ThinkJava-输入和输出
package com.java.io; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException; public class BufferedInputFile {
public static String read(String pathname) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(pathname)));
String s;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while((s = in.readLine())!=null){
sb.append(s + "\n") ;
}
in.close();
return sb.toString();
} public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.print(read("src/com/java/io/BufferedInputFile.java"));
}
}
console将当前的BufferedInputFile.java文件原封不动的打印出来;
package com.java.io; import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StringReader; public class MemoryInput {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
StringReader in = new StringReader(BufferedInputFile.read("src/com/java/io/MemoryInput.java"));
int c; //read是以int形式返回下一字节,因此必须类型转换为char才能正确打印。
//read()一个字符一个字符的读的。 Reads a single character.
while((c=in.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) c);
}
}
}
package com.java.io; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.EOFException;
import java.io.IOException; public class FormattedMemoryInput {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ try {
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(
new ByteArrayInputStream(
BufferedInputFile.read("src/com/java/io/FormattedMemoryInput.java").getBytes()));
while(true){
byte b = in.readByte();
System.out.print((char) b);
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
System.err.println("End of stream") ;
}
}
}
package com.java.io; import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException; public class TestEOF {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("src/com/java/io/TestEOF.java")));
while(in.available() != 0){
System.out.print((char)in.readByte());
} }
}
package com.java.io; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringReader; /**
* 一旦读完输入数据流, readLine()会返回null。
* 我们可以看到要为out显式调用c1ose.如果我们不为所有的输出文件调用close()
* 就会发现缓冲区内容不会被刷新清空 那么它们也就不完整。
*/
public class BasicFileOutput {
static String file = "BasicFileOutput.out";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new StringReader(
BufferedInputFile.read("src/com/java/io/BasicFileOutput.java")));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file))); int lineCount = 1;
String s;
while((s = in.readLine()) != null ){
out.println(lineCount++ + ": " + s);
}
out.close();
System.out.println(BufferedInputFile.read(file));
}
}
package com.java.io; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringReader; public class FileOutputShortcut {
static String file = "FileOutputShortcut.out";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new StringReader(BufferedInputFile.read("src/com/java/io/FileOutputShortcut.java")));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(file); int lineCount = 1;
String s;
while((s = in.readLine()) != null ){
out.println(lineCount++ + ": " + s);
}
out.close();
System.out.println(BufferedInputFile.read(file));
}
}
package com.java.io; import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException; public class StoringAndRecoveringData {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("Data.txt")));
out.writeDouble(3.14159);
out.writeUTF("That was pi");
out.writeDouble(1.41413);
out.writeUTF("Square root of 2");
out.close();
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("Data.txt")));
System.out.println(in.readDouble());
// Only readUTF() will recover the
// Java-UTF String properly:
System.out.println(in.readUTF());
System.out.println(in.readDouble());
System.out.println(in.readUTF());
}
}
package com.java.io; import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile; public class UsingRandomAccessFile {
static String file = "rtest.dat";
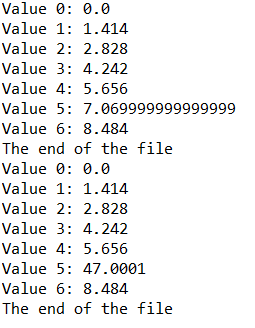
static void display() throws IOException {
//我们可指定以"只读"( r ) 方式或"读写" ( rw ) 方式打开一个RandomAccessFile文件。
RandomAccessFile rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
System.out.println("Value " + i + ": " + rf.readDouble());
}
System.out.println(rf.readUTF());
rf.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
rf.writeDouble(i*1.414);
}
rf.writeUTF("The end of the file");
rf.close();
display();
rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); //因为double总是8字节长,所以为了用Seek查找第5个双精度值,你只需用5*8来产生查找位置。
rf.seek(5*8);
rf.writeDouble(47.0001);
rf.close();
display();
}
}
// Static functions for reading and writing text files as
// a single string, and treating a file as an ArrayList.
package com.java.io; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.TreeSet; public class TextFile extends ArrayList<String> {
// Read a file as a single string:
public static String read(String fileName) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
BufferedReader in= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile()));
try {
String s;
while((s = in.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(s);
sb.append("\n");
}
} finally {
in.close();
}
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sb.toString();
} // Write a single file in one method call:
public static void write(String fileName, String text) {
try {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(
new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile());
try {
out.print(text);
} finally {
out.close();
}
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} public void write(String fileName) {
try {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(
new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile());
try {
for(String item : this)
out.println(item);
} finally {
out.close();
}
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} // Read a file, split by any regular expression:
public TextFile(String fileName, String splitter) {
super(Arrays.asList(read(fileName).split(splitter)));
// Regular expression split() often leaves an empty
// String at the first position:
if(get(0).equals("")){
remove(0);
}
} // Normally read by lines:
public TextFile(String fileName) {
this(fileName, "\n");
} public static void main(String[] args) {
String file = read("src/com/java/io/TextFile.java");
write("test.txt", file);
TextFile text = new TextFile("test.txt");
text.write("test2.txt"); // Break into unique sorted list of words:
//TreeSet是有序的set
//\\W+以非单词分割,得到的都是单词list,TextFile本身就是一个ArrayList,组成了TextFile;
//TreeSet的构造函数 TreeSet<集合>
TreeSet<String> words = new TreeSet<String>(new TextFile("src/com/java/io/TextFile.java", "\\W+")); // Display the capitalized words:
//打印出TreeSet中小于'a'的,就是打印出大写字母的
System.out.println(words.headSet("a"));
}
}
输出:
[0, ArrayList, Arrays, Break, BufferedReader, Display, File, FileReader, IOException, List, Normally, PrintWriter, Read, Regular, RuntimeException, Static, String, StringBuilder, System, TextFile, TreeSet, W, Write]
package com.java.io; import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException; public class BinaryFile {
public static byte[] read(File bFile) throws IOException{
BufferedInputStream bf = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(bFile));
try {
byte[] data = new byte[bf.available()];
bf.read(data);
return data;
} finally {
bf.close();
}
}
public static byte[] read(String bFile) throws IOException {
return read(new File(bFile).getAbsoluteFile());
}
}
read() : 从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节,返回0到255范围内的int字节值。如果因为已经到达流末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回-1。在输入数据可用、检测到流末尾或者抛出异常前,此方法一直阻塞。
read(byte[] b) : 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b 中。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。在输入数据可用、检测到文件末尾或者抛出异常前,此方法一直阻塞。
如果 b 的长度为 0,则不读取任何字节并返回 0;否则,尝试读取至少一个字节。如果因为流位于文件末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1;否则,至少读取一个字节并将其存储在 b 中。
将读取的第一个字节存储在元素 b[0] 中,下一个存储在 b[1] 中,依次类推。读取的字节数最多等于b 的长度。设 k 为实际读取的字节数;这些字节将存储在 b[0] 到 b[k-1] 的元素中,不影响 b[k] 到b[b.length-1] 的元素。 由帮助文档中的解释可知,read()方法每次只能读取一个字节,所以也只能读取由ASCII码范围内的一些字符。这些字符主要用于显示现代英语和其他西欧语言。而对于汉字等unicode中的字符则不能正常读取。只能以乱码的形式显示。
对于read()方法的上述缺点,在read(byte[] b)中则得到了解决,就拿汉字来举例,一个汉字占有两个字节,则可以把参数数组b定义为大小为2的数组即可正常读取汉字了。当然b也可以定义为更大,比如如果b=new byte[4]的话,则每次可以读取两个汉字字符了,但是需要注意的是,如果此处定义b 的大小为3或7等奇数,则对于全是汉字的一篇文档则不能全部正常读写了。
ThinkJava-输入和输出的更多相关文章
- 了解一下C++输入和输出的概念
我们经常用到的输入和输出,都是以终端为对象的,即从键盘输入数据,运行结果输出到显示器屏幕上.从操作系统的角度看,每一个与主机相连的输入输出设备都被看作一个文件.除了以终端为对象进行输入和输出外,还经常 ...
- [总结] I/O输入,输出
I/O输入,输出第一:先判断到底是输入还是输出,站在程序的立场第二:判断是传递字节,还是字符,决定管道粗细,字节流是最基本的数据输出管道.字符类型管道专门用来传送文本数据.Java流的四大父类:1.字 ...
- C#语言基础— 输入与输出
C#语言基础— 输入与输出 1.1函数的四要素:名称.输入.输出.加工 1.2主函数:输出语句.输入语句: Static viod Main(string[] stgs)//下划线部分可以自己指定 { ...
- Shell编程基础教程3--Shell输入与输出
3.Shell输入与输出 3.1.echo echo命令可以显示文本行或变量,或者把字符串输出到文件 echo [option] string ...
- 不可或缺 Windows Native (4) - C 语言: 预处理命令,输入,输出
[源码下载] 不可或缺 Windows Native (4) - C 语言: 预处理命令,输入,输出 作者:webabcd 介绍不可或缺 Windows Native 之 C 语言 预处理命令 输入 ...
- 输入和输出的总结(c语言)
c语言中有多种的输入和输出方式,下面就简单总结一下: 一.输入的三种方式 (1)scanf scanf 函数可以在变量中使用,也可以在数组中使用,当然指针上也能用到,是一个很好的输入函数.scanf是 ...
- C++——输入、输出和文件
一.C++输入和输出概述 1.1.流和缓冲区 C++程序把输入和输出看作字节流.输入时,程序从输入流中抽取字节:输出时,程序将字节插入到输出流中.对于面相文本的程序,每个字节代表一个字符,更通俗地说, ...
- C++学习42 输入和输出的概念
我们经常用到的输入和输出,都是以终端为对象的,即从键盘输入数据,运行结果输出到显示器屏幕上.从操作系统的角度看,每一个与主机相连的输入输出设备都被看作一个文件.除了以终端为对象进行输入和输出外,还经常 ...
- C++:文件的输入和输出
1.共同的打开文件方式: fin.open("test.txt",ios::binary) fout.open("test.txt",ios::binary) ...
- YTU 2609: A改错题--学生信息的输入和输出
2609: A改错题--学生信息的输入和输出 时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB 提交: 238 解决: 157 题目描述 注:本题只需要提交标记为修改部分之间的代码,请按照C++方 ...
随机推荐
- perl模块终极解决方案--转载
不管别人怎么说,反正我是非常喜欢perl语言的! 也会继续学习,以前写过不少perl模块的博客,发现有点乱,正好最近看到了关于local::lib这个模块. 居然是用来解决没有root权限的用户安装, ...
- python学习笔记(自定义库文件路径)
博主最近在弄接口自动化.主要是基于python自带的unittest框架.包括 Pubilc模块定义所有接口. Main模块根据业务需求重新封装接口便于测试. config文件导入测试业务的固定参数. ...
- Java 数组如何转成List集合
问题描述:对于给定的如下数组,如何转换成List集合? String[] array = {"a","b","c"}; 参考stackove ...
- PHP-----------HTTP请求的第三方接口
开发中常常遇到接口请求这个功能,后台也不例外,因为遇到了,所以写一篇. 前段时间做商城后台时,需要用到第三方物流接口查询物流信息. post: /**** * @param $url * @param ...
- Android之自定义控件实现天气温度折线图和饼状图
以前写了个天气的APP,最近把他更新了一个版本,就抽取其中的天气温度折现图这个功能写了这篇博客,来与大家分享,希望对你有所帮助. 效果如图: 代码: MainActivity.Java /**** * ...
- IOS-网络(文件压缩和解压缩)
// // ViewController.m // IOS_0206_文件上传 // // Created by ma c on 16/2/6. // Copyright © 2016年 博文科技. ...
- 第一个mpvue小程序开发总结
前言 说起小程序,其实在去年我都还只试着照着官方文档写过demo的,不过现在这家公司小程序做得比较多,我来之后也参与了几个小程序的开发了,最开始那几个是用的wepy,最近一个开始转用mpvue开发,最 ...
- @Column实体类中的使用(二十三)
- laravel中数据库迁移的使用:
创建数据库迁移文件: php artisan make:migration create_links_table 创建完表之后,设置字段: public function up() { Schema: ...
- RGB2YCbCr RGB2Gray
Y = 0.2990R+0.5870G+0.1140B; Cb=-0.1687R-0.3313G+0.5000B+128; ...
