Android(java)学习笔记95:Android原理揭秘系列之View、ViewGroup
1. 作过Android 应用开发的朋友都知道,Android的UI界面都是由View和ViewGroup及其派生类组合而成的。其中,View是所有UI组件的基类,而ViewGroup是容纳这些组件的容器,其本身也是从View派生出来的。AndroidUI界面的一般结构可参见下面的示意图: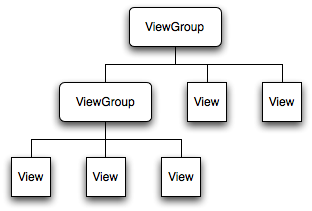
可见,作为容器的ViewGroup可以包含作为叶子节点的View,也可以包含作为更低层次的子ViewGroup,而子ViewGroup又可以包含下一层的叶子节点的View和ViewGroup。事实上,这种灵活的View层次结构可以形成非常复杂的UI布局,开发者可据此设计、开发非常精致的UI界面。
一般来说,开发Android应用程序的UI界面都不会直接实用View和ViewGroup,而是使用这两大基类的派生类。
View派生出的直接子类有:AnalogClock,ImageView,KeyboardView, ProgressBar,SurfaceView,TextView,ViewGroup,ViewStub
View派生出的间接子类有:AbsListView,AbsSeekBar, AbsSpinner, AbsoluteLayout, AdapterView<T extends Adapter>,AdapterViewAnimator, AdapterViewFlipper, AppWidgetHostView, AutoCompleteTextView,Button,CalendarView, CheckBox, CheckedTextView, Chronometer, CompoundButton,
ViewGroup派生出的直接子类有:AbsoluteLayout,AdapterView<T extends Adapter>,FragmentBreadCrumbs,FrameLayout,LinearLayout,RelativeLayout,SlidingDrawer
ViewGroup派生出的间接子类有:AbsListView,AbsSpinner, AdapterViewAnimator, AdapterViewFlipper, AppWidgetHostView, CalendarView, DatePicker, DialerFilter, ExpandableListView, Gallery, GestureOverlayView,GridView,HorizontalScrollView, ImageSwitcher,ListView,
上面View、ViewGroup的直接子类和间接别子类中标记为红色的类是我们再应用开发中接触和用得比较频繁的类,需要初学者重点熟悉和掌握,其详细的API及用法可参见SDK的说明。这里特别指出,ImageView是布局具有图片效果的UI常用的类,SurfaceView是用来进行游戏开发的与一般View相比较为特殊的非常重要的类(后续会对原理作深入分析),而AbsoluteLayout、FrameLayout,LinearLayout, RelativeLayout这几个ViewGroup的直接子类是Android UI布局中最基本的布局元素。
值得一提的是,上述的所有基类、派生类都是Android framework层集成的标准系统类,开发者在应用开发中可直接引用SDK中这些系统类及其API。但事实上,在UI开发的很多场景下,直接使用这些系统类并不能满足应用开发的需要。比如说,我们想用ImageView在默认情况下加载一幅图片,但是希望在点击该View时View变换出各种图像处理效果,这个时候直接使用ImageView是不行的,此时我们可以重载ImageView,在新派生出的子控件中重载OnDraw等方法来实现我们的定制效果。这种派生出系统类的子类方法我们通常称之为自定义控件。自定义控件可像标准View控件那样在XML及我们的Java文件中进行布局和实例化,但在布局时必须指出其完整的包名和类名。事实上,自定义控件的使用是我们进行Android 开发的必不可少的基本用法,是必须掌握的基本技巧。
2. 下面我们来看一个典型的例子,我们待机Launcher 的XML布局,这个例子能够很好的说明上面的一些概念。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
<com.android.launcher2.DragLayer
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:launcher="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.android.launcher"
android:id="@+id/drag_layer"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<include layout="@layout/all_apps" />
<!-- The workspace contains 3 screens of cells -->
<com.android.launcher2.Workspace
android:id="@+id/workspace"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
launcher:defaultScreen="2">
<include android:id="@+id/cell1" layout="@layout/workspace_screen" />
<include android:id="@+id/cell2" layout="@layout/workspace_screen" />
<include android:id="@+id/cell3" layout="@layout/workspace_screen" />
<include android:id="@+id/cell4" layout="@layout/workspace_screen" />
<include android:id="@+id/cell5" layout="@layout/workspace_screen" />
</com.android.launcher2.Workspace>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/previous_screen"
android:layout_width="93dip"
android:layout_height="@dimen/button_bar_height"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|left"
android:layout_marginLeft="6dip"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@drawable/home_arrows_left"
android:onClick="previousScreen"
android:focusable="true"
android:clickable="true" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/next_screen"
android:layout_width="93dip"
android:layout_height="@dimen/button_bar_height"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|right"
android:layout_marginRight="6dip"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@drawable/home_arrows_right"
android:onClick="nextScreen"
android:focusable="true"
android:clickable="true" />
<com.android.launcher2.DeleteZone
android:id="@+id/delete_zone"
android:layout_width="@dimen/delete_zone_size"
android:layout_height="@dimen/delete_zone_size"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/delete_zone_padding"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|center_horizontal"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@drawable/delete_zone_selector"
android:visibility="invisible"
launcher:direction="horizontal"
/>
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/all_apps_button_cluster"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/button_bar_height"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|center_horizontal"
android:paddingTop="2dip"
>
<com.android.launcher2.HandleView
style="@style/HotseatButton"
android:id="@+id/all_apps_button"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:src="@drawable/all_apps_button"
launcher:direction="horizontal"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/hotseat_left"
style="@style/HotseatButton.Left"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/all_apps_button"
android:src="@drawable/hotseat_phone"
android:onClick="launchHotSeat"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/hotseat_right"
style="@style/HotseatButton.Right"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/all_apps_button"
android:src="@drawable/hotseat_browser"
android:onClick="launchHotSeat"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
</com.android.launcher2.DragLayer>
在上面的XML布局中,最顶层的控件com.android.launcher2.DragLayer是一个自定义控件,其继承自ViewGroup的直接子类FrameLayout。在DragLayer的布局内部,其子View既有ImageView类本身,也有从ImageView的派生出的子定义控件HandleView,既有ViewGroup的框架中的直接子类RelativeLayout,也有从派生出的自定义控件Workspace。总之,这布局的例子是大家学习Android布局、应用开发和理解Android View、ViewGroup概念的非常优秀的例子,大家可下载Launcher模块的源代码来进行深入分析(Launcher单个模块的下载方法可参见博文Android源码下载——用git clone实现单个目录下载 )。
最后,给大家介绍下View和ViewGroup最重要的几个方法:
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas):View类中用于重绘的方法,这个方法是所有View、ViewGroup及其派生类都具有的方法,也是Android UI绘制最重要的方法。开发者可重载该方法,并在重载的方法内部基于参数canvas绘制自己的各种图形、图像效果。
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom):View类中布局发生改变时会调用的方法,这个方法是所有View、ViewGroup及其派生类都具有的方法,重载该类可以在布局发生改变时作定制处理,这在实现一些特效时非常有用。
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas):ViewGroup类及其派生类具有的方法,这个方法主要用于控制子View的绘制分发,重载该方法可改变子View的绘制,进而实现一些复杂的视效,典型的例子可参见Launcher模块Workspace的dispatchDraw重载。
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime)):ViewGroup类及其派生类具有的方法,这个方法直接控制绘制某局具体的子view,重载该方法可控制具体某个具体子View。
View、ViewGroup是Android UI体系至关重要的两大基类,本文仅对一些最基本的概念、原理和API进行了介绍,大家要全面掌握还需要阅读SDK中对这两个类的介绍并熟悉其API ,并在应用开发中逐渐的加深理解和掌握其用法。
Android(java)学习笔记95:Android原理揭秘系列之View、ViewGroup的更多相关文章
- Android(java)学习笔记34:Android原理揭秘系列之View、ViewGroup
1. 作过Android 应用开发的朋友都知道,Android的UI界面都是由View和ViewGroup及其派生类组合而成的.其中,View是所有UI组件的基类,而ViewGroup是容纳这些组件的 ...
- Android开发学习笔记-关于Android的消息推送以及前后台切换
下面是最简单的Android的消息推送的实现方法 package com.example.shownotic; import java.util.Random; import android.supp ...
- Android 数字签名学习笔记
Android 数字签名学习笔记 在Android系统中,所有安装到系统的应用程序都必有一个数字证书,此数字证书用于标识应用程序的作者和在应用程序之间建立信任关系,如果一个permission的pro ...
- Android动画学习笔记-Android Animation
Android动画学习笔记-Android Animation 3.0以前,android支持两种动画模式,tween animation,frame animation,在android3.0中 ...
- Android:日常学习笔记(6)——探究活动(4)
Android:日常学习笔记(6)——探究活动(4) 活动的启动模式 standard模式 standard是活动默认的启动模式,在不进行显示定义的情况下,所有活动都会自动使用这种启动模式. stan ...
- Android Studio 学习笔记(一)环境搭建、文件目录等相关说明
Android Studio 学习笔记(一)环境搭建.文件目录等相关说明 引入 对APP开发而言,Android和iOS是两大主流开发平台,其中区别在于 Android用java语言,用Android ...
- Android自动化学习笔记:编写MonkeyRunner脚本的几种方式
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- Android自动化学习笔记之MonkeyRunner:官方介绍和简单实例
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- android开发学习笔记000
使用书籍:<疯狂android讲义>——李刚著,2011年7月出版 虽然现在已2014,可我挑来跳去,还是以这本书开始我的android之旅吧. “疯狂源自梦想,技术成就辉煌.” 让我这个 ...
随机推荐
- JAVA中的数据结构——集合类(线性表:Vector、Stack、LinkedList、set接口;键值对:Hashtable、Map接口<HashMap类、TreeMap类>)
Java的集合可以分为两种,第一种是以数组为代表的线性表,基类是Collection:第二种是以Hashtable为代表的键值对. ... 线性表,基类是Collection: 数组类: person ...
- adb常用命令介绍
adb connect 命令格式:adb connect <host>[:<port>] 作用:connect to a device via TCP/IP,Port 5555 ...
- 怎么利用SQL语句查询数据库中具体某个字段的重复行
select * from [tablename] group by SeriNohaving count(SeriNo)<>1
- Spark系列(七)Master中的资源调度
资源调度 说明: Application的调度算法有两种,分别为spreadOutApps和非spreadOutApps spreadOutApps 在spark-submit脚本中,可以指定要多少个 ...
- lsof,nc
安装nc, yum -y install nc; 用nc传输同步文件 A,被同步端-即需要备份复制端; tar -czvf - /|nc 192.168.1.204(同步机ip,复制文件位置机) 88 ...
- 转】Nginx+tomcat集群环境搭建(Windows下)
原博文出自于: http://blog.csdn.net/clj198606061111/article/details/22621003 感谢! 实验环境 windows xp s ...
- HDU 3265 Posters (线段树+扫描线)(面积并)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3265 给你n个中间被挖空了一个矩形的中空矩形,让你求他们的面积并. 其实一个中空矩形可以分成4个小的矩 ...
- POJ 2777 Count Color (线段树成段更新+二进制思维)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2777 题意是有L个单位长的画板,T种颜色,O个操作.画板初始化为颜色1.操作C讲l到r单位之间的颜色变为c,操作P查询l到r单位之间的 ...
- POJ1328Radar Installation(贪心)
对于每一个点,可以找到他在x轴上的可行区域,这样的话就变为了对区间的贪心. #include<iostream> #include<stdio.h> #include<s ...
- 微软IIS服务器的最佳优化工具- IIS Tuner
dudu的 <让Windows Server 2008 + IIS 7+ ASP.NET 支持10万个同时请求>,里面涉及到需要手工调整参数的地方.在这篇文章中,我们给你介绍一个IIS ...
