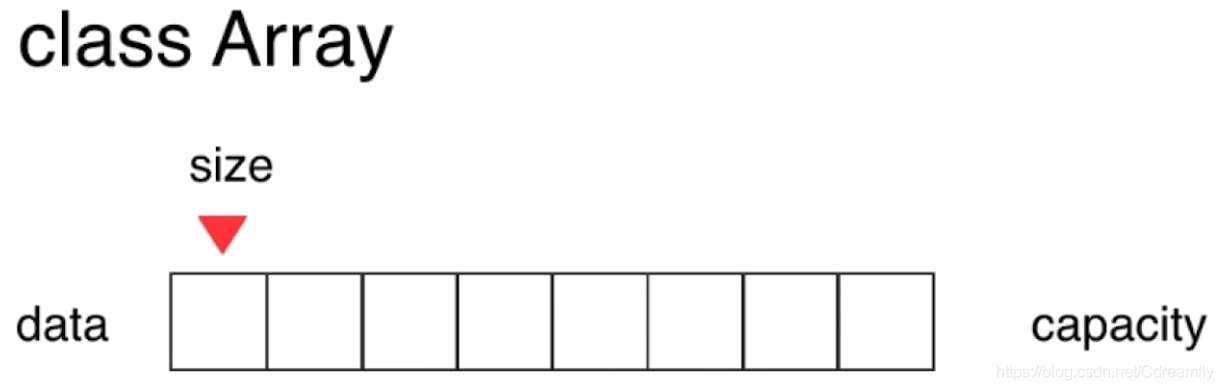
动态数组(Array)
Array
- 存储具有一对一逻辑关系数据的存储顺序结构。
- 数组最大的优点:快速查询,最好应用于索引有语义的情况。
插入元素
template<typename T>
bool Array<T>::add(const int index, const T& e)
{
if (index<0 || index>size)return false; //判断索引是否正确
if (size == capacity)resize(1.5 * capacity); //判断空间是否足够,不够扩容为当前的2倍
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; --i) //从后向前循环
{
data[i + 1] = data[i]; //全部元素向后移一位
}
data[index] = e; //插入元素
++size; //数组元素的个数+1
return true;
}
扩容与缩减
template<typename T>
void Array<T>::resize(const int newcapacity)
{
T* newdata = new T[newcapacity]; //创建新的传入大小数组空间
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) //把原本的数组元素放入新的数组空间
{
newdata[i] = data[i];
}
delete[] data; //释放原数组的空间
data = newdata; //把原本的数组指向新的数组
newData = nullptr;
capacity = newcapacity; //新的空间大小给原本的空间大小
}
删除元素
template<typename T>
T Array<T>::remove(const int index)
{
if (index<0 || index>size)return -1; //判断索引是否正确
T ret = data[index]; //保存临时元素
for (int i = index + 1; i < size; ++i)
{
data[i - 1] = data[i]; //从要插入的元素后一位所有元素向前移一位
}
--size; //元素个数-1
if (size == capacity / 4 && capacity / 2 != 0) //判断元素个数是否为数组容量的1/4并且数组空间不为0
{
resize(capacity / 2); //调用resize传入当前容量的一半
}
return ret; //返回被删除的元素
}
时间复杂度

均摊复杂度
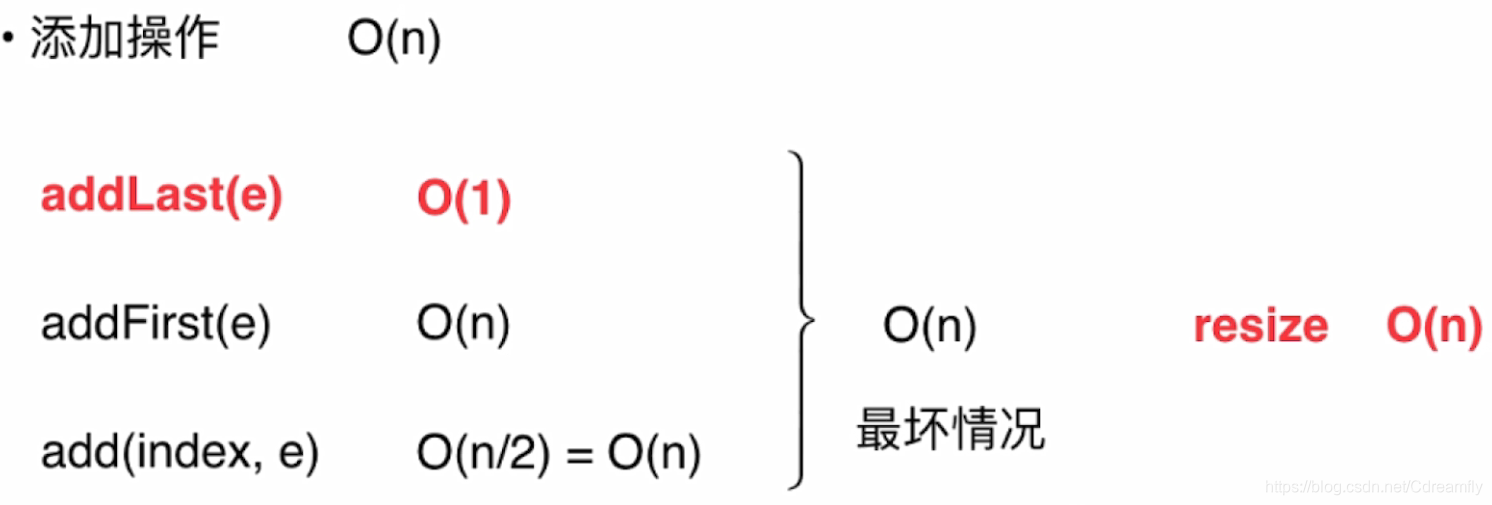

9次addLast操作,触发resize,总共进行了17次基本操作,平均每次addLast操作,进行2次基本操作。
假设capacity = n,n+1次addLast,触发resize,总共进行2n+1次基本操作,平均每次addLast操作进行2次基本操作。
这样均摊计算时间复杂度是O(1),同理removeLast操作,均摊复杂度也为O(1)。
代码清单
Array.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
template<typename T>
class Array
{
public:
//无参构造
Array() :size(0), capacity(10)
{
data = new T[10]; //默认初始化10个空间
}
//有参构造
Array(int capacity) :size(0), capacity(capacity)
{
data = new T[capacity];
}
//返回元素个数
int getSize()const;
//返回数组容量
int getCapacity()const;
//返回第一个元素
T getFirst();
//返回最后一个元素
T getLast();
//判断是否为空
bool isEmpty()const;
//插入元素
bool add(const int index, const T& e);
//头插
bool addFirst(const T& e);
//尾插
bool addLast(const T& e);
//查找数组中是否存在该元素
bool contains(const T& e)const;
//查找数组中元素的索引,不存在返回-1
int find(const T& e)const;
//删除索引元素,返回删除元素
T remove(const int index);
//删除头,返回头
T removeFirst();
//删除尾,返回尾
T removeLast();
//设置索引值
bool set(const int index, const T& e);
//获取索引值
T get(const int index)const;
//打印元素
void print()const;
//释放空间
~Array();
public:
void swap(const int i, const int j) {
if (i < 0 || i >= size || j < 0 || j >= size) {
throw Range();
}
T t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
Array(T arr[], const int n) : size(n), capacity(n) {
data = new T[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
data[i] = arr[i];
}
}
private:
void resize(const int newcapacity); //重新分配空间
T* data;
int size; //数组大小
int capacity; //数组容量
};
template<typename T>
int Array<T>::getSize() const
{
return size; //返回数组长度
}
template<typename T>
int Array<T>::getCapacity() const
{
return capacity; //返回数组容量
}
template<typename T>
inline T Array<T>::getFirst()
{
return get(0);
}
template<typename T>
inline T Array<T>::getLast()
{
return get(size - 1);
}
template<typename T>
bool Array<T>::isEmpty() const
{
return size == 0; //判断是否为空,
}
template<typename T>
bool Array<T>::add(const int index, const T& e)
{
if (index<0 || index>size)return false; //判断索引是否正确
if (size == capacity)resize(2 * capacity); //判断空间是否足够,不够扩容为当前的2倍
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; --i) //从后向前循环
{
data[i + 1] = data[i]; //全部元素向后移一位
}
data[index] = e; //插入元素
++size; //数组元素的个数+1
return true;
}
template<typename T>
bool Array<T>::addFirst(const T& e)
{
return add(0, e); //调用add从0号索引元素插入
}
template<typename T>
bool Array<T>::addLast(const T& e)
{
return add(size, e); //调用add从size号索引元素插入
}
template<typename T>
bool Array<T>::contains(const T& e) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) //遍历是否有查找的元素
{
if (data[i] == e)return true;
}
return false;
}
template<typename T>
int Array<T>::find(const T& e) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) //遍历是否有查找的元素,有返回索引,无返回-1
{
if (data[i] == e)return i;
}
return -1;
}
template<typename T>
T Array<T>::remove(const int index)
{
if (index<0 || index>size)return -1; //判断索引是否正确
T ret = data[index]; //保存临时元素
for (int i = index + 1; i < size; ++i)
{
data[i - 1] = data[i]; //从要插入的元素后一位所有元素向前移一位
}
--size; //元素个数-1
if (size == capacity / 4 && capacity / 2 != 0) //判断元素个数是否为数组容量的1/4并且数组空间不为0
{
resize(capacity / 2); //调用resize传入当前容量的一半
}
return ret; //返回被删除的元素
}
template<typename T>
T Array<T>::removeFirst()
{
return remove(0); //删除0号索引元素
}
template<typename T>
T Array<T>::removeLast()
{
return remove(size - 1); //删除size-1号索引元素
}
template<typename T>
bool Array<T>::set(const int index, const T& e)
{
if (index<0 || index>size)return false; //判断索引元素是否正确
data[index] = e; //设置索引的新元素
return true;
}
template<typename T>
T Array<T>::get(const int index) const
{
if (index<0 || index>size)return -1; //判断索引元素是否正确
return data[index]; //返回索引元素
}
template<typename T>
void Array<T>::print() const
{
std::cout << "Array:size = " << size << " Array:capacity = " << capacity << std::endl;
std::cout << "Array:data = " << "[";
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
std::cout << data[i] << ",";
}
std::cout << "]" << std::endl;
}
template<typename T>
Array<T>::~Array()
{
delete[] data; //释放空间
data = nullptr;
}
template<typename T>
void Array<T>::resize(const int newcapacity)
{
T* newdata = new T[newcapacity]; //创建新的传入大小数组空间
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) //把原本的数组元素放入新的数组空间
{
newdata[i] = data[i];
}
delete[] data; //释放原数组的空间
data = newdata; //把原本的数组指向新的数组
newData = nullptr;
capacity = newcapacity; //新的空间大小给原本的空间大小
}
main.cpp
#include"Array.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Array<int>* arr = new Array<int>(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
arr->addLast(i);
}
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->add(1, 1)" << arr->add(1, 1) << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->addLast(0) " << arr->addLast(0) << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->addFirst(0)" << arr->addFirst(0) << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->contains(0)" << arr->contains(0) << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->find(0)" << arr->find(0) << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->get(1)" << arr->get(1) << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->set(0, 5)" << arr->set(0, 5) << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->getCapacity()" << arr->getCapacity() << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->getSize()" << arr->getSize() << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->isEmpty()" << arr->isEmpty() << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->remove(1)" << arr->remove(1) << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->removeFirst()" << arr->removeFirst() << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->removeLast()" << arr->removeLast() << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->getFirst" << arr->getFirst() << endl;
arr->print();
cout << endl;
cout << "arr->getLast" << arr->getLast() << endl;
arr->print();
delete arr;
return 0;
}
动态数组(Array)的更多相关文章
- python数据结构之动态数组
数组列表:动态数组(Array List) 简介: 最基础简单的数据结构.最大的优点就是支持随机访问(O(1)),但是增加和删除操作效率就低一些(平均时间复杂度O(n)) 动态数组也称数组列表,在py ...
- array of TVarRec 动态数组使用
FDQuery.AppendRecord()里是一个array of TVarRec.我们一般都是直接用[Var1,Var2,...].这样手工输入,但如果增加的元素我们预先不知道,就要声明一个arr ...
- 封装动态数组类Array
功能: 1.增.删.改.查 2.扩容.缩容 3.复杂度分析 4.均摊复杂度 5.复杂度震荡 分析动态数组的时间复杂度: 分析resize的时间复杂度: public class Array<E& ...
- DelphiXe 中静态数组TByteArray和动态数组TBytes /array of byte 的区别
在应用中发现静态数组和动态数组是有区别的: procedure TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject);var RsltStream: TMemoryStream; ...
- 常用数据结构-线性表及Java 动态数组 深究
[Java心得总结六]Java容器中——Collection在前面自己总结的一篇博文中对Collection的框架结构做了整理,这里深究一下Java中list的实现方式 1.动态数组 In compu ...
- Java ArrayList和Vector、LinkedList与ArrayList、数组(Array)和列表集合(ArrayList)的区别
ArrayList和Vector的区别ArrayList与Vector主要从二方面来说. 一.同步性: Vector是线程安全的,也就是说是同步的,而ArrayList是线程序不安全的,不是同步 ...
- javascript类型系统——数组array
× 目录 [1]创建 [2]本质 [3]稀疏[4]长度[5]遍历[6]类数组 前面的话 除了对象之外,数组Array类型可能是javascript中最常用的类型了.而且,javascript中的数组与 ...
- C#中数组Array、ArrayList、泛型List<T>的比较
在C#中数组Array,ArrayList,泛型List都能够存储一组对象,但是在开发中根本不知道用哪个性能最高,下面我们慢慢分析分析. 一.数组Array 数组是一个存储相同类型元素的固定大小的顺序 ...
- delphi动态数组指针问题
就一个button事件 procedure TForm1.btn7Click(Sender: TObject); Type TMyArr = array of array of array of In ...
- JS 索引数组、关联数组和静态数组、动态数组
JS 索引数组.关联数组和静态数组.动态数组 数组分类: 1.从数组的下标分为索引数组.关联数组 var ary1 = [1,3,5,8]; //按索引去取数组元素,从0开始(当然某些语言实现从1开始 ...
随机推荐
- SpringBoot的自动装配原理及应用
什么是SpringBoot自动装配 所谓的"SpringBoot自动装配"就是指:通过注解和一些简单的配置就能将某些组件载入Spring容器环境中,便于使用. 比如,很多sprin ...
- 在Hexo中引入本地图片的实现
实现步骤 第一步:修改项目根目录下的_config.yml文件参数post_asset_folder值为true. # 开始使用本地静态资源 post_asset_folder: true 第二步:安 ...
- Google Chrome 开启多下载下载,提高文件下载速度
在地址栏输入: chrome://flags/#enable-parallel-downloading Parallel downloading改为Enabled后重启浏览器即可打开多线程下载 (多线 ...
- 【LeetCode哈希表#3】快乐数(set)
快乐数 力扣题目链接(opens new window) 编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数. 「快乐数」定义为:对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和,然后重复这个过程 ...
- require和import的区别以及相互使用的方式
Node.js 里可分为 CommonJS 模块和 ECMAScript 模块(ESM)两种不同的模块系统. CommonJS 模块是 Node.js 最初支持的模块系统,它使用 require() ...
- A left join B B表有多条记录,max(create_time)取最新一条
例如:A表合同表t_contract B表合同审核表t_contract_audit.两个表根据contract_id关联.且一条合同有多条审核记录.求:A.合同状态.B.最新审核记录结果. 简单: ...
- 定时器之PWM
void PWM_Init(void) { RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB1Periph_TIM2, ENABLE); RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RC ...
- 魅族16T屏幕尺子
- C语言中的强制转换
许久没有遇到的问题 C语言真是博大精深,越使用它,就越发感觉到它的威力和恐怖,最近在做算法的时候,遇到了一个强转的错误,把人折腾的够受,这次要好好梳理一下了,希望下次不能再犯此类的问题. 强制转换 ...
- Android Studio源码导入与调试
从事Android开发都需要涉及到Android源码的阅读,特别是系统应用或者Framework开发,读代码的时间远远比写代码的时间更多. 一. 生成iml与ipr 在Android Studio中导 ...
