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵.请不要使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像. 示例 : 给定 ma ...
- [LeetCode] Search a 2D Matrix II 搜索一个二维矩阵之二
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the follo ...
- [LeetCode] Search a 2D Matrix 搜索一个二维矩阵
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the follo ...
- [LeetCode] 74. Search a 2D Matrix 搜索一个二维矩阵
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the follo ...
- [LeetCode] 240. Search a 2D Matrix II 搜索一个二维矩阵 II
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the follo ...
- IT公司100题-35- 求一个矩阵中最大的二维矩阵(元素和最大)
问题描述: 求一个矩阵中最大的二维矩阵(元素和最大).如: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 中最大的是: 4 5 9 10 分析: 2*2子数组的最大和.遍历求和,时 ...
- 用Python+qrcode库创建一个包含信息的二维码
安装qrcode库和PIL库 在命令行中分别输入pip install qrcode 和pip install pillow 导入库格式如下: import PIL import qrcode 下面以 ...
- 一个不错的PHP二维数组排序函数简单易用存用
一个不错的PHP二维数组排序函数简单易用存用 传入数组,传入排序的键,传入排序顺序 public function array_sort($arr,$keys,$type='asc') { $keys ...
- 小程序踩过的一个小坑---解析二维码decodeURIComponent() url解码
因为我们需要用户扫码进入小程序,每一个货柜都有一个对应的二维码,当然每个二维码里的信息也不一样.用户扫码进入小程序之后,二维码的信息会以参数q带进去,而我们只能在onLoad事件中拿到这个参数, 但是 ...
随机推荐
- git-bash打开自动执行某条命令的快捷方式创建
"C:\Program Files\Git\git-bash.exe" -c "npm run dev" 创建一个快捷方式,在目标里面加上以上参数,然后运行. ...
- 学习记录--C++继承与派生编程题
1.设计一个圆类circle和一个桌子类table,另设计一个圆桌类roundtable,它是从前两个类派生出来的 要求输出一个圆桌的高度,面积与颜色等. #include<iostream&g ...
- Glist 按钮属性
grayed 变灰与否不影响点击等事件 touchable 为false,不会变灰,但会无法点击, enabled为false自动变灰,且无法点击
- Pod概述
Pod的类型 Pod的类型有如下两个: 自主式Pod:自主式Pod的含义简白来说就是不是被控制器管理的Pod,另一种就是被控制管理的Pod,不被控制器管理的Pod你会发现,它一旦死亡的话,就没有人把它 ...
- SpringCloud微服务实战——搭建企业级开发框架(五十一):微服务安全加固—自定义Gateway拦截器实现防止SQL注入/XSS攻击
SQL注入是常见的系统安全问题之一,用户通过特定方式向系统发送SQL脚本,可直接自定义操作系统数据库,如果系统没有对SQL注入进行拦截,那么用户甚至可以直接对数据库进行增删改查等操作. XSS ...
- STL常用容器用法总结
vector 变长数组,倍增的思想 size() 返回元素个数 empty() 返回是否为空 clear() 清空 front()/back() push_back()/pop_back() begi ...
- Tomcat启动报错,Server Tomcat v8.0 Server at localhost failed to start
Eclipse 中Tomcat 启动报错Eclipse的提示窗口 Server Tomcat v8.0 Server at localhost failed to start .日志输出中报 F ...
- STM32 HAL库学习 (3) 中断!
中断在单片机开发中有着重中之重的地位. 中断即打断,实至CPU再执行当前程序时,由于系统出现了某种需要处理的紧急情况,CPU暂停正在执行的程序,转而去执行另一段特殊程序来处理的出现的紧急 ...
- ACM-NEFUOJ-P209湖南修路
思路 prim的最小生成树,套上肝就完事了 代码 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<string.h> #d ...
- [Linux]RabbitMQ - 解决Error: unable to connect to node rabbit@localhost: nodedown
1 问题 环境: CentOS7.8.2003 (x86 / 64bit) 版本: RabbitMQ 3.6.15 (Erlang 19.3) 安装方式: 二进制源码压缩安装 2 解决思路 2.1 思 ...
