【转载】 tensorflow中的batch_norm以及tf.control_dependencies和tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS的探究
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/huitailangyz/article/details/85015611
————————————————————————————————
笔者近来在tensorflow中使用batch_norm时,由于事先不熟悉其内部的原理,因此将其错误使用,从而出现了结果与预想不一致的结果。事后对其进行了一定的调查与研究,在此进行一些总结。
一、错误使用及结果
笔者最先使用时只是了解到了在tensorflow中tf.layers.batch_normalization这个函数,就在函数中直接将其使用,该函数中有一个参数为training,在训练阶段赋值True,在测试阶段赋值False。但是在训练完成后,出现了奇怪的现象时,在training赋值为True时,测试的正确率正常,但是training赋值为False时,测试正确率就很低。上述错误使用过程可以精简为下列代码段
is_traing = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool)
input = tf.ones([1, 2, 2, 3])
output = tf.layers.batch_normalization(input, training=is_traing)
loss = ...
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
sess.run(train_op)
二、batch_normalization
下面首先粗略的介绍一下batch_normalization,这种归一化方法的示意图和算法如下图,
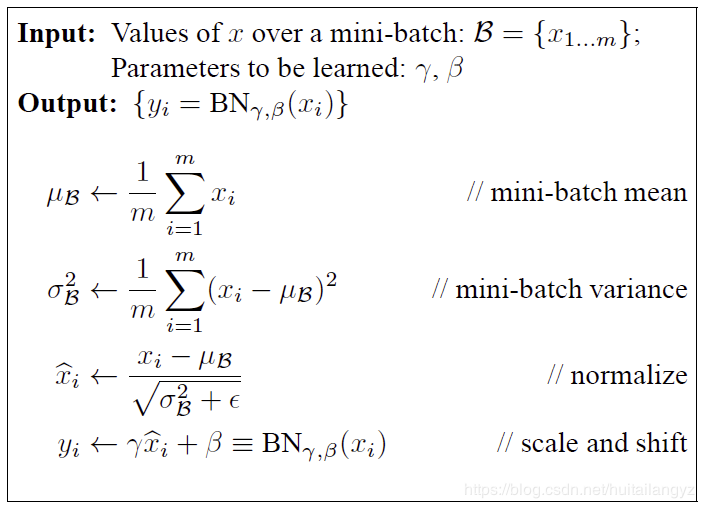
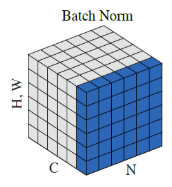
总的来说就是对于同一batch的input,假设输入大小为[batch_num, height, width, channel],逐channel地计算同一batch中所有数据的mean和variance,再对input使用mean和variance进行归一化,最后的输出再进行线性平移,得到batch_norm的最终结果。伪代码如下:
for i in range(channel):
x = input[:,:,:,i]
mean = mean(x)
variance = variance(x)
x = (x - mean) / sqrt(variance)
x = scale * x + offset
input[:,:,:,i] = x
在实现的时候,会在训练阶段记录下训练数据中平均mean和variance,记为moving_mean和moving_variance,并在测试阶段使用训练时的moving_mean和moving_variance进行计算,这也就是参数training的作用。另外,在实现时一般使用一个decay系数来逐步更新moving_mean和moving_variance,moving_mean = moving_mean * decay + new_batch_mean * (1 - decay)
三、tensorflow中的三种实现
tensorflow中关于batch_norm现在有三种实现方式。
1、tf.nn.batch_normalization(最底层的实现)
tf.nn.batch_normalization(
x,
mean,
variance,
offset,
scale,
variance_epsilon,
name=None
)
该函数是一种最底层的实现方法,在使用时mean、variance、scale、offset等参数需要自己传递并更新,因此实际使用时还需自己对该函数进行封装,一般不建议使用,但是对了解batch_norm的原理很有帮助。
封装使用的实例如下:
import tensorflow as tf def batch_norm(x, name_scope, training, epsilon=1e-3, decay=0.99):
""" Assume nd [batch, N1, N2, ..., Nm, Channel] tensor"""
with tf.variable_scope(name_scope):
size = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
scale = tf.get_variable('scale', [size], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
offset = tf.get_variable('offset', [size]) pop_mean = tf.get_variable('pop_mean', [size], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), trainable=False)
pop_var = tf.get_variable('pop_var', [size], initializer=tf.ones_initializer(), trainable=False)
batch_mean, batch_var = tf.nn.moments(x, list(range(len(x.get_shape())-1)))
train_mean_op = tf.assign(pop_mean, pop_mean * decay + batch_mean * (1 - decay))
train_var_op = tf.assign(pop_var, pop_var * decay + batch_var * (1 - decay)) def batch_statistics():
with tf.control_dependencies([train_mean_op, train_var_op]):
return tf.nn.batch_normalization(x, batch_mean, batch_var, offset, scale, epsilon)
def population_statistics():
return tf.nn.batch_normalization(x, pop_mean, pop_var, offset, scale, epsilon) return tf.cond(training, batch_statistics, population_statistics) is_traing = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool)
input = tf.ones([1, 2, 2, 3])
output = batch_norm(input, name_scope='batch_norm_nn', training=is_traing) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.save(sess, "batch_norm_nn/Model")
在batch_norm中,首先先计算了x的逐通道的mean和var,然后将pop_mean和pop_var进行更新,并根据是在训练阶段还是测试阶段选择将当批次计算的mean和var或者训练阶段保存的mean和var与新定义的变量scale和offset一起传递给tf.nn.batch_normalization
2、tf.layers.batch_normalization
tf.layers.batch_normalization(
inputs,
axis=-1,
momentum=0.99,
epsilon=0.001,
center=True,
scale=True,
beta_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
gamma_initializer=tf.ones_initializer(),
moving_mean_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
moving_variance_initializer=tf.ones_initializer(),
beta_regularizer=None,
gamma_regularizer=None,
beta_constraint=None,
gamma_constraint=None,
training=False,
trainable=True,
name=None,
reuse=None,
renorm=False,
renorm_clipping=None,
renorm_momentum=0.99,
fused=None,
virtual_batch_size=None,
adjustment=None
)
该函数也就是笔者之前使用的函数,在官方文档中写道
Note: when training, the moving_mean and moving_variance need to be updated.
By default the update ops are placed in tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS, so they need to be added as a dependency to the train_op.
Also, be sure to add any batch_normalization ops before getting the update_ops collection.
Otherwise, update_ops will be empty, and training/inference will not work properly. For example:
x_norm = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x, training=training) # ... update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss)
可以看到,与笔者之前的错误实现方法的差异主要在
update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):
这两句话,同时可以看到在第一种方法tf.nn.batch_normalization的封装过程中也用到了类似的处理方法,具体会在下一段进行说明。
3、tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm (slim)
tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(
inputs,
decay=0.999,
center=True,
scale=False,
epsilon=0.001,
activation_fn=None,
param_initializers=None,
param_regularizers=None,
updates_collections=tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
is_training=True,
reuse=None,
variables_collections=None,
outputs_collections=None,
trainable=True,
batch_weights=None,
fused=None,
data_format=DATA_FORMAT_NHWC,
zero_debias_moving_mean=False,
scope=None,
renorm=False,
renorm_clipping=None,
renorm_decay=0.99,
adjustment=None
)
这种方法与tf.layers.batch_normalization的使用方法差不多,两者最主要的差别在参数scale和centre的默认值上,这两个参数即是我们之前介绍原理时所说明的对input进行mean和variance的归一化之后采用的线性平移中的scale和offset,可以看到offset的默认值两者都是True,但是scale的默认值前者为True后者为False,也就是说明在tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm中,默认不对处理后的input进行线性缩放,只是加一个偏移。
四、关于tf.GraphKeys.UPDATA_OPS
介绍到这里,还有两个概念没有介绍,一个是tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,另一个是tf.control_dependencies。
1、tf.control_dependencies
首先我们先介绍tf.control_dependencies,该函数保证其辖域中的操作必须要在该函数所传递的参数中的操作完成后再进行。请看下面一个例子。
import tensorflow as tf
a_1 = tf.Variable(1)
b_1 = tf.Variable(2)
update_op = tf.assign(a_1, 10)
add = tf.add(a_1, b_1) a_2 = tf.Variable(1)
b_2 = tf.Variable(2)
update_op = tf.assign(a_2, 10)
with tf.control_dependencies([update_op]):
add_with_dependencies = tf.add(a_2, b_2) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
ans_1, ans_2 = sess.run([add, add_with_dependencies])
print("Add: ", ans_1)
print("Add_with_dependency: ", ans_2)
输出:
Add: 3
Add_with_dependency: 12
可以看到两组加法进行的对比,正常的计算图在计算add时是不会经过update_op操作的,因此在加法时a的值为1,但是采用tf.control_dependencies函数,可以控制在进行add前先完成update_op的操作,因此在加法时a的值为10,因此最后两种加法的结果不同。
2、tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS
关于tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,这是一个tensorflow的计算图中内置的一个集合,其中会保存一些需要在训练操作之前完成的操作,并配合tf.control_dependencies函数使用。
关于在batch_norm中,即为更新mean和variance的操作。通过下面一个例子可以看到tf.layers.batch_normalization中是如何实现的。
import tensorflow as tf is_traing = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool)
input = tf.ones([1, 2, 2, 3])
output = tf.layers.batch_normalization(input, training=is_traing) update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
print(update_ops)
# with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):
# train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.save(sess, "batch_norm_layer/Model")
输出:
[<tf.Tensor 'batch_normalization/AssignMovingAvg:0' shape=(3,) dtype=float32_ref>,
<tf.Tensor 'batch_normalization/AssignMovingAvg_1:0' shape=(3,) dtype=float32_ref>]
可以看到输出的即为两个batch_normalization中更新mean和variance的操作,需要保证它们在 train_op 前完成。
这两个操作是在tensorflow的内部实现中自动被加入tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS这个集合的,在tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm的参数中可以看到有一项updates_collections的默认值即为 tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
而在tf.layers.batch_normalization中则是直接将两个更新操作放入了上述集合。
五、关于最初的错误使用的思考
最后我对于一开始的使用方法为什么会导致错误进行了思考,tensorflow 中具体实现batch_normalization的代码在
tensorflow\python\layers\normalization.py中,下面展示一些关键代码。
( tf.layers.batch_normalization :)
if self.scale:
self.gamma = self.add_variable(
name='gamma',
shape=param_shape,
dtype=param_dtype,
initializer=self.gamma_initializer,
regularizer=self.gamma_regularizer,
constraint=self.gamma_constraint,
trainable=True)
else:
self.gamma = None if self.center:
self.beta = self.add_variable(
name='beta',
shape=param_shape,
dtype=param_dtype,
initializer=self.beta_initializer,
regularizer=self.beta_regularizer,
constraint=self.beta_constraint,
trainable=True)
else:
self.beta = None scale, offset = _broadcast(self.gamma), _broadcast(self.beta) self.moving_mean = self._add_tower_local_variable(
name='moving_mean',
shape=param_shape,
dtype=param_dtype,
initializer=self.moving_mean_initializer,
trainable=False) self.moving_variance = self._add_tower_local_variable(
name='moving_variance',
shape=param_shape,
dtype=param_dtype,
initializer=self.moving_variance_initializer,
trainable=False) def _assign_moving_average(self, variable, value, momentum):
with ops.name_scope(None, 'AssignMovingAvg', [variable, value, momentum]) as scope:
decay = ops.convert_to_tensor(1.0 - momentum, name='decay')
if decay.dtype != variable.dtype.base_dtype:
decay = math_ops.cast(decay, variable.dtype.base_dtype)
update_delta = (variable - value) * decay
return state_ops.assign_sub(variable, update_delta, name=scope) def _do_update(var, value):
return self._assign_moving_average(var, value, self.momentum) # Determine a boolean value for `training`: could be True, False, or None.
training_value = utils.constant_value(training)
if training_value is not False:
mean, variance = nn.moments(inputs, reduction_axes, keep_dims=keep_dims)
moving_mean = self.moving_mean
moving_variance = self.moving_variance
mean = utils.smart_cond(training,
lambda: mean,
lambda: moving_mean)
variance = utils.smart_cond(training,
lambda: variance,
lambda: moving_variance)
else:
new_mean, new_variance = mean, variance mean_update = utils.smart_cond(
training,
lambda: _do_update(self.moving_mean, new_mean),
lambda: self.moving_mean)
variance_update = utils.smart_cond(
training,
lambda: _do_update(self.moving_variance, new_variance),
lambda: self.moving_variance)
if not context.executing_eagerly():
self.add_update(mean_update, inputs=inputs)
self.add_update(variance_update, inputs=inputs)
outputs = nn.batch_normalization(inputs,
_broadcast(mean),
_broadcast(variance),
offset,
scale,
self.epsilon)
可以看到其内部逻辑和我在介绍tf.nn.batch_normalization一节中展示的封装时所使用的方法类似。
如果不在使用时添加tf.control_dependencies函数,即在训练时(training=True)每批次时只会计算当批次的mean和var,并传递给tf.nn.batch_normalization进行归一化,由于mean_update和variance_update在计算图中并不在上述操作的依赖路径上,因为并不会主动完成,也就是说,在训练时mean_update和variance_update并不会被使用到,其值一直是初始值。
因此在测试阶段(training=False)使用这两个作为mean和variance并进行归一化操作,这样就会出现错误。而如果使用tf.control_dependencies函数,会在训练阶段每次训练操作执行前被动地去执行mean_update和variance_update,因此moving_mean和moving_variance会被不断更新,在测试时使用该参数也就不会出现错误。
【转载】 tensorflow中的batch_norm以及tf.control_dependencies和tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS的探究的更多相关文章
- [转载]Tensorflow中reduction_indices 的用法
Tensorflow中reduction_indices 的用法 默认时None 压缩成一维
- tensorflow中的batch_norm以及tf.control_dependencies和tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS的探究
https://blog.csdn.net/huitailangyz/article/details/85015611#
- [转载]tensorflow中使用tf.ConfigProto()配置Session运行参数&&GPU设备指定
tf.ConfigProto()函数用在创建session的时候,用来对session进行参数配置: config = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True ...
- tensorflow笔记4:函数:tf.assign()、tf.assign_add()、tf.identity()、tf.control_dependencies()
函数原型: tf.assign(ref, value, validate_shape=None, use_locking=None, name=None) Defined in tensorflo ...
- 第二十二节,TensorFlow中RNN实现一些其它知识补充
一 初始化RNN 上一节中介绍了 通过cell类构建RNN的函数,其中有一个参数initial_state,即cell初始状态参数,TensorFlow中封装了对其初始化的方法. 1.初始化为0 对于 ...
- 第十四节,TensorFlow中的反卷积,反池化操作以及gradients的使用
反卷积是指,通过测量输出和已知输入重构未知输入的过程.在神经网络中,反卷积过程并不具备学习的能力,仅仅是用于可视化一个已经训练好的卷积神经网络,没有学习训练的过程.反卷积有着许多特别的应用,一般可以用 ...
- Tensorflow 中的优化器解析
Tensorflow:1.6.0 优化器(reference:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40170902/article/details/80092628) I: t ...
- [转]tensorflow中的gather
原文链接 tensorflow中取下标的函数包括:tf.gather , tf.gather_nd 和 tf.batch_gather. 1.tf.gather(params,indices,vali ...
- tensorflow中常量(constant)、变量(Variable)、占位符(placeholder)和张量类型转换reshape()
常量 constant tf.constant()函数定义: def constant(value, dtype=None, shape=None, name="Const", v ...
- tf.name_scope()和tf.variable_scope() (转)
网络层中变量存在两个问题: 随着层数的增多,导致变量名的增多: 在调用函数的时候,会重复生成变量,但他们存储的都是一样的变量. tf.variable不能解决这个问题. 变量作用域使用tf.var ...
随机推荐
- INFINI Labs 产品更新 | Easysearch 支持 SQL 查询、Console 告警功能支持邮件等多渠道
INFINI Labs 产品又更新啦~.本次更新概要如下:Easysearch 新增 SQL 插件和JDBC 驱动,支持 SQL 查询,支持 SQL 常用函数等:Console 针对告警功能做了升级优 ...
- EF 开始的片段时有问题 具有潜在运行时冲突
错误 3002: 映射从第 149 行开始的片段时有问题:表 t_Apply 的键(t_Appl .Id)具有潜在运行时冲突: 列(t_Apply .Id)映射到概念端 EntitySet t_Ap ...
- STM32 + RT-Thread + LVGL
一.基本信息 MCU:STM32F103ZET6 RT-Thread:5.0.2 LVGL:8.3.11 LCD:ST7735s 编译环境:RTThread studio 二.LVGL 移植要求 16 ...
- 太卷了,史上最简单的监控系统 catpaw 简介
指标监控的痛点 当下比较流行的监控系统,比如 Prometheus.Nightingale.VictoriaMetrics,都是基于数值型指标的监控系统,这类监控系统的痛点在于:告警的时候只能拿到异常 ...
- 解读surging 的内存过高的原因
前言 对于.NET开发人员来讲,一个程序占用内存过高,是极其糟糕,是一款不合格的程序软件,.NET开发人员也不会去使用服务器垃圾收集器(ServerGarbageCollection),而是选用工作站 ...
- es6.6.1 rest常规操作
ES 内置的REST接口/ 获取版本信息/index/_search 搜索指定索引下的数据 test/_search/_aliases 获取或者操作索引下的别名 _aliases/index/ 查看指 ...
- Python做点击率数据预测
点击率(Click-Through Rate, CTR)预测是推荐系统.广告系统和搜索引擎中非常重要的一个环节.在这个场景中,我们通常需要根据用户的历史行为.物品的特征.上下文信息等因素来预测用户点击 ...
- c语言生成随机数
记录示例,留作自用 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) ...
- WTM的项目中EFCore如何适配人大金仓数据库
一.WTM是什么 WalkingTec.Mvvm框架(简称WTM)最早开发与2013年,基于Asp.net MVC3 和 最早的Entity Framework, 当初主要是为了解决公司内部开发效率低 ...
- oracle 实现任务编码自增
业务需求:任务编号前面4位数(通过查询其他表,值不确定),后面5位数实现自增 实现方法如下 1.创建序列 1 create sequence GENERAL_DES_TASK_SEQ_1 2 incr ...
