深度优先搜索DFS(一)
/**
* Copyright(c)
* All rights reserved.
* Author : Mered1th
* Date : 2019-02-20-13.12.15
* Description : Bag
*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std; const int maxn=30;
int n,V,maxValue=0;//物品件数,背包容量,最大价值
int w[maxn],c[maxn]; //每件物品的重量,每件物品的价值
void DFS(int index,int sumW,int sumC){
if(index==n){
if(sumW<=V&&sumC>maxValue){
maxValue=sumC;
}
return;
}
DFS(index+1,sumW,sumC); //不选
DFS(index+1,sumW+w[index],sumC+c[index]); //选
} int main(){
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#else
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
scanf("%d%d",&n,&V);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&w[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&c[i]);
}
DFS(0,0,0);
printf("%d\n",maxValue);
return 0;
}
5 8
3 5 1 2 2
4 5 2 1 3
输出:
10
void DFS2(int index,int sumW,int sumC){
if(index==n){
return;
}
DFS2(index+1,sumW,sumC);
if(sumW+w[index]<=V){ //放的进去则选index件物品
if(sumC+c[index]>maxValue){
maxValue=sumC+c[index];
}
DFS2(index+1,sumW+w[index],sumC+c[index]);
}
}
bool in[maxn]={0};
void DFS3(int index,int sumW,int sumC){
if(index==n||sumW>=V){
if(sumC>maxValue){
maxValue=sumC;
}
return;
}
int i=index;
for(;i<n;i++){
if(w[i]+sumW<=V && in[i]==false){ //如果能放进去,且该物品不在背包里面
sumW+=w[i];
sumC+=c[i];
in[i]=true;
DFS3(index+1,sumW,sumC);
sumW-=w[i]; //回溯
sumC-=c[i];
in[i]=false;
}
}
}
vector<int> ans;
map<int,vector<int> > temp;
void DFS4(int index,int sumW,int sumC){
if(index==n||sumW>=V){
if(sumC>maxValue){
maxValue=sumC;
temp[maxValue]=ans;
}
return;
}
int i=index;
for(;i<n;i++){
if(w[i]+sumW<=V&&in[i]==false){
sumW+=w[i];
sumC+=c[i];
in[i]=true;
ans.push_back(i);
DFS4(index+1,sumW,sumC);
ans.pop_back();
sumW-=w[i];
sumC-=c[i];
in[i]=false;
}
}
} int main(){
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#else
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
scanf("%d%d",&n,&V);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&w[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&c[i]);
}
DFS4(0,0,0);
printf("%d\n",maxValue);
for(int i=0;i<temp[maxValue].size();i++){
cout<<temp[maxValue][i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
问题:给定一个序列,枚举这个序列的所有子序列(可以不连续),例如对序列{1,2,3}来说,它的所有子序列为{1}、{2}、{3}、{1,2},{1,3}、{2,3}、{1,2,3}。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
vector<int> ans;
void dfs(string str,int index,string res){
if(index==str.length()){
if(res.size()==0) return; //否则会把“”也输出
int temp=stoi(res);
ans.push_back(temp);
return;
}
dfs(str,index+1,res); //选index
dfs(str,index+1,res+str[index]);//不选index
}
int main(){
string a="123";
dfs(a,0,"");
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end()); //排序
for(auto it=ans.begin();it!=ans.end();it++){
cout<<*it<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
变式:给定N个整数(可能有负数),从中选择K个数,使得这K个数之和恰好等于一个给定的整数X;如果有多种方案,选择他们中元素平方和最大的一个。
const int maxn=110;
int n,k,x,maxsumSqu=-1,A[maxn];
vector<int> temp,ans;
void DFS(int index,int nowK,int sum,int sumSqu){
if(nowK==k && sum==x){
if(sumSqu>maxsumSqu){
maxsumSqu=sumSqu;
ans=temp;
}
return;
}
if(index==n || nowK>k || sum>x){
return;
}
temp.push_back(A[index]);
DFS(index+1,nowK+1,sum+A[index],sumSqu+A[index]*A[index]);
temp.pop_back();
DFS(index+1,nowK,sum,sumSqu);
}
实例三 全排列问题:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10;
bool isUsed[maxn]={0};
vector<int> num;
int n;
void dfs(int index){
if(index==n){
for(int i=0;i<num.size();i++){
printf("%d",num[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(isUsed[i]==true) continue;
num.push_back(i);
isUsed[i]=true;
dfs(index+1);
num.pop_back();
isUsed[i]=false;
}
} int main(){
n=3;
dfs(0);
return 0;
}
实例四 素数环问题(含剪枝):
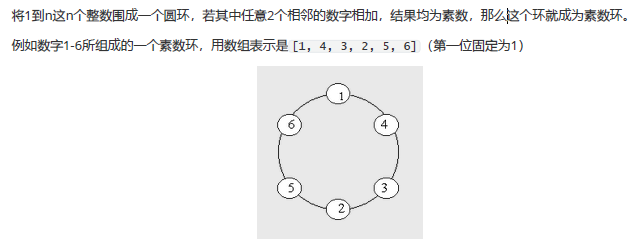
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;
bool isPrime[maxn]; //假设都为质数
vector<int> ans;
bool isUsed[maxn];
int n; void getPrimeTable(){
memset(isPrime,1,sizeof(isPrime));
isPrime[0]=isPrime[1]=false;
for(int i=2;i<maxn;i++){
if(isPrime[i]){
for(int j=i+i;j<maxn;j=j+i){
isPrime[j]=false;
}
}
}
} void dfs(int index){
if(index>=n){
int temp=ans[0]+ans[index-1]; //判断第一个数和最后一个数之和
if(isPrime[temp]==false){
return;
}
for(int x:ans){
printf("%d ",x);
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(isUsed[i]==true) continue;
int temp=ans[index-1]+i;
if(isPrime[temp]==false) continue; //剪枝
ans.push_back(i);
isUsed[i]=true;
dfs(index+1);
ans.pop_back();
isUsed[i]=false;
}
} int main(){
getPrimeTable();
n=4;
ans.push_back(1);
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
6 7
0 1 1 1 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 0
1 1 1 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 1 0 0 0
4
 求如图所示“块”的个数
求如图所示“块”的个数
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;
int X[4]={0,0,1,-1};
int Y[4]={1,-1,0,0};
struct node{
int x,y;
}Node;
int n,m; //¾ØÕó´óСΪn*m
int matrix[maxn][maxn];
bool inq[maxn][maxn]; bool judge(int x,int y){
if(x>=n||x<0||y>=m||y<0) return false;
if(matrix[x][y]==0||inq[x][y]==true) return false;
return true;
} void DFS(int u,int v){
inq[u][v]=true;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int newX=u+X[i];
int newY=v+Y[i];
if(judge(newX,newY)){
inq[newX][newY]=true;
DFS(newX,newY);
}
}
}
int main(){
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#else
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int x=0;x<n;x++){
for(int y=0;y<m;y++){
scanf("%d",&matrix[x][y]);
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int x=0;x<n;x++){
for(int y=0;y<m;y++){
if(matrix[x][y]==1&&inq[x][y]==false){
ans++;
DFS(x,y);
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
这里用到一个技巧就是:
int X[4]={0,0,1,-1};
int Y[4]={1,-1,0,0};
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int newX=u+X[i];
int newY=v+Y[i];
}
当矩阵过大时,DFS效率远不如BFS,下面给出BFS解法:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;
int X[4]={0,0,1,-1};
int Y[4]={1,-1,0,0};
struct node{
int x,y;
}Node;
int n,m;
int matrix[maxn][maxn];
bool inq[maxn][maxn]; bool judge(int x,int y){
if(x>=n||x<0||y>=m||y<0) return false;
if(matrix[x][y]==0||inq[x][y]==true) return false;
return true;
} void BFS(int x,int y){
queue<node> Q;
Node.x=x;
Node.y=y;
Q.push(Node);
inq[x][y]=true;
while(!Q.empty()){
node top=Q.front();
Q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int newX=top.x+X[i];
int newY=top.y+Y[i];
if(judge(newX,newY)){
Node.x=newX,Node.y=newY;
Q.push(Node);
inq[newX][newY]=true;
}
}
}
} int main(){
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#else
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int x=0;x<n;x++){
for(int y=0;y<m;y++){
scanf("%d",&matrix[x][y]);
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int x=0;x<n;x++){
for(int y=0;y<m;y++){
if(matrix[x][y]==1&&inq[x][y]==false){
ans++;
BFS(x,y);
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}

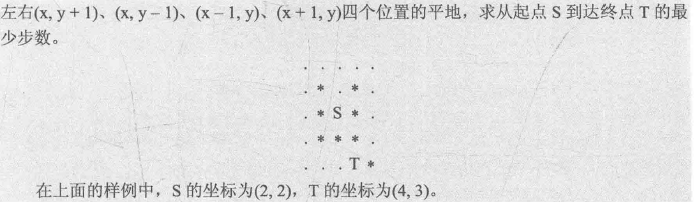
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;
struct node{
int x,y;
int step;
}S,T,Node;
int n,m;
char matrix[maxn][maxn];
bool inq[maxn][maxn]={false};
int X[4]={0,0,1,-1};
int Y[4]={0,0,1,-1}; bool judge(int x,int y){
if(x>=n||x<0||y>=m||y<0) return false;
if(matrix[x][y]=='*') return false;
if(inq[x][y]==false) return false;
return true;
} int BFS(){
queue<node> q;
q.push(S);
while(!q.empty()){
node top=q.front();
q.pop();
if(top.x==T.x&&top.y==T.y) return top.step; //到达终点,直接返回当前步数
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int newX=top.x+X[i];
int newY=top.y+Y[i];
if(judge(newX,newY)){
Node.x=newX,Node.y=newY;
Node.step=top.step+1;
q.push(Node);
inq[newX][newY]=true;
}
}
}
return -1;
} int main(){
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#else
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
getchar();
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
matrix[i][j]=getchar();
}
matrix[i][m+1]='\0';
}
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&S.x,&S.y,&T.x,&T.y);
S.step=0;
printf("%d\n",BFS());
return 0;
}
深度优先搜索DFS(一)的更多相关文章
- 深度优先搜索DFS和广度优先搜索BFS简单解析(新手向)
深度优先搜索DFS和广度优先搜索BFS简单解析 与树的遍历类似,图的遍历要求从某一点出发,每个点仅被访问一次,这个过程就是图的遍历.图的遍历常用的有深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索,这两者对于有向图和无向图 ...
- 利用广度优先搜索(BFS)与深度优先搜索(DFS)实现岛屿个数的问题(java)
需要说明一点,要成功运行本贴代码,需要重新复制我第一篇随笔<简单的循环队列>代码(版本有更新). 进入今天的主题. 今天这篇文章主要探讨广度优先搜索(BFS)结合队列和深度优先搜索(DFS ...
- 深度优先搜索DFS和广度优先搜索BFS简单解析
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/FZfangzheng/p/8529132.html 深度优先搜索DFS和广度优先搜索BFS简单解析 与树的遍历类似,图的遍历要求从某一点出发,每 ...
- 【算法入门】深度优先搜索(DFS)
深度优先搜索(DFS) [算法入门] 1.前言深度优先搜索(缩写DFS)有点类似广度优先搜索,也是对一个连通图进行遍历的算法.它的思想是从一个顶点V0开始,沿着一条路一直走到底,如果发现不能到达目标解 ...
- 深度优先搜索 DFS 学习笔记
深度优先搜索 学习笔记 引入 深度优先搜索 DFS 是图论中最基础,最重要的算法之一.DFS 是一种盲目搜寻法,也就是在每个点 \(u\) 上,任选一条边 DFS,直到回溯到 \(u\) 时才选择别的 ...
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)
[算法入门] 郭志伟@SYSU:raphealguo(at)qq.com 2012/05/12 1.前言 深度优先搜索(缩写DFS)有点类似广度优先搜索,也是对一个连通图进行遍历的算法.它的思想是从一 ...
- 算法总结—深度优先搜索DFS
深度优先搜索(DFS) 往往利用递归函数实现(隐式地使用栈). 深度优先从最开始的状态出发,遍历所有可以到达的状态.由此可以对所有的状态进行操作,或列举出所有的状态. 1.poj2386 Lake C ...
- HDU(搜索专题) 1000 N皇后问题(深度优先搜索DFS)解题报告
前几天一直在忙一些事情,所以一直没来得及开始这个搜索专题的训练,今天做了下这个专题的第一题,皇后问题在我没有开始接受Axie的算法低强度训练前,就早有耳闻了,但一直不知道是什么类型的题目,今天一看,原 ...
- [LeetCode OJ] Word Search 深度优先搜索DFS
Given a 2D board and a word, find if the word exists in the grid. The word can be constructed from l ...
- 广度优先(bfs)和深度优先搜索(dfs)的应用实例
广度优先搜索应用举例:计算网络跳数 图结构在解决许多网络相关的问题时直到了重要的作用. 比如,用来确定在互联网中从一个结点到另一个结点(一个网络到其他网络的网关)的最佳路径.一种建模方法是采用无向图, ...
随机推荐
- day14 生成器迭代器
迭代器(iterator) 可迭代对象: 可以使用迭代器取出数据的对象 判断一个对象是否是可迭代对象,就看这个对象有没有实现__iter__方法 所有的容器类型(包括字符串)都是可迭代的 迭代器的使用 ...
- 周强、张季跃,马凯军《面向对象与程序设计Java》第十四周学习总结
实验十四 Swing图形界面组件 实验时间 20178-11-29 理论部分:不使用布局管理器 有时候可能不想使用任何布局管理器,而只 是想把组件放在一个固定的位置上.下面是将一 个组件定位到某个绝 ...
- sqlite当天时间的23:59:59
select strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S','now','+1 day','localtime','start of day','-1 seconds')
- TrustManagerService.java
/* * Copyright (C) 2014 The Android Open Source Project * * Licensed under the Apache License, Versi ...
- 开发Canvas 绘画应用(三):实现对照绘画
需求分析 在我的毕设中,提出了视图引导的概念,由两部分功能组成: (1)可以对照着图片进行绘画,即将图片以半透明的方式呈现在绘图板上,然后用户可以对照着进行绘画: (2)可以直接将简笔画图片直接拖拽到 ...
- Sql Server数据字典
1:添加字段属性或者表属性 execute sys.sp_addextendedproperty @name = N'MS_Description', @value = N'要添加的属性信息', @l ...
- Django_ORM相关操作
一般的操作 1.all():查询所有的结果 2.filter():包含与所有筛选条件匹配的对象 3.get():返回与所给筛选条件相匹配的对象,返回结果有且只有一个,如果对象没有或者超过一个会报错 4 ...
- HTML下标签之应用
<!doctype html><html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- 设计简单的VB程序
1.模拟对话程序 [程序源码] Option Explicit Private Sub Command1_Click() Text2.Text = "" Text1.Text = ...
- 构建之法 chapter1 心得
阅读完了<构建之法>第一章后,觉得我们平时使用的软件并不是自己想象中的那样简单,用的时候是觉得很方便,但从来没有考虑过一个软件的背后需要一个团队多少的付出才能换来一个获得用户频频好评的软件 ...
