数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第7章:栈
- 栈概览
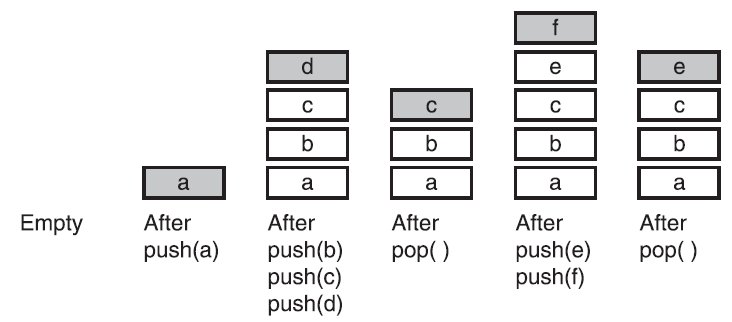
- 栈是线性集合,遵从后进先出原则( Last - in first - out , LIFO )原则
- 栈常用的操作包括压入( push ) 和弹出( pop )
- 栈的应用
- 将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并且计算后缀表达式的值
- 回溯算法
- 管理计算机内存以支持函数和方法调用
- 支持应用程序中的撤消功能
- 维护Web浏览器访问链接的历史记录
- 使用栈
- 栈不是Python的内建类型,可以用列表代替,但是列表可以在任何位置插入,删除,替换元素,这些违背了栈作为一种抽象数据类型的本意,因此需要为栈定义一种更为严格的接口
- 栈接口
- 初始化一个栈
s1 = ArrayStack()
] )
- 示例应用程序:匹配括号
- 步骤
- 扫描表达式,将开始的括号压入栈中
- 当遇到一个结束的括号时,如果栈为空,或者如果栈项的项不是相同的类型开始括号,括号不匹配
- 如果是正确类型的括号,从栈顶弹出一项,继续扫描表达式
- 当到达表达式未尾时,栈应为空,否则括号不匹配
- 代码
- index 方法返回列表中项的位置
- 可以自定义括号的类型
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
"""
File: brackets.py
Checks expressions for matching brackets.
"""
from linkedstack import LinkedStack
def bracketsBalance( exp, startBracketList = ['(', '['], endBracketList = [')', ']'] ):
"""exp is a string that represents the expressions.
startBracketList is the list of start brackets list.
endBracketList is the list of end brackets list.
precondition: startBracketList must have the same length of endBracketList.
raise: Exception if startBracketList don't have the same length of endBracketList."""
if len( startBracketList ) != len( endBracketList ):
raise Exception( "The startBracketList must have the same length with the endBracketList." )
stk = LinkedStack()
for ch in exp:
if ch in startBracketList:
stk.push( ch )
elif ch in endBracketList:
if stk.isEmpty():
return False
chFromStack = stk.pop()
if chFromStack != startBracketList[ endBracketList.index( ch ) ]:
return False
return stk.isEmpty()
def main():
"""Test the bracketsBalance function."""
while True:
exp = input( "Enter a brackets expressions: ")
if exp == "":
break
if bracketsBalance(exp,['(','[', '{'],[')', ']', '}'] ):
print("OK!")
else:
print( "Not OK!" )
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- 栈的 3 种应用
- 计算算术表达式
- 中缀表达式
- 运算符位于两个运算数之间
- 计算涉及优先级问题,有时需要括号来表示优先级
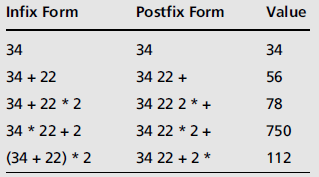
- 后缀表达式
- 运算符紧跟在运算数之后
- 没有优先级问题,一遇到运算符就立即运用
- 示例
- 计算后缀表达式
- 步骤(需要一个数字栈)
- 从左到右的遍历表达式,遇到运算数,则将其压入数字栈中
- 碰到一个运算符时,从数字栈中弹出两个运算数,对其应用运算符,并将所得的结果压入数字栈
- 继续遍历,直到到达表达式的未尾,此时,数字栈中只剩表达式的值
- 示例

- 时间复杂度为 O(n)
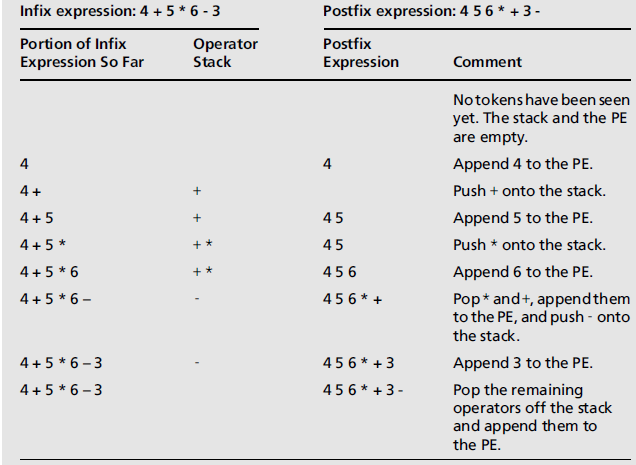
- 将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式
- 步骤
- 开始时,有一个空的后缀表达式和一个空的栈,栈用来保存运算符和左圆括号
- 从左到右,扫描中缀表达式
- 遇到一个运算数时,将其添加到后缀表达式中
- 遇到一个左圆括号时,将其压入栈中
- 遇到一个运算符,从栈中弹出和它具有相等或更高优先级的所有运算符,并将其依次添加到后缀表达式中
- 遇到一个右圆括号时,将运算符从栈中移动到后缀表达式中,直到碰到与之匹配的左圆括号,并将其丢弃
- 遇到中缀表达式的结束时,将栈中剩余的运算符全部转移到后缀表达式中
- 示例
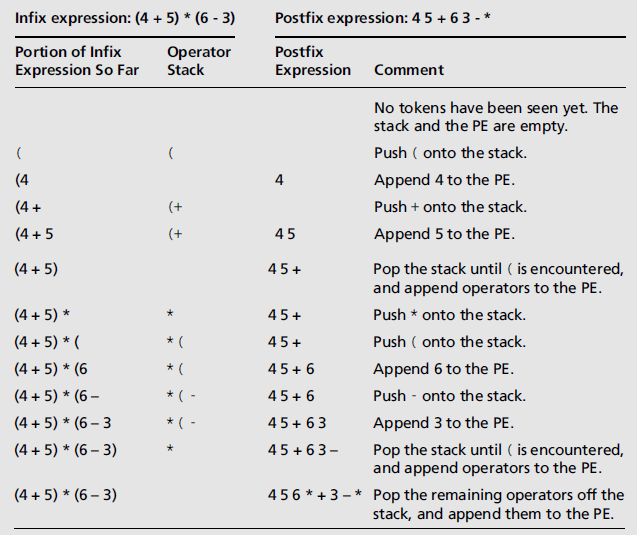
- 时间复杂度为 O(n)
- 回溯算法
- 描述
- 回溯算法从一个预定义的起始状态开始,随后从一个状态移动到另一个状态,以搜索想要的最终状态。
- 在任何状态下,如果有多个选择,则会随机选取一种状态,然后继续
- 如果算法到达了不希望结果的一个状态,它会回到上一个拥有一个末探索的、可替代选项的位置,并尝试这个可替代选项。
- 最后,要么算法到达了想要的结果,要么穷尽了对所有算法的搜索
- 栈的作用是在每一个关头记住可替代的状态
- 伪代码
Create an empty stack
Push the starting state onto the stack
while the stack in not empty:
Pop the stack and eaxmine the state
if the state represents an ending state
return SUCCESSFUL CONCLUSION
elif the state hasn't been visited previously
Mark the state as visited
Push onto the stack all unvisited adjacent states.
return UNSUCCESSFUL CONCLUSION
- 算法整体复杂度为 O(n)
- 内存管理
- PVM( Python Virtual Machine ) 运行时的环境架构
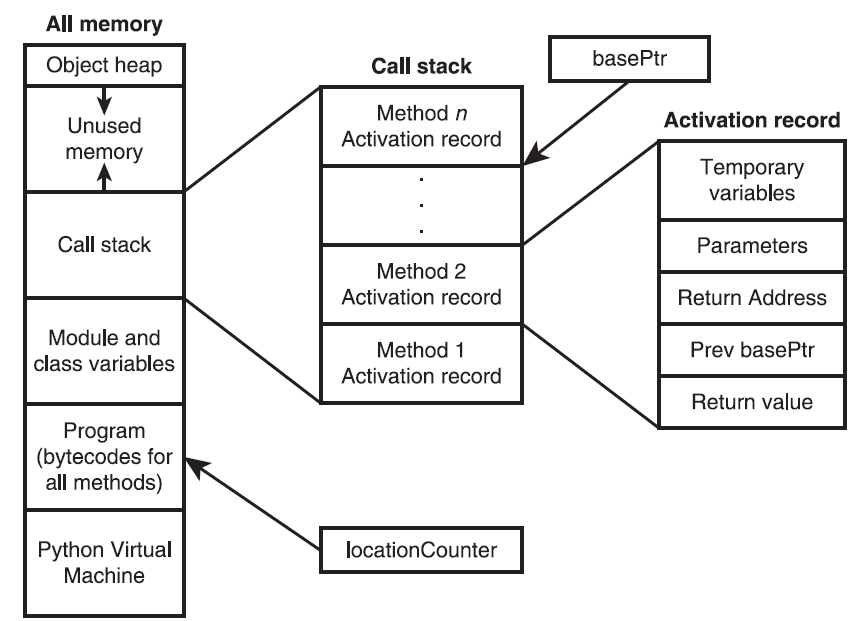
- locationCounter 指向 PVM 下一步将要执行的指令
- basePtr指向基本活动记录的顶部
- 调用子例程的步骤
- 创建子例程的活动记录,并将其压入栈
- 在标记为 Prev basePtr 的区域中保存 basePtr 的当前值,并将 basePtr 设置为新的活动记录位置
- 条指令
- 将调用参数复制到 Parameters 的区域中
- 开始执行位于 locationCounter 所指示位置的子程序
- 在子例程执行的过程中,通过给 basePtr 加上一个偏移量,以引用活动记录中的临时变量和参数
- 在返回之前,一个子例程将其返回值存储在Return Value 的位置。
- 当子例程执行完成后,PVM执行以下操作:
- 使用活动记录中存储的值来恢复locationCounter 和 basePtr 的值,从而重新建立调用子例程所需的设置
- 从调用栈中弹出活动记录
- 在locationCounter 所指示的位置,继续指定调用子例程
- 栈的实现
- 测试驱动程序
- 代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
"""
File: teststack.py
A tester program for stack implementations.
"""
# from arraystack import ArrayStack
from linkedstack import LinkedStack
def test( stackType ):
"""Test any implementation with the same code."""
s = stackType()
print( "Length: ", len( s ) )
print( "Empty: ", s.isEmpty )
print( "Push 1-10" )
for i in range( 10 ):
s.push( i + 1 )
print( "Peeking: ", s.peek() )
print( "Item ( bottom to top ): ", s )
print( "Length: ", len( s ) )
print( "Empty: ", s.isEmpty )
theClone = stackType( s )
print( "Items in clone ( bottom to top ): ", theClone )
theClone.clear()
print( "Length of clone after clear: ", len( theClone ) )
print( "Push 11" )
s.push( 11 )
print( "Poping items( top to bottom):", end = "" )
while not s.isEmpty():print( s.pop(), end = " " )
print( "\nLength: ", len( s ) )
print( "Empty: ", s.isEmpty() )
print( "Test precondition of pop." )
try:
s.pop()
except KeyError:
print( "KeyError" )
print( "Test precondition of peek." )
try:
s.peek()
except KeyError:
print( "KeyError" )
# test( ArrayStack )
test( LinkedStack )
- 将栈添加到集合层级中
- 集合层级中的栈资源

- 数组实现
- 当数组填满或者装填因子小于 1/4 时,需要对数组的容量进行调整
- 代码
##!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
from abstractstack import AbstractStack
from arrays import Array
class ArrayStack( AbstractStack ):
"""An array-based stack."""
#Class variable
def __init__( self, sourceCollection = None ):
"""Sets the initial state of self, which includes the contents
of sourceCollection, if it's present."""
self._items = Array( ArrayStack.DEFAULT_CAPACITY )
AbstractStack.__init__( self, sourceCollection )
# Accessor method
def __iter__( self ):
"""Support iteration over a view of self.
From bottom to top."""
while cursor < len( self ):
yield self._items[ cursor ]
def peek( self ):
"""Returns the items at top of the stack
Precondition: stack is not empty.
Raise: KeyError if stack is empty"""
if self.isEmpty():
raise KeyError( "The stack is empty." )
]
# Mutator method
def clear( self ):
"""Clear the stack."""
self._items = Array( ArrayStack.DEFAULT_CAPACITY )
def push( self, item ):
"""Push an item at the top of the stack"""
# Resize the array if necessary.
self.grow()
] = item
def pop( self ):
""" Returns and remove the item at the top of the stack.
precondition: the stack is not empty.
raise: raise KeyError if the stack is empty."""
if self.isEmpty():
raise KeyError( "The stack is empty." )
oldItem = self._items[ len(self) - 1 ]
# Resize the array if necessary.
self.shrink()
return oldItem
def grow( self ):
"""Grow the capacity of the array if necessary """
physicalSize = len( self._items )
if len( self ) >= physicalSize:
temp = Array( physicalSize * 2 )
for item in self:
temp[index] = item
self._items = temp
def shrink( self ):
"""Shrink the capacity of the array if necessary. """
physicalSize = len( self._items )
if len( self ) <= physicalSize // 4 and physicalSize >= 2 * ArrayStack.DEFAULT_CAPACITY:
temp = Array( physicalSize//2 )
for item in self:
temp[index] = item
self._items = temp
- 链表实现
- 在链表的头部实现压入和弹出操作
- 为了实现从底部向顶部遍历,需要使用迭代方法
- 代码
##!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
from abstractstack import AbstractStack
from node import Node
class LinkedStack( AbstractStack ):
"""An linked-based stack."""
def __init__( self, sourceCollection = None ):
"""Sets the initial state of self, which includes the contents
of sourceCollection, if it's present."""
self._items = None
AbstractStack.__init__( self, sourceCollection )
# Accessor method
def __iter__( self ):
"""Support iteration over a view of self.
From bottom to top."""
def visitNode( node ):
if node != None:
visitNode( node.next )
tempList.append( node.data )
tempList = list()
visitNode( self._items )
return( iter( tempList ) )
def peek( self ):
"""Returns the items at top of the stack
Precondition: stack is not empty.
Raise: KeyError if stack is empty"""
if self.isEmpty():
raise KeyError( "The stack is empty." )
return self._items.data
# Mutator method
def clear( self ):
"""Clear the stack."""
self._items = None
def push( self, item ):
"""Push an item at the top of the stack"""
# Resize the array if necessary.
self._items = Node( item, self._items )
def pop( self ):
""" Returns and remove the item at the top of the stack.
precondition: the stack is not empty.
raise: raise KeyError if the stack is empty."""
if self.isEmpty():
raise KeyError( "The stack is empty." )
oldItem = self._items.data
self._items = self._items.next
return oldItem
- AbstractStack 类的作用
- 定义 add 类,以避免修改AbstractCollection类
- 代码
##!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
"""
File name: abstractstack.py
"""
from abstractcollection import AbstractCollection
class AbstractStack( AbstractCollection ):
""" An abstract stack class """
#Constructor
def __init__( self, sourceCollection = None ):
"""Sets the initial state of self, which includes the contents
of sourceCollection, if it's present."""
AbstractCollection.__init__( self, sourceCollection )
# Mutator method
def add( self, item ):
"""Add item to self"""
self.push( item )
- 两种实现的时间和空间分析
- 时间性能
- 除了 __iter__ 方法,所有的栈方法的运行时间均不大于 O(1)
- 数组实现,在数组容量翻倍或者减半时,运行时间会增加到 O(n)
- 使用数组栈时,需要决定响应时间上的波动是否可以接受
- __iter__方法都是线性时间运行的
- 空间性能
- 链表实现使用了迭代,由于系统调用栈,从而导致内存线性增长
- 当数组的填充因子大于 1/2 时,数组的内存性能优于链表
- 案例学习:计算后缀表达式
- 要求
- 编写交互式程序,来计算后缀表达式
- 分析
- 用户交互
- 用户在提示符下输入一个表达式,程序显示结果。输入表达式时,限制在一行文本之内,标记之间可以有任意空白。用户按下Enter 或 Return键后,按照每个标记之间只有一个空格的形式输出表达式。并且在后面新的一行中,输出表达式的值,或者是错误信息加上当前运行状态。
- 可能包含的错误
- 表达式包含了太多的运算数
- 表达式包含的运算数不够
- 表达式包含了不识别的标志
- 的情况
- 设计
- 计算程序的交互图
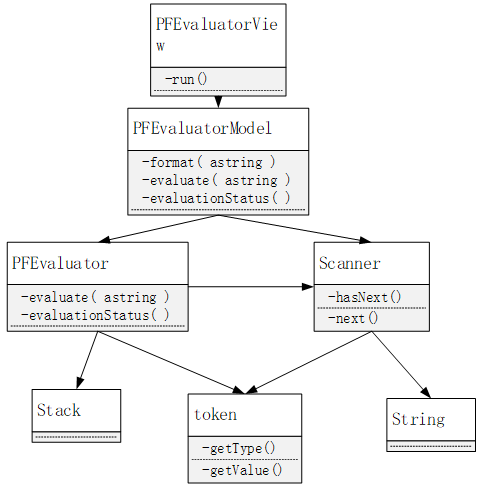
- PFEvaluatorView类的实例变量和方法
PFEvaluatorView()
Create and saves a reference to the model.
run()
while True:
Retrieve the expressions string from keyboard.
Send it to the model for fromating and print the format string.
Send it to the model for evaluation.
Either print the value or catch exceptions raised by the evaluator.
ask the model for the associated details, and display error.
messages.
- PFEvaluatorModel 类的实例变量和方法
- Model 模型需要与扫描程序和计算程序进行通信。
- 方法如下:
format( expressionStr ):
Instantiate a scanner on the expression string.
Build a response string by iterating acorss the scanner and appending a
string representation of each token to the response string.
Return the reponse string.
evaluate( expressionStr ):
Ask the evaluator to evaluate the expression string.
Return the value.
evaluationStatus():
Ask the evaluator for its status.
Return the status
- PFEvaluator 类的实例变量和方法
- 计算程序的属性包括一个栈,一个扫描程序和一个名为 expressionSoFar的字符串变量
- 方法:
PFEvaluator( scanner )
Intialize expressionSoFar
Instantiate an ArrayStack
Save a reference to the scanner
evaluate()
Iterate across the scanner and evaluate the expression.
Raise exception in the following situation:
The scanner is None or empty
There are too many operands
There are too few operands
There are unrecognizable tokens.
exception is raised by the PVM
evaluationStatus()
Return a multipart stirng that contains the portion of the expression
processed and the contents of the stack.
- Scanner 类的实例变量和方法
Scanner( sourceStr ):
Save a reference to the string that will be scanned and tokenized
hasNext()
Return True if the string contains another token and False otherwise.
next()
Return the next token. Raise an exception if hasnext() return False.
- Token 类的实例变量与方法
- Type定义
#unknow
#interger
#minus operator
#plus operator
#multiply operator
#divide operator
- 方法
Token( vlaue ):
Construct a new integer token with the specified value
Token(ch):
if ch is an operator( + - * / ), then construct a new operator token;
otherwise, construct a token of unknow type.
getType()
return a token's type
getValue()
return a token's value.
isOperator():
Return True if the token is an operator, and False Otherwise
__str__():
Retrun the token's numeric value as a string if the token is an
integer; otherwise, return the token's character representation.
数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第7章:栈的更多相关文章
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第10章:树
树的概览 树是层级式的集合 树中最顶端的节点叫做根 个或多个后继(子节点). 没有子节点的节点叫做叶子节点 拥有子节点的节点叫做内部节点 ,其子节点位于层级1,依次类推.一个空树的层级为 -1 树的术 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第5章:接口、实现和多态
接口 接口是软件资源用户可用的一组操作 接口中的内容是函数头和方法头,以及它们的文档 设计良好的软件系统会将接口与其实现分隔开来 多态 多态是在两个或多个类的实现中使用相同的运算符号.函数名或方法.多 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第9章:列表
概念 列表是一个线性的集合,允许用户在任意位置插入.删除.访问和替换元素 使用列表 基于索引的操作 基本操作 数组与列表的区别 数组是一种具体的数据结构,拥有基于单个的物理内存块的一种特定的,不变的实 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第8章:队列
队列概览 队列是线性的集合 队列的插入限制在队尾,删除限制在队头.支持先进先出协议( FIFIO, first-in first-out ) 两个基本操作 add:在队尾添加一项 pop:从队头弹出一 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第3章:搜索、排序和复杂度分析
评估算法的性能 评价标准 正确性 可读性和易维护性 运行时间性能 空间性能(内存) 度量算法的运行时间 示例 """ Print the running times fo ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第2章:集合概览
集合类型 定义 个或多个其他对象的对象.集合拥有访问对象.插入对象.删除对象.确定集合大小以及遍历或访问集合的对象的操作 分类 根据组织方式进行 线性集合 线性集合按照位置排列其项,除了第一项,每一项 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第4章:数据和链表结构
数据结构是表示一个集合中包含的数据的一个对象 数组数据结构 数组是一个数据结构 支持按照位置对某一项的随机访问,且这种访问的时间是常数 在创建数组时,给定了用于存储数据的位置的一个数目,并且数组的长度 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第11章:集和字典
使用集 集是没有特定顺序的项的一个集合,集中的项中唯一的 集上可以执行的操作 返回集中项的数目 测试集是否为空 向集中添加一项 从集中删除一项 测试给定的项是否在集中 获取两个集的并集 获取两个集的交 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第1章:Python编程基础
变量和赋值语句 在同一条赋值语句中可以引入多个变量 交换变量a 和b 的值 a,b = b,a Python换行可以使用转义字符\,下一行的缩进量相同 )\ 帮助文档 help() 控制语句 条件式语 ...
随机推荐
- JAVA常用知识总结(九)——线程
sleep和wait的区别? sleep()来自Thread类,和wait()来自Object类.调用sleep()方法的过程中,线程不会释放对象锁.而 调用 wait 方法线程会释放对象锁 slee ...
- html 手机端click 事件去掉黑色阴影效果
添加css样式 html{-webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%;-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);} 1. -web ...
- asp.net调试技巧
一眨眼的功夫,自己已经学习asp.net的有一年的功夫了.虽然称不上什么大神,但是也有一点知识的积累.就写一片调试的入门文章给那些刚刚入门迷茫的童鞋们.希望你学习了我这篇文章能从迷茫的生活中找回编程的 ...
- 单线程异步回调机制的缺陷与node的解决方案
一.node单线程异步的缺陷: 单线程异步的优点自然不必多说,node之所以能够如此快的兴起,其单线程异步回调机制相比于传统同步执行编程语言的优势便是原因之一.然而,开发一个node程序,其缺陷也是不 ...
- Sass基本特性
Sass扩展/继承@extend 代码的继承,声明方式:.class;调用方式:@extend 如: .btn { border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 6px 10px; ...
- Easyui combobox如何默认选中第一项???
以下代码可以实现combobox默认选中第一项,在实际开发中我们可能会用到! // 处理combobox默认选中的问题 <input id="user_type" class ...
- IOS之UIAlertController
你知道 UIAlertView.UIActionSheet (以及它们各自的 delegate protocols) 在 iOS 8 中已经被废弃了吗? 这是真的.在你的代码中按住 ⌘ 点击 UIAl ...
- 洛谷 P2617 Dynamic Ranking
题目描述 给定一个含有n个数的序列a[1],a[2],a[3]……a[n],程序必须回答这样的询问:对于给定的i,j,k,在a[i],a[i+1],a[i+2]……a[j]中第k小的数是多少(1≤k≤ ...
- 遍历PspCidTable枚举进程
//测试环境:win7 32位 1 // DriverEntry.cpp #include "ntddk.h" #include <ntddvol.h> #includ ...
- UVA 10003 cuting sticks 切木棍 (区间dp)
区间dp,切割dp[i][j]的花费和切法无关(无后效性) dp[i][j]表示区间i,j的花费,于是只要枚举切割方法就行了,区间就划分成更小的区间了.O(n^3) 四边形不等式尚待学习 #inclu ...
