HandlerMapping 详解
HandlerMapping 详解
1. 导言
万丈高楼平地起,SpringMVC的辉煌离不开每个组件的相互协作,上一章详细阐述了SpringMVC整个体系结构及实现原理,知道HandlerMapping在这个SpringMVC体系结构中有着举足轻重的地位,充当着url和Controller之间映射关系配置的角色。主要有三部分组成:HandlerMapping映射注册、根据url获取对应的处理器、拦截器注册。本文将立足于RequestMappingHandlerMapping详细阐述HandlerMapping的整个体系。其结构如图所示。
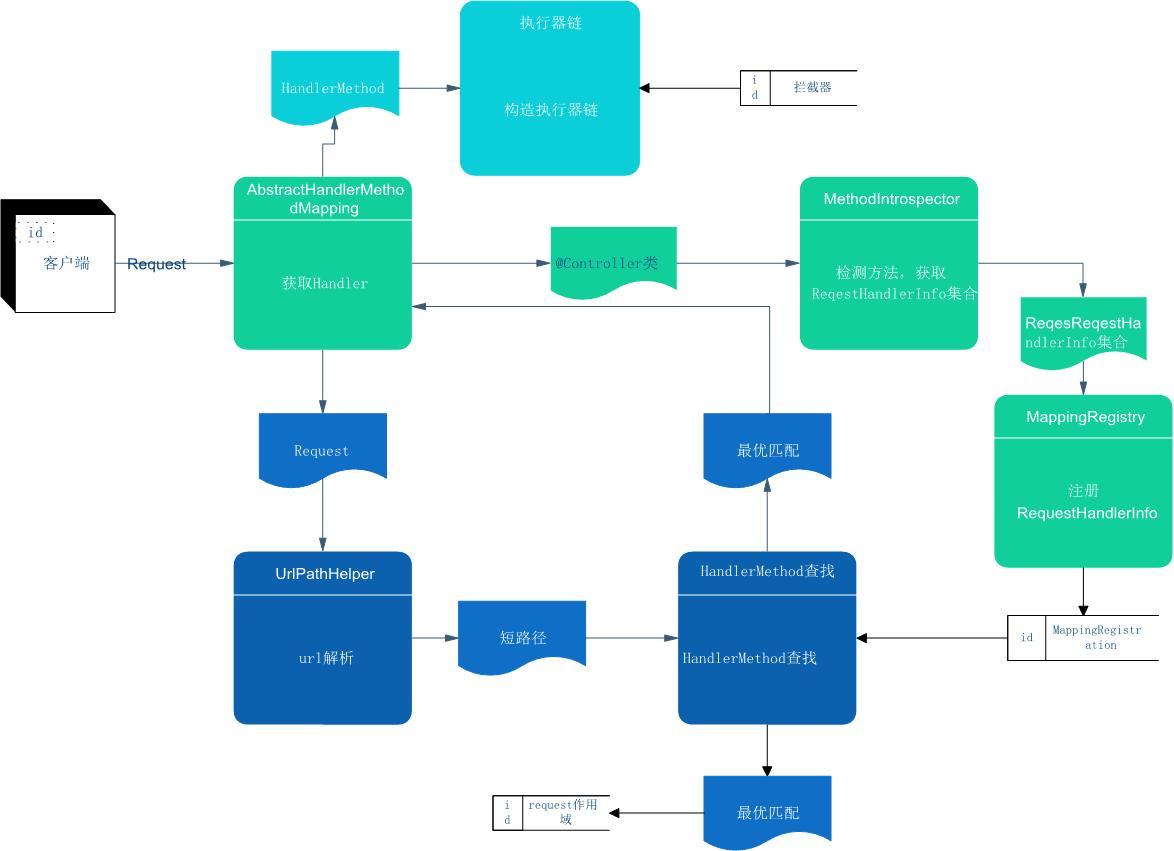
笔者可以以不同颜色表示三大主要过程,下面笔者将逐步分析RequestMappingHandlerMapping的整个体系。
2. 检测方法,构造RequestHandlerInfo映射集合
- AbstractHandlerMethodMapping一个并不陌生的方法,afterPropertiesSet()
注意AbstractHandlerMethodMapping继承自InitializingBean,会在Bean初始化完成后调用afterPropertiesSet()方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
initHandlerMethods的实现如下图所示:

判断beanType是否是满足要求的handler和检测并生存handlerMethod是最为关键的两个过程。其中判断是否满足要求的handler,实现如下:
protected abstract boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType);
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
注意到,isHandler方法是一个抽象方法,在父类不能确定如何实现,这边将具体的实现交子类来进行,在 RequestMappingHandlerMapping中的实现为只要有@Controller注解或者@RequestMapping注解的均为满足要求的handler。
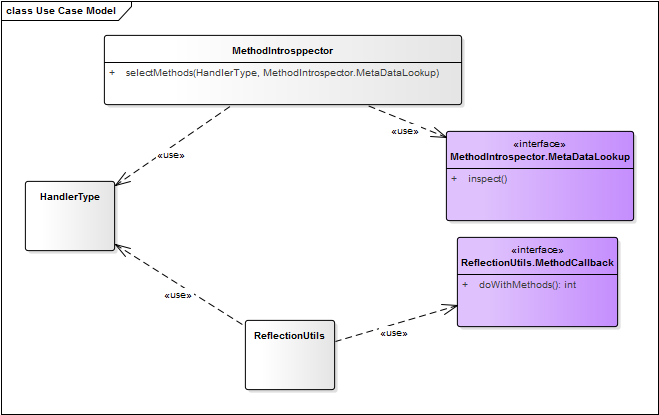
检测HandlerMethods是在detectHandlerMethods方法中实现的,其几个关键的类、接口及方法实现如图所示:
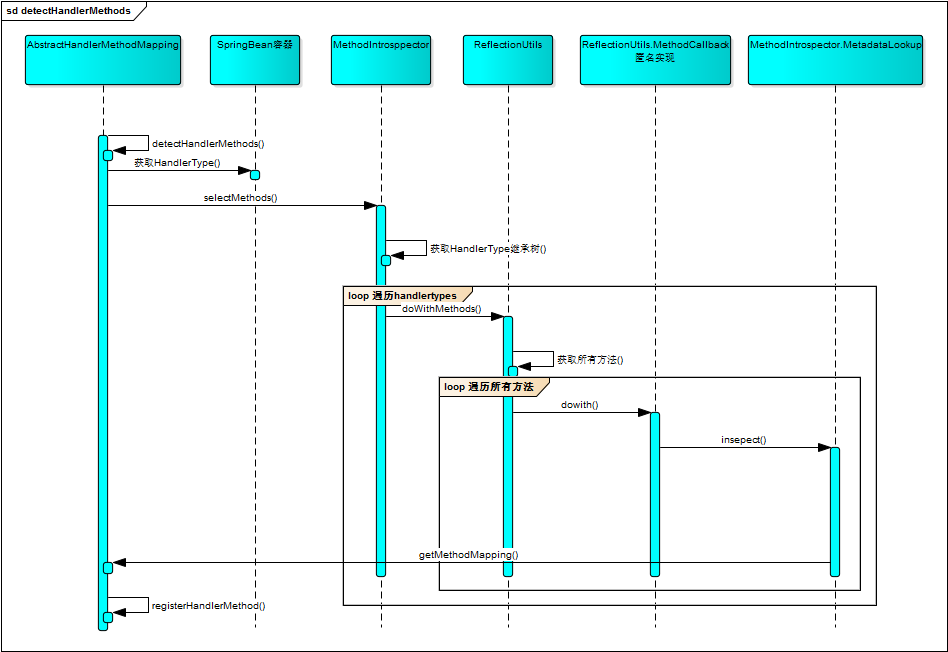
detectHandlerMethods的实现序列图如图所示
- what?selectMethods感觉好凌乱,这么复杂,是否有跟笔者一样的想法?
selectMethods其实是两个命令模式的变体的叠加。笔者看来每个设计模式都有多种变体,重要的是理解每个设计模式解决的问题。命令模式的主要目的是为了将触发和命令的具体实现解耦,以实现触发命令操作和具体的命令的实现相互隔离。当命令触发时,命令对象就会执行操作,这是java事件的处理方式。java中典型的命令模式,就是多线程的start方法和Runnable的run方法,相信读者并不会陌生。
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
log.info("简单的测试");
}
});
...
thread.start();
首先传入一个命令对象,这个命令(run方法)并不会立马执行,会在事件触发后才会调用命令(start方法),但在什么时候触发事件,在传入命令对象的时候,我们并不关心,也没办法知道如何触发事件。
简单解释了命令模式,解决的问题,现在回到主题,selectMethods是怎么实现的?
第一个命令模式:
public interface MetadataLookup<T> {
/**
* Perform a lookup on the given method and return associated metadata, if any.
* @param method the method to inspect
* @return non-null metadata to be associated with a method if there is a match,
* or {@code null} for no match
*/
T inspect(Method method);
}
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>() {
@Override
public T inspect(Method method) {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
}
});
传入一个命令,MetadataLookup的实现,在selectMethods方法内部会调用对象的inspect方法。(实际上是在第二命令中调用的这个命令)。
第二个命令模式:
public interface MethodCallback {
/**
* Perform an operation using the given method.
* @param method the method to operate on
*/
void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException;
}
for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) {
final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType);
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Method method) {
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
if (result != null) {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
}
传入一个命令,MethodCallback的实现,在doWithMethods方法内部会调用对象的dowith方法方法。
- 再谈selectMethods实现
第一个命令模式,即selectMethods方法中,
(1)首先选择所有HandlerType的所有继承体系的所有class:
final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<Method, T>();
Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>();
Class<?> specificHandlerType = null;
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {
handlerTypes.add(targetType);
specificHandlerType = targetType;
}
handlerTypes.addAll(Arrays.asList(targetType.getInterfaces()));
(2)遍历每一个handlerType
(3)选择每一个满足要求的方法,执行dowith方法
public static void doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc, MethodFilter mf) {
// Keep backing up the inheritance hierarchy.
Method[] methods = getDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (mf != null && !mf.matches(method)) {
continue;
}
try {
mc.doWith(method);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Not allowed to access method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex);
}
}
if (clazz.getSuperclass() != null) {
doWithMethods(clazz.getSuperclass(), mc, mf);
}
else if (clazz.isInterface()) {
for (Class<?> superIfc : clazz.getInterfaces()) {
doWithMethods(superIfc, mc, mf);
}
}
}
public static final MethodFilter USER_DECLARED_METHODS = new MethodFilter() {
//只选择用户定义的方法,Object方法和代理方法不满则需求
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method) {
return (!method.isBridge() && method.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class);
}
};
(4)针对每一个method调用metadataLookup的dowith方法,以{method,result}的形式缓存:
public void doWith(Method method) {
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
if (result != null) {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}
(5)重头戏,inspect方法
public T inspect(Method method) {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
}
其关键之关键为getMappingForMethod,首先会读取方法上的@RequestMapping注解,然今读取类上面的注解,最后进行联合操作。
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
(6)注册RequestMappingInfo
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
T mapping = entry.getValue();
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
registerHandlerMethod会调用MappingRegistry的registry方法,其实现流程如图所示
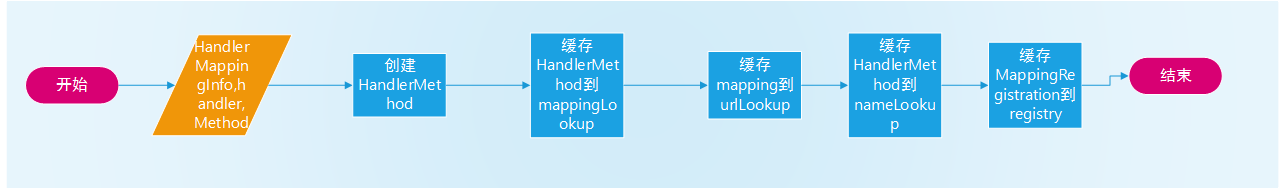
这个过程主要针对HandlerMethod做了一些缓存,方便查询,根据url,name,mapping均做了相应缓存,主要是为了优化查询handlerMethod的性能。
3. getHandler方法,获取执行器链。
- 获取执行器链入口:
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler map [" + hm + "] DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
遍历配置的handlerMappings,依次调用getHandler方法,只要找到满足要求的handlerMapping,立马返回。
- HandlerMapping的getHandler方法:
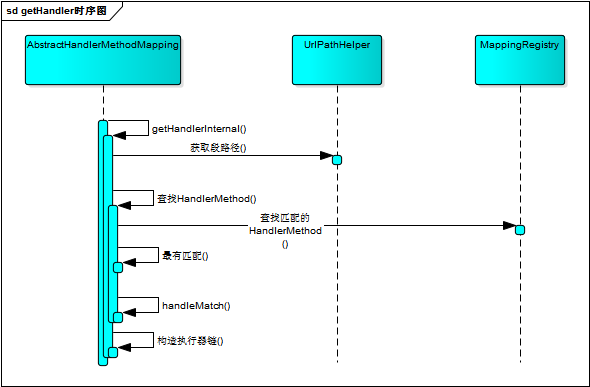
查找到匹配项后,handlerMethod做一些处理,RequestHandlerMethodMapping是会将相关内容缓存在request域中,当然,使用的时候也可以定制一些内容。笔者猜想,这些都是为了性能提升而努力的,毕竟性能提升在每一小步。
构造执行器链,执行器链中包含HandlerMethod和相关拦截器,同时包含有跨域的解决方案。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
4. 再谈拦截器
从上一节的代码可以看出,拦截器至少包含两种,实现MappedInterceptor和实现普通HandlerInterceptor接口的类。
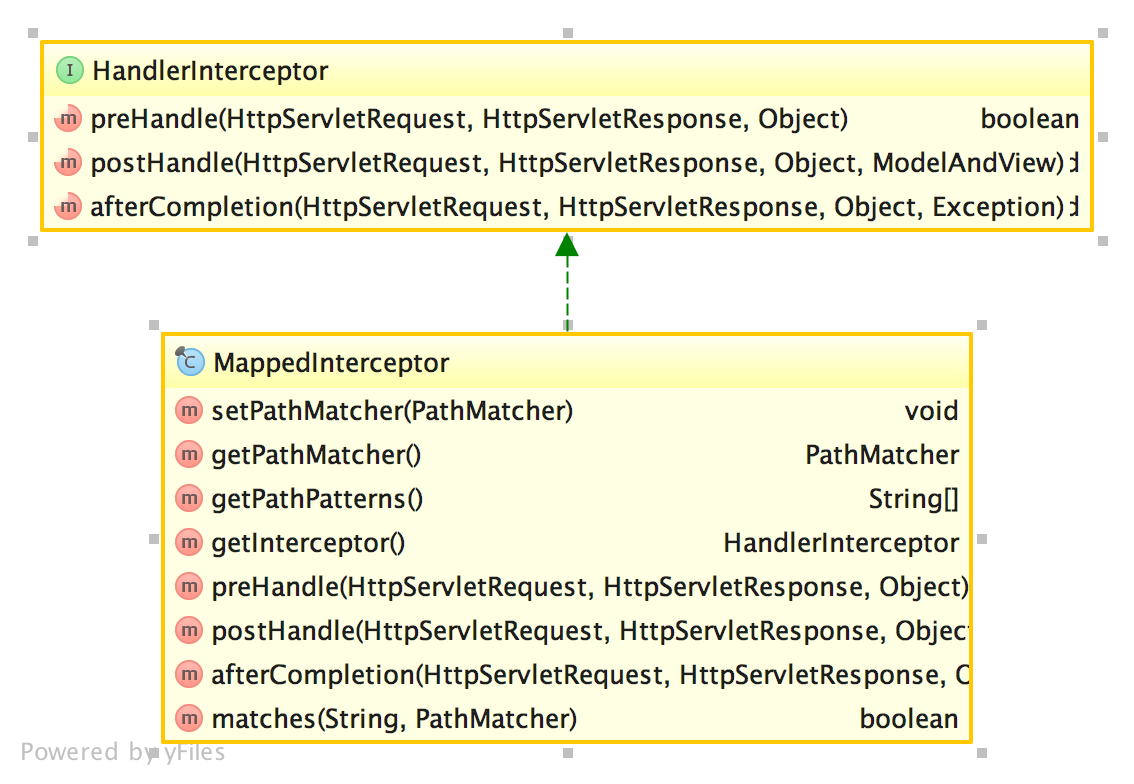
普通handler接口,会直接加入到拦截器链中,而MappedInterceptor则只会加入matches方法返回true的拦截器。
至此HandlerMapping已分析完毕,SpringMVC的其它内容也将陆续推出。
HandlerMapping 详解的更多相关文章
- Web.xml详解(转)
这篇文章主要是综合网上关于web.xml的一些介绍,希望对大家有所帮助,也欢迎大家一起讨论. ---题记 一. Web.xml详解: (一) web.xml加载过程(步骤) 首 ...
- Spring MVC 学习总结(二)——控制器定义与@RequestMapping详解
一.控制器定义 控制器提供访问应用程序的行为,通常通过服务接口定义或注解定义两种方法实现. 控制器解析用户的请求并将其转换为一个模型.在Spring MVC中一个控制器可以包含多个Action(动作. ...
- EndPoint详解
EndPoint详解 EndPoint主要用于暴露一些SpringMvc内部运行的信息,通常是通过SpringMvc的请求地址获取相关信息.如/health获取健康检查信息. 简单单元测试 @Test ...
- 详解SpringMVC请求的时候是如何找到正确的Controller
详解SpringMVC请求的时候是如何找到正确的Controller[附带源码分析] 目录 前言 源码分析 重要接口介绍 SpringMVC初始化的时候做了什么 HandlerExecutionCha ...
- Spring详解(一)------概述
本系列教程我们将对 Spring 进行详解的介绍,相信你在看完后一定能够有所收获. 1.什么是 Spring ? Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开 ...
- SpringMVC 框架系列之组件概述与配置详解
在上一篇文章 SpringMVC 框架系列之初识与入门实例 的实例中,我们已经知道,SpringMVC 框架是一个 web 层的框架,本篇文章就详细解释一下 SpringMVC 框架具体文件的配置以及 ...
- Spring详解
https://gitee.com/xiaomosheng888老师的码云 1.核心容器:核心容器提供 Spring 框架的基本功能(Spring Core).核心容器的主要组件是 BeanFacto ...
- web.xml的加载过程配置详解
一:web.xml加载过程 简单说一下,web.xml的加载过程.当我们启动一个WEB项目容器时,容器包括(JBoss,Tomcat等).首先会去读取web.xml配置文件里的配置,当这一步骤没有 ...
- 第5章—构建Spring Web应用程序—SpringMVC详解
SpringMVC详解 5.1.跟踪Springmvc的请求 SpringMVC的核心流程如下: 具体步骤: 第一步:发起请求到前端控制器(DispatcherServlet) 第二步:前端控制器请求 ...
随机推荐
- php 图片处理类
<?php /** * 图片类 * @author <420012223@qq.cn> */ class Image { public $uploadImagePath = './t ...
- Spring+MyBatis多数据源配置实现
最近用到了MyBatis配置多数据源,原以为简单配置下就行了,实际操作后发现还是要费些事的,这里记录下,以作备忘 不多废话,直接上代码,后面会有简单的实现介绍 jdbc和log4j的配置 #定义输出格 ...
- 去掉UItableview headerview黏性(sticky)
// 去掉UItableview headerview黏性(sticky) - (void)scrollViewDidScroll:(UIScrollView *)scrollView { CGFlo ...
- PHP类中私有方法的内部引用
以前习惯了美工和前端开发,现在进阶后端,开始学习PHP,在学习类的时候,碰到了一个私有方法调用的问题. 代码如下: <?php class Person { public function sa ...
- iOS模拟各种网络状态
在iOS开发中我们有在各种不同网络状态下测试app运行状态的需求.苹果给我们提供了在模拟器和真机状态下,模拟各种网络状态的软件. 在模拟器中 苹果提供的模拟网络状态的工具官网地址下载该工具需要登录Ap ...
- Spring+Struts2/Hibernate 学习笔记
============Spring与Struts2整合============ (1)拷JAR包(Spring.Struts2) (2)配置org.springframework.web.conte ...
- vb.net下载代码
'后台 Partial Public Class Download2 Inherits System.Web.UI.Page Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender ...
- DevExpress组件之——PopupMenu组件(转)
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/xlx0210/archive/2010/07/14/1777366.html 目录在项目中使用了第三方控件DevExpress,得开始研究其他控件 ...
- hibernate的五大接口
Hibernate有五大核心接口,分别是:Session Transaction Query SessionFactoryConfiguration .这五个接口构成了Hibernate运行的基本要素 ...
- 以太网客户端提示windows系统自带共享代理解决方法
以太网客户端(Dr.COM)登陆出现windows系统自带共享代理,如下图: 系统win+R调出运行: 在服务中,找到Internet Connection Sharing (ICS): 右键属性,将 ...
