Android布局之相对布局——RelativeLayout
此博文主要是相对布局xml属性的解析及实例。
android:layout_above:此控件底部的边缘位于设定ID控件的上方
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello "
android:layout_above="@+id/btn2" /> //<<<<------
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="world"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true" />
显示结果:

android:layout_below:此控件顶部的边缘位于设定ID控件的下方
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello " />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="world"
android:layout_below="@+id/btn1" //<<<<<<-------
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true" />
显示结果:
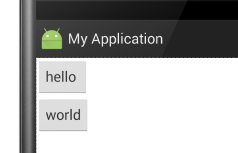
android:layout_alignBaseline:将此控件内容的基线与给定ID控件内容的基线对齐。
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello "
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="world"
android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/btn1" //<<<<<------
android:textSize="56sp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btn1"
此属性没加时显示效果:
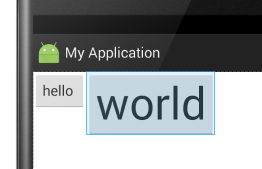
此属性加了之后的显示效果(此示例会超出布局,具体情况请自己多加练习):

android:layout_alignBottom:将此控件的底部边缘与给定ID的控件底部边缘对齐。
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello "
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="world"
android:textSize="34sp"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btn1" //<<<<----
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btn1" />
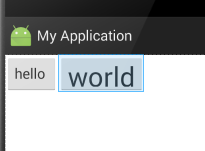
此属性没加时显示效果:
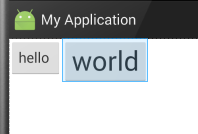
添加后显示的效果:
android:layout_alignEnd:将此控件与给定ID控件的末端对齐。以下的例子,很容易懂
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/button" //<<<<<--------
android:layout_below="@+id/button" />
此属性未添加时的显示结果:
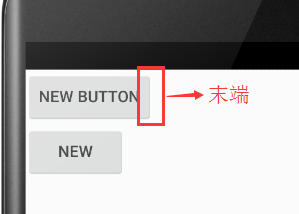
当添加此属性时的显示结果:

android:layout_alignLeft:将此控件的左边缘与给定ID控件的左边缘对齐
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button" //<<<<<------
android:layout_below="@+id/button" />
未添加此属性时显示效果:

添加此属性之后显示效果:
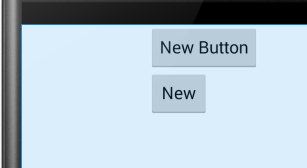
android:layout_alignParentBottom:如果设置为true,那么就将此控件的底部边缘与父容器的底部边缘匹配。
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" /> //<<<<<------
未添加此属性显示效果:

添加后:
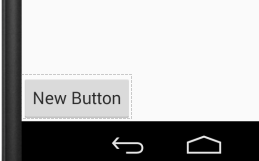
android:layout_alignParentEnd:如果设置为true,那么此控件的末边缘与父容器匹配
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true" /> //<<<<<<-------
未加此属性之前:

加了之后:
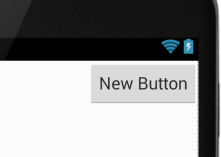
android:layout_alignParentLeft:如果设置为true,那么此控件的左边缘与父容器的左边缘匹配。这个属性可以用到的时候再用,这里可以参考layout_alignParentBottom属性,只是这个在左部而已。
android:layout_alignParentRight:如果设置为true,那么此控件的右边缘与父容器的右边缘匹配。此属性效果和 android:layout_alignParentEnd 属性效果差不多,显示效果参照 android:layout_alignParentEnd 的图
android:layout_alignParentStart:如果设置为true,那么此控件的开始边缘与父容器的开始边缘匹配。这个属性和android:layout_alignParentEnd 属性应该有别的用法,虽然在此例子中与left和right那两个属性显示效果差不多一样......
android:layout_alignParentTop:如果设置为true,那么此控件的顶部边缘与父容器的顶部边缘匹配。与layout_alignParentBottom相对。
android:layout_alignRight:将此控件的右边缘与给定ID控件的右边缘对齐。
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
android:layout_below="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/button"/> //<<<<<------
未添加此属性时显示的效果:

添加后:
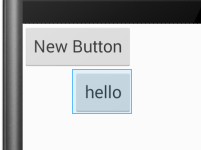
android:layout_alignStart:将此控件的开始边缘与给定ID控件的开始边缘对齐。和android:layout_alignLeft作用差不多感觉。
android:layout_alignTop:将此控件的顶部边缘与给定ID控件的顶部边缘对齐。
android:layout_toEndof:将此控件的开始边缘与给定ID控件的结束边缘对齐。
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
android:layout_below="@+id/button"
android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/button" /> //<<<<<<-----
未添加此属性时显示效果:
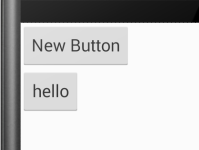
添加后显示效果:
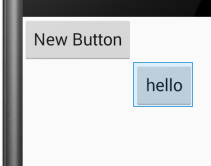
android:layout_toLeftof:将此控件的右边缘与给定ID控件的左边缘对齐。
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
android:layout_below="@+id/button"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/button"/> //<<<<<<------
未添加此属性时显示结果:

添加后显示结果:
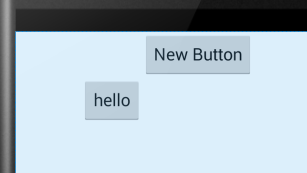
android:layout_toRightof:将此控件的左边缘与给定ID控件的右边缘对齐。
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
android:layout_below="@+id/button"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/button" /> //<<<<<<<-------
未添加显示效果:

添加后显示效果:

android:layout_toStartof:将此控件的末边缘与给定ID控件的开始边缘对齐。和android:layout_toLeftof属性的显示效果一样。
android:layout_centerHorizontal:如果设置为true,此控件将设置为水平居中
在这一条绿线上都是范围
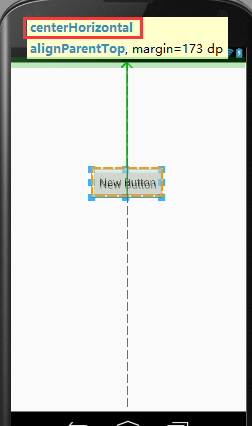
android:layout_centerVertical:如果设置为true,此控件将设置为垂直居中
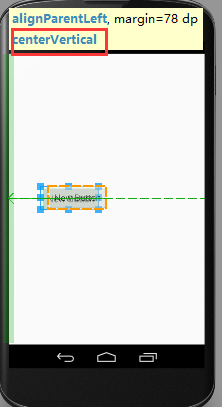
android:layout_centerInParent:如果设置为true,则此控件在他的父容器的中心位置。
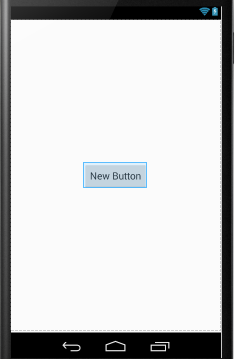
android:layout_alignWithParentIfMissing:如果设置为true,当控件的 layout_toLeftOf、layout_toRightOf、等等 属性找不到时,就以父元素作为参考。
------------------------------------------------------------------------
android:padding:指定控件中的内容与到此控件的四边缘的距离
android:layout_margin:设置此控件的四边缘与其他控件的距离
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:textSize="36sp"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_dark"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:padding="50dp" //<<<<<<-------
android:layout_alignParentStart="true" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="New Button"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:textSize="36sp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_dark"
android:layout_margin="20dip" //<<<<<<--------
android:layout_below="@+id/button" />
显示效果:

android:paddingBottom:设置控件内容与控件下边缘的距离
android:paddingTop:设置控件内容与控件上边缘的距离
android:paddingLeft:设置控件内容与控件左边缘的距离
android:paddingRight:设置控件内容与控件右边缘的距离
android:layout_marginBottom:设置此控件的下边缘与其他控件的距离
android:layout_marginTop:设置此控件的上边缘与其他控件的距离
android:layout_marginLeft:设置此控件的左边缘与其他控件的距离
android:layout_marginRight:设置此控件的右边缘与其他控件的距离
Android布局之相对布局——RelativeLayout的更多相关文章
- Android UI -- 布局介绍(布局包括FrameLayout, LinearLayout, RelativeLayout, GridLayout)
首先介绍常用布局类 FrameLayout 最简单的布局管理器. 这个布局管理类有几个特性: 添加组件默认在左上角的. 如果添加多个组件会叠加到一起,并且都在左上角.(可以通过一gravity属性改变 ...
- Android 自学之相对布局 RelativeLayout
相对布局(RelativeLayout),相对布局容器内子组件的位置总是相对兄弟组件.父容器来决定的. RelativeLayout的XML属性及相关方法说明 XML属性 相关方法 说明 androi ...
- .Net程序猿玩转Android开发---(7)相对布局RelativeLayout
相对布局RelativeLayout是Android布局中一个比較经常使用的控件,使用该控件能够布局出适合各种屏幕分辨率的布局,RelativeLayout採用相对位置进行 ...
- Android精通:TableLayout布局,GridLayout网格布局,FrameLayout帧布局,AbsoluteLayout绝对布局,RelativeLayout相对布局
在Android中提供了几个常用布局: LinearLayout线性布局 RelativeLayout相对布局 FrameLayout帧布局 AbsoluteLayout绝对布局 TableLayou ...
- [转]浅谈Android五大布局(二)——RelativeLayout和TableLayout
在浅谈Android五大布局(一)中已经描述了LinearLayout(线性布局).FrameLayout(单帧布局)和AbsoulteLayout(绝对布局)三种布局结构,剩下的两种布局Relati ...
- 浅谈Android样式开发之布局优化
引言 今天我们来谈一下Android中布局优化常用的一些手段.官方给出了3种优化方案,分别是</include>.</viewstub>.</merge>标签,下面 ...
- Android开发-之五大布局
在html中大家都知道布局是什么意思了,简单来说就是将页面划分模块,比如html中的div.table等.那么Android中也是这样的.Android五大布局让界面更加美化,开发起来也更加方便.当然 ...
- Android开发自学笔记(Android Studio)—4.1布局组件
一.引言 Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完成的,布局好比是建筑里的框架,而组件则相当于建筑里的砖瓦.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用户所看见的界面.在Android4.0之前,我们通常说 ...
- Android成长日记-五大布局
1. 五布局之线性布局LinearLayout 特点:它包含的子控件将以横向或竖向的方式排列 ps:android:gravity=”center|bottom”(gravity允许多级联用) Tip ...
- Android性能优化之布局优化
最新最准确内容建议直接访问原文:Android性能优化之布局优化 本文为Android性能优化的第二篇——布局优化,主要介绍使用抽象布局标签(include, viewstub, merge).去除不 ...
随机推荐
- 编译安装Apache:出现错误configure: error: mod_deflate
在进行编译安装Apache时,出现如下错误 checking whether to enable mod_deflate... configure: error: mod_deflate has be ...
- bryce1010专题训练——树状数组
Bryce1010模板 1.一维树状数组 https://vjudge.net/contest/239647#problem/A[HDU1556] #include<bits/stdc++.h& ...
- tsconfig.json No inputs were found in config file
Build:No inputs were found in config file '/tsconfig.json'. Specified 'include' paths were '["* ...
- 486 Predict the Winner 预测赢家
给定一个表示分数的非负整数数组. 玩家1从数组任意一端拿取一个分数,随后玩家2继续从剩余数组任意一端拿取分数,然后玩家1拿,…….每次一个玩家只能拿取一个分数,分数被拿取之后不再可取.直到没有剩余分数 ...
- 474 Ones and Zeroes 一和零
在计算机界中,我们总是追求用有限的资源获取最大的收益.现在,假设你分别支配着 m 个 0 和 n 个 1.另外,还有一个仅包含 0 和 1 字符串的数组.你的任务是使用给定的 m 个 0 和 n 个 ...
- 使用 Realm 和 Swift 创建 ToDo 应用
原文出处: HOSSAM GHAREEB 译文出处:Prayer’s blog(@EclipsePrayer) 智能手机的快速发展的同时,涌现出了很多对开发者友好的开发工具,这些工具不仅使得开发变 ...
- 看Facebook是如何优化React Native性能
原文出处: facebook 译文出处:@Siva海浪高 该文章翻译自Facebook官方博客,传送门 React Native 允许我们运用 React 和 Relay 提供的声明式的编程模型, ...
- props.children 和容器类组件
有一类组件,充当了容器的作用,它定义了一种外层结构形式,然后你可以往里面塞任意的内容.这种结构在实际当中非常常见,例如这种带卡片组件: 组件本身是一个不带任何内容的方形的容器,我可以在用这个组件的时候 ...
- Java-学完一个月总结(javaSe学习路线)
JavaSe的一个月 第一周 0410 基本数据类型:数据类型的转换:运算符:导入删除项目0411 分支结构if else:switch case ;while0412 do while ;for / ...
- expect下命令不能解析通配符*的问题
曾遇到这样一段代码:(Bash脚本) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #!/usr/bin/expect -f set HOST "192.168.102.1" ...
